29+ Harvard Reference Style Examples to Download
Properly citing sources is a fundamental aspect of academic and scholarly writing. Various citation styles exist to provide structure and consistency to references. Among them, the Harvard Reference Style stands out as one of the most widely used and recognized formats. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of Harvard referencing, learn how to draft references in this style, explore its components, and provide practical examples and templates for accurate citations.
1. Harvard Reference Style Format
pengreen.org
2. Journal Harvard Reference Style

bath.ac.uk
3. Harvard Book Reference Style
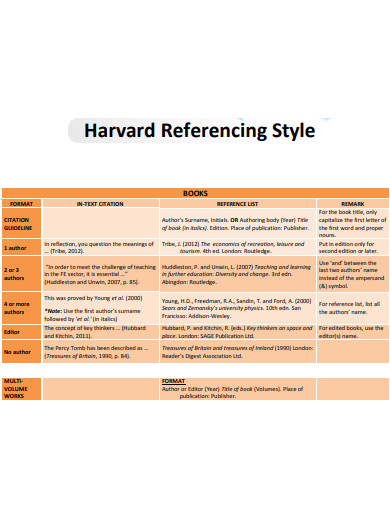
taylorslibrary.taylors.edu.my
4. Harvard Citation Reference Style

otago.ac.nz
5. Harvard Bibliography Reference Style

aydin.edu.tr
6. Harvard Article Reference Style

library.westernsydney.edu.au
7. Harvard Reference Style Cover Page

uvocorp.com
8. Harvard Reference Style Essay

adelaide.edu.au
9. Harvard Reference Style Text Citation

ub.uio.no
10. Harvard Reference Style in PDF

abdn.ac.uk
11. APA Harvard Reference Style

iseg.ulisboa.pt
12. Harvard Reference Style Endnote

lib.rmit.edu.au
13. Harvard Reference Style Paper

barnsley.ac.uk
14. Harvard Reference Style Author

library.lit.ie
15. Harvard Reference Style Quote

schmidt-bremen.de
16. Harvard Reference Style Header

aramsociety.org
17. Harvard Reference Style Mendeley
cd-uat.ljmu.ac.uk
18. Harvard Reference Style Intext

adelaide.edu.au
19. Harvard Reference Style Multiple Author

hup.harvard.edu
20. Harvard Reference Style Academic

s1234057.stacksdiscovery.com
21. Harvard Reference Style Assignment

clevelanddistrictshs.eq.edu.au
22. University Harvard Reference Style

moodle.bl.rdi.co.uk
23. Harvard Reference Style Paragraph

students.flinders.edu.au
24. Harvard Reference Style Footnote

history.fas.harvard.edu
25. Standard Harvard Reference Style

librarydevelopment.group.shef.ac.uk
26. Introduction to Harvard Reference Style
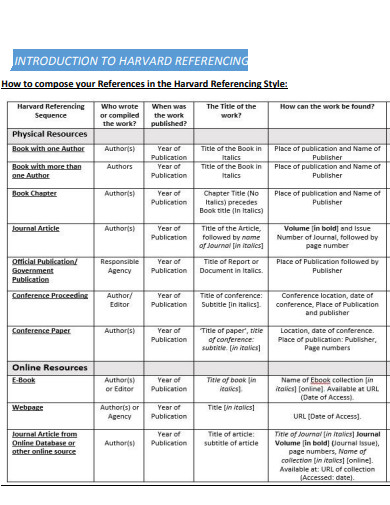
library.cit.ie
27. Guide to Harvard Reference Style

herts.ac.uk
28. Simple Harvard Reference Style

cbs.dk
29. Basic Harvard Reference Style

lecturehub.ie
30. Harvard Reference Style Sources

biblioteca.ucm.es
What is Harvard Reference Style?
The Harvard Reference Style, also known as the author-date referencing system, is a popular citation style used in academic writing across diverse disciplines. It was developed by the Harvard University in the 1880s and has since become widely adopted by institutions worldwide. In this style, sources are cited within the text by mentioning the author’s name and the year of publication, while the full bibliographic details are listed in the reference list at the end of the document.
How to write your References in Harvard Style
Before we proceed with the steps, it’s essential to gather all the necessary information about the sources you will be citing, such as the author’s name, publication date, title, publisher, and page numbers. Once you have this information at hand, follow these steps:
Step 1: Citing Books and Monographs
When citing a book or a monograph using Harvard style, begin with the author’s last name followed by their initials. Then, include the publication year in parentheses. Next, provide the title of the book in italics or underlined, followed by the place of publication and the publisher.
Example: Doe, J. (2023). The Art of Writing: A Comprehensive Guide. New York, NY: Publishing House.
Step 2: Citing Journal Articles
For citing journal articles, start with the author’s last name and initials, followed by the publication year in parentheses. Next, include the article title in sentence case and enclose it in single quotation marks. After that, provide the journal name in italics or underlined, followed by the volume and issue number (if available) and page range of the article.
Example: Smith, L. (2022). The Impact of Climate Change on Biodiversity. ‘Environmental Science Review,’ 15(3), 245-259.
Step 3: Citing Websites
When referencing online sources, begin with the author’s last name and initials, followed by the publication year in parentheses. Then, include the title of the webpage or article in sentence case, followed by the name of the website or organization. Conclude by providing the full URL and the date of access in parentheses.
Example: Johnson, P. (2021). Sustainable Energy Solutions. World Environment Organization. Available at: www.example.com/sustainable-energy (Accessed: 25th June 2023).
Step 4: In-Text and Parenthetical Citations
In Harvard referencing, in-text citations are used when directly quoting or paraphrasing a source within the text. Use the author’s last name, publication year, and page number (for direct quotes) within parentheses after the citation. Example: “The effects of climate change are far-reaching and must be urgently addressed” (Smith, 2022, p. 250).
FAQs
What is the difference between in-text citation and parenthetical citation?
In-text citation refers to the brief mention of the author’s name and year of publication within the text, while parenthetical citation includes this information within parentheses after a direct quote or paraphrased content.
Is there any specific structure for a research paper format in Harvard style?
Yes, Harvard style requires a title page, an abstract (if applicable), introduction, main body, conclusion, and a reference list.
Can I use the Harvard Reference Style for my literature review?
Absolutely! Harvard referencing is commonly used for literature reviews and other academic papers as it provides a clear and consistent way to cite sources.
Mastering the Harvard Reference Style is a valuable skill for every academic writer. By following the step-by-step guide provided above and using the examples and templates, you can ensure accurate and proper citations. Remember, adhering to a recognized citation style enhances the credibility and integrity of your research, making it more accessible and understandable to readers.


