49+ Broadcasting Mass Communication Examples
Broadcasting in mass communication is a dynamic field, pivotal in disseminating information to a wide audience through mediums like television and radio. This guide provides an in-depth look into the world of broadcasting, exploring various facets from news production to entertainment programming. It illustrates key concepts using practical communication examples, shedding light on how broadcasting effectively captures public attention, shapes opinions, and informs society. Whether it’s a breaking news report or a captivating radio show, broadcasting remains a crucial element in the tapestry of mass media.
What is Broadcasting in Mass Communication?
Broadcasting in mass communication refers to the distribution of audio or video content to a dispersed audience via electronic mass communication mediums. Typically, this involves using television and radio platforms to transmit information, entertainment, news, and advertisements to a wide range of viewers and listeners. Broadcasting plays a vital role in mass communication by enabling the rapid dissemination of information and entertainment to a large audience simultaneously, making it a key component in the landscape of modern media communication.
50 Broadcasting Mass Communication Examples
Broadcasting in mass communication encompasses a wide range of formats and styles, each serving unique purposes in disseminating information and entertainment to the public. This collection of 50 examples demonstrates the versatility and impact of broadcasting across television and radio, highlighting its role in shaping public discourse, providing entertainment, and delivering news. From local news reports to international sporting events, these examples illustrate how broadcasting serves as a vital medium in the media communication landscape.

- National Evening News Broadcast: “Tonight on National News: The latest updates on the global economic summit.” Evening news programs on television provide daily updates on national and international news.
- Morning Radio Talk Show: “Start your day with ‘Morning Talk’ – discussing today’s top stories and weather forecasts.” Radio talk shows blend news updates with discussions and listener interactions.
- Live Sports Commentary on Radio: “Live from the stadium, bringing you play-by-play action of the championship game.” Sports radio broadcasts offer real-time commentary and updates of sporting events.
- Weather Forecasting on TV: “Your reliable source for weather updates every hour, on the hour.” Television weather forecasts provide regular updates on local and national weather conditions.
- Television Sitcoms: “Tune in for laughs on ‘Family Antics’ every Friday at 8 PM.” Sitcoms are a popular form of television entertainment, featuring comedic storylines and characters.
- Educational Children’s Programs on TV: “Join us for fun learning adventures on ‘Kids’ World’ every morning.” Educational programs for children combine entertainment with learning opportunities.
- Documentary Series Broadcast: “‘Our Planet’ – a documentary series exploring the wonders of nature.” Documentaries on television provide in-depth exploration of various topics.
- Radio Music Countdown: “Counting down this week’s top hits on ‘Radio Top 40’.” Music countdown shows on radio play and discuss the most popular songs of the week.
- Breaking News Alerts on TV: “Breaking News: A special report on the unfolding crisis in the capital.” Television news channels provide immediate coverage of breaking news events.
- Late-Night Talk Shows on TV: “Stay up late for celebrity interviews and comedy sketches on ‘Night Talks’.” Late-night talk shows feature interviews, entertainment, and comedy segments.
- Live Radio Coverage of Community Events: “We’re live at the downtown parade, bringing you all the festivities.” Radio stations often provide live coverage of local community events.
- Television Reality Shows: “Witness real-life drama unfold on ‘The Real Challengers’ every Thursday night.” Reality shows on TV focus on real-life situations and personal stories.

- Radio Dramas and Storytelling: “Tune in for our weekly radio drama ‘Mystery at Midnight’.” Radio dramas use voice acting and sound effects to tell stories.
- TV Cooking Shows: “Learn new recipes and cooking tips on ‘The Gourmet Chef’ every weekday.” Cooking shows on television offer culinary demonstrations and cooking advice.
- Health and Wellness Programs on TV: “Join ‘Health Today’ for the latest in wellness and lifestyle tips.” Television programs focusing on health and wellness provide valuable information and tips.
- Radio News Hour: “Every hour, on the hour, get the latest news updates on ‘Radio News Hour’.” Radio news programs offer hourly updates on current events and news.
- TV Shopping Networks: “Find exclusive deals and products on ‘Shop TV’ available only for our viewers.” Shopping networks on television offer products for purchase via telephonic orders.
- Local Access Television Shows: “Local voices, local stories – watch ‘Community Matters’ every Wednesday.” Local access TV shows focus on community news, issues, and interests.
- Radio Call-In Shows for Advice: “Call us with your questions and join the discussion on ‘Ask the Expert’.” Call-in radio shows allow listeners to seek advice and discuss topics.
- Travel and Adventure Shows on TV: “Explore exotic destinations from your home with ‘Globe Trekkers’ every Sunday.” Travel shows on television take viewers on journeys to various places.
- Political Analysis and Commentary on TV: “Dive into political debates and analyses on ‘Capitol Watch’ every evening.” Shows focusing on political commentary provide insights into current political issues.
- Radio Classic Hits Station: “Relive the classics – all your favorite oldies play here on ‘Retro Radio’.” Classic hit radio stations play a mix of popular old-time songs.

- TV Game Shows: “Test your knowledge and win big on ‘Quiz Master’ every Saturday night.” Game shows on television offer entertainment through quizzes and competitions.
- Live Radio Broadcasts of Concerts: “Experience the live concert of ‘The Rockers’ exclusively on our station.” Radio stations sometimes broadcast live music concerts and events.
- Cultural and Arts Programs on TV: “Celebrating art and culture with ‘Canvas of Life’ every Tuesday.” Television programs dedicated to arts and culture showcase creativity and artistic endeavors.
- Investigative Journalism Shows on TV: “Uncovering the truth – ‘Investigative Reports’ presents its latest findings.” Investigative journalism programs delve deep into significant issues and uncover truths.
- Special Interest Radio Shows: “Exploring the world of science fiction on ‘Galaxy Tales’ radio show.” Special interest radio shows cater to niche topics and hobbies.
- TV Historical Documentaries: “Journey through history with ‘Epochs of Time’ documentary series.” Historical documentaries provide educational content on various historical events and eras.
- Business and Finance Programs on TV: “Stay ahead in the business world with ‘Market Trends’ every morning.” Business programs offer insights into the financial markets and business news.
- Radio Interviews with Celebrities: “Hear from your favorite celebrities on our exclusive interview segment.” Radio interviews provide listeners with insights into the lives of famous personalities.
- Youth-Oriented Television Shows: “‘Youth Voice’ – a show dedicated to the perspectives of the younger generation.” Youth-oriented TV shows focus on topics and issues relevant to young viewers.
- Radio Public Service Announcements (PSAs): “Bringing you important public service messages for our community’s well-being.” PSAs on the radio are used to convey important community messages.
- Television News Magazine Programs: “In-depth reporting on ‘World This Week’ – your weekly news magazine show.” News magazine TV shows offer comprehensive reports on various topics.
- Radio Sports Coverage and Analysis: “All the latest in sports, tune in for our ‘Sports Roundup’.” Radio provides coverage and analysis of sporting events and news.
- Satirical News Shows on TV: “Get your dose of satire and humor on ‘The Daily Scoop’.” Satirical TV shows offer a comedic take on current news events.
- Public Radio for Educational Content: “Public radio brings you educational programming for lifelong learning.” Public radio stations often focus on educational content and cultural programming.

- Infotainment Television Shows: “Where information meets entertainment – watch ‘InfoFun’ every weekday.” Infotainment shows blend educational content with an entertaining presentation.
- Radio Coverage of Election Campaigns: “Follow every twist and turn of the election campaigns with us.” Radio provides comprehensive coverage of political campaigns and elections.
- Nature and Wildlife Television Programs: “Discover the wonders of the natural world with ‘Wild Earth’.” TV programs focusing on nature and wildlife educate and inspire viewers.
- TV Mini-Series and Specials: “Don’t miss our mini-series event ‘The Untold Stories’ starting this week.” Mini-series and TV specials provide in-depth exploration of specific themes or stories.
- Music and Entertainment News on Radio: “Stay updated with the latest in music and entertainment on ‘Star Buzz’.” Radio shows dedicated to music and entertainment news keep listeners informed.
- Lifestyle and Fashion Shows on TV: “Tune in to ‘Style and Living’ for the latest in lifestyle and fashion trends.” TV shows focusing on lifestyle and fashion cover the latest trends and tips.
- Educational Radio Programming for Kids: “Fun and learning on ‘Kids’ Radio Hour’ every Saturday morning.” Educational radio programs for children combine learning with fun activities.
- Science and Technology Programs on TV: “Exploring the future with ‘Tech Tomorrow’ – your science and tech guide.” TV programs dedicated to science and technology discuss latest developments and discoveries.
- Radio Literary and Book Shows: “Dive into the world of books with ‘Literary Hour’ on your favorite station.” Literary shows on the radio explore books, authors, and literary trends.
- Television Coverage of Cultural Festivals: “Bringing you the vibrant colors of the ‘Global Cultural Fest’.” TV coverage of cultural festivals showcases diverse traditions and celebrations.
- Radio Health and Wellness Segments: “Tune in for health tips and wellness advice on ‘Healthy Living’ radio.” Health and wellness segments on the radio provide valuable health information.
- Environmental and Sustainability Programs on TV: “‘Green Tomorrow’ – a show dedicated to environmental awareness and sustainability.” Environmental TV programs focus on ecological issues and sustainable living.
- Community Radio for Local News and Events: “Your community connection – bringing you local news and events.” Community radio stations focus on local news, events, and issues.
- Television Biographies and Profiles: “In-depth profiles of inspiring individuals on ‘Life Stories’.” TV biographies provide detailed insights into the lives of notable personalities.
What are Career Opportunities in Broadcasting and Mass Communication?
The field of broadcasting and mass communication offers a wide range of exciting and dynamic career opportunities. These careers are not just about being in front of the camera or behind the microphone; they span various roles requiring diverse skills in content creation, production, and management. Here’s an overview of some of the key career paths available in this vibrant industry.
Television and Radio Broadcasting
- News Anchor/Presenter: Being the face of news programs, presenting stories and interviews on TV or radio.
- Radio DJ/Host: Hosting radio shows, playing music, and interacting with listeners on various topics.
Behind-the-Scenes Roles
- Producer: Managing the production of broadcast content, from conceptualization to final output.
- Director: Overseeing the creative aspects of production, including visual and audio elements.
Journalism
- Broadcast Journalist/Reporter: Reporting on news and events, often involving field reporting and research.
- Investigative Journalist: Specializing in in-depth reporting to uncover truths about significant issues.
Technical Roles
- Sound Engineer: Managing the audio components of broadcasts, ensuring clear sound quality.
- Camera Operator: Operating camera equipment to capture high-quality visual content for broadcasts.
Digital Media
- Social Media Manager: Overseeing the broadcasting organization’s presence on social media platforms.
- Digital Content Creator: Producing content for digital platforms, including video, audio, and text.
Production Support
- Video Editor: Editing video footage to create coherent and engaging broadcast content.
- Graphic Designer: Designing visual elements like graphics and animations for TV shows and digital platforms.
Marketing and Public Relations
- Public Relations Specialist: Managing the public image and communication strategies of the broadcasting organization.
- Marketing Coordinator: Developing and executing marketing plans to promote broadcasts and increase viewership.
Management and Administrative Roles
- Broadcast Manager: Overseeing the operations of broadcast stations or departments.
- Program Scheduler: Planning and scheduling programming for television or radio stations.
Sales and Advertising
- Advertising Sales Representative: Selling advertising space or time on television and radio.
- Media Planner/Buyer: Strategizing and purchasing advertising spots on various media platforms.
Research and Analysis
- Media Analyst/Researcher: Conducting research on audience trends and preferences to inform programming decisions.
- Ratings Analyst: Analyzing viewership data and ratings to gauge the success of broadcasts.
Educational and Training Roles
- Media Educator: Teaching broadcasting and mass communication courses in academic institutions.
- Training Coordinator: Providing training for staff in broadcasting techniques and technologies.
The broadcasting and mass communication industry offers a diverse range of career options that cater to various interests and skills, from creative and technical roles to research, management, and education. With the evolving landscape of media and technology, these careers provide opportunities for continuous learning, innovation, and growth in the exciting world of mass media.
How Does Broadcasting in Mass Communication Work?
Broadcasting in mass communication is a complex process that involves the dissemination of information, entertainment, and news to a wide audience through various electronic media channels. This process combines technical, creative, and logistical elements to deliver content effectively to viewers and listeners.

Here’s an insight into how broadcasting works in the realm of mass communication.
Content Creation and Development
- Conceptualization: The process begins with the conceptualization of content, be it a news story, a radio program, or a television show.
- Scriptwriting and Planning: Detailed scripting, storyboard creation, and planning of the production are essential steps.
Technical Production
- Recording and Filming: For television, this involves filming scenes or recording live events. In radio, it involves recording audio segments or preparing for live broadcasts.
- Editing and Post-Production: Recorded content is edited, and elements like special effects, soundtracks, and graphics are added.
Signal Transmission
- Signal Preparation: The final content is prepared for transmission. In television, it’s encoded into a suitable format for broadcasting.
- Transmission via Broadcast Stations: Television and radio stations transmit the content using high-power antennas for television and radio waves.
Reaching the Audience
- Satellite and Cable Systems: For television, satellites and cable systems relay the signal to households.
- Online Streaming: Additionally, many broadcasts are now streamed online, expanding reach through digital platforms like websites and apps.
Audience Engagement
- Feedback Mechanisms: Audience feedback through call-ins, social media, and ratings help broadcasters gauge the reception of their content.
- Interactive Elements: Modern broadcasting often includes interactive elements like live tweets, polls, and audience participation segments.
Regulatory Compliance
- Adhering to Regulations: Broadcasters must comply with regulatory standards set by governing bodies, ensuring content appropriateness and ethical standards.
- Frequency Allocation: Radio and television broadcasters are allocated specific frequencies to avoid signal interference.
Advertising and Monetization
- Commercial Advertising: Most broadcasting stations include commercial advertisements as a key revenue source.
- Sponsorships and Partnerships: Sponsorship deals and partnerships with businesses also contribute to monetization.
Continuous Adaptation and Evolution
- Technological Advancements: Broadcasting continuously evolves with technological advancements, adopting new formats and platforms.
- Content Innovation: To stay relevant, broadcasters constantly innovate in their content delivery and presentation.
Broadcasting in mass communication is an intricate blend of creativity, technology, and strategic planning, all aimed at delivering compelling content to a broad audience. From the initial stages of content creation to the final broadcast and audience engagement, each step is crucial in ensuring the effective communication of messages across various media platforms.
What are the Types of Broadcasting in Mass Communication?
Broadcasting in mass communication is a diverse field, encompassing various types that cater to different audiences and serve different purposes. From traditional mediums like television and radio to modern digital platforms, the scope of broadcasting is vast and varied. Understanding these types is crucial to appreciate the full spectrum of broadcasting in mass communication.
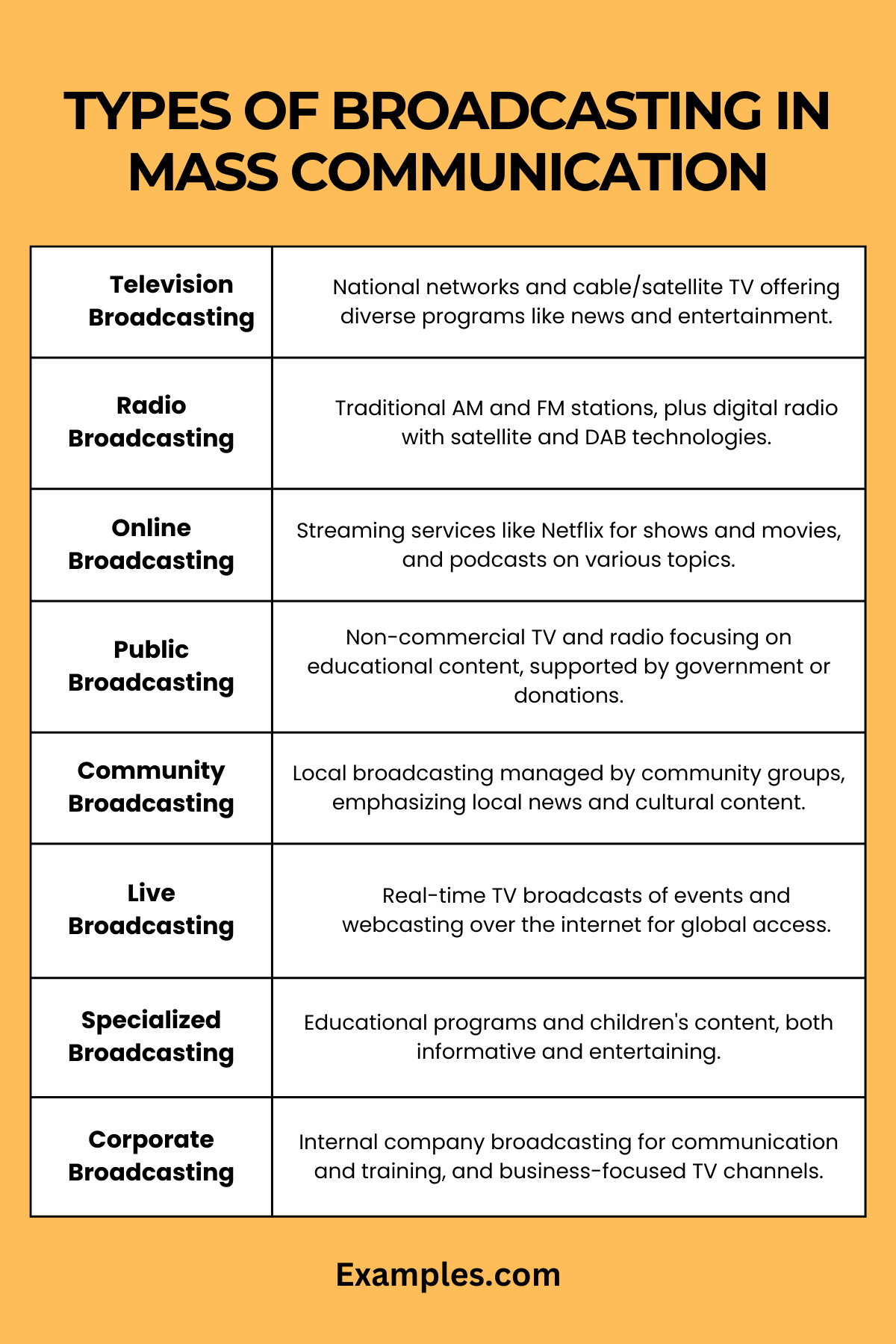
Television Broadcasting
- Network Television: Involves national TV networks broadcasting a range of programs, from news to entertainment, to a wide audience.
- Cable and Satellite TV: Offers specialized channels with specific content themes, such as sports, news, or movies.
Radio Broadcasting
- AM and FM Radio: Traditional radio broadcasting with AM (Amplitude Modulation) and FM (Frequency Modulation) stations offering music, news, and talk shows.
- Digital Radio: Includes newer technologies like satellite radio and digital audio broadcasting (DAB), providing higher-quality sound and more station choices.
Online Broadcasting
- Streaming Services: Platforms like Netflix, Hulu, and Amazon Prime that stream TV shows, movies, and documentaries over the internet.
- Podcasts: Digital audio or video files available for download or streaming, often as a series, on various topics.
Public Broadcasting
- Public Television and Radio: Non-commercial broadcasting that focuses on educational and informative content, often funded by government or public donations.
- Community Broadcasting: Smaller-scale broadcasting focused on local content, often run by community groups for specific local or cultural interests.
Live Broadcasting
- Live TV: Includes real-time broadcasting of events such as sports matches, award shows, and news events.
- Webcasting: Live streaming of events or content over the internet, accessible to a global audience.
Specialized Broadcasting
- Educational Broadcasting: Programs specifically designed for educational purposes, often in collaboration with educational institutions.
- Children’s Broadcasting: Content specifically created for children, including educational and entertainment programs.
Corporate Broadcasting
- Internal Broadcasting: Used by companies for internal communication, training, and corporate messages.
- Business TV: Specialized channels focused on business news, market trends, and financial analysis.
Mobile Broadcasting
- Mobile TV and Radio: Broadcasting content that is accessible on mobile devices, allowing audiences to consume media on the go.
Each type of broadcasting in mass communication serves unique functions, targeting specific audience segments, and employing different content styles and delivery methods. From providing entertainment and news to educational content and niche programming, broadcasting continues to be a major force in shaping public discourse and influencing societal trends.
What is the Difference Between Broadcast Journalism and Mass Communication?
Broadcast journalism and mass communication are closely related fields but differ in scope, content, and method. Understanding these differences is crucial for aspiring professionals in the media industry. Here’s a comprehensive comparison presented in a tabular format to highlight their distinct characteristics.
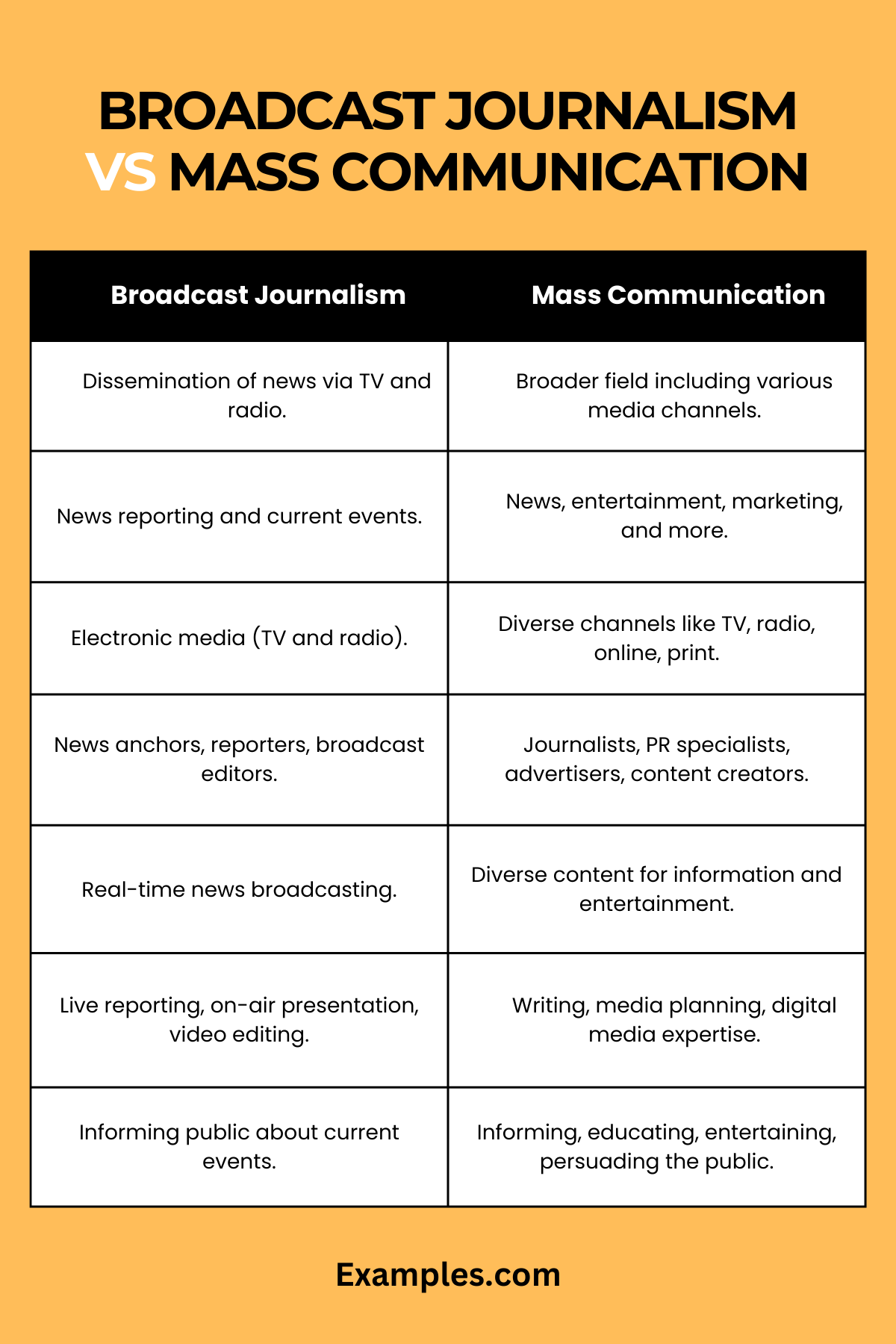
| Aspect | Broadcast Journalism | Mass Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Broadcast journalism refers to the dissemination of news and current events through electronic media, specifically television and radio. | Mass communication encompasses a broader spectrum, including broadcasting, but also covers print media, online platforms, advertising, public relations, and more. |
| Content Focus | Primarily focused on news reporting, storytelling, and presenting current events. | Encompasses a wider range of content, including news, entertainment, educational material, marketing, and public information. |
| Medium of Delivery | Utilizes electronic media channels like TV and radio. | Includes a variety of media channels like television, radio, newspapers, online platforms, social media, and more. |
| Professional Roles | Involves roles like news anchors, reporters, correspondents, and broadcast editors. | Covers a wider range of roles, including journalists, PR specialists, advertisers, content creators, and media researchers. |
| Audience Engagement | Engages audiences through real-time news broadcasting and live updates. | Engages a diverse audience through various formats and messages, including advertising, entertainment, and informational content. |
| Skillset Required | Requires skills in live reporting, on-air presentation, scriptwriting, and video editing. | Demands a diverse skillset, including writing, media planning, marketing strategies, content creation, and digital media expertise. |
| Objective | Aims to inform and update the public about current events and news stories. | Aims for a broader objective of informing, educating, entertaining, and persuading the public. |
| Educational Focus | Specialized training in broadcast media, journalism ethics, and electronic news production. | Covers a broader educational spectrum, including media theories, communication research, media law and ethics, and various forms of media production. |
| Technological Use | Heavily relies on broadcasting technology like cameras, microphones, and editing software. | Utilizes a wider range of technologies, encompassing broadcasting equipment, digital media tools, printing technology, and online platforms. |
While broadcast journalism is a specific branch focused on news reporting via electronic media, mass communication is a more expansive field that includes broadcast journalism but also extends to other forms of media and communication disciplines. Both play significant roles in the dissemination of information and shaping public opinion, each with its unique approach and method.
Tips for Effective Broadcasting in Mass Communication
Effective broadcasting in mass communication is essential for reaching and engaging a wide audience through television, radio, and digital platforms. To excel in this dynamic field, it’s important to combine creativity with technical expertise and audience understanding. Here are some key tips to enhance the effectiveness of broadcasting in the diverse landscape of mass communication.
Understand Your Audience
- Audience Demographics: Know your audience’s age, interests, and preferences to tailor your content effectively.
- Feedback and Engagement: Use audience feedback, ratings, and social media interactions to understand their preferences and adjust your content accordingly.
Focus on Content Quality
- Relevant and Engaging Content: Create content that is both informative and engaging to hold the audience’s attention.
- Diverse Content Formats: Experiment with different formats like interviews, documentaries, and interactive segments to keep the content fresh and interesting.
Invest in Technology and Training
- Up-to-Date Equipment: Use the latest broadcasting equipment and technology for high-quality audio and visuals.
- Continuous Learning: Encourage ongoing training and development for your team in the latest broadcasting techniques and trends.
Master Storytelling Techniques
- Compelling Narratives: Craft stories that resonate with your audience, using a mix of emotion, facts, and compelling narratives.
- Visual Storytelling: In television broadcasting, use visual elements effectively to enhance the storytelling.
Maintain Ethical Standards
- Journalistic Integrity: Uphold ethical standards and journalistic integrity in all your broadcasting content.
- Fact-Checking: Ensure all information broadcasted is accurate and thoroughly fact-checked.
Engage with Digital Platforms
- Social Media Integration: Use social media to extend the reach of your broadcasting content and engage with audiences online.
- Online Streaming: Offer online streaming options to reach a broader audience, including those who prefer digital platforms.
Pay Attention to Production Values
- High Production Quality: Invest in high-quality production to make your broadcast visually and audibly appealing.
- Professional Editing: Ensure professional editing to maintain a smooth flow and coherence in your broadcast.
Be Responsive to Change
- Adaptability: Be adaptable to changes in the media landscape, audience preferences, and technological advancements.
- Innovative Approaches: Continuously seek innovative ways to present content and engage with your audience.
Utilize Effective Marketing Strategies
- Promotional Activities: Promote your broadcasting content through various channels to maximize reach and viewership.
- Brand Building: Work on building a strong brand identity for your broadcasting channel or program.
Foster a Collaborative Environment
- Team Collaboration: Encourage collaboration and idea-sharing among your team members for creative and effective broadcasting.
- Cross-Departmental Coordination: Coordinate effectively across different departments, such as content creation, technical support, and marketing, for a cohesive broadcasting strategy.
Implementing these tips in broadcasting mass communication can significantly enhance your reach, audience engagement, and the overall impact of your broadcasting content. Staying informed, adaptable, and audience-centric are key to thriving in the fast-paced and evolving world of broadcasting.
In conclusion, broadcasting in mass communication is a powerful tool for reaching diverse audiences through compelling storytelling and engaging content. By embracing technological advancements and adhering to ethical standards, broadcasters can effectively inform, entertain, and influence public opinion. The future of broadcasting lies in its ability to adapt, innovate, and resonate with the ever-changing needs of a global digital audience.



