29+ Agenda-Setting Theory in Mass Communication Examples
The Agenda-Setting Theory in Mass Communication is a pivotal concept that underscores how media channels shape public discourse. This guide delves into various facets of Mass Communication, explaining how media entities, through selective emphasis, influence public perception and priorities. Understanding this theory is crucial in today’s digitally driven world, where Mass Communication in Broadcasting and Journalism plays a significant role. This comprehensive guide offers real-world Mass Communication Examples, demonstrating the theory’s impact across different media forms, from Television Mass Communication to Social media Mass Communication.
What is Agenda-Setting Theory in Mass Communication?
Agenda-Setting Theory in Mass Communication is a concept that highlights the significant influence of media in shaping public perception. It suggests that the topics and issues emphasized by mass media outlets become the same topics and issues considered important by the public. This theory underscores the role of media as a gatekeeper, deciding which stories and events get covered and how they are presented. This, in turn, guides the audience’s attention towards certain subjects while omitting others.
How Agenda-Setting Works in Mass Communication
In the realm of Mass Communication, Agenda-Setting Theory plays a crucial role. For example, when Journalism Mass Communication focuses on specific political issues, it inevitably influences the public to perceive these issues as more important. Similarly, Social Media Mass Communication has transformed how information is disseminated and discussed, amplifying certain topics over others. By consistently highlighting specific themes, the media essentially sets the agenda for public discourse, subtly guiding what people talk and think about.
Real-Life Examples of Agenda-Setting Theory
Mass Communication in Real Life provides tangible examples of Agenda-Setting Theory. During election seasons, Television Mass Communication and Broadcasting Mass Communication often focus on specific candidates or policies, which can significantly influence public opinion and voting behaviors. Similarly, Mass Communication in Advertising routinely uses this theory to sway consumer preferences by repeatedly emphasizing certain products or brands. These scenarios illustrate how media channels can prioritize certain narratives, shaping public awareness and opinion on a wide range of issues.

History of Agenda-Setting Theory in Mass Communication
The Agenda-Setting Theory is a fundamental concept in the field of mass communication, offering profound insights into how media shapes public perception and priorities. Its roots date back to the 1960s and 1970s, a pivotal era in media studies.
The Emergence of Agenda-Setting Theory
The theory was first introduced by Dr. Maxwell McCombs and Dr. Donald Shaw in 1972. Their groundbreaking study during the 1968 U.S. presidential election analyzed the relationship between what the media covered and what the public thought was important. This study was a pivotal moment, illustrating that the media doesn’t necessarily tell us what to think, but rather what to think about – a core tenet of the Agenda-Setting Theory.
Expanding the Scope of the Theory
Over the years, the theory expanded beyond just news media. With the advent of mass personal communication and the proliferation of social media Mass Communication, the way agendas are set has diversified significantly. The theory now encompasses a broader spectrum of media forms, including broadcasting Mass Communication, journalism Mass Communication, and even blog Mass Communication.
The Theory in a Digital Age
In today’s digital age, the relevance of the Agenda-Setting Theory has only increased. With the rise of digital platforms, the power dynamics in agenda-setting have shifted. Now, not only mainstream media but also bloggers, social media influencers, and even individuals have the potential to influence the public agenda. This shift reflects a move from traditional models to more contemporary forms like email Mass Communication and social media Mass Communication.
Global Impact and Real-Life Applications
Globally, the Agenda-Setting Theory is used to understand various socio-political dynamics. For instance, in political campaigns, public relations strategies often revolve around this theory to shape public opinion. Similarly, in the realm of public health, understanding how different media platforms set agendas can significantly impact public awareness and behavior.
What is the Best Example of Agenda-Setting Theory in Mass Communication?
The Influence of Television News on Public Opinion
One of the most compelling examples of the Agenda-Setting Theory in action involves television news and its impact on public opinion. This instance vividly illustrates the “Mass Communication Examples in Real Life” and highlights “Why Mass Communication is Important.”
Television News and Public Perception
Television news has long been a dominant source of information for the public. In the context of Agenda-Setting Theory, the choices made by news producers and editors about which stories to broadcast and emphasize can significantly influence what viewers consider to be important. This process does not necessarily involve persuading the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint but rather focuses on highlighting specific issues over others.
Case Study: Election Coverage
A prime example of this phenomenon can be observed during election coverage. Television news channels often allocate extensive coverage to certain political issues, candidates, or events, which, in turn, shapes public perception about what is significant. For instance, if a news channel persistently covers a particular political scandal, viewers are more likely to perceive that issue as crucial, even if, in the broader spectrum of political discourse, it might not be as significant.
This phenomenon was strikingly evident in the 2016 U.S. Presidential election. Extensive media coverage of specific candidates and their controversies significantly influenced public discourse and perception. The media’s focus on particular aspects of the candidates’ policies, personalities, and scandals played a crucial role in setting the agenda for public discussion and opinion.
Impact Beyond Politics
The influence of television news in setting the public agenda extends beyond politics. It can shape public opinion on various issues, including social matters, health crises (like the COVID-19 pandemic), and international events. The selection of news stories and the emphasis they receive can determine what the public talks about, worries about, and gives importance to.

30 Examples of Agenda-Setting Theory in Mass Communication
Agenda-Setting Theory in Mass Communication highlights how media shapes public focus. It underscores the importance of media in determining which issues are at the forefront of public discussion. This theory reflects on various mass communication scenarios, demonstrating how media channels influence public perception by prioritizing certain topics. Understanding this theory is vital in fields like journalism, public relations, and social media, offering insights into effective communication strategies in the digital age.
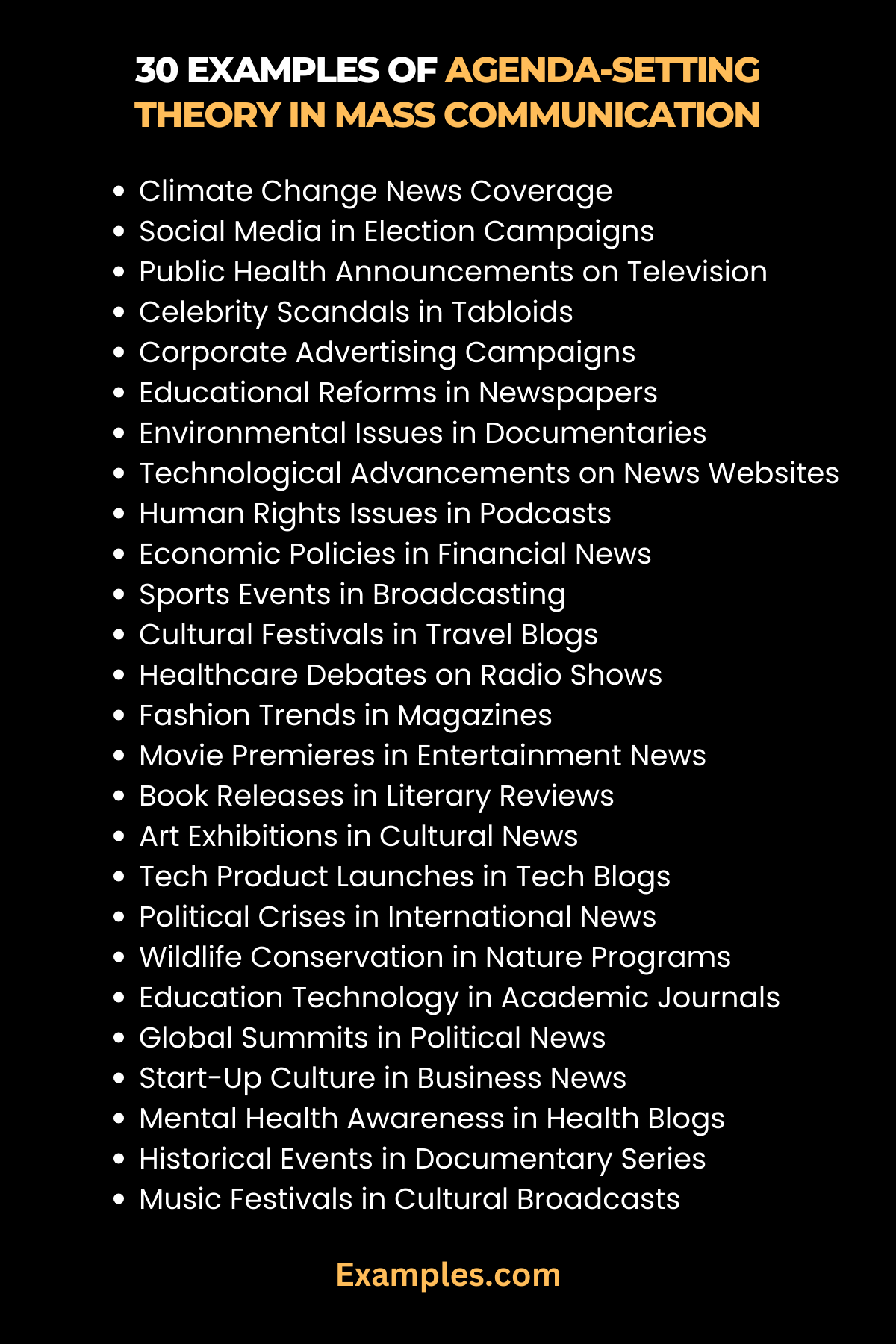
- News Coverage on Climate Change: A major news outlet consistently highlights climate change, shaping public concern and discourse.
- Election Campaigns on Social Media: Political parties using social media to steer conversations towards their key policies.
- Public Health Announcements on Television: Television channels focusing on a health crisis, leading to increased public awareness and concern.
- Celebrity Scandals in Tabloids: Extensive tabloid coverage of celebrity scandals, shifting public attention away from more pressing issues.
- Corporate Advertising Campaigns: Major companies using advertising to highlight specific consumer trends or needs.
- Educational Reforms Coverage in Newspapers: Newspapers prioritizing discussions on educational reforms, influencing public opinion on policy changes.
- Environmental Issues in Documentaries: Documentaries focusing on environmental issues, raising public awareness and concern.
- Technology Advancements on News Websites: Continuous coverage of technological advancements, shaping public interest and investment trends.
- Human Rights Issues in Podcasts: Podcasts dedicating episodes to human rights issues, increasing listener awareness and engagement.
- Economic Policies in Financial News: Financial news channels concentrating on specific economic policies, influencing investor behavior and opinions.
- Sports Events in Broadcasting: Broadcasting channels giving extensive coverage to certain sports, impacting public interest and participation.
- Cultural Festivals in Travel Blogs: Travel blogs emphasizing certain cultural festivals, influencing tourist attractions and perceptions.
- Healthcare Debates on Radio Shows: Radio shows focusing on healthcare debates, shaping public opinion on healthcare policies.
- Fashion Trends in Magazines: Fashion magazines highlighting certain trends, influencing public fashion choices.
- Movie Premieres in Entertainment News: Entertainment news channels focusing on certain movie premieres, affecting box office success.
- Book Releases in Literary Reviews: Literary reviews giving prominence to specific book releases, influencing reading trends.
- Art Exhibitions in Cultural News: Cultural news segments covering specific art exhibitions, impacting public interest in the arts.
- Tech Product Launches in Tech Blogs: Tech blogs extensively covering new product launches, shaping consumer preferences.
- Political Crises in International News: International news channels concentrating on certain political crises, influencing global awareness and responses.
- Wildlife Conservation in Nature Programs: Nature programs focusing on wildlife conservation, enhancing public concern and support for environmental initiatives.
- Education Technology in Academic Journals: Academic journals emphasizing developments in education technology, influencing educational trends and investments.
- Global Summits in Political News: Political news outlets focusing on global summits, shaping public understanding of international relations.
- Start-Up Culture in Business News: Business news channels highlighting start-up culture, influencing entrepreneurial trends.
- Mental Health Awareness in Health Blogs: Health blogs prioritizing mental health awareness, increasing public understanding and empathy.
- Historical Events in Documentary Series: Documentary series focusing on specific historical events, influencing public interest and understanding of history.
- Music Festivals in Cultural Broadcasts: Cultural broadcasts giving extensive coverage to music festivals, shaping music trends and popularity.
- Urban Development in Local News: Local news channels concentrating on urban development projects, impacting public opinion and community involvement.
- Social Justice Movements in Online Forums: Online forums dedicating space to social justice movements, enhancing public participation and advocacy.
- Travel Restrictions in Travel Advisories: Travel advisories focusing on travel restrictions, influencing public travel decisions and perceptions.
- Nutritional Guidelines in Health Shows: Health shows emphasizing new nutritional guidelines, impacting public dietary habits and health awareness.
Role of Agenda-Setting Theory in Mass Communication
Agenda-Setting Theory plays a pivotal role in mass communication, impacting how media shapes public perception and priorities. This theory suggests that the media doesn’t tell us what to think, but rather what to think about. By focusing on specific issues, the media sets the agenda for public discourse, influencing the topics and issues that people discuss and consider important.
Key Points:
- Media’s Influence on Public Perception: Media outlets, through their coverage, highlight certain events, issues, or personalities, thereby directing public attention towards these topics.
- Prioritization of Issues: Media can amplify the importance of specific topics, making them more salient in the public’s mind. This, in turn, can influence public opinion and even policy decisions.
- Framing of News: How media frames a story – the context, tone, and focus – can significantly affect how audiences interpret and understand the issue.
In-depth Exploration:
- Mass Communication Examples: For instance, extensive coverage of climate change in news media elevates its importance among public concerns, shaping policy discussions.
- Influence Across Platforms: The theory is applicable not just in traditional media like newspapers and television but also in digital media platforms, altering the way audiences engage with news and information.
Importance of Agenda-Setting Theory in Mass Communication
Understanding the importance of Agenda-Setting Theory is crucial in comprehending the dynamics of mass communication. This theory helps explain the powerful role media plays in shaping societal issues and public discourse.
Key Points:
- Guide for Media Practitioners: It serves as a guideline for journalists and media professionals in understanding the impact of their work on public opinion.
- Public Awareness and Engagement: By highlighting certain topics, the media can increase public awareness and engagement with critical social issues.
- Media Responsibility and Ethics: The theory underscores the responsibility of the media in fair and balanced reporting, as their choices can significantly influence public opinion and discourse.
In-depth Exploration:
- Media’s Role in Democracy: In a democratic society, the media’s role in agenda-setting is crucial for an informed citizenry and for holding those in power accountable.
- Mass Communication Characteristics: The theory highlights key characteristics of mass communication, such as its ability to reach a wide audience and influence the public agenda.
How to use Agenda-Setting Theory in Mass Communication
Implementing Agenda-Setting Theory in mass communication involves strategic media practices to influence public discourse and perception effectively.
Key Points:
- Strategic Media Coverage: Media professionals can use the theory to strategically cover issues that need public attention, thus setting the agenda for public discourse.
- Balancing News Content: It’s essential to balance news content to avoid overemphasis on certain topics at the expense of others, ensuring a diverse range of issues are brought to public attention.
- Engaging Audience Interests: Understanding audience interests and concerns can help media outlets tailor their content to align with public priorities, enhancing engagement and impact.
In-depth Exploration:
- Influencing Policy and Public Opinion: Through selective coverage and emphasis, media can influence policy-making and public opinion on various issues.
- Mass Communication in Real Life: Real-world examples include campaigns on public health issues, where media coverage can significantly impact public awareness and behavior.
Understanding the Agenda-Setting Theory is crucial for anyone involved in Mass Communication. Whether you’re exploring careers, crafting messages in journalism, or utilizing social media, this theory offers invaluable insights. It helps navigate the complex landscape of media influence, ensuring your communication is both impactful and relevant in today’s digitally connected world.