What is the scientific name of the sunflower?
Rosa indica
Helianthus annuus
Zea mays
Triticum aestivum

Dive into the verdant world of botany with our all-encompassing guide to the scientific names of plants. This meticulously crafted resource unveils the essence of plant taxonomy, offering insights into the naming conventions that underpin the botanical universe. From the majestic Sequoiadendron giganteum (Giant Sequoia) to the delicate Rosa chinensis (Chinese Rose), our guide is brimming with examples that illuminate the intricate relationships within the plant kingdom. Perfect for enthusiasts and scholars alike, explore the foundational language of botany and discover the stories behind the scientific names of your favorite flora.
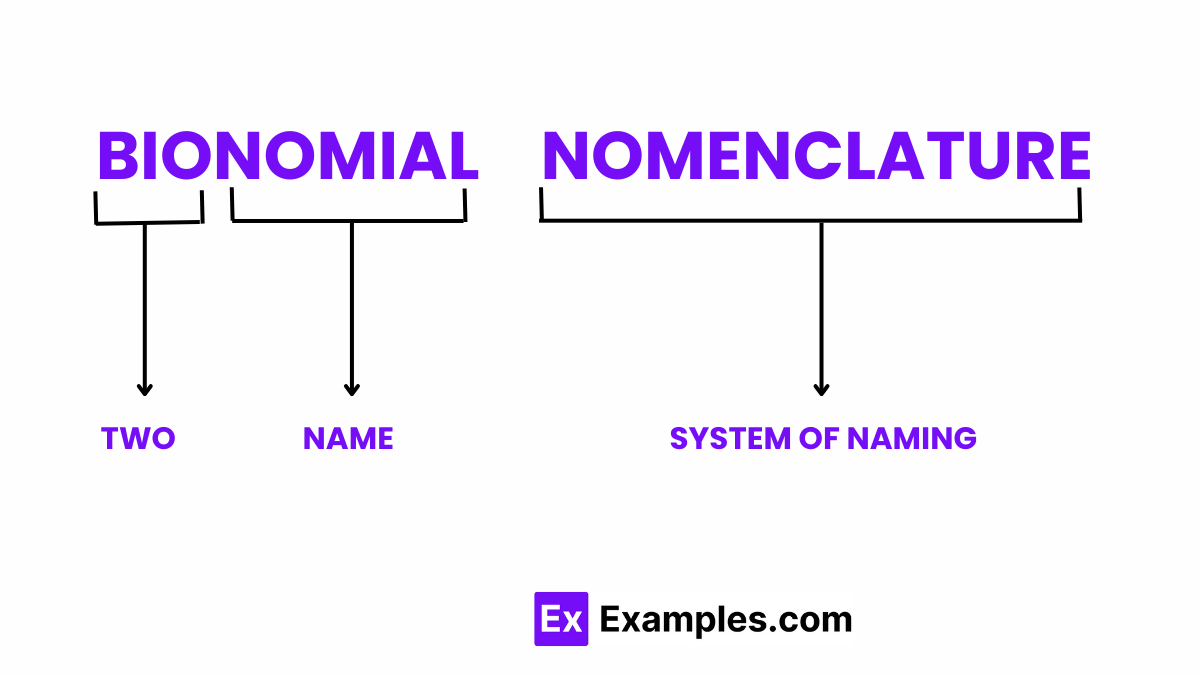
Nomenclature in plants refers to the systematic approach to naming plant species and groups according to a set of agreed-upon rules and standards. This ensures consistent and universal identification and classification of plants worldwide, facilitating clear communication among botanists, researchers, and enthusiasts. The primary system used for plant nomenclature is governed by the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN), formerly known as the International Code of Botanical Nomenclature (ICBN).
The ICN sets out principles for naming plants, fungi, and algae, including how names are to be chosen, published, and applied to taxonomic groups. A fundamental aspect of plant nomenclature is the use of binomial nomenclature (two-part names), which was popularized by Carl Linnaeus. Each plant species is given a unique Latin name consisting of two parts: the genus name (capitalized) and the specific epithet (lowercase), both italicized, e.g., Acer saccharum for the sugar maple.
| Common Name | Scientific Name |
| Sunflower | Helianthus annuus |
| Giant Sequoia | Sequoiadendron giganteum |
| Venus Flytrap | Dionaea muscipula |
| English Ivy | Hedera helix |
| African Violet | Saintpaulia ionantha |
| Bamboo | Bambusoideae spp. |
| Cactus | Cactaceae spp. |
| Daffodil | Narcissus spp. |
| Eucalyptus | Eucalyptus spp. |
| Fern | Pteridophyta spp. |
| Geranium | Pelargonium spp. |
| Hibiscus | Hibiscus rosa-sinensis |
| Iris | Iris spp. |
| Jasmine | Jasminum spp. |
| Lavender | Lavandula spp. |
| Mint | Mentha spp. |
| Nettle | Urtica dioica |
| Orchid | Orchidaceae spp. |
| Poppy | Papaver spp. |
| Quaking Aspen | Populus tremuloides |
| Rose | Rosa spp. |
| Sage | Salvia officinalis |
| Tulip | Tulipa spp. |
| Umbrella Plant | Cyperus alternifolius |
| Vervain | Verbena officinalis |
| Water Lily | Nymphaea spp. |
| Xerophyte | Xerophyta spp. |
| Yucca | Yucca spp. |
| Zinnia | Zinnia elegans |
| Aloe Vera | Aloe vera |
| Banana Tree | Musa spp. |
| Cedar Tree | Cedrus spp. |
| Dahlia | Dahlia spp. |
| Elderberry | Sambucus spp. |
| Fig Tree | Ficus carica |
| Grapevine | Vitis vinifera |
| Hydrangea | Hydrangea spp. |
| Indian Paintbrush | Castilleja spp. |
| Jack Pine | Pinus banksiana |
| Kiwi Plant | Actinidia deliciosa |
| Lemon Tree | Citrus limon |
| Maple Tree | Acer spp. |
| Norway Spruce | Picea abies |
| Olive Tree | Olea europaea |
| Pineapple Plant | Ananas comosus |
| Quince | Cydonia oblonga |
| Redwood | Sequoia sempervirens |
| Strawberry Plant | Fragaria × ananassa |
| Tea Plant | Camellia sinensis |
| Uva Ursi | Arctostaphylos uva-ursi |
| Vanilla Orchid | Vanilla planifolia |
| Wheat | Triticum spp. |
| Yellowwood Tree | Cladrastis kentukea |
| Zebra Plant | Aphelandra squarrosa |
The use of scientific names for plants is fundamental in the field of botany and across various disciplines that study plant life, ecology, agriculture, horticulture, and environmental science. These names serve several crucial purposes:
Scientific names provide a universal language for scientists around the world, allowing for precise and unambiguous communication. Unlike common names, which can vary significantly between languages and even regions within the same country, scientific names ensure that everyone is speaking about the same plant.
The system of scientific naming, or binomial nomenclature, is integral to the classification of plants. It helps in organizing plants into hierarchical categories such as genus and species, reflecting evolutionary relationships and similarities among organisms. This organization aids in understanding the diversity and complexity of plant life.
Scientific names follow internationally accepted rules and criteria, providing consistency and stability in naming conventions. Once a plant is given a scientific name, that name is recognized globally, reducing confusion and overlap that can occur with common names.
The use of scientific names facilitates the identification and study of plants. Researchers and scientists can accurately identify plants, understand their characteristics, and study their uses, distribution, ecology, and conservation status. This is essential for biodiversity studies, conservation efforts, and the exploration of new species.
Scientific names often contain information about the plant’s discoverer, geographic origin, or physical characteristics. This can provide insight into the history of the plant’s discovery and its importance to different cultures or regions.
In agriculture and medicine, scientific names are used to specify plants that are sources of food, medicine, or are otherwise beneficial or harmful to crops and human health. This precise identification ensures that the correct species are used for cultivation, research, and healthcare, avoiding potentially dangerous mix-ups.
Scientific names are used in legal and regulatory contexts to enforce laws related to endangered species protection, biosecurity, and the trade of plants and plant products. Accurate naming is crucial for enforcing regulations and protecting biodiversity.
In horticulture and gardening, scientific names help in the accurate identification and selection of plants for landscaping, gardening, and conservation purposes. They ensure that gardeners and landscapers are purchasing and growing the correct species and varieties.
A scientific name is a formal system of naming plant species using a two-part Latin or Latinized name, consisting of the genus name (capitalized) and the specific epithet (lowercase). This binomial nomenclature ensures each plant is given a unique, universally recognized name.
Plants have scientific names to provide a standardized, universally accepted naming system that avoids the confusion and ambiguity of common names. This system facilitates precise communication among scientists, gardeners, and others worldwide, regardless of language.
Scientific names are assigned based on the rules established by the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN). These names often reflect the plant’s characteristics, the region it’s from, or honor a person in the field of botany.
Yes, the scientific name of a plant can change due to new discoveries or reclassifications in the understanding of plant relationships. Taxonomists may update a plant’s name to better reflect its genetics, phylogeny, or to correct historical naming errors.
Using scientific names is crucial for ensuring clarity and consistency in the identification and classification of plants. It aids in scientific research, conservation efforts, botanical education, and the global trade of plant materials.
A scientific name should be written in italics or underlined if handwritten, with the genus name capitalized and the specific epithet in lowercase (e.g., Rosa canina). When a scientific name is abbreviated, only the first letter of the genus name is used followed by a period (e.g., R. canina).
Common names are the everyday terms used by the public, which can vary widely and be used for multiple species. Scientific names are unique to each species, standardized, and used globally, minimizing confusion and ensuring accurate identification.
While there are scientific names for a vast majority of known plant species, new species are continually being discovered and described. The process of naming and classifying these new species follows the guidelines of the ICN.
No, according to the principles of botanical nomenclature, each plant species must have a unique scientific name. However, synonyms (different names for the same species based on separate discoveries) may exist until one valid name is agreed upon.
The scientific names of plants are decided by taxonomists and botanical researchers who study plant classifications. These names are then published in peer-reviewed botanical literature and must adhere to the rules set by the ICN
In sum, the adoption of scientific names for plants transcends mere nomenclature, providing a universal lexicon that underpins botanical research, conservation, and education. This system facilitates precise identification, fosters global collaboration, and underscores the interconnectedness of all life forms. Emphasizing the importance of scientific names enriches our understanding of plant biodiversity and its pivotal role in sustaining ecological balance.
Text prompt
Add Tone
Uses of Scientific Names of Plants
List of Scientific Names of Plants
What is the scientific name of the sunflower?
Rosa indica
Helianthus annuus
Zea mays
Triticum aestivum
Which plant has the scientific name Quercus alba?
White oak
Black walnut
Black walnut
Red pine
What is the scientific name for the tomato plant?
Solanum tuberosum
Capsicum annuum
Solanum lycopersicum
Cucumis sativus
The scientific name of the common wheat plant is:
Oryza sativa
Zea mays
Triticum aestivum
Hordeum vulgare
Which of the following plants is scientifically named Rosa indica?
Lily
Rose
Tulip
Sunflower
The plant with the scientific name Zea mays is commonly known as:
Wheat
Barley
Rice
Corn
What is the scientific name for the apple tree?
Pyrus communis
Malus domestica
Prunus armeniaca
Citrus sinensis
The scientific name for the coconut palm is:
Cocos nucifera
Phoenix dactylifera
Musa paradisiaca
Ficus carica
Which plant is known scientifically as Brassica oleracea?
Spinach
Broccoli
Carrot
Potato
What is the scientific name of the pea plant?
Vigna radiata
Pisum sativum
Phaseolus vulgaris
Glycine max
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

