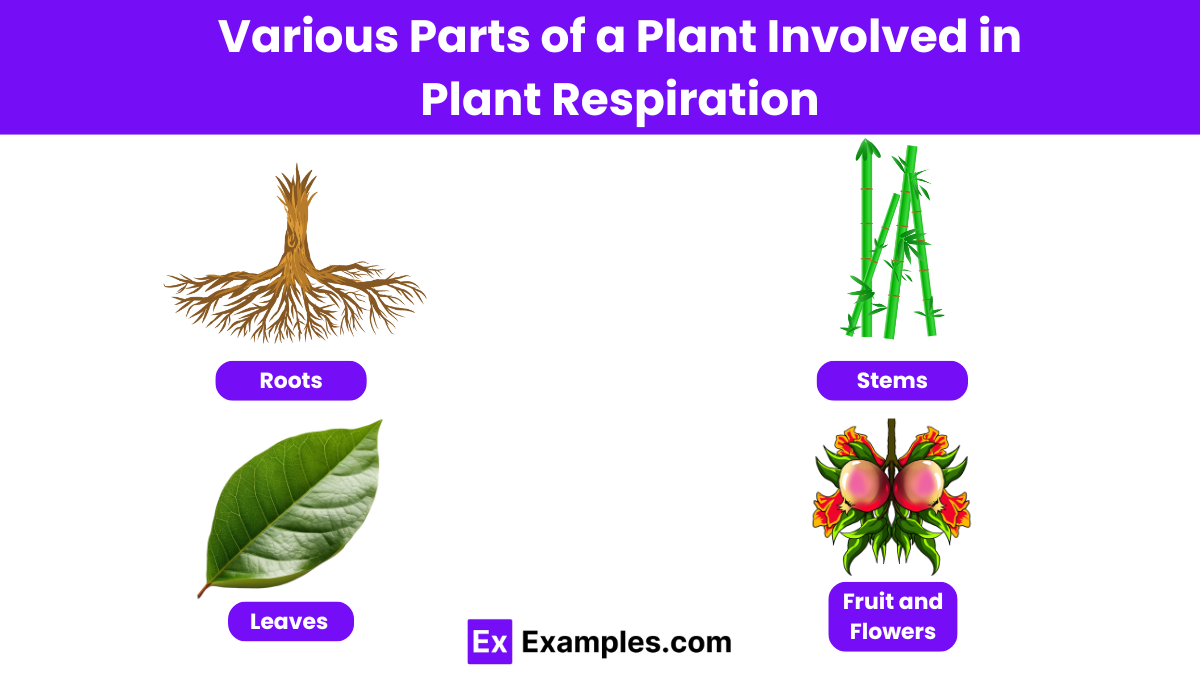
Which part of the plant is primarily responsible for respiration?
Leaves
Roots
Stems
All of the above

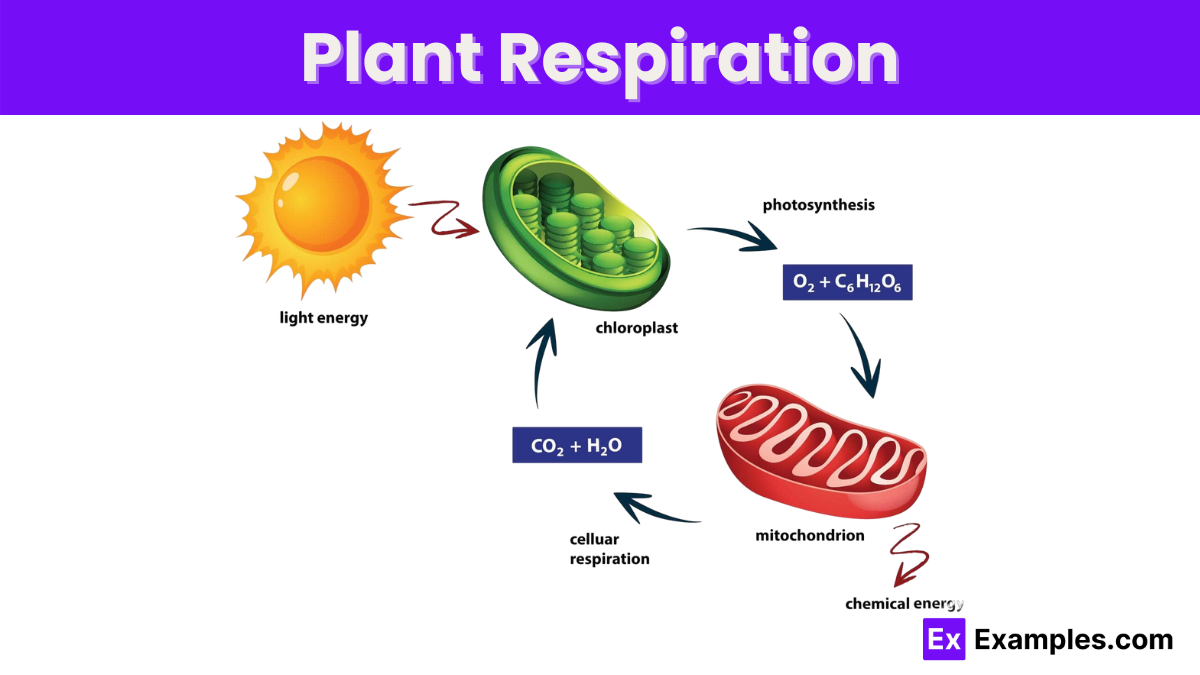
Plant respiration is a crucial biological process through which plants convert glucose and oxygen into energy, facilitating growth, maintenance, and overall vitality. This vital function occurs within the cells of plants, mirroring aspects of the respiration seen in animals. However, plant respiration uniquely contributes to the carbon cycle, releasing carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere. Understanding this process is essential not only for botany but also for broader applications in agriculture and ecology, influencing everything from crop yield optimization to global carbon flux analyses.
Plant respiration is a fundamental biological process where plants convert nutrients from sugars into energy, which is essential for their growth and survival. This process involves the intake of oxygen and the release of carbon dioxide, mirroring the respiratory process found in animals but occurring in every cell of the plant.
During respiration, plants use oxygen to break down sugar (glucose) obtained through photosynthesis. This breakdown generates energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is necessary for various physiological and biochemical processes within the plant. This process occurs in the mitochondria, the powerhouse of the cell, where glucose is converted into ATP through a series of reactions known as the Krebs cycle or the citric acid cycle.
Plant respiration involves several steps that occur in the mitochondria, often referred to as the powerhouse of the cell. These steps can be grouped into three main stages: glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and electron transport phosphorylation.
Plant respiration is essential for:
The equation for plant respiration is a critical component in understanding how plants convert sugars into energy, a process vital for their survival and growth. Here is the detailed equation:
C6H12O6+6O2→6CO2+6H2O+energy (ATP)C6H12O6+6O2→6CO2+6H2O+energy (ATP)
The carbon cycle is a complex system where carbon is exchanged between the earth’s atmosphere, oceans, soil, and biological organisms. Plants play a crucial role in this cycle in several ways:
Plant respiration at night is a crucial aspect of their metabolic process. Unlike photosynthesis, which only occurs during daylight when sunlight is available, respiration occurs 24 hours a day, including throughout the night. This continuous cycle is essential for plant survival, growth, and energy management.
Plant respiration converts glucose into energy, releasing CO2; photosynthesis uses CO2 and sunlight to create glucose and O2.
Plants primarily perform aerobic respiration but can switch to anaerobic respiration under oxygen-deficient conditions.
Plant cell respiration is the metabolic process of converting glucose into ATP in the presence of oxygen.
The plant respiration cycle is known as the Krebs cycle or the citric acid cycle.
Plant respiration is the biochemical process by which plants convert organic materials into energy, releasing carbon dioxide.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
Which part of the plant is primarily responsible for respiration?
Leaves
Roots
Stems
All of the above
Plant respiration mainly occurs in:
Chloroplasts
Mitochondria
Nucleus
Ribosomes
The process of plant respiration produces:
Oxygen and glucose
Glucose and water
Carbon dioxide and water
Oxygen and water
During which time of day do plants typically respire?
Only during the day
Only at night
Only at dawn
Both day and night
What is the primary purpose of plant respiration?
To produce oxygen
To produce glucose
To release energy
To absorb carbon dioxide
Which of the following molecules is broken down during plant respiration?
Water
Oxygen
Glucose
Carbon dioxide
Respiration in plants is essential for:
Photosynthesis
Growth and maintenance
Seed dispersal
Flowering
In which plant organ does the majority of gas exchange for respiration occur?
Roots
Leaves
Flowers
Stems
What is the role of oxygen in plant respiration?
To produce glucose
To break down water
To act as a final electron acceptor
To absorb carbon dioxide
Which of the following is a by-product of plant respiration?
Carbon dioxide
Hydrogen
Nitrogen
Glucose
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

