Advantages & Disadvantages of Oral Communication Examples
Oral communication, involving spoken interactions, offers significant advantages such as immediacy and clarity, enabling quick feedback and fostering personal connections. However, it also presents challenges like the potential for misunderstandings and the lack of a permanent record, which can complicate matters in detailed or formal communications. Balancing these pros and cons is essential for effective communication in both personal and professional settings.
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Oral Communication?

Oral communication is the process of expressing information or ideas verbally. It’s a vital part of everyday interactions, ranging from informal chats to structured business meetings. The primary advantage of oral communication is the immediacy and dynamic nature of spoken words, enabling quick feedback and adjustments. However, it also faces challenges like potential misunderstandings and the lack of a physical record, which can be crucial in formal settings. Grasping these aspects is essential for effective communication in various contexts.
15 Advantages and Disadvantages of Oral Communication
Discover the vital aspects of oral communication with our comprehensive guide on its 15 advantages and disadvantages. Gain insights into why mastering this skill is crucial in various settings, from business to education. Understand how oral communication enhances interactions, fosters immediate feedback, and sometimes faces challenges like misunderstandings or limited reach. Ideal for anyone looking to improve their communication skills, this article is rich in keywords like effective oral communication, active listening, and public speaking.
Advantages
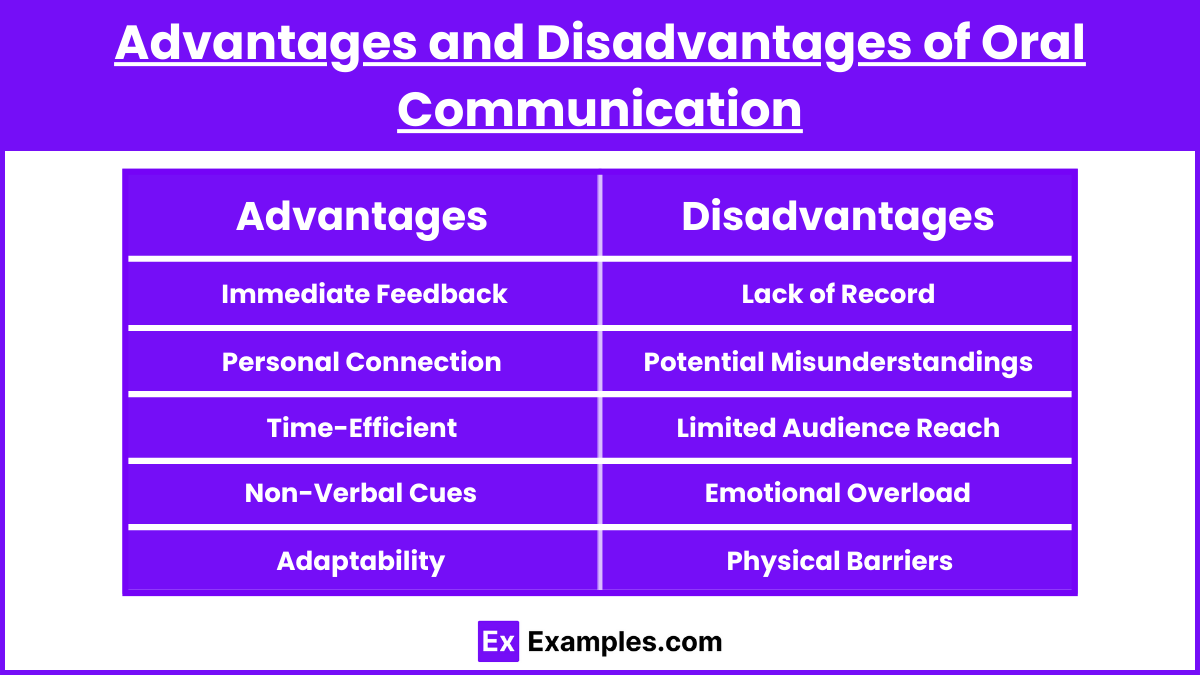
- Immediate Feedback: Oral communication enables real-time understanding of the listener’s response. This immediacy allows the speaker to clarify or modify their message instantly, ensuring better communication and understanding, crucial in dynamic conversations or negotiations.
- Personal Connection: It creates a deeper bond by allowing emotional and tonal expression. This personal touch in conversations can enhance the effectiveness of the message, fostering stronger relationships in both personal and professional settings.
- Time-Efficient: Speaking directly can convey messages faster than writing, especially beneficial in urgent or time-sensitive situations. This efficiency makes oral communication preferable in fast-paced environments, streamlining decision-making processes.
- Non-Verbal Cues: Body language, facial expressions, and voice tone in oral communication add critical non-verbal elements to the spoken words, providing a fuller, more nuanced understanding of the message.
- Adaptability: The ability to adapt speech on the fly based on audience feedback is a significant advantage. This flexibility allows for more effective and tailored communication, especially in group discussions or public speaking.
- Engagement: Oral communication typically engages audiences more effectively than written texts. The dynamic nature of spoken interactions keeps the audience more focused and involved.
- Ease of Use: It is accessible to everyone, regardless of their literacy levels. This universality makes it an inclusive mode of communication, bridging gaps across diverse groups.
- Spontaneity: Encourages impromptu ideas and dynamic discussions, leading to innovative and creative outcomes. This spontaneity can be particularly beneficial in brainstorming sessions or creative meetings.
- Builds Relationships: Effective in building and nurturing both personal and professional relationships. The interactive nature of speaking and listening fosters mutual understanding and trust.
- Persuasive: The emotional and emphatic aspects of oral communication make it more persuasive. This is particularly beneficial in sales, leadership, and motivational settings where convincing others is crucial.
- Team Building: Facilitates collaboration and brainstorming in team settings. Direct verbal interactions promote a sense of unity and collective problem-solving.
- Cultural Expression: Allows the speaker to incorporate cultural nuances and expressions, which can enhance the richness and relatability of the communication, especially in diverse settings.
- Conflict Resolution: More effective for resolving misunderstandings and conflicts through direct, face-to-face dialogue. This immediate interaction allows for quicker resolution and understanding.
- Learning Tool: An essential tool in education, fostering interactive learning and student participation. This makes the learning process more engaging and effective.
- Versatility: Useful across various contexts, from casual conversations to formal presentations. This adaptability makes it an essential skill in numerous scenarios.
Disadvantages
- Lack of Record: Without a permanent record, it’s challenging to reference or verify spoken words later, which can lead to issues in legal, academic, or business contexts where documentation is crucial.
- Potential Misunderstandings: Oral communication can lead to misunderstandings if the message is not clearly articulated or if the listener misinterprets the speech, especially in noisy or distracting environments.
- Limited Audience Reach: It’s not as effective for communicating with large groups simultaneously, as opposed to written communication that can be distributed widely and quickly.
- Emotional Overload: The emotional component of oral communication might overwhelm the message, leading to misinterpretation or perceived unprofessionalism, especially in sensitive or formal contexts.
- Physical Barriers: Distance, ambient noise, and poor audio equipment can significantly hinder the effectiveness of oral communication, making it challenging to convey messages clearly.
- Requires Presence: The necessity for both the speaker and the audience to be physically present can be limiting, especially in today’s globalized world where remote communication is often necessary.
- Short-Lived: The impact of spoken words can be fleeting compared to written documents, which can be reviewed and reflected upon over time.
- Language Barriers: Differences in language can pose significant challenges in oral communication, leading to misunderstandings or exclusion in multilingual environments.
- Overdependence: Relying too heavily on oral communication can lead to the neglect of written communication skills, which are also crucial in many professional and academic contexts.
- Privacy Concerns: It can be challenging to have private conversations in public or group settings, leading to potential breaches of confidentiality or difficulty in discussing sensitive topics.
- Varying Interpretations: Different listeners might interpret the same spoken message in various ways, leading to confusion and inconsistency in understanding.
- Nervousness: Fear or anxiety associated with public speaking can hinder an individual’s ability to communicate effectively, impacting the clarity and delivery of the message.
- Cultural Misunderstandings: Cultural differences in communication styles can lead to unintended offenses or misinterpretations, particularly in diverse and international settings.
- Inconsistency: There’s a risk of inconsistency in conveying the same message to different groups or at different times, which can lead to confusion and miscommunication.
- Requires Skills: Effective oral communication requires a set of skills, like clarity, conciseness, and confidence, which not everyone possesses naturally and may need to be developed over time.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Oral Communication Essay
Oral communication, the art of conveying messages through spoken words, is a cornerstone in human interaction. This essay delves into the various advantages and disadvantages of oral communication.
Advantages
- Immediate Feedback: The instant feedback aspect of oral communication allows for real-time understanding and immediate response, which is essential in fast-paced environments.
- Emotional Expression: Spoken communication enables the expression of emotions and sentiments, making messages more impactful and relatable.
- Efficiency: Oral communication is often more time-efficient than written forms, particularly in conveying urgent or complex information.
- Flexibility: The ability to modify the message on the spot based on audience reaction makes oral communication highly adaptable.
- Enhanced Relationships: It fosters stronger interpersonal relationships through personal interactions and shared experiences.
Disadvantages
- Lack of Record: The transient nature of spoken words means there is no permanent record, which can be problematic for future reference or legal purposes.
- Misinterpretations: Oral communication can be prone to misunderstandings if not delivered clearly or if the listener misinterprets the message.
- Limited Reach: Speaking to a large audience can be challenging, as it doesn’t have the extensive reach that written communication offers.
- Physical Barriers: Factors like distance, noise, and poor audio quality can impede the effectiveness of oral communication.
- Skill Dependency: Effective oral communication relies heavily on the speaker’s skills, such as clarity, tone, and body language, which might not be innate to everyone.
Advantages And Disadvantages of Oral and Written Communication
Understanding the differences between oral and written communication is crucial for effective information exchange. Each mode has its own set of advantages and disadvantages, impacting how messages are conveyed and received.
Advantages of Oral Communication
- Personal Touch: Oral communication offers a personal touch, enhancing the emotional connection between the speaker and the audience.
- Quick Clarification: It allows for immediate clarification of doubts, ensuring better understanding and reduced miscommunication.
- Spontaneity: Encourages spontaneous and creative exchanges, often leading to innovative solutions and ideas.
Disadvantages of Oral Communication
- Non-Permanent: Lack of a permanent record can lead to challenges in tracking and referencing past communications.
- Scope for Misunderstanding: Proneness to misunderstandings due to lack of clarity, accents, or speech impediments.
- Limited Documentation: The absence of written documentation makes it difficult to share or archive information for future reference.
Advantages of Written Communication
- Permanent Record: Provides a permanent record of the communication, useful for future reference and legal documentation.
- Wide Reach: Written communication, especially digital, can reach a larger audience across geographical boundaries.
- Clarity and Structure: Offers the opportunity to structure information logically, enhancing clarity and comprehension.
Disadvantages of Written Communication
- Time-Consuming: Often more time-consuming than oral communication, especially in drafting, editing, and finalizing.
- Lack of Personal Touch: Lacks the emotional and personal touch that is often conveyed through tone and body language in oral communication.
- Potential for Misinterpretation: Without the cues of tone and expression, written words can be misinterpreted, leading to misunderstandings.