40+ Brainstorming Examples
Often, great ideas are the product of great efforts pushed by multiple people under the same group. Brainstorming is a great way to create a team of individuals that can push and create ideas with one another.
What Is a Brainstorming?
Brainstorming is the act of creating or ideating ideas and concepts of a specific topic or with a group of people. This method is a group problem-solving method that creates a conducive environment for the creation of ideas. If you need Brainstorming templates or need a brainstorming checklist you may use any of the links on the list above.
Brainstorming Examples for Students
- Theme Development: Students brainstorm themes for an upcoming school festival, including activities, decorations, and promotional strategies.
- Project Ideas: Brainstorm potential topics for a science fair, considering interests, available resources, and innovative approaches.
- Group Assignments: Generate ideas for a group project in history class, focusing on less-known historical events or figures.
- Essay Writing: Come up with different thesis statements for an English assignment on contemporary social issues.
- Study Techniques: Brainstorm various study methods that cater to different learning styles to improve understanding and retention.
- Club Activities: Develop a list of possible events or activities for a school club, aiming to boost membership and engagement.
- Fundraising Ideas: Generate creative fundraising ideas for a school trip or charity event, considering budget and impact.
Brainstorming Examples for Writing
- Character Development: Brainstorm unique traits, backgrounds, and motivations for a protagonist in a novel.
- Plot Twists: Generate surprising plot twists for a short story to keep readers engaged.
- Setting Exploration: Explore different settings for a fantasy world, including the physical environment, culture, and laws.
- Dialogue Scenarios: Create engaging dialogue exchanges for key scenes in a screenplay.
- Conflict Resolution: Brainstorm various resolutions to a central conflict in a narrative essay.
- Opening Lines: Develop intriguing opening lines that immediately capture the reader’s interest.
- Title Ideas: Generate catchy titles for a series of blog posts related to personal development.
Brainstorming Examples in Business
- Product Innovation: Brainstorm ideas for new products that meet emerging market needs.
- Marketing Strategies: Develop unique marketing strategies for launching a new service.
- Customer Engagement: Generate ideas to increase customer engagement through social media.
- Operational Efficiency: Explore ways to improve operational efficiency in manufacturing.
- Brand Expansion: Discuss potential markets for brand expansion and the strategies to enter them.
- Employee Wellness: Create initiatives to enhance employee wellness and work-life balance.
- Sustainability Practices: Brainstorm sustainable business practices that could be implemented to reduce environmental impact.
Brainstorming Examples for in School
- Interactive Learning: Develop interactive learning activities that can be integrated into various subjects.
- Peer Teaching: Brainstorm methods for implementing peer teaching sessions in math classes.
- Technology Use: Explore innovative ways to incorporate technology in classroom lessons.
- Field Trips: Generate ideas for educational field trips that complement the curriculum.
- Classroom Layout: Discuss different classroom layouts that facilitate active learning.
- Learning Games: Create educational games that can be used to teach complex subjects like chemistry.
- Student Feedback: Brainstorm methods for collecting and using student feedback to improve teaching practices.
Brainstorming Examples for in Real Life
- Home Organization: Brainstorm ways to maximize space and organize a small living area.
- Travel Plans: Generate ideas for budget-friendly travel itineraries.
- Meal Prep: Discuss various meal preparation strategies for busy weekdays.
- Community Events: Brainstorm community event ideas that encourage local participation.
- Personal Goals: Generate a list of achievable personal goals for the year with steps to accomplish them.
- Fitness Routines: Develop fitness routines that can be done at home with minimal equipment.
- Budgeting Techniques: Explore different budgeting techniques to manage personal finances more effectively.
Brainstorming Examples for in Healthcare
- Patient Education: Brainstorm methods to improve patient education on chronic diseases.
- Health Campaigns: Generate ideas for public health campaigns that promote vaccinations.
- Wellness Programs: Discuss wellness program ideas for hospital staff to reduce stress and burnout.
- Technology Integration: Explore ways to integrate new technologies into patient care for better outcomes.
- Community Health: Brainstorm strategies to address health disparities in underserved communities.
- Preventive Measures: Develop preventive measures to reduce the incidence of hospital-acquired infections.
- Mental Health: Generate initiatives to enhance mental health services within the community.
How to Brainstorm?
- Define the Problem:
Clearly define the problem or challenge at hand. Make sure everyone understands the main focus and the objectives of the brainstorming session. - Set the Rules:
Before starting, establish ground rules. Common rules include withholding criticism, welcoming unusual ideas, combining and improving ideas, and aiming for quantity over quality during the brainstorming phase. - Warm-Up Session:
Conduct a short warm-up exercise to get the creative juices flowing. This can be a simple game or a fun question unrelated to the main topic. - Idea Generation:
Begin the session. Use techniques like mind mapping or free writing to generate ideas. Encourage participants to build on or combine ideas from others. - Record Ideas:
Make sure to capture all ideas without evaluation. Use whiteboards, sticky notes, or digital tools to record everything. - Encourage Everyone to Participate:
Ensure that all participants have the opportunity to contribute. The facilitator should encourage quieter members to share their ideas too. - Time Management:
Keep the session timed to maintain focus and energy. Typical brainstorming sessions last from 15 minutes to an hour. - Review and Analyze Ideas:
Once the brainstorming is complete, group similar ideas, eliminate duplicates, and evaluate the ideas based on the criteria set for the solution. - Follow-Up:
Decide on the next steps. This could involve taking some ideas to a more detailed evaluation phase or assigning tasks for further research.
Tools and Techniques
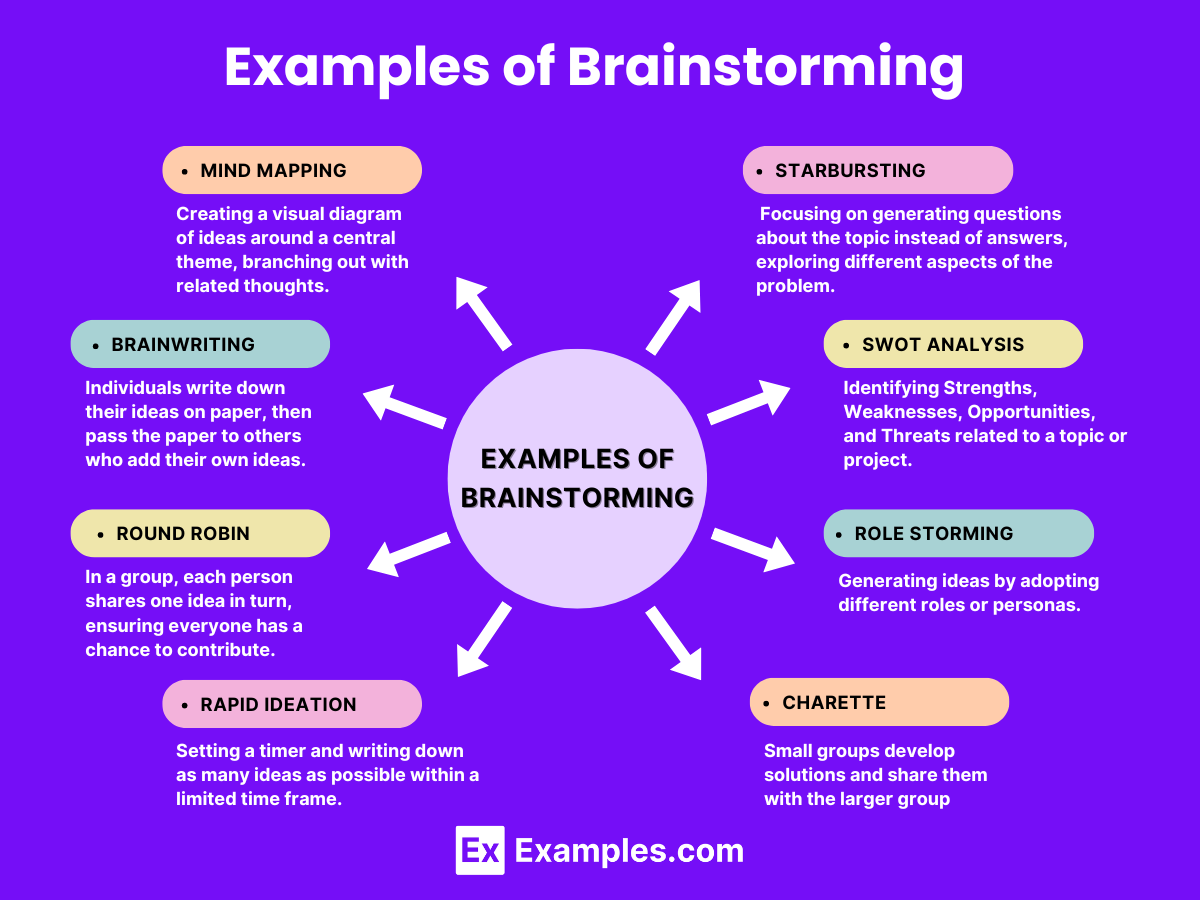
- Mind Mapping: This involves creating a visual diagram of ideas around a central concept. It helps in visualizing the relationships between ideas.
- Brainwriting: Participants write down their ideas on paper or sticky notes before sharing them with the group. This method can reduce the influence of louder voices and gives time for individual thinking.
- Role Storming: Participants take on different roles or personas and generate ideas from these perspectives. This can unlock new viewpoints and solutions.
- Online Collaboration Tools: Use digital platforms like Miro, Google Jamboard, or Trello for virtual brainstorming sessions. These tools allow remote teams to contribute and visualize ideas synchronously or asynchronously.
Brainstorming Ideas
- Photo Documentary: Start a photo documentary on a local interest, like the evolution of a neighborhood or a community project.
- Short Film: Write and direct a short film based on a local legend or personal story.
- Art Installation: Create an interactive art installation that involves community participation.
- Pop-Up Shop: Launch a pop-up shop to test a business idea, such as eco-friendly products or handmade crafts.
- Subscription Box Service: Start a subscription box service focused on a niche interest, like local artisan foods or DIY craft kits.
- Mobile App: Develop a mobile app that solves a local problem, like finding available parking spots or connecting local freelancers.
- Skill Swap: Organize a community skill swap where people can trade skills like cooking, photography, or coding.
- Meditation Retreat: Plan a weekend meditation retreat that focuses on mindfulness and mental health.
- Language Exchange: Set up a language exchange meet-up to help people learn new languages through conversation.
- Community Garden: Start a community garden to encourage local food production and provide a space for community gathering.
- Recycling Drive: Organize a recycling drive to help educate the community about environmental sustainability.
- Mentoring Program: Establish a mentoring program linking professionals with local students to foster career development.
- Tech Workshops: Conduct workshops on new technologies like blockchain or artificial intelligence for beginners.
- Maker Faire: Host a local maker faire to showcase inventions and DIY projects from the community.
- Hackathon: Organize a hackathon to address local issues like traffic management or public health.
- Fitness Challenge: Start a community fitness challenge to promote health and wellness, with activities suited for all ages.
- Healthy Eating Workshop: Conduct workshops on healthy eating, including cooking demonstrations and nutritional education.
- Yoga in the Park: Organize free yoga sessions in a local park, encouraging physical activity in a peaceful setting.
- Outdoor Movie Nights: Set up a series of outdoor movie nights that feature classic films or local filmmakers.
- Board Game Café: Open a board game café where people can socialize and play a variety of board games.
Why do we Use Brainstorming?
- Idea Generation: Brainstorming encourages the free flow of ideas from all participants, fostering creativity and innovation.
- Problem Solving: It helps groups identify and solve complex problems by leveraging diverse perspectives and approaches.
- Team Building: The collaborative nature of brainstorming can strengthen team cohesion and improve communication among members.
- Overcoming Biases: Brainstorming can help reduce individual biases as ideas are freely shared and collectively refined.
- Flexibility: It adapts to various contexts, whether for business strategy, product development, or academic research.
- Encourages Participation: It ensures everyone has a voice, promoting equal participation among team members.
- Stimulates Critical Thinking: By evaluating and building on ideas, participants enhance their analytical and critical thinking skills.
How does Brainstorming Work?
Brainstorming is a creative group activity designed to generate a broad range of ideas or solutions around a specific problem or topic. During a brainstorming session, participants are encouraged to freely express their thoughts and ideas, no matter how unconventional, without fear of criticism or judgment. This open and inclusive atmosphere helps to foster creativity and can lead to a diverse set of solutions. Typically, the session is guided by a facilitator who ensures that the conversation stays on track and that all participants have an opportunity to contribute. The goal is to collect a wide variety of ideas, which can later be refined and analyzed to determine the most viable solutions.
Types of Brainstorming
Traditional Brainstorming
Traditional brainstorming involves generating ideas freely in a group setting without criticism. Participants are encouraged to think broadly and contribute as many ideas as possible, often building on each other’s suggestions.
Silent Brainstorming
Silent brainstorming, also known as brainwriting, involves participants writing their ideas down privately before sharing them with the group. This method helps to avoid the influence of dominant personalities and encourages contributions from all participants.
Online Brainstorming
Online brainstorming uses digital tools to gather ideas from participants who may be in different locations. This method is particularly useful for remote teams and can include tools like shared documents, specialized brainstorming software, or online whiteboards.
Round Robin Brainstorming
In round robin brainstorming, participants take turns sharing ideas one at a time in a circular fashion. This systematic approach ensures that everyone has a chance to contribute.
Starbursting
Starbursting focuses on generating questions rather than answers. Participants brainstorm questions about the topic, which helps to explore different aspects and ensures a thorough understanding before seeking solutions.
Reverse Brainstorming
Reverse brainstorming involves thinking about the opposite of what you want to solve or improve. For example, instead of brainstorming ways to improve customer satisfaction, you would brainstorm ways to make customer experience worse, and then reverse those ideas to find positive solutions.
Stepladder Technique
The stepladder technique starts with a core group discussing ideas, then gradually introduces additional members one at a time. Each new member adds their ideas before hearing the group’s previously discussed points, allowing fresh perspectives to enter the conversation.
Strategies for Brainstorming
Traditional Brainstorming
This is the classic approach where all participants gather and share ideas spontaneously. The key principles include:
- No Criticism: All ideas are welcomed without immediate judgment to encourage open communication.
- Quantity Over Quality: The goal is to generate as many ideas as possible, refining them later.
- Freewheeling is Welcome: The wilder the idea, the better; it can lead to more creative and innovative solutions.
- Combination and Improvement: Building on others’ ideas can lead to unique and refined solutions.
Brainwriting
Brainwriting involves writing ideas down on paper instead of speaking them out loud. This can be particularly useful for introverted team members. Here’s how it typically works:
- Each participant writes down their ideas on paper.
- Papers are exchanged among the group, and others can build upon or modify the ideas presented.
- After several rounds, the papers are reviewed, and the best ideas are chosen for further discussion.
Online Brainstorming
With the rise of remote work, online brainstorming has become more prevalent. It uses digital tools to mimic traditional brainstorming sessions:
- Digital Whiteboards: Tools like Miro or Microsoft Whiteboard allow participants to post and manipulate ideas visually.
- Collaboration Platforms: Platforms like Slack or Microsoft Teams can facilitate brainstorming sessions with features like polls, threads, and shared documents.
Round Robin Brainstorming
In a round-robin session, participants share ideas in a sequential order, ensuring everyone has a chance to contribute:
- Each person in the circle contributes one idea at a time.
- The process continues until ideas are exhausted or time runs out.
- This method ensures that all voices are heard, especially in groups where some members may dominate the conversation.
Starbursting
Starbursting focuses on generating questions rather than answers. This method helps in thoroughly understanding the problem before jumping to solutions:
- The central idea or challenge is placed at the center of a star diagram.
- Each point of the star represents a question about the “what”, “who”, “when”, “where”, “why”, or “how” of the idea.
- This method helps in uncovering aspects of the problem that might not have been considered earlier.
Reverse Brainstorming
This method involves thinking about what could cause the project or idea to fail, rather than how to make it succeed:
- Participants identify potential problems or failures.
- Solutions are then developed to avoid these pitfalls, effectively strengthening the overall plan.
SCAMPER
SCAMPER is an acronym that stands for Substitute, Combine, Adapt, Modify, Put to another use, Eliminate, and Reverse. It is a checklist tool that helps think about a problem or product in different ways:
- Each letter prompts users to think about how they could improve a product, service, or process.
- This method encourages looking at existing elements in new ways.
How to Conduct a Brainstorming Session
A good brainstorming session will brainstorm ideas and have various brainstorming techniques used in the whole session. These sessions can be divided into a couple of days spanning one topic or subject.
1.) Choose a Topic for the Brainstorming Session
Begin by selecting the topic the brainstorming session will tackle. This topic should be a relevant subject, problem, or issue the group needs to discuss. The more complex the topic, the greater the need for a brainstorming session.
2.) Set the Date for the Brainstorming Session and Invite the Right People
After you have selected the topic of the brainstorming session, you will need to set the date when the brainstorming session will occur. You must make sure that the right people are accounted for and will be present during the brainstorming session. This means that you will need to find the best time for the brainstorming session. You may use any brainstorming software or tools to help with the brainstorming method.
3.) Select a Facilitator for the Brainstorming Session
The facilitator may not be the same person who will schedule and start the brainstorming session. If you do not want to be the facilitator and have someone else in mind, ask if they can be the facilitator of the brainstorming session. Just be sure that before the day of the brainstorming session, you have assigned a facilitator to the brainstorming session.
4.) Conduct the Brainstorming Session
When the set day has started, begin the brainstorming session with the group you have invited. Be sure to conduct brainstorming activities and ideation exercises within the brainstorming session. While sharing your ideas, be sure to properly document all the ideas and thoughts brought about by the brainstorming session through a brainstorming report.
5.) Close or Conclude the Brainstorming Session
Finish the brainstorming session and have the facilitator conclude the whole session with a concluding statement. Be sure to wrap up the session and create a call to action based on what was discussed.
What is a Brainstorming Tool?
A brainstorming tool refers to any instrument, software, or methodology that facilitates the brainstorming process. The primary goal of these tools is to enhance creativity, generate ideas, encourage participation, and organize thoughts in a collaborative environment. They can be used in various contexts, such as business planning, educational activities, problem-solving sessions, and creative projects.
Types of Brainstorming Tools
- Digital Software Applications:
- Mind Mapping Tools: Applications like MindMeister or XMind help users visually organize information, connecting thoughts and ideas around a central concept.
- Idea Management Software: Tools like Miro and Trello allow teams to generate, categorize, and prioritize ideas. They often include features for voting and commenting to facilitate collaborative decision-making.
- Real-time Collaboration Platforms: Software like Microsoft Teams or Zoom can be used for live brainstorming sessions, integrating video conferencing with real-time document editing.
- Analog Tools:
- Whiteboards and Sticky Notes: Traditional tools where participants write ideas on sticky notes and place them on a whiteboard. This method is excellent for visualizing and grouping concepts.
- Flip Charts or Paper Sheets: Often used in face-to-face settings, these tools provide a space for drawing and noting ideas as they are discussed.
- Techniques and Methodologies:
- Brainwriting: In this approach, participants write down their ideas on paper or cards before discussing them with the group, reducing the influence of dominant personalities.
- Round Robin: A structured method where each participant contributes one idea at a time in a circular fashion, ensuring everyone has a chance to participate.
Four Rules of Brainstorming
1. Withhold Criticism
One of the foundational rules of brainstorming is to withhold any form of criticism. During the brainstorming phase, the goal is to generate as many ideas as possible, regardless of their feasibility or practicality. This rule helps participants feel open to suggesting any and all ideas without fear of judgment or immediate rejection.
2. Welcome Wild Ideas
Encouraging wild and unusual ideas can lead to creative and innovative solutions. By allowing the imagination to run free, participants might stumble upon genius ideas that a conventional approach would never yield. This rule supports the creation of a creative environment where anything is possible.
3. Aim for Quantity
The principle of aiming for quantity over quality in the initial stages of brainstorming is vital. The more ideas generated, the greater the chances of finding a truly effective solution. High volume thinking pushes boundaries and uncovers unexpected solutions.
4. Combine and Improve Ideas
Brainstorming is also about collaboration and building on existing ideas. Participants are encouraged to combine, refine, and improve upon the ideas of others. This not only increases the quality of ideas but also promotes a collaborative team spirit.
What is the golden rule of brainstorming?
There are a couple of golden rules that we should monitor when we are a participant in a brainstorming session. The first rule that should be at the forefront of brainstorming is that all ideas matter and should be considered even if said ideas are bad or small. Everyone participating in the brainstorming session should be open to sharing their ideas and have enough space to create said ideas. The second rule of brainstorming sessions is to find new ways to ideate and create ideas in a specific amount of time. This could include different brainstorming exercises and programs used to refine the ideation process and give space for the person to ideate. The third rule should be to document all the ideas generated by the brainstorming session, even if the idea is shot or brought down. This is because some good ideas may be skimmed or skipped, doing this will ensure that the missed ideas are properly documented and tracked.
Benefits of Brainstorming
- Encourages creative thinking and idea generation.
- Fosters collaboration and team building.
- Helps identify multiple solutions to a problem.
- Promotes open communication and diverse perspectives.
- Reduces the risk of groupthink.
- Enhances problem-solving skills.
- Increases engagement and participation.
- Facilitates a deeper understanding of the topic.
- Provides a platform for all voices to be heard.
- Can lead to innovative and unconventional solutions.
Alternatives to Brainstorming
- Mind Mapping: Visualizing ideas and their connections in a diagram.
- Brainwriting: Writing ideas on paper and then sharing with the group.
- Reverse Brainstorming: Focusing on negatives or opposites of the desired outcome.
- Rapid Ideation: Setting a time limit to generate as many ideas as possible.
- Starbursting: Developing questions instead of answers about the topic.
- The Stepladder Technique: Adding team members to the discussion one at a time.
- Role Storming: Adopting different personas to generate ideas.
- Six Thinking Hats: Using different perspectives, symbolized by colored hats, to explore ideas.
Tips for brainstorming activities
- Set Clear Objectives: Before starting, clearly define the goals and objectives of the brainstorming session.
- Choose the Right Environment: Select a comfortable, distraction-free environment that encourages creativity.
- Establish Ground Rules: Set rules like “no idea is a bad idea” to create a safe space for sharing.
- Encourage Open Communication: Make sure everyone feels comfortable and encourage participants to build on each other’s ideas.
- Use Visual Aids: Utilize whiteboards, sticky notes, or digital tools to visually map out ideas.
- Limit Time: Set a time limit to keep the session focused and productive.
- Diversify the Group: Include participants from various backgrounds to enhance creativity.
- Assign Roles: Designate a moderator to guide the session and a scribe to take notes.
- Warm-Up Activities: Start with a simple exercise to get creative juices flowing.
- Review and Follow Up: Summarize the session’s outcomes and plan steps for implementing the best ideas.
Why is brainstorming important?
Brainstorming encourages diverse ideas, promotes creative solutions, and involves team members in problem-solving.
How do you prepare for a brainstorming session?
Prepare by defining the problem clearly, choosing a diverse group, setting rules, and arranging a conducive environment.
What are the main rules of brainstorming?
Key rules include withholding criticism, welcoming unusual ideas, aiming for quantity over quality, and combining ideas.
What are the best techniques for effective brainstorming?
Techniques include brainwriting, round-robin, starbursting, and the stepladder technique to enhance idea generation.
How long should a brainstorming session last?
Optimal sessions last between 15 to 60 minutes, depending on the complexity of the issue.
Can brainstorming be done individually?
Yes, solo brainstorming allows for flexibility and uninterrupted idea flow but may lack diverse perspectives.
What tools can enhance a brainstorming session?
Use whiteboards, sticky notes, online collaboration tools, and mind mapping software to boost creativity.
How do you evaluate ideas from a brainstorming session?
Evaluate ideas based on relevance, feasibility, and potential impact, often through follow-up sessions.
What are common mistakes to avoid in brainstorming?
Avoid dominating participants, rushing the process, and overlooking the implementation of feasible ideas.



