Which of the following is the main function of phloem?Transport water
Transport water
Transport nutrients
Transport sugars
Transport oxygen
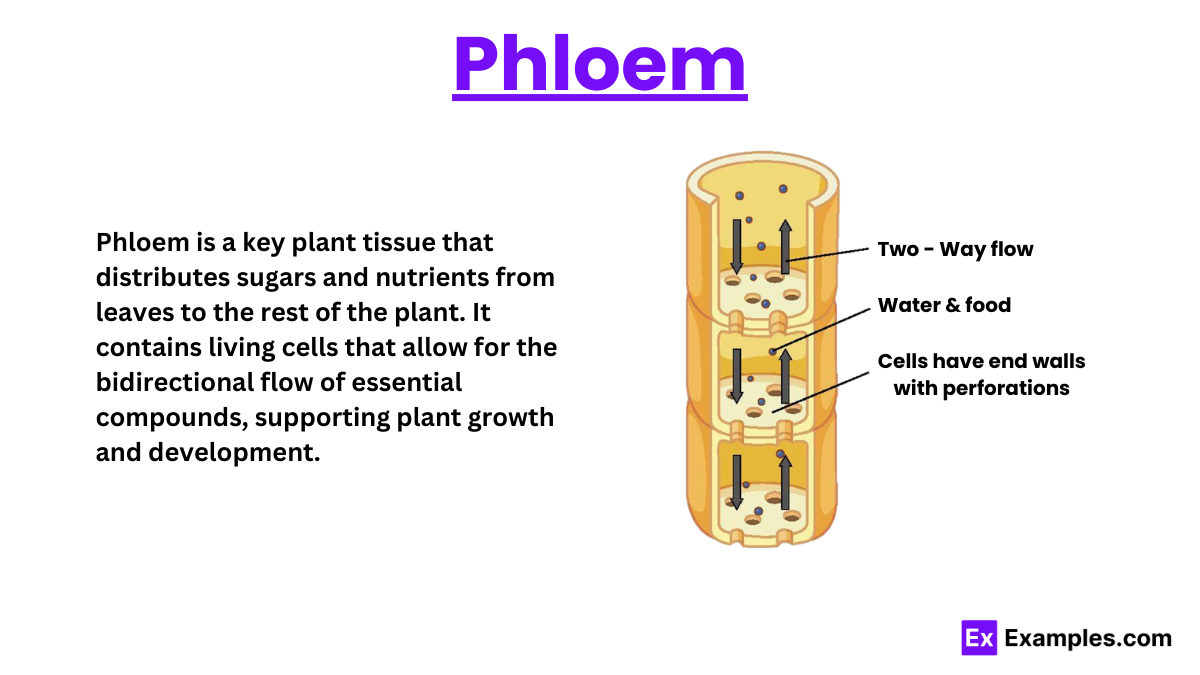
In the intricate network of plant biology, the phloem stands out as a critical component of the plant’s long-distance transport system. Together with the xylem, the phloem forms a duo of tissues that are pivotal in sustaining plant life, facilitating the movement of vital nutrients and water throughout the plant’s structure. This article delves into the fascinating world of phloem, exploring its origin, structure, function, and the increasing recognition of its role in plant signaling.

Companion cells are only found in angiosperms and are closely associated with sieve-tube members. They originate from the same parent cell and have a dense cytoplasm and a prominent nucleus. Companion cells play a crucial role in loading and unloading sugars into the sieve-tube elements, essentially regulating the material that gets transported through the phloem.
Phloem fibres, also known as bast fibres, are specialized sclerenchyma cells that provide structural support to the phloem. They are characterized by their thick cell walls, which are lignified, making them strong and rigid. Phloem fibres are not involved in nutrient transport but are crucial for the plant’s mechanical strength.
Phloem parenchyma cells are the most versatile cells within the phloem. These cells are involved in the storage and lateral transport of nutrients. They are living cells that can store starch and other organic substances. Phloem parenchyma also aids in the repair and regeneration of sieve elements and plays a role in defense against pathogens.
Phloem transports nutrients, especially sugars from leaves to all plant parts.
Xylem carries water and minerals upward; phloem distributes sugars throughout the plant.
Phloem is plant tissue that translocates sugars and other organic compounds.
Phloem is responsible for transporting food, mainly sugars, not water.
Phloem is composed of living cells, unlike some parts of xylem.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
Which of the following is the main function of phloem?Transport water
Transport water
Transport nutrients
Transport sugars
Transport oxygen
Phloem is part of which plant tissue system?
Dermal
Ground
Vascular
Epidermal
Which cells in the phloem are mainly responsible for the transport of sugars?
Tracheids
Vessel elements
Sieve tube elements
Guard cells
Companion cells are closely associated with which phloem cells?
Tracheids
Vessel elements
Sieve tube elements
Fibers
The process by which phloem transports food is known as:
Transpiration
Osmosis
Translocation
Diffusion
Which of the following is NOT a component of phloem?
Sieve tube elements
Companion cells
Xylem vessels
Phloem fibers
What type of sugar is most commonly transported in the phloem?
Glucose
Fructose
Sucrose
Maltose
Phloem transport can move substances:
Both upwards and downwards
Only downwards
Only upwards
Only horizontally
Which structure regulates the entry and exit of materials in phloem sieve tubes?
Guard cells
Sieve plates
Stomata
Xylem vessels
Phloem loading and unloading refer to:
Transport of water in the xylem
Movement of substances into and out of phloem cells
Root absorption
Photosynthesis
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

