Which of the following animals is a reptile?
Frog
Snake
Salamander
Newt


Reptiles and amphibians fascinate many people with their unique characteristics and behaviors. These two groups of vertebrates often confuse students and nature enthusiasts due to their similar appearances and habitats. However, understanding the distinct differences between reptiles and amphibians is crucial for appreciating their roles in ecosystems. Reptiles, including snakes, lizards, and turtles, typically have dry, scaly skin and lay eggs on land. Amphibians, such as frogs, toads, and salamanders, usually have moist skin and undergo a metamorphosis from aquatic larvae to terrestrial adults. This article delves into the key differences between reptiles and amphibians, highlighting their unique adaptations, life cycles, and ecological significance.
Reptiles are a diverse group of vertebrates that belong to the class Reptilia. They are characterized by their dry, scaly skin, which prevents water loss and allows them to thrive in a variety of terrestrial environments. Reptiles are ectothermic, meaning they rely on external sources of heat to regulate their body temperature. This group includes snakes, lizards, turtles, crocodiles, and alligators.
Reptiles play vital roles in ecosystems as predators, prey, and contributors to biodiversity. They help control pest populations, such as insects and rodents, and serve as important prey for larger animals. Additionally, reptiles contribute to nutrient cycling and energy flow within their habitats. Their adaptations to various environments make them resilient survivors, capable of thriving in deserts, forests, wetlands, and even urban areas. Understanding reptiles’ unique characteristics and ecological roles enhances our appreciation of their importance in maintaining ecological balance.
Amphibians are a class of vertebrates known for their distinctive life cycle, which includes both aquatic and terrestrial phases. They belong to the class Amphibia and are characterized by their moist, permeable skin, which plays a crucial role in respiration. Amphibians include frogs, toads, salamanders, and caecilians.
Amphibians play critical roles in ecosystems as both predators and prey. They help control insect populations, acting as natural pest controllers, and serve as an essential food source for many animals, including birds, fish, and mammals. Amphibians are also important bioindicators, meaning their health reflects the overall health of their environment. Because of their permeable skin and sensitivity to environmental changes, amphibians are often among the first species to be affected by pollution, climate change, and habitat destruction. Their presence or absence can provide valuable information about ecosystem health and environmental quality. Understanding amphibians’ unique adaptations and ecological roles highlights their importance in maintaining biodiversity and ecosystem balance.
| Characteristic | Reptiles | Amphibians |
|---|---|---|
| Skin | Dry, scaly skin | Moist, permeable skin |
| Thermoregulation | Ectothermic (rely on external heat sources) | Ectothermic (rely on external heat sources) |
| Respiration | Lungs only | Lungs and skin (some also have gills in larval stage) |
| Life Cycle | Direct development | Metamorphosis (aquatic larvae to terrestrial adults) |
| Eggs | Amniotic eggs with leathery or hard shells | Eggs without shells, laid in water or moist environments |
| Fertilization | Internal | Mostly external |
| Major Groups | Snakes, lizards, turtles, crocodilians | Frogs, toads, salamanders, caecilians |
| Habitat | Primarily terrestrial | Both aquatic and terrestrial |
| Presence of Scales | Yes | No |
| Larval Stage | None | Present (e.g., tadpoles in frogs) |
| Heart Structure | Three-chambered heart (except crocodilians with four chambers) | Three-chambered heart |
| Locomotion | Primarily use legs or slithering | Varied (swimming in larvae, jumping, walking in adults) |
| Hearing | External ear openings and tympanic membrane | No external ears, some have tympanic membrane |
| Vision | Well-developed vision, color vision in some species | Variable vision, often well-developed in adults |
| Defense Mechanisms | Venom (in some species), camouflage, biting | Toxic skin secretions, camouflage, playing dead |
| Water Dependence | Low; many can survive in arid environments | High; require moist environments for skin respiration and reproduction |
| Body Covering | Covered with scales | Smooth or warty skin without scales |
| Reproductive Modes | Oviparous, ovoviviparous, viviparous | Mostly oviparous |
| Tail | Present in most species | Present in larvae, may or may not be present in adults (e.g., frogs lose tails) |
| Evolutionary Origin | Originated from early amniotes | Originated from early lobe-finned fish |
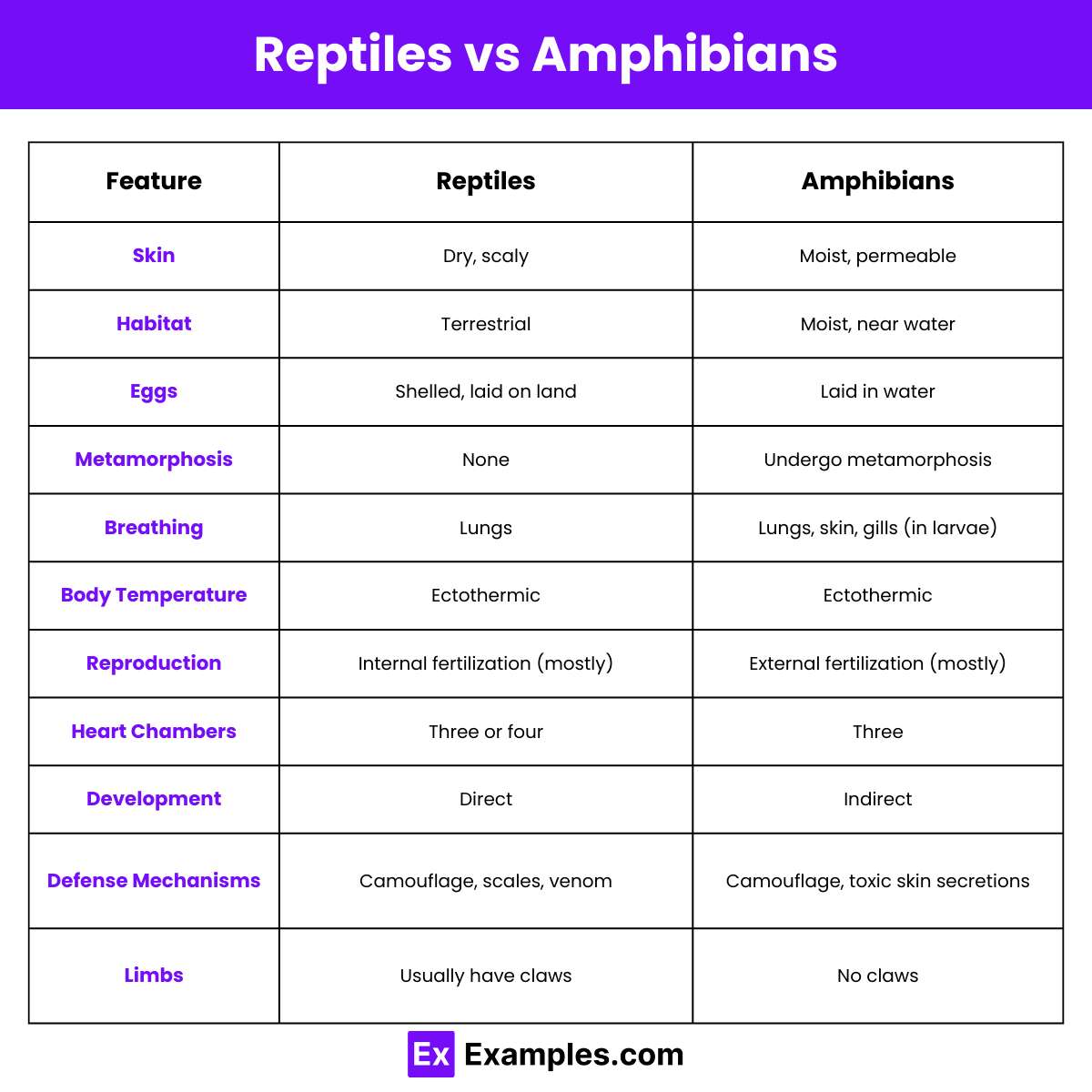
Reptiles have dry, scaly skin and lay shelled eggs, while amphibians have moist, permeable skin and lay eggs in water.
Reptiles prefer dry, terrestrial habitats; amphibians thrive in moist environments, often near water.
Only amphibians undergo metamorphosis, transitioning from larval to adult forms.
Reptiles: snakes, lizards, turtles. Amphibians: frogs, salamanders, newts.
Reptiles breathe through lungs. Amphibians breathe through lungs, skin, and gills (in larvae).
Both are mostly carnivorous, but amphibians often consume more aquatic prey.
Both are ectothermic, relying on external heat sources to regulate body temperature.
Reptiles lay shelled eggs on land; amphibians lay eggs in water.
Reptiles have dry, scaly skin; amphibians have moist, permeable skin.
Reptiles use camouflage, scales, and venom; amphibians use camouflage, toxic skin secretions, and jumping.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
Which of the following animals is a reptile?
Frog
Snake
Salamander
Newt
Amphibians typically have which type of skin?
Dry and scaly
Moist and smooth
Feathers
Fur
Reptiles primarily lay their eggs:
In water
On land
Inside other animals
In nests built in trees
Which of the following is a characteristic of amphibians?
Scales
Feathers
Undergo metamorphosis
Live only in deserts
Reptiles are primarily:
Warm-blooded
Cold-blooded
Warm-blooded as juveniles and cold-blooded as adults
Neither warm-blooded nor cold-blooded
Which of the following is an amphibian?
Turtle
Lizard
Frog
Crocodile
Amphibians typically reproduce by:
Internal fertilization
External fertilization
Asexual reproduction
Budding
The skin of reptiles is covered in:
Feathers
Fur
Scales
Slimy mucus
Which of these animals is known for undergoing a dramatic change from larva to adult?
Snake
Crocodile
Frog
Tortoise
Where do most amphibians lay their eggs?
In nests on trees
Buried in sand
In water
On leaves
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

