10 Communication Barriers with Dementia Patients Examples
Embark on a comprehensive journey through the intricacies of communication barriers with dementia patients in this complete guide. Explore insightful examples that illuminate effective strategies to overcome challenges. Learn how to navigate these barriers with finesse, enhancing your communication skills. This guide is your key to unlocking a deeper understanding of communication with dementia patients, featuring practical examples that bridge the gap and foster meaningful connections. Delve into the world of Communication Examples to enrich your caregiving experience.
What is Communication Barriers with Dementia Patients?

Communication barriers with dementia patients refer to obstacles that hinder effective interaction between individuals with dementia and their caregivers or peers. In simple terms, these barriers impede the smooth exchange of thoughts, feelings, and information. Understanding and addressing these challenges are crucial for providing compassionate care and fostering meaningful connections with those affected by dementia.
Communication Barriers with Dementia Patients Symptoms:
Delve into the realm of dementia communication barriers by exploring their distinct symptoms. Recognize subtle cues and manifestations that hinder effective interaction, such as confusion, repetition, and difficulty in expressing thoughts. Uncover strategies to navigate these challenges and enhance your communication skills, fostering more meaningful connections with individuals affected by dementia.
- Repetition Struggle: Patients may repeat questions; respond with patience and offer reassurance to ease their uncertainty.
- Confusion Comprehension: Address confusion gently by providing clear, simple instructions and visual aids.
- Word Retrieval Difficulty: Encounter patience, allowing extra time for patients to express thoughts and finding alternative words when needed.
- Agitation Alleviation: When faced with agitation, maintain a calm demeanor and use soothing tones to comfort the patient.
- Emotional Expression Challenges: Patients may find it hard to express emotions; encourage non-verbal cues like gestures and facial expressions.
- Lost Train of Thought: Guide patients back to the topic gracefully, avoiding frustration and promoting a relaxed conversation environment.
- Sensory Overload Awareness: Be mindful of sensory overload; choose quiet settings and minimize distractions for effective communication.
- Difficulty Understanding Humor: Simplify jokes or use light humor that aligns with the patient’s understanding to create a positive interaction.
- Temporal Disorientation Management: Ground patients in the present; incorporate time-oriented cues to ease temporal disorientation.
- Unresponsive Moments: During unresponsive phases, maintain a comforting presence, allowing patients time to process information at their pace.
Barriers to Effective Communication with Dementia Patients:
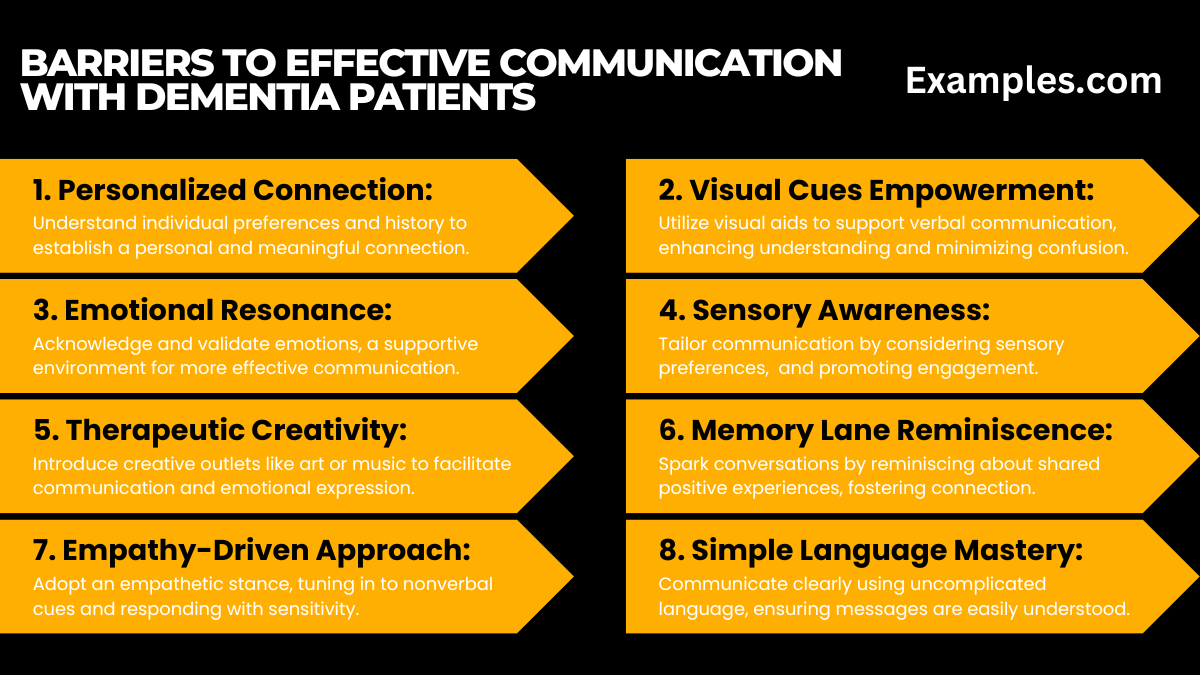
Dive into the complexities of communicating with dementia patients, understanding and overcoming barriers to foster meaningful connections. Explore practical strategies and discover a wealth of examples to enhance your communication skills in this insightful guide.
- Repetition Relief: Gently redirect the conversation when faced with repetitive questions, ensuring engagement without frustration.
- Visual Cues Empowerment: Utilize visual aids to support verbal communication, enhancing understanding and minimizing confusion.
- Emotional Resonance: Acknowledge and validate emotions, promoting a supportive environment for more effective communication.
- Sensory Awareness: Tailor communication by considering sensory preferences, easing potential discomfort and promoting engagement.
- Therapeutic Creativity: Introduce creative outlets like art or music to facilitate communication and emotional expression.
- Memory Lane Reminiscence: Spark conversations by reminiscing about shared positive experiences, fostering connection.
- Empathy-Driven Approach: Adopt an empathetic stance, tuning in to nonverbal cues and responding with sensitivity.
- Simple Language Mastery: Communicate clearly using uncomplicated language, ensuring messages are easily understood.
- Personalized Connection: Understand individual preferences and history to establish a personal and meaningful connection.
- Routine Consistency: Maintain a consistent routine, providing a sense of familiarity and ease for smoother communication.
Understanding the Barriers of Dementia Care:Improving Communication for the Caregiver:
Embark on a transformative journey as a caregiver, unraveling the intricacies of dementia care communication barriers. Elevate your skills with ensuring a seamless caregiving experience.
- Nonverbal Cues Harmony: Explore the art of aligning nonverbal cues with dementia patients’ needs, fostering a deeper connection.
- Intrapersonal Strategies: Unveil personalized communication approaches, enhancing the caregiver’s understanding of the patient’s unique needs.
- Visual Storytelling: Master the technique of visual storytelling to convey messages effectively, transcending verbal limitations in dementia care.
- Transactional Communication Dynamics: Navigate the transactional communication model, adapting responses to the evolving needs of dementia patients.
- Interpersonal Sensitivity: Cultivate sensitivity in interpersonal communication, recognizing nuances crucial for connecting with individuals experiencing dementia.
- Empathetic Dialogue Pacing: Fine-tune the pace of empathetic dialogue, creating a comforting environment for dementia patients during interactions.
- Crisis Resolution Through Communication: Learn to resolve crises through effective communication, ensuring the well-being of both the caregiver and the individual with dementia.
- Assertive Language Mastery: Develop mastery in assertive language, empowering caregivers to express needs and choices respectfully in the caregiving journey.
- Effective Communication Tools: Explore a diverse toolkit of effective communication methods tailored to the unique challenges presented by dementia care.
- Digital Communication Integration: Integrate digital communication methods into caregiving, leveraging technology to enhance connections and support for dementia patients.
How to Overcome Communication Barriers with Dementia Patients?

Navigating communication barriers with dementia patients demands a nuanced approach, emphasizing empathy and adaptability. Explore effective strategies to enhance connections with those affected by dementia.
Nonverbal Cues: Unlock the power of nonverbal communication by interpreting gestures, facial expressions, and body language. Tailor your responses to foster a deeper understanding between caregiver and patient.
Promoting Intrapersonal Communication: Delve into personalized communication strategies, recognizing the importance of the caregiver’s self-awareness and emotional intelligence. Adjust your approach to accommodate the patient’s individual needs.
Visual Communication Techniques: Master the art of visual storytelling to convey messages without relying solely on verbal communication. Utilize visual aids, images, and cues to enhance comprehension and connection.
Adapting to Transactional Communication Dynamics: Navigate the dynamic nature of transactional communication, adjusting your responses based on the patient’s evolving cognitive state. Foster a two-way exchange that accommodates the challenges presented by dementia.
Cultivating Interpersonal Sensitivity: Develop heightened sensitivity in interpersonal interactions, considering the unique needs and preferences of individuals with dementia. Build connections through empathy, patience, and understanding.
Fine-Tuning Empathetic Dialogue Pacing: Adjust the pace of communication to align with the cognitive abilities of the individual. Create a supportive and comfortable environment by adapting your dialogue to suit the patient’s processing speed.
Resolving Crises Through Communication: Equip yourself with crisis resolution skills that center around effective communication. Address challenging situations with compassion, ensuring the safety and well-being of both caregiver and patient.
Mastering Assertive Language: Develop proficiency in assertive language, empowering caregivers to express needs and preferences respectfully. Navigate potential conflicts with clarity and confidence in the caregiving journey.
Utilizing Effective Communication Tools: Build a diverse toolkit of communication methods tailored to the unique challenges posed by dementia. Explore innovative approaches, such as sensory stimulation and creative expression, to enhance connections.
Integrating Digital Communication: Explore the integration of digital communication methods in caregiving. Leverage technology to foster connections, provide support, and enhance the overall communication experience for individuals with dementia.
In conclusion, this guide illuminates effective strategies for overcoming communication barriers with dementia patients. By exploring real-life examples and practical tips, caregivers can enhance their skills and foster meaningful connections. Empower yourself with insights that go beyond mere understanding, creating a compassionate and supportive environment for individuals facing the challenges of dementia. Elevate your caregiving journey with this comprehensive resource.