The atmosphere is a layer of gases surrounding a planet, held by gravity. Earth’s atmosphere consists mainly of nitrogen (78%) and oxygen (21%), with traces of other gases. It protects life by absorbing solar radiation, regulating temperature, and providing essential elements for life. The atmosphere has distinct layers: the troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere, and exosphere.
What is Atmosphere?
The atmosphere is the envelope of gases surrounding a planet, held by gravity, which for Earth includes primarily nitrogen and oxygen, along with trace amounts of other gases such as argon, carbon dioxide, and water vapor. It plays a crucial role in protecting life by regulating temperature, filtering harmful solar radiation, and enabling weather patterns and climate.
Examples of Atmosphere
- Earth’s Atmosphere:
- Composed of 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, and trace amounts of argon, carbon dioxide, and water vapor.
- Supports life by providing breathable air and protecting against harmful solar radiation.
- Mars’ Atmosphere:
- Thin and composed mostly of carbon dioxide (95.3%), with traces of nitrogen and argon.
- Lacks sufficient pressure and temperature to support liquid water on its surface.
- Venus’ Atmosphere:
- Dense and composed mainly of carbon dioxide (96.5%), with clouds of sulfuric acid.
- Creates an extreme greenhouse effect, making Venus the hottest planet in the solar system.
- Jupiter’s Atmosphere:
- Composed mainly of hydrogen (90%) and helium (10%), with traces of methane, ammonia, and water vapor.
- Features the Great Red Spot, a massive storm larger than Earth.
- Titan’s Atmosphere (Saturn’s moon):
- Thick and nitrogen-rich (about 98%), with small amounts of methane and hydrogen.
- Contains organic compounds, making it of interest for studying prebiotic chemistry.
- Europa’s Atmosphere (Jupiter’s moon):
- Very thin, primarily composed of oxygen.
- Generated by the interaction of Jupiter’s magnetic field with water ice on Europa’s surface.
- Exoplanet Atmospheres:
- Vary widely in composition; some may have thick hydrogen-helium atmospheres, while others could have atmospheres rich in water vapor or carbon dioxide.
- Studies of exoplanet atmospheres help scientists understand planet formation and the potential for life beyond our solar system.
- Neptune’s Atmosphere:
- Composed mainly of hydrogen (80%) and helium (19%), with traces of methane.
- Exhibits dynamic weather patterns, including the fastest winds in the solar system, reaching speeds of up to 1,300 mph (2,100 km/h).
- Pluto’s Atmosphere:
- Thin and primarily nitrogen (90%), with traces of methane and carbon monoxide.
- Exhibits seasonal changes where its atmosphere freezes and collapses as Pluto moves away from the Sun.
- Enceladus’ Atmosphere (Saturn’s moon):
- Extremely thin, composed mostly of water vapor.
- Emitted from geysers at the moon’s south pole, which are fueled by water-ice jets erupting from subsurface oceans.
- Mercury’s Atmosphere:
- Extremely thin and composed mainly of oxygen, sodium, hydrogen, helium, and potassium.
- Subject to high temperatures during the day due to its proximity to the Sun, but very cold at night due to lack of significant atmosphere to retain heat.
Layers of Atmosphere
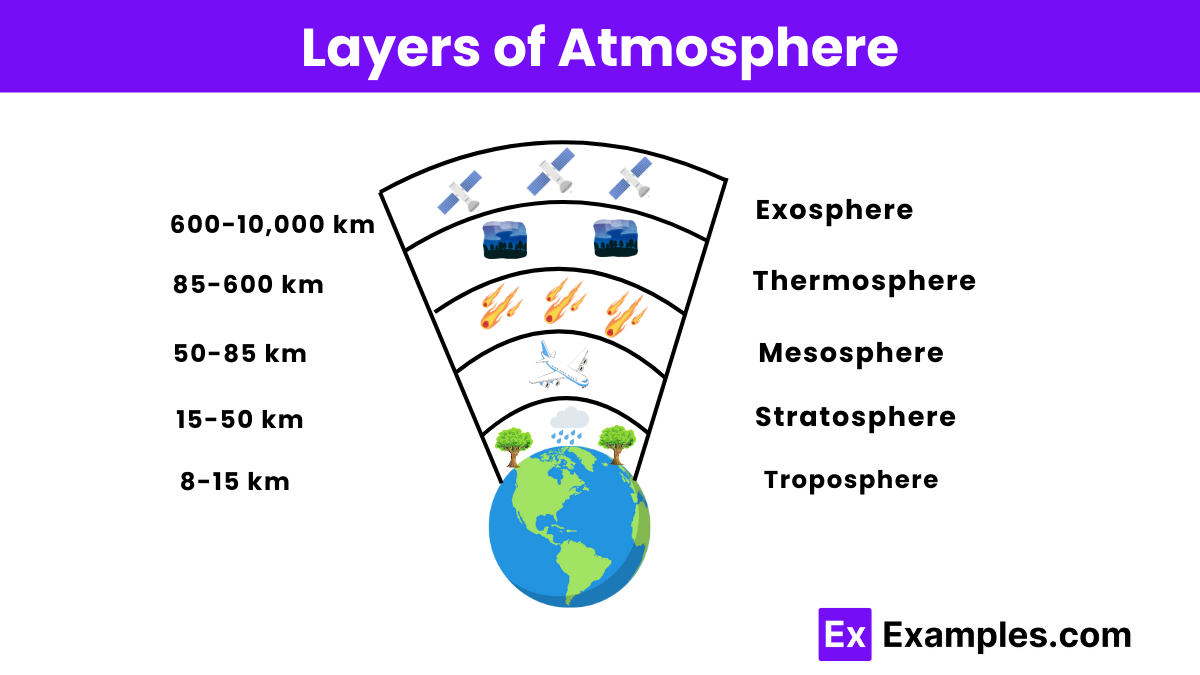
The Earth’s atmosphere is divided into several distinct layers, each with its own unique characteristics:
Troposphere
The troposphere is the lowest layer of the atmosphere, extending from the Earth’s surface up to about 8-15 kilometers (5-9 miles) high. It contains about 75% of the atmosphere’s mass and 99% of its water vapor and aerosols. This layer is where weather phenomena like clouds, rain, and storms occur. The temperature decreases with altitude in the troposphere, and it is the densest layer of the atmosphere, providing the air we breathe.
Stratosphere
The stratosphere lies above the troposphere, extending from about 15 kilometers (9 miles) to 50 kilometers (31 miles) high. It contains the ozone layer, which absorbs and scatters ultraviolet solar radiation, protecting living organisms from harmful UV rays. Unlike the troposphere, the temperature in the stratosphere increases with altitude due to the absorption of radiation by ozone. This temperature inversion creates a stable atmospheric layer, which is why commercial jet aircraft typically fly in the lower stratosphere to avoid turbulence.
Mesosphere
Above the stratosphere is the mesosphere, which extends from about 50 kilometers (31 miles) to 85 kilometers (53 miles) high. The temperature decreases with altitude in this layer, making it the coldest layer of the atmosphere. Meteors entering the Earth’s atmosphere burn up in the mesosphere, creating the phenomenon known as shooting stars. Despite its thin air, the mesosphere plays a crucial role in dissipating the energy of meteoroids before they reach the Earth’s surface.
Thermosphere
The thermosphere is the layer above the mesosphere, extending from about 85 kilometers (53 miles) to 600 kilometers (373 miles) high. Temperatures in the thermosphere increase significantly with altitude due to the absorption of high-energy X-rays and ultraviolet radiation from the sun. This layer is where the auroras, or northern and southern lights, occur. The thermosphere also contains the ionosphere, a sublayer rich in charged particles that is vital for radio communication and GPS signals.
Exosphere
The exosphere is the outermost layer of the atmosphere, extending from about 600 kilometers (373 miles) to 10,000 kilometers (6,200 miles) high. It gradually fades into the vacuum of space and contains very sparse particles of hydrogen and helium. The exosphere is where many satellites orbit the Earth, as it offers minimal atmospheric drag. This layer marks the transition between the Earth’s atmosphere and outer space.
| Layer | Altitude | Features |
|---|---|---|
| Troposphere | Up to 8-15 km (5-9 miles) | Contains 75% of atmospheric mass and 99% of water vapor. Weather occurs here. Temperature decreases with altitude. |
| Stratosphere | 15-50 km (9-31 miles) | Contains the ozone layer, absorbs UV radiation. Temperature increases with altitude. Stable layer where jets fly. |
| Mesosphere | 50-85 km (31-53 miles) | Coldest layer. Meteors burn up here, creating shooting stars. Temperature decreases with altitude. |
| Thermosphere | 85-600 km (53-373 miles) | Temperatures increase with altitude. Contains the ionosphere and auroras. Important for radio communication. |
| Exosphere | 600-10,000 km (373-6,200 miles) | Outermost layer, transitioning into space. Contains sparse particles. Satellites orbit here. |
Composition of Atmosphere – Gases in the Atmospher
| Component | Percentage | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen | 78% | The most abundant gas, relatively inert, crucial in the nitrogen cycle. |
| Oxygen | 21% | Vital for respiration in most living organisms. |
| Argon | 0.93% | A chemically inert noble gas. |
| Carbon Dioxide | 0.04% | Essential for photosynthesis and a significant greenhouse gas. |
| Water Vapor | 0% to 4% | Crucial for weather and climate patterns. |
| Cloud Formation | N/A | Process involving water vapor leading to cloud creation. |
The composition of atmosphere includes 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, and trace amounts of argon, carbon dioxide, and water vapor. These gases are vital for various atmospheric processes like cloud formation and weather patterns.
Air composition properties influence humidity, the amount of water vapor in the air, affecting precipitation and climate. An anemometer measures wind speed and direction, helping to understand different types of wind, from breezes to gales.
Knowing how to make a windmill is practical for harnessing wind energy, showcasing a sustainable use of natural resources. Understanding the atmosphere’s composition and properties is key to studying Earth’s weather and climate systems.
Features of the Atmosphere
The atmosphere has several key features that are essential for sustaining life and shaping our planet’s climate:
- Composition: The atmosphere is primarily composed of nitrogen (78%) and oxygen (21%), with trace amounts of other gases like argon, carbon dioxide, and water vapor.
- Layers: It is divided into distinct layers, including the troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere, and exosphere. Each layer has unique characteristics and functions.
- Weather and Climate: The atmosphere regulates the Earth’s weather and climate. The troposphere is where most weather events occur, while the stratosphere influences climate patterns.
- Protection from Radiation: The ozone layer in the stratosphere absorbs and scatters harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun, protecting living organisms.
- Temperature Regulation: The atmosphere helps regulate the Earth’s temperature through the greenhouse effect, trapping heat and keeping the planet warm enough to support life.
- Breathable Air: The atmosphere provides oxygen necessary for respiration in humans and animals, and carbon dioxide needed for photosynthesis in plants.
- Sound Propagation: The atmosphere allows for the propagation of sound waves, enabling communication and the perception of sound.
- Pressure: Atmospheric pressure decreases with altitude. It is crucial for the functioning of the human body and many weather phenomena.
- Aerosols: The atmosphere contains aerosols (tiny particles) that can influence climate and weather patterns by affecting cloud formation and sunlight scattering.
- Water Cycle: The atmosphere plays a key role in the water cycle, including evaporation, condensation, and precipitation, which are vital for distributing fresh water across the planet.
FAQ’s
The atmosphere primarily contains nitrogen (78%), oxygen (21%), argon (0.93%), and trace amounts of other gases, including carbon dioxide and water vapor.
The ozone layer, located in the stratosphere, absorbs and scatters ultraviolet radiation, protecting living organisms from harmful UV rays.
The atmosphere regulates temperature through the greenhouse effect, where gases trap heat, maintaining Earth’s climate within a habitable range.
Weather occurs in the troposphere due to the interaction of heat from the sun, moisture, and wind, creating various weather patterns and phenomena.
Atmospheric pressure decreases with increasing altitude because the density of air molecules decreases as the distance from Earth’s surface increases.
The greenhouse effect is the process where certain gases in the atmosphere trap heat from the sun, warming the Earth’s surface.
Nitrogen is essential for living organisms as it is a key component of amino acids, proteins, and DNA, crucial for life processes.
The atmosphere is vital in the water cycle, facilitating processes like evaporation, condensation, and precipitation, distributing water globally.
Human activities, such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation, release greenhouse gases, contributing to global warming and climate change.
Atmospheric pressure is the force exerted by the weight of air in the atmosphere on Earth’s surface, measured in units like pascals or millibars.