200+ Talents Examples
Talents are the unique abilities and skills that individuals possess. These innate or acquired capabilities can range from artistic and musical abilities to athletic prowess and intellectual strengths. Talents help individuals excel in various fields, setting them apart and often leading to personal and professional success. Identifying and nurturing these talents from a young age is crucial for maximizing potential and achieving one’s goals. In this article, we will explore the different types of talents, how to recognize them, and ways to develop and leverage them for success.
Definition of Talents
Talents refer to the natural abilities or aptitudes a person possesses, which enable them to excel in specific activities or areas. These inherent skills or capabilities are often evident early in life and can be developed and honed over time through practice and experience.
Examples of Talents

Artistic Talents
- Drawing and Painting: The ability to create visual art using various mediums like pencils, charcoal, oil paints, and watercolors.
- Music: Skills in playing musical instruments, singing, composing music, or understanding musical theory.
- Dancing: Proficiency in various dance forms, from ballet and jazz to hip-hop and contemporary.
- Acting: The talent for performing in plays, movies, or TV shows, bringing characters to life with expression and emotion.
Intellectual Talents
- Critical Thinking: The ability to analyze situations, think logically, and solve problems efficiently.
- Mathematical Skills: Proficiency in understanding and working with numbers, equations, and mathematical concepts.
- Linguistic Ability: Talent in learning languages, writing creatively, or communicating effectively.
- Scientific Research: Skills in conducting experiments, analyzing data, and making scientific discoveries.
Physical Talents
- Sports: Proficiency in sports such as basketball, soccer, swimming, or tennis, often involving a combination of strength, agility, and strategy.
- Coordination and Balance: Talents in activities requiring precise control of body movements, such as gymnastics or martial arts.
- Endurance: The ability to sustain prolonged physical activity, important in long-distance running, cycling, and other endurance sports.
- Strength: Exceptional physical power, often utilized in weightlifting, wrestling, and other strength-based activities.
Interpersonal Talents
- Leadership: The ability to guide, motivate, and inspire others towards a common goal.
- Empathy: The talent to understand and share the feelings of others, crucial in counseling, nursing, and social work.
- Negotiation: Skills in mediating conflicts, finding common ground, and reaching mutually beneficial agreements.
- Public Speaking: The ability to speak clearly and persuasively in front of an audience.
Creative Talents
- Writing: Crafting compelling stories, articles, or scripts, demonstrating a command of language and narrative structure.
- Design: Creating aesthetically pleasing and functional designs in fields like fashion, interior design, and graphic design.
- Innovation: The ability to think outside the box, developing new ideas, products, or processes.
- Cooking: Skills in preparing delicious and visually appealing meals, combining flavors, and techniques innovatively.
Technical Talents
- Programming: Writing and understanding code, developing software, and solving technical problems.
- Engineering: Applying scientific principles to design and build structures, machines, and systems.
- Craftsmanship: The talent for making high-quality handmade goods, such as woodworking, metalworking, or pottery.
- Mechanics: Skills in understanding and repairing machines, engines, and other mechanical systems.
Organizational Talents
- Project Management: The ability to plan, execute, and oversee projects efficiently.
- Time Management: Skills in organizing and prioritizing tasks to make the best use of time.
- Event Planning: Talents in organizing and coordinating events, ensuring all details are managed smoothly.
- Logistics: The ability to manage the flow of goods, information, and resources effectively.
Examples of Talents for Students
- Public Speaking: Ability to effectively communicate ideas to an audience.
- Critical Thinking: Analyzing information to solve problems.
- Creative Writing: Crafting engaging stories or essays.
- Mathematical Skills: Proficiency in solving mathematical problems.
- Artistic Ability: Skills in drawing, painting, or sculpture.
- Musical Talent: Playing an instrument or singing.
- Athletic Skills: Proficiency in sports like basketball, soccer, or track.
- Scientific Inquiry: Conducting experiments and making discoveries.
- Leadership: Guiding groups towards common goals.
- Technological Skills: Proficiency in using computers and software.
- Foreign Language: Fluency in speaking, writing, and understanding a second language.
- Dancing: Performing various dance styles.
- Problem-Solving: Finding solutions to complex issues.
- Time Management: Efficiently organizing tasks to meet deadlines.
- Collaboration: Working effectively with others to achieve a common goal.
Examples of Talents for Kids
- Drawing: Creating pictures with crayons, markers, or pencils.
- Storytelling: Making up and telling imaginative stories.
- Singing: Performing songs with a pleasant voice.
- Playing an Instrument: Learning to play instruments like piano or guitar.
- Dancing: Enjoying and performing various dance routines.
- Building with Blocks: Creating structures with Lego or other building toys.
- Reading: Reading books with good comprehension.
- Writing: Writing short stories or poems.
- Acting: Performing roles in plays or skits.
- Sports: Playing games like soccer, basketball, or baseball.
- Cooking: Helping in the kitchen and making simple recipes.
- Puzzles: Solving jigsaw puzzles or brainteasers.
- Drawing Comics: Creating cartoon characters and stories.
- Gardening: Growing and taking care of plants.
- Origami: Making shapes and figures out of paper.
Examples of Talents for Talent Show
- Singing: Performing a song solo or with accompaniment.
- Dancing: Showcasing a choreographed dance routine.
- Magic Tricks: Performing entertaining illusions and tricks.
- Comedy: Delivering a stand-up comedy routine.
- Juggling: Displaying skill in juggling balls, rings, or other objects.
- Playing an Instrument: Performing a piece on the piano, violin, or other instruments.
- Martial Arts: Demonstrating karate, taekwondo, or other martial arts forms.
- Poetry Recitation: Dramatically reciting a poem.
- Acting: Performing a short skit or monologue.
- Gymnastics: Showing gymnastic routines like flips and cartwheels.
- Beatboxing: Creating music and beats using only the mouth.
- Ventriloquism: Performing with a puppet while speaking without moving lips.
- Speed Painting: Creating a painting quickly in front of an audience.
- Storytelling: Captivating the audience with an engaging story.
- Balloon Twisting: Making various shapes and figures out of balloons.
Examples of Talents for Resume
- Project Management: Leading projects from conception to completion.
- Communication: Excellent verbal and written communication skills.
- Team Leadership: Managing and motivating teams effectively.
- Analytical Skills: Ability to analyze data and make informed decisions.
- Technical Proficiency: Expertise in specific software or technical tools.
- Problem Solving: Quickly identifying and solving issues.
- Customer Service: Providing excellent service and support to customers.
- Time Management: Prioritizing tasks to meet deadlines efficiently.
- Sales Skills: Ability to sell products or services effectively.
- Marketing Expertise: Creating and implementing marketing strategies.
- Financial Analysis: Assessing financial data to guide decision-making.
- Content Creation: Producing engaging written or visual content.
- Event Planning: Organizing and executing events successfully.
- Graphic Design: Creating visual concepts using graphic design software.
- Research Skills: Conducting thorough and accurate research.
Characteristics of Talents
1. Innate Ability
Talents are natural aptitudes that individuals are born with. These abilities often manifest early in life and distinguish themselves from skills acquired through practice alone.
2. Ease and Proficiency
Talented individuals often perform certain tasks with ease and proficiency that seem effortless compared to others. This natural ability allows them to excel quickly in specific areas.
3. Consistency
People with talents typically demonstrate consistent high performance in their area of talent. This consistency is often maintained over time, even with varying levels of effort.
4. Passion and Enthusiasm
Talented individuals usually show a strong passion and enthusiasm for their area of talent. This intrinsic motivation drives them to engage in and enjoy activities related to their talent.
5. Creativity and Innovation
Talents often come with a high degree of creativity and innovation. Talented individuals can think outside the box and develop unique solutions or create original works in their field.
6. Early Recognition
Talents are often recognized at an early age. Parents, teachers, and mentors can usually identify these natural abilities in children through observation and interaction.
7. Adaptability
Talented individuals often exhibit a high level of adaptability. They can easily adjust to new challenges and environments within their talent area, quickly learning and applying new skills.
8. High Learning Curve
When engaging in activities related to their talent, individuals often experience a steep learning curve. They pick up new concepts and techniques faster than others.
9. Strong Memory
Many talented individuals have a strong memory for details relevant to their talent area. This helps them recall techniques, patterns, or information crucial to their performance.
10. Resilience
Talented people often show resilience and determination. They are willing to face challenges and setbacks, using them as opportunities to grow and improve.
11. Focus and Concentration
High levels of focus and concentration are common among talented individuals. They can immerse themselves in their activities for extended periods, often losing track of time.
12. Positive Feedback Loop
The natural ability and success that come with talent often create a positive feedback loop. Success and recognition boost confidence and motivation, leading to further development and achievement.
How to Identify Talents
Identifying talents in individuals involves recognizing their unique abilities, skills, and potential. Whether you’re a teacher, employer, or team leader, understanding how to spot and nurture talent can lead to significant personal and organizational growth. Here are some effective strategies to identify talents
Observe Behavior and Performance
1. Pay Attention to Enthusiasm: Talented individuals often display a high level of enthusiasm and passion for certain activities or subjects. Look for those who are eager to take on new challenges and show a genuine interest in their work.
2. Monitor Consistent High Performance: Consistently high performance in specific tasks or areas can be a strong indicator of talent. Track achievements and assess how individuals handle different responsibilities over time.
Assess Skills and Abilities
3. Conduct Skills Assessments: Use formal assessments, tests, or practical exercises to evaluate specific skills. This can help you identify strengths and areas where individuals excel.
4. Seek Feedback from Others: Gather feedback from peers, supervisors, or teachers who interact with the individual regularly. Their observations can provide valuable insights into hidden talents.
Encourage and Provide Opportunities
5. Offer Diverse Experiences: Provide opportunities for individuals to explore various roles, projects, or subjects. This can help uncover latent talents and allow individuals to discover their strengths.
6. Encourage Self-Reflection: Promote self-assessment and reflection. Encourage individuals to think about what they enjoy and where they believe their strengths lie. Self-awareness is a crucial component of talent identification.
Look for Natural Leadership and Innovation
7. Identify Natural Leaders: Observe who naturally takes on leadership roles, even in informal settings. Leadership skills can be a strong indicator of talent, especially in group activities or team projects.
8. Recognize Creative Problem Solving: Talented individuals often come up with innovative solutions to problems. Pay attention to those who think outside the box and approach challenges creatively.
Create a Supportive Environment
9. Foster a Culture of Recognition: Create an environment where achievements are acknowledged and celebrated. Recognition can motivate individuals to further develop their talents.
10. Provide Mentorship and Guidance: Offer mentorship programs to help individuals refine their skills and reach their potential. Experienced mentors can guide and support emerging talents.
Utilize Technology and Data
11. Leverage Data Analytics: Use data analytics to identify patterns in performance and behavior. Technology can help track progress and highlight areas where individuals consistently excel.
12. Implement Talent Management Software: Consider using talent management software to streamline the identification and development process. These tools can provide insights into skills, performance, and potential growth areas.
Types of Talents
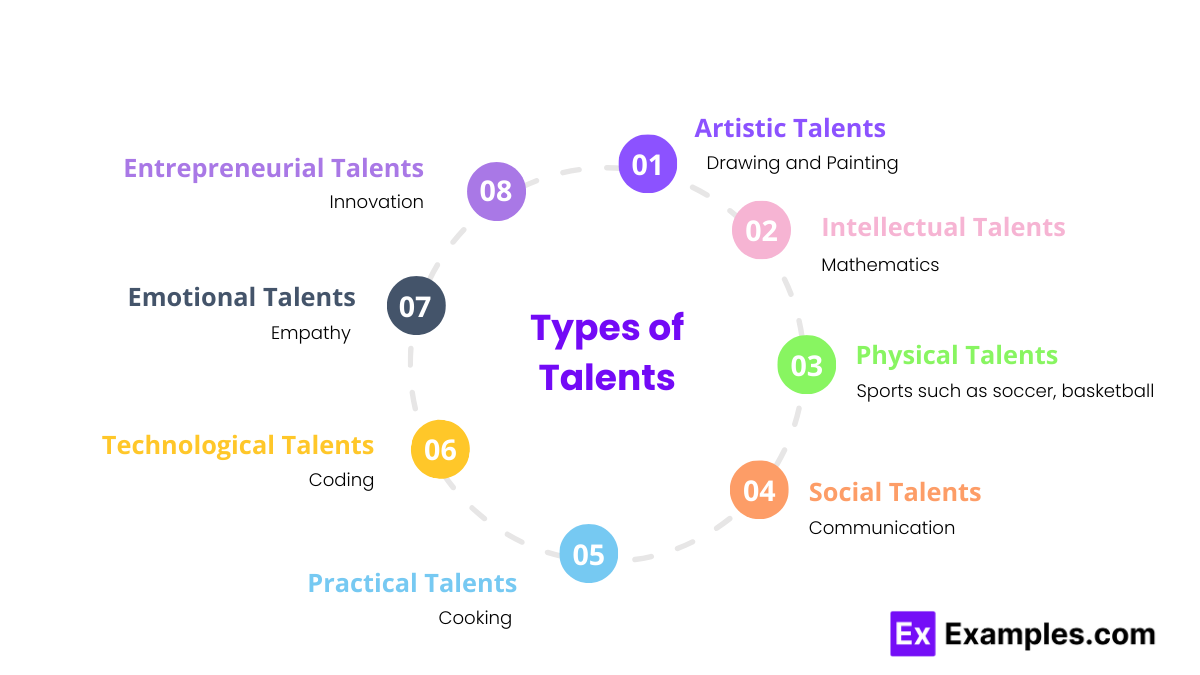
Talents are diverse and can manifest in various forms. Here are some broad categories of talents with a brief explanation and one example for each:
1. Artistic Talents
Artistic talents involve creative expression and are often associated with the arts. These talents allow individuals to produce work that is visually or emotionally captivating.
- Example: Drawing and Painting – Skills in visual arts, creating detailed and expressive artwork.
2. Intellectual Talents
Intellectual talents involve cognitive abilities and academic skills. These talents enable individuals to excel in fields that require critical thinking, problem-solving, and specialized knowledge.
- Example: Mathematics – Natural aptitude for understanding and applying mathematical concepts.
3. Physical Talents
Physical talents involve bodily coordination, strength, and athleticism. These talents are essential for activities requiring physical exertion and precise movements.
- Example: Sports – Skills in specific sports such as soccer, basketball, or swimming.
4. Social Talents
Social talents involve interpersonal skills and the ability to connect with others. These talents are crucial for building relationships, effective communication, and leadership.
- Example: Communication – Talent for effective verbal and written communication.
5. Practical Talents
Practical talents involve skills that are useful in everyday life and various professions. These talents help individuals perform practical tasks efficiently and creatively.
- Example: Cooking – Ability to prepare delicious and nutritious meals.
6. Technological Talents
Technological talents involve skills related to modern technology and digital environments. These talents are increasingly important in a tech-driven world, enabling individuals to innovate and excel in various digital fields.
- Example: Coding – Ability to write and understand computer programs and software.
7. Emotional Talents
Emotional talents involve understanding, managing, and expressing emotions effectively. These talents contribute to personal well-being and successful social interactions.
- Example: Empathy – Strong ability to understand and share the feelings of others.
8. Entrepreneurial Talents
Entrepreneurial talents involve the ability to identify opportunities, take risks, and innovate in the business world. These talents drive economic growth and create new ventures.
- Example: Innovation – Talent for developing new ideas, products, or services.
9. Teaching Talents
Teaching talents involve the ability to convey information effectively and inspire learning in others. These talents are crucial for educators and mentors.
- Example: Instruction – Skill in explaining complex concepts in an understandable way.
10. Leadership Talents
Leadership talents involve guiding, motivating, and directing groups of people toward a common goal. These talents are essential for managing teams and organizations.
- Example: Visionary Thinking – Ability to see the big picture and inspire others to work towards long-term objectives.
Differences Between Gifts and Talents
| Aspect | Gifts | Talents |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Often believed to be divinely bestowed | Naturally occurring abilities or skills |
| Development | May be seen as inherent and requiring less effort to develop | Requires practice, training, and refinement |
| Nature | Often seen as unique and extraordinary | Can be common and widespread |
| Recognition | Sometimes recognized as spiritual or supernatural | Recognized as a result of natural aptitude |
| Scope | Can encompass a wide range of areas including spiritual and moral attributes | Usually related to specific skills or fields |
| Examples | Healing, prophecy, wisdom | Playing a musical instrument, athletic skills |
| Cultural Perception | Highly valued in religious and spiritual contexts | Valued in cultural, artistic, and professional contexts |
| Impact | Often believed to have a significant impact on community or spiritual life | Impacts personal and professional achievement |
List of Talents
- Sculpting: Creating three-dimensional art pieces using materials like clay, metal, or stone.
- Photography: Capturing images with artistic quality and technical skill using cameras and editing software.
- Filmmaking: Directing, producing, and editing films, involving storytelling through moving images.
- Graphic Novel Creation: Writing and illustrating graphic novels, combining text and visuals to tell a story.
- Calligraphy: The art of beautiful handwriting, often using special pens or brushes.
- Tattoo Artistry: Designing and applying tattoos on the skin using needles and ink.
- Fashion Illustration: Creating sketches of clothing and accessories for fashion design.
- Philosophical Analysis: Pondering and critically examining complex ethical and existential questions.
- Historical Research: Uncovering and interpreting past events through documents, artifacts, and other sources.
- Literary Criticism: Analyzing and critiquing literary works to understand deeper meanings and contexts.
- Economics: Understanding and applying economic theories and principles to analyze financial systems.
- Cultural Anthropology: Studying and understanding different cultures and their development.
- Political Science: Analyzing political systems, behaviors, and theories.
- Linguistics: Studying language structure, development, and usage across different languages.
- Yoga: Mastering yoga postures and techniques for physical and mental well-being.
- Pilates: Practicing Pilates exercises to improve flexibility, strength, and body awareness.
- Rock Climbing: Skills in climbing natural rock formations or indoor walls using technical equipment.
- Parkour: Navigating obstacles efficiently and creatively using running, jumping, and climbing techniques.
- Archery: Precision and skill in using a bow and arrow for sport or hunting.
- Equestrianism: Riding and managing horses in various equine activities.
- Surfing: Riding ocean waves skillfully on a surfboard.
- Teaching: Educating and inspiring students through lessons and activities.
- Mentoring: Guiding and supporting someone’s personal or professional growth through advice and encouragement.
- Customer Service: Providing excellent assistance and resolving issues for customers.
- Team Building: Creating and maintaining strong, cohesive team dynamics in various settings.
- Networking: Building and maintaining professional relationships for career or business growth.
- Conflict Resolution: Mediating disputes effectively to reach amicable solutions.
- Interviewing: Conducting insightful and productive interviews for various purposes.
- Animation: Creating animated sequences and characters for films, games, and other media.
- Flower Arranging: Designing aesthetically pleasing floral arrangements for various occasions.
- Game Design: Developing engaging and interactive games for entertainment or education.
- Songwriting: Composing original songs, including lyrics and melodies.
- Interior Decorating: Designing and arranging interior spaces for aesthetics and functionality.
- Origami: The art of paper folding to create intricate designs and figures.
- Makeup Artistry: Applying makeup for various effects and occasions, including beauty and special effects.
- Data Analysis: Interpreting and making sense of data to inform decisions and strategies.
- Cybersecurity: Protecting systems and networks from digital attacks.
- Drone Operation: Flying and managing drones for various purposes, including photography and surveying.
- Artificial Intelligence: Developing AI algorithms and applications for various uses.
- 3D Modeling: Creating digital three-dimensional models for use in design, gaming, and simulations.
- Network Administration: Managing and maintaining computer networks to ensure smooth operation.
- Web Development: Building and maintaining websites with various functionalities.
- Financial Planning: Managing finances and investments for individuals or organizations.
- Inventory Management: Keeping track of goods and supplies to ensure availability and efficiency.
- Human Resources: Managing employee relations and organizational culture.
- Quality Control: Ensuring products or services meet specific standards and requirements.
- Risk Management: Identifying and mitigating potential risks in various contexts.
- Supply Chain Management: Overseeing the production flow of goods from suppliers to customers.
- Strategic Planning: Developing long-term goals and plans for organizations or projects.
- Multitasking: Handling multiple tasks efficiently and effectively.
- Persuasion: Convincing others to see a particular viewpoint or take specific actions.
- Adaptability: Adjusting quickly to new situations and challenges.
- Resourcefulness: Finding quick and clever solutions to problems.
- Patience: Maintaining composure in challenging situations.
- Detail Orientation: Paying attention to small details to ensure accuracy and quality.
- Emotional Intelligence: Understanding and managing your own and others’ emotions.
- Mindfulness: Maintaining awareness and focus on the present moment.
- Intuition: Using gut feelings to make decisions and solve problems.
- Self-Motivation: Driving yourself to achieve goals without external encouragement.
- Resilience: Bouncing back from setbacks and failures.
- Storytelling: Crafting and narrating engaging tales, whether orally or in writing.
- Pottery: Creating functional and decorative objects from clay, then firing them in a kiln.
- Gardening: Cultivating and maintaining plants, flowers, and vegetables.
- Candle Making: Producing candles using wax, wicks, and molds.
- Voice Acting: Performing character voices for animations, video games, or a books.
- Cartooning: Drawing and creating humorous or satirical illustrations.
- Mosaic Art: Assembling small pieces of glass, stone, or other materials to create images or patterns.
- Glass Blowing: Shaping molten glass into artistic or functional items using a blowpipe.
- Embroidery: Decorating fabric with needle and thread, creating intricate designs.
- Knitting: Using needles to interlock yarn into fabric, making items like scarves and sweaters.
- Quilting: Sewing together layers of fabric and padding to create quilts.
- Wood Carving: Sculpting wood into various shapes and designs using carving tools.
- Digital Art: Creating artwork using digital tools and software.
- Street Performing: Entertaining passersby in public spaces through music, magic, or other acts.
- Mime: Performing without speaking, using gestures and expressions to convey stories.
- Puppetry: Manipulating puppets to perform in shows or educational programs.
- Stand-Up Comedy: Performing humorous monologues and engaging with audiences.
- Illustration: Creating visual representations to complement texts or stand alone.
- Ceramics: Making objects from clay that are then fired to achieve hardness.
- Cake Decorating: Designing and applying decorations on cakes using icing, fondant, and other materials.
- Mixology: The art of crafting and mixing cocktails and other beverages.
- Baking: Preparing and cooking a variety of baked goods, including bread, pastries, and cakes.
- Cheese Making: Producing cheese through processes of curdling and aging milk.
- Soap Making: Creating soaps using various fats, oils, and fragrances.
- Perfume Making: Crafting fragrances by blending aromatic compounds.
- Leatherworking: Crafting items from leather, such as bags, belts, and shoes.
- Metal Smithing: Shaping and forging metal into tools, jewelry, or decorative items.
- Blacksmithing: Forging and shaping iron and steel to create various items.
- Jewelry Making: Designing and crafting jewelry using metals, gemstones, and other materials.
- Beekeeping: Managing bee colonies to produce honey and other bee products.
- Herbalism: Using plants for medicinal purposes and creating herbal remedies.
- Bird Watching: Observing and identifying different bird species in their natural habitats.
- Astrology: Interpreting the positions of celestial bodies to understand their influence on human affairs.
- Astronomy: Studying celestial objects and phenomena using scientific methods.
- Genealogy: Tracing and studying family histories and ancestries.
- Cosplaying: Creating and wearing costumes to represent characters from various media.
- Brewing: Making beer through the fermentation of grains.
- Winemaking: Producing wine from grapes or other fruits through fermentation.
- Survival Skills: Knowledge and techniques for surviving in the wilderness or in emergency situations.
- Foraging: Gathering wild food resources like plants, mushrooms, and berries.
How to Recognize Talents
Recognizing talent is crucial for fostering growth and ensuring the right individuals are in positions where they can thrive. Here are some key strategies to identify talents effectively
1. Observe Behavior and Performance
Key Indicators:
- Consistency: Talented individuals consistently deliver high-quality work.
- Problem-Solving: They approach challenges with innovative solutions.
- Leadership: They naturally take charge and inspire others.
2. Seek Feedback
Sources of Feedback:
- Peers: Colleagues often notice skills that may go unseen by supervisors.
- Supervisors: They can provide insights based on performance metrics and observations.
- Self-assessment: Encourage individuals to reflect on their own strengths and areas for improvement.
3. Conduct Assessments
Types of Assessments:
- Skills Tests: Measure specific abilities relevant to the job.
- Personality Tests: Understand how their traits align with team dynamics and company culture.
- Performance Reviews: Regular evaluations to track progress and identify areas of excellence.
4. Encourage Open Communication
Methods:
- One-on-One Meetings: Personalized discussions to understand aspirations and strengths.
- 360-Degree Feedback: Comprehensive evaluations from multiple perspectives.
- Surveys and Questionnaires: Anonymously gather insights on performance and skills.
5. Provide Opportunities for Growth
Growth Strategies:
- Training Programs: Offer courses and workshops to enhance skills.
- Mentorship: Pair them with experienced mentors to guide their development.
- Challenging Projects: Assign tasks that push their boundaries and reveal hidden talents.
6. Monitor Adaptability and Learning Agility
Key Traits:
- Flexibility: Talented individuals can adjust to new situations and roles.
- Continuous Learning: They seek out new knowledge and skills proactively.
- Resilience: They handle setbacks with a positive attitude and learn from them.
7. Analyze Work Ethics and Attitude
Key Indicators:
- Dedication: They show commitment to their work and go the extra mile.
- Team Player: They collaborate effectively and contribute to team success.
- Passion: Their enthusiasm for their work is evident and inspiring to others.
8. Use Data and Analytics
Tools:
- Performance Metrics: Track key performance indicators (KPIs) to identify high performers.
- Analytics Software: Utilize tools to analyze patterns in performance data.
- Benchmarking: Compare individuals’ performance against industry standards.
Advantages of Having Talents
Talents are natural abilities or skills that can significantly impact an individual’s personal and professional life. Here are some key advantages of having talents:
1. Personal Fulfillment
Talents often align with personal interests and passions, leading to a greater sense of satisfaction and fulfillment in life. Engaging in activities that utilize one’s talents can boost happiness and reduce stress.
2. Career Success
Possessing unique talents can set individuals apart in the job market. Talented individuals often find it easier to excel in their careers, as they bring specialized skills and expertise that are highly valued by employers.
3. Increased Confidence
Recognizing and nurturing one’s talents can lead to higher self-esteem and confidence. Talented individuals are often more assured in their abilities and are willing to take on new challenges and opportunities.
4. Contribution to Society
Talents enable individuals to make meaningful contributions to their communities and society at large. Whether through artistic expression, scientific discovery, or athletic prowess, talented individuals can inspire and uplift others.
5. Enhanced Learning
Talented individuals often find it easier to learn and master new skills related to their area of expertise. Their natural abilities can accelerate the learning process, allowing them to achieve higher levels of proficiency in a shorter time.
6. Recognition and Opportunities
Talented individuals are more likely to receive recognition and accolades for their achievements. This recognition can lead to additional opportunities, such as scholarships, grants, promotions, and invitations to exclusive events or projects.
7. Personal Growth
Engaging in activities that utilize one’s talents can foster personal growth and development. It encourages individuals to set goals, overcome obstacles, and continually improve their skills.
8. Improved Relationships
Talents can help build stronger relationships by creating common ground with others who share similar interests. Talented individuals often find it easier to connect with like-minded people, fostering supportive and enriching social networks.
9. Financial Benefits
Talents can translate into financial gains, especially if they are marketable skills. For instance, talented musicians, athletes, or entrepreneurs can monetize their abilities, leading to increased financial stability and wealth.
10. Lifelong Enjoyment
Talents provide a source of lifelong enjoyment and engagement. Whether through hobbies, volunteer work, or professional endeavors, talented individuals can continue to find joy and purpose in their activities throughout their lives.
How to Develop Talents
Developing talents is essential for personal growth and success. Here are some effective ways to nurture and enhance your talents:
1. Identify Your Talents
- Reflect on your interests and strengths.
- Seek feedback from others to uncover hidden talents.
- Take assessments or personality tests to identify potential talents.
2. Set Clear Goals
- Define what you want to achieve with your talents.
- Set short-term and long-term goals.
- Create a plan to reach these goals.
3. Practice Regularly
- Dedicate time each day or week to practice your talent.
- Focus on improving specific aspects of your talent.
- Maintain consistency to see gradual improvement.
4. Seek Guidance and Mentorship
- Find a mentor who excels in your area of interest.
- Join clubs or groups with similar interests.
- Attend workshops, seminars, and training sessions.
5. Embrace Challenges
- Step out of your comfort zone to tackle new challenges.
- Learn from failures and mistakes.
- Use obstacles as opportunities for growth.
6. Stay Committed and Patient
- Understand that talent development takes time.
- Stay motivated and avoid becoming discouraged by slow progress.
- Celebrate small achievements along the way.
7. Stay Curious and Keep Learning
- Continuously seek new knowledge related to your talent.
- Read books, watch videos, and take online courses.
- Stay updated with the latest trends and advancements.
8. Network with Like-Minded Individuals
- Connect with others who share your interests.
- Collaborate on projects or join study groups.
- Share experiences and learn from each other.
9. Maintain a Positive Mindset
- Cultivate a growth mindset, believing you can improve with effort.
- Stay optimistic and resilient.
- Surround yourself with supportive and encouraging people.
10. Track Your Progress
- Keep a journal to document your journey and improvements.
- Regularly review and adjust your goals.
- Use metrics or benchmarks to measure your success.
11. Use Technology and Resources
- Utilize apps and software that aid in talent development.
- Access online communities and forums for support.
- Leverage multimedia resources like podcasts and webinars.
12. Balance Rest and Work
- Ensure you get enough rest to avoid burnout.
- Balance practice with leisure activities.
- Listen to your body and mind to maintain overall well-being.
Importance of Talents
- Personal Fulfillment: Talents often align with our passions and interests. When we engage in activities that utilize our talents, we experience a sense of fulfillment and satisfaction.
- Career Success: In the professional realm, talents play a crucial role in career success. Whether you’re an artist, a scientist, a teacher, or any other professional, your talents contribute to your effectiveness and productivity.
- Innovation and Creativity: Talented individuals often push the boundaries of what’s possible. They bring fresh perspectives and innovative ideas to the table, driving progress and creativity in various fields.
- Collaboration: In collaborative environments, talents complement each other, leading to synergy and better outcomes. Recognizing and leveraging each team member’s talents can lead to more efficient and effective teamwork.
- Personal Growth: Developing and honing talents require dedication and effort. Through this process, individuals not only improve their skills but also undergo personal growth, building resilience, perseverance, and confidence.
- Contribution to Society: Talents contribute to the betterment of society in numerous ways. From providing entertainment and inspiration to solving complex problems and advancing technology, talented individuals enrich the lives of others.
- Self-Expression: Talents offer a means of self-expression. Whether it’s through music, art, writing, or any other medium, individuals can express their thoughts, emotions, and perspectives, fostering connection and understanding with others.
Similar and Opposite Words of “Talent”
| Word | Similar Words | Opposite Words |
|---|---|---|
| Talent | Skill, Gift, Ability, Aptitude, Expertise, Proficiency, Knack, Competence, Flair, Capability | Incompetence, Ineptitude, Inability, Incapability, Weakness, Clumsiness, Mediocrity, Inefficiency, Unskillfulness, Deficiency |
How can I identify my talents?
Identify talents by exploring different activities, seeking feedback from others, and paying attention to what comes naturally and brings joy.
Why are talents important?
Talents are important because they enhance personal growth, boost self-confidence, and provide opportunities for success in various fields.
Can talents be developed?
Yes, talents can be developed through practice, dedication, and continuous learning, allowing individuals to improve their skills and abilities.
Are talents and skills the same?
No, talents are natural abilities, while skills are developed through practice and experience. Talents can make acquiring related skills easier.
How do talents affect career choices?
Talents influence career choices by guiding individuals towards professions where their natural abilities can be utilized and further developed.
Can talents change over time?
Talents can evolve with experience and practice, allowing individuals to discover new abilities or enhance existing ones.
How can parents nurture their children’s talents?
Parents can nurture talents by providing opportunities, encouragement, and resources to explore different activities and interests.
What role do teachers play in developing talents?
Teachers play a crucial role by identifying students’ talents, offering guidance, and creating an environment that supports skill development.
Are there any disadvantages to having talents?
While talents are beneficial, they can lead to pressure and high expectations, making it important to balance and manage them effectively.



