Affective vs Effective – Differences, Example sentences, Uses
Affective primarily functions as an adjective, relating to emotions or feelings. It describes aspects or phenomena that are influenced by or result from emotions. Affective is often used in psychological contexts to discuss emotional processes, responses, or disorders. For example, when discussing how certain stimuli evoke emotional responses in individuals, the term “affective” is appropriate.
Effective is predominantly used as an adjective, signifying the capability of achieving intended results or the success in producing a desired outcome. It refers to something that works well and produces results efficiently. Effective can be used in various contexts, from management strategies to medication. When you want to convey that a method or tool accomplishes its goals successfully, you typically use “effective.”
Affective and Effective – Meanings
Affective: Relating to emotions or feelings, “affective” is an adjective used primarily in psychological contexts. It describes emotional processes or phenomena, such as how certain events or stimuli can trigger emotional responses in individuals. This term is essential in discussions about emotional disorders or the emotional aspects of human behavior.
Effective: As an adjective, “effective” refers to something that achieves its intended results successfully. It is commonly used to describe methods, strategies, or tools that are efficient and work well in producing a desired outcome. Whether in management, medicine, or personal productivity, “effective” highlights functionality and success.
Summery
“Affective” relates to emotions, often used in psychological contexts to describe emotional influences or reactions. It is always an adjective. “Effective” denotes the ability to achieve desired outcomes, used across various contexts to signify efficiency and success in accomplishing goals. Understanding these terms helps distinguish their usage in language, as “affective” pertains to emotional states while “effective” emphasizes practical effectiveness.
Difference between Affective and Effective
| Aspect | Affective | Effective |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Relates to emotions and feelings. | Denotes the capability to achieve desired results or outcomes. |
| Usage | Used as an adjective in psychological and emotional contexts. | Used as an adjective to describe methods, strategies, or tools. |
| Contexts | Commonly used in discussions about emotional responses or psychological states. | Applied in various fields such as business, medicine, and personal productivity. |
| Implications | Involves emotional impact or influence on behavior. | Focuses on efficiency and success in reaching specific goals or objectives. |
| Examples | “Her affective response to the film was intense sadness.” | “The strategy was effective in increasing sales by 20%.” |
When to Use Affective and Effective
Usage of Affective:
- Emotional Contexts: Use “affective” when discussing emotions, feelings, or mood states, especially in psychology or emotional studies.
- Describing Emotional Responses: It’s appropriate when describing how something affects someone emotionally. For example, in a sentence like “The affective aspect of the movie caused many viewers to cry.”
- Psychological Analysis: In clinical or counseling settings when discussing affective disorders such as depression or bipolar disorder.
Usage of Effective:
- Achieving Goals: Use “effective” when discussing strategies, methods, or actions that successfully achieve desired outcomes. For instance, “The new policy was effective at reducing pollution.”
- Evaluating Success: It’s suitable for reviews or evaluations where the focus is on how well something works or performs, like “This software is effective for data management.”
- Practical Applications: In contexts where practical results are discussed, such as in business, education, healthcare, or personal productivity.
Key Points to Remember:
- Affective is always an adjective and is used to describe something related to emotions or feelings.
- Effective can be an adjective describing something that successfully produces a desired result, and occasionally a noun (as in “have an effect”), though it’s most commonly used as an adjective to denote efficacy and success.
How to Use Affective and Effective
Affective
- Always use “affective” when referring to things related to emotions or feelings. It’s particularly relevant in psychology, psychiatry, and related fields discussing emotional conditions or responses.
- Examples in Sentences:
- “The therapist analyzed the patient’s affective reactions to stress.”
- “Affective symptoms of the disorder include prolonged sadness and irritability.”
Effective
- Use “effective” when you want to describe something that is successful in producing a desired or intended result. This can apply in business, education, technology, or any scenario where the efficiency of a method or tool is discussed.
- Examples in Sentences:
- “The new marketing strategy proved to be highly effective.”
- “She found an effective solution to the problem that saved the company time and money.”
Tips for Correct Usage:
- Modifiers: Pay attention to the words that typically accompany “affective” and “effective.” For “affective,” look for emotional adjectives or psychological terms. For “effective,” look for adjectives like “highly,” “very,” or phrases that discuss success.
- Check the Function in the Sentence: “Affective” will always act as an adjective modifying nouns related to psychological or emotional phenomena. “Effective” usually modifies nouns that are objects or goals of a process, strategy, or action, indicating the success of these endeavors.
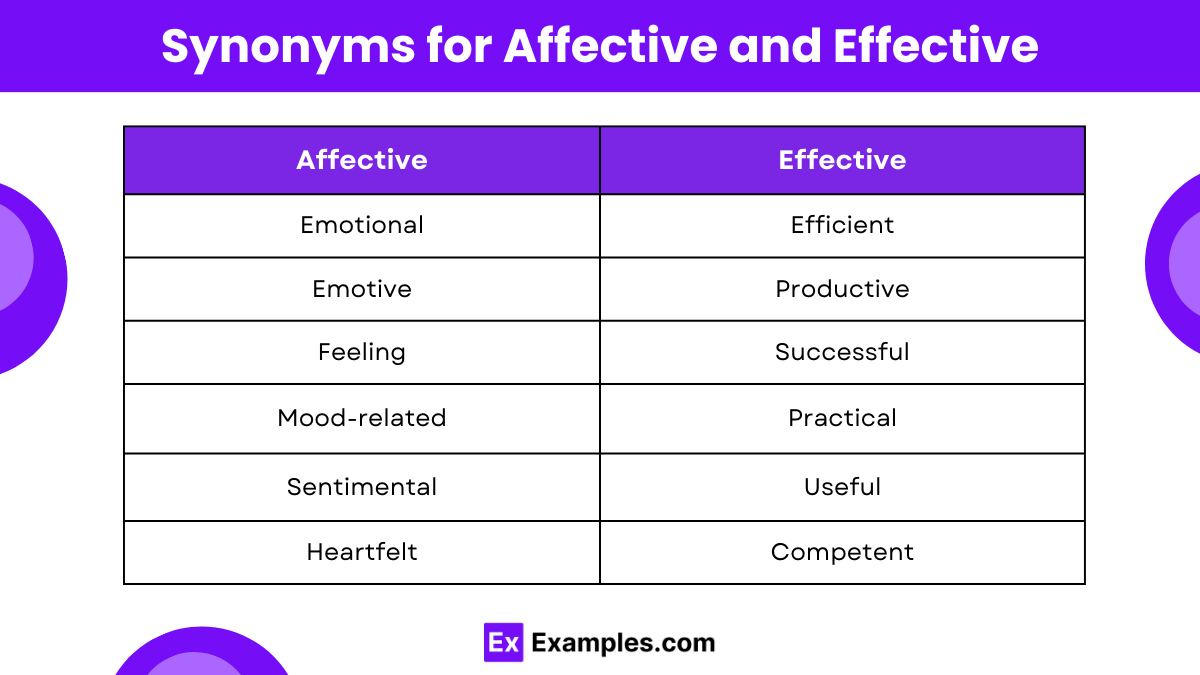
Synonyms for Affective and Effective
| Affective | Effective |
|---|---|
| Emotional | Efficient |
| Emotive | Productive |
| Feeling | Successful |
| Mood-related | Practical |
| Sentimental | Useful |
| Heartfelt | Competent |
| Responsive | Potent |
| Impassioned | Functional |
| Sensitive | Result-oriented |
| Expressive | Operational |
Affective Synonyms:
- Emotional: Pertaining to emotions, often used when discussing topics that provoke feelings.
- Emotive: Capable of arousing emotions in others, similar to emotional but often implying a stronger, more immediate reaction.
- Feeling: Related to the subjective experience of emotion, used to describe a sensation that is more about perception than cognition.
- Mood-related: Directly connected to or affecting one’s mood or general emotional state.
- Sentimental: Reflecting tender or nostalgic emotions, often used when emotions are influenced by personal feelings or memories.
- Heartfelt: Genuine and deep emotion, used when someone’s emotions are deeply sincere.
- Responsive: Sensitive to situations or emotions, capable of reacting quickly and emotionally to stimuli.
- Impassioned: Filled with or showing strong emotion, used for intense or heated emotional expressions.
- Sensitive: Easily affected by external conditions or stimuli, particularly in emotional contexts.
- Expressive: Effectively conveying emotion or feeling, often through art, speech, or other forms of communication.
Effective Synonyms:
- Efficient: Achieving maximum productivity with minimum wasted effort or expense, often used in business and production.
- Productive: Yielding good or useful results; effective especially in terms of producing a significant volume of output.
- Successful: Achieving desired visions and planned goals, commonly used in contexts where objectives are clearly met or exceeded.
- Practical: Involving real-world applications that work well and are related to everyday activities.
- Useful: Capable of being used for a practical purpose or in several ways, often referring to something that serves or fulfills a need.
- Competent: Adequate for the purpose, effectively capable of performing its function.
- Potent: Having great power, influence, or effect, used in contexts where something is notably impactful.
- Functional: Designed to be practical and useful rather than attractive, emphasizing utility over form.
- Result-oriented: Focused on achieving a specific outcome or result, typically in professional settings.
- Operational: In a condition of functioning or being able to function, often used in technical or mechanical contexts.
Antonyms for Affective and Effective
| Affective | Effective |
|---|---|
| Unemotional | Ineffective |
| Non-emotional | Inefficient |
| Dispassionate | Unproductive |
| Stoic | Useless |
| Indifferent | Futile |
| Impassive | Incompetent |
| Cold | Inadequate |
| Detached | Worthless |
| Numb | Nonfunctional |
| Unresponsive | Ineffectual |
Antonyms for Affective:
- Unemotional: Not influenced by or showing any emotions, often used to describe someone who does not outwardly express feelings.
- Non-emotional: Similar to unemotional, emphasizing a lack of emotional content or response.
- Dispassionate: Free from or unaffected by strong emotions; impartial or objective, typically used in situations requiring neutrality.
- Stoic: Pertaining to or resembling the Stoics, who were known for their philosophy that advocates detachment from emotion.
- Indifferent: Showing no interest or concern, used when someone does not react emotionally to situations that typically elicit a response.
- Impassive: Not feeling or showing emotion, often used to describe a face or demeanor that does not reveal internal states.
- Cold: Lacking affection or warmth of feeling, can refer to behavior that is seemingly devoid of emotional engagement.
- Detached: Separate or disconnected from emotions, often used to describe a state of emotional disengagement or objectivity.
- Numb: Deprived of the power of physical sensation or emotional expression, often due to shock or other overwhelming experiences.
- Unresponsive: Not reacting to stimuli or not exhibiting any emotional responses, used in both physical and emotional contexts.
Antonyms for Effective:
- Ineffective: Not producing an intended effect, used when methods, efforts, or tools fail to achieve their goals.
- Inefficient: Not achieving maximum productivity; wasting time, energy, or resources, often in a business or operational context.
- Unproductive: Not productive or yielding little or no result, used when work or efforts do not lead to meaningful outcomes.
- Useless: Having no ability or not useful in any situation, typically a strong term denoting complete ineffectiveness.
- Futile: Incapable of producing any significant result; useless, often used to describe efforts that are doomed to fail from the start.
- Incompetent: Lacking the skill or ability to perform effectively; inadequate to the demands of a role or task.
- Inadequate: Lacking the quality or quantity required; insufficient for a purpose, highlighting a shortfall in effectiveness.
- Worthless: Having no real value or use, used to describe objects, efforts, or methods that fail to meet any standards of utility.
- Nonfunctional: Not functioning or not working normally, specifically in the context of machinery or systems that are out of order.
- Ineffectual: Not producing any or the desired effect, similar to ineffective but often implying a persistent lack of success.
Examples of Affective and Effective in a Sentence
Examples of “Affective”:
- The affective component of the therapy focuses on helping patients understand and manage their emotions.
- Her affective response to the novel was profound, leaving her contemplative and moved.
- In the movie, the affective use of music enhances the emotional impact of the scenes.
- The teacher’s affective teaching style engaged the students emotionally, making the lessons memorable.
- Understanding the affective aspects of consumer behavior is crucial for designing effective marketing strategies.
Examples of “Effective”:
- The new software proved highly effective in streamlining our data processing tasks.
- To be effective in crisis management, one must remain calm and focused under pressure.
- The teacher’s effective communication skills ensured that the students understood complex concepts easily.
- He found an effective solution to the problem by using his extensive industry knowledge.
- For the medication to be effective, it must be taken consistently as prescribed by the doctor.
Exercise
Instructions:
- Read each sentence provided.
- Choose either “affective” or “effective” to correctly complete the sentence.
- Fill in the blanks with your chosen word.
Sentences:
- The therapy sessions were very _______ at helping him manage his stress better.
- The movie’s _______ qualities made it a tear-jerker for many in the audience.
- As a manager, she found an _______ strategy to boost team productivity and morale.
- His speech was _______ in evoking strong patriotic feelings among the listeners.
- The new software update is _______ in preventing the previous security issues.
- The documentary aimed to explore the _______ impact of social media on teenagers.
- Finding an _______ solution to this complex problem required innovative thinking.
- The novel’s _______ depth was appreciated by readers who favored character-driven stories.
- To combat the virus outbreak, the government’s response needed to be highly _______.
- Her ability to understand the _______ needs of her clients made her an exceptional therapist.
Answers:
- Effective – Here, the focus is on achieving good results in stress management.
- Affective – Refers to the emotional qualities that affected the audience.
- Effective – Discusses a strategy that successfully improves productivity.
- Affective – About evoking emotional responses.
- Effective – Pertains to the functionality of the software in addressing issues.
- Affective – Concerns the emotional impact on teenagers.
- Effective – Relates to finding a practical and successful solution.
- Affective – Discusses the emotional depth which appeals to readers’ feelings.
- Effective – Needs a result-oriented approach to combat the virus effectively.
- Affective – Focuses on understanding emotional aspects of clients.
What is the Difference between Affect and Affective?
“Affect” is a verb meaning to influence or produce a change, while “Affective” is an adjective referring to emotions or feelings, relating to affectivity or emotional response.
What is the Difference between Effective and Effect?
“Effective” is an adjective describing something successful in producing a desired result, while “Effect” is a noun referring to the result or outcome of an action.
Is it Work Effectively or Work Affectively?
It’s “work effectively.” “Effectively” implies working in a way that produces the desired results. “Affectively” relates more to emotions or feelings, which isn’t typically used in the context of work efficiency.



