19+ Communication Barriers with Patients Examples
Unlock the secrets to effective healthcare communication in our comprehensive guide on “Communication Barriers with Patients.” This illuminating resource delves into the nuances of overcoming obstacles, offering actionable examples to enhance understanding. Navigate through practical tips and real-life scenarios to foster better patient relationships. From verbal misunderstandings to nonverbal cues, discover the pivotal role of communication examples in navigating the intricate landscape of patient interactions. Elevate your communication skills to provide optimal care.
What is Communication Barriers with Patients?
Communication barriers with patients encompass obstacles that hinder effective interaction between healthcare providers and individuals seeking care. In straightforward language, these barriers can be verbal or nonverbal, impeding the smooth exchange of information. From language disparities to non-understandable medical jargon, understanding these hurdles is vital for healthcare professionals. Let’s dissect the essence of communication barriers, simplifying the intricacies to ensure clarity and improved patient-provider relationships.
What is the best Example of Communication Barriers with Patients?
Consider a scenario where a patient receives a complex medical diagnosis laden with technical terms. The communication barrier arises when the healthcare provider fails to translate this information into understandable language, leaving the patient confused and anxious. This breakdown in conveying crucial medical details showcases a common yet impactful example of communication barriers. Our detailed exploration will unravel the intricacies of this scenario, shedding light on its implications and providing insights into overcoming such challenges for improved patient understanding.
20 Communication Barriers with Patients Examples
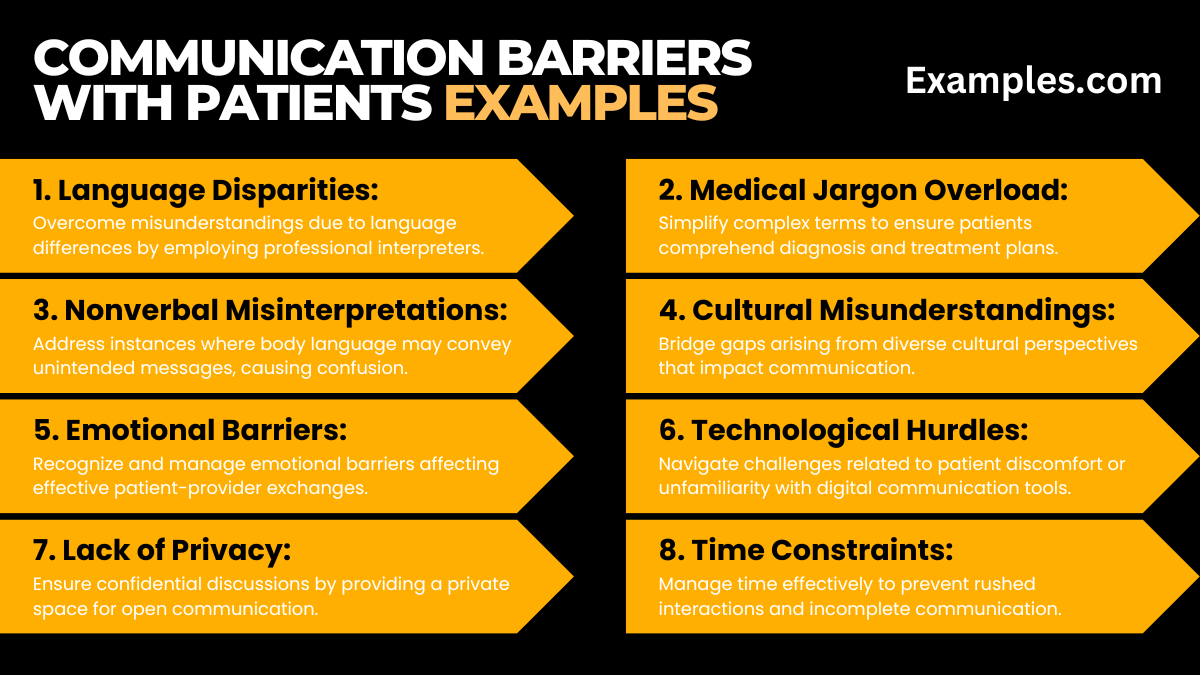
In this detailed compilation, explore diverse scenarios representing communication barriers in healthcare. From linguistic challenges to nonverbal cues, each example illustrates a facet of potential miscommunication. Enhance your grasp on these situations, and discover effective strategies for improved patient-provider dialogues.
- Language Disparities: Overcome misunderstandings due to language differences by employing professional interpreters.
- Medical Jargon Overload: Simplify complex terms to ensure patients comprehend diagnosis and treatment plans.
- Nonverbal Misinterpretations: Address instances where body language may convey unintended messages, causing confusion.
- Limited Health Literacy: Tackle situations where patients struggle to understand medical information due to low health literacy.
- Cultural Misunderstandings: Bridge gaps arising from diverse cultural perspectives that impact communication.
- Emotional Barriers: Recognize and manage emotional barriers affecting effective patient-provider exchanges.
- Technological Hurdles: Navigate challenges related to patient discomfort or unfamiliarity with digital communication tools.
- Lack of Privacy: Ensure confidential discussions by providing a private space for open communication.
- Assumptions and Stereotypes: Address preconceived notions or stereotypes that hinder unbiased communication.
- Inattentiveness to Patient Concerns: Prioritize active listening to address patient queries and alleviate concerns.
- Time Constraints: Manage time effectively to prevent rushed interactions and incomplete communication.
- Hierarchy and Power Dynamics: Address power imbalances to create a more open and collaborative healthcare environment.
- Fear and Anxiety: Recognize patient fears and anxieties, fostering an atmosphere of empathy and understanding.
- Limited Visual Aids: Utilize visual aids to enhance patient comprehension, especially for complex medical information.
- Mismatched Expectations: Align patient expectations with realistic outcomes, avoiding disappointments.
- Ineffective Use of Technology: Ensure proper training for patients on using technological tools for communication.
- Healthcare Provider Burnout: Mitigate the impact of provider burnout on patient interactions through support systems.
- Inadequate Follow-up: Implement efficient follow-up procedures to address post-appointment questions or concerns.
- Socioeconomic Factors: Consider socioeconomic factors influencing communication, adapting strategies accordingly.
- Lack of Cultural Competence Training: Prioritize cultural competence training for healthcare staff to enhance patient interactions.
Communication Barriers with Elderly Patients:
In understanding communication barriers with elderly patients, it’s essential to address unique challenges associated with age-related factors. Explore this guide to enhance patient-provider interactions for the aging population, promoting clearer communication and fostering trust.
- Sensory Impairments: Speak clearly and use visual aids to accommodate hearing or vision impairments in elderly patients.
- Cognitive Decline: Adjust communication pace, simplify information, and allow time for comprehension in cases of cognitive decline.
- Technological Gaps: Bridge the digital divide by offering alternative communication methods for elderly patients unfamiliar with technology.
- Cultural Differences: Acknowledge diverse backgrounds, adapting communication styles to respect the cultural nuances of elderly patients.
- Health Literacy Challenges: Use plain language and repetition to overcome potential barriers related to limited health literacy in the elderly.
- Fear of Technology: Encourage openness to technology by patiently guiding elderly patients through the use of digital communication tools.
- Memory Issues: Implement memory aids and repetition to reinforce key information for elderly patients with memory challenges.
- Healthcare Provider Patience: Exercise patience and compassion, allowing elderly patients time to express themselves and ask questions.
- Medication Management: Simplify medication instructions and provide written guides to assist elderly patients in managing their medications.
- Empathy and Understanding: Display empathy, acknowledging the unique needs and concerns of elderly patients, fostering a trusting relationship.
Types of Communication Barriers with Patients:
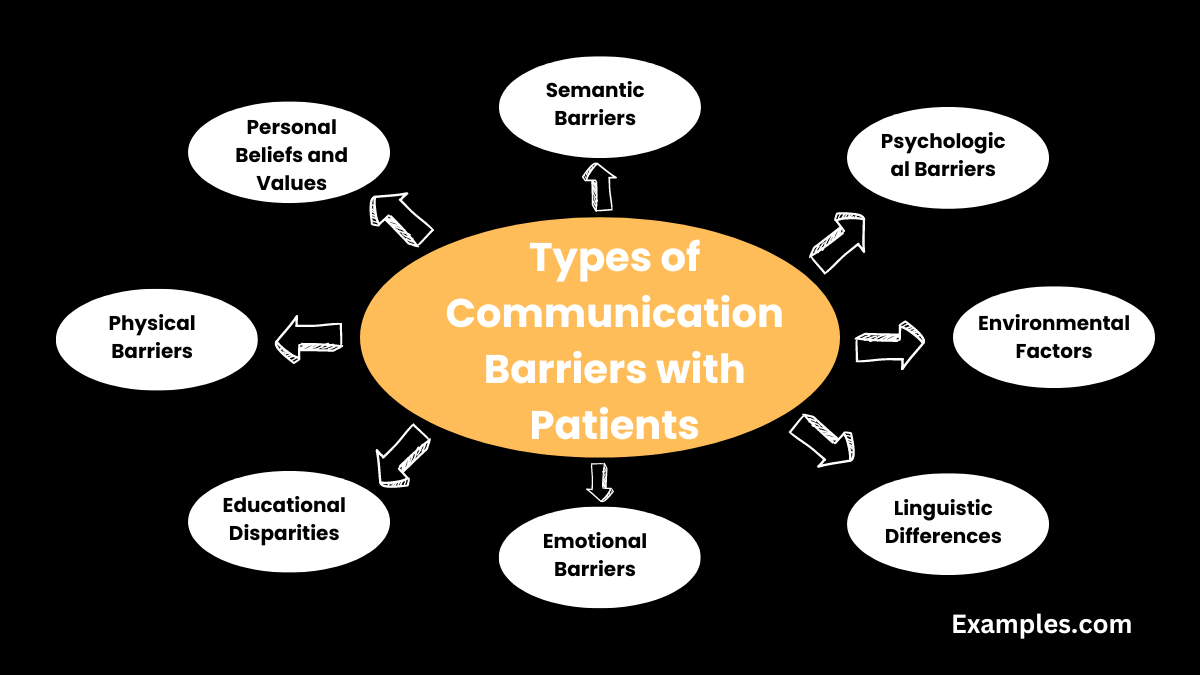
Explore various types of communication barriers that can arise in healthcare settings, impacting the quality of patient-provider interactions. Gain insights into recognizing and overcoming these barriers to ensure effective communication and improved healthcare outcomes.
- Semantic Barriers: Clarify and simplify language to overcome misunderstandings arising from different interpretations of medical terms.
- Psychological Barriers: Build rapport to address psychological barriers, fostering trust and openness in patient-provider relationships.
- Environmental Factors: Optimize communication spaces by minimizing noise and ensuring privacy to mitigate environmental communication barriers.
- Linguistic Differences: Utilize translation services or multilingual staff to bridge communication gaps due to linguistic diversity.
- Personal Beliefs and Values: Respect diverse beliefs and values, fostering open dialogue to overcome potential conflicts in patient communication.
- Emotional Barriers: Recognize and address emotional barriers by providing a supportive and empathetic healthcare environment.
- Educational Disparities: Adapt communication styles to accommodate varying levels of education among patients for better understanding.
- Communication Channel Preferences: Identify and utilize the preferred communication channels of patients to enhance accessibility and responsiveness.
- Physical Barriers: Address physical limitations by ensuring clear visibility and utilizing adaptive communication tools for patients with disabilities.
- Generational Communication Gaps: Understand generational differences in communication preferences, adapting approaches for varied age groups to promote effective dialogue.
How to deal with Communication Barriers with Patients?
Effective communication in healthcare is paramount, yet barriers can impede understanding between patients and providers. This comprehensive guide offers practical strategies to overcome communication hurdles, fostering a harmonious and empathetic healthcare environment.
Identifying the Challenge: Recognize and pinpoint the specific communication hurdle, whether linguistic, cultural, or technological.
Active Listening and Empathy: Engage in active listening, fostering empathy to understand patients’ concerns and build trust.
Adaptation and Tailoring: Adjust communication styles based on age, cultural background, and individual preferences for a personalized approach.
Clear Communication: Avoid jargon, opting for clear language, and incorporate visual aids for better comprehension.
Encourage Questions: Create an open environment that invites questions, addressing concerns promptly.
Embrace Technology Mindfully: Integrate technology while respecting patient preferences, offering guidance as needed.
Language Services and Cultural Competence: Utilize language services, multilingual staff, and cultural competence training to bridge gaps.
Team Collaboration: Promote teamwork for effective communication within the healthcare team, ensuring a cohesive approach.
Follow-Up and Feedback: Implement thorough follow-up procedures and seek patient feedback for continuous improvement.
How to Overcome Communication Barriers with Patients?
Identify the Challenge: Pinpoint specific barriers – linguistic, cultural, or technological – to tailor effective solutions.
Active Listening and Empathy: Engage in attentive listening and cultivate empathy to understand patient concerns and build trust.
Adapt Communication Styles: Recognize diverse patient needs, adjusting communication based on age, culture, and preferences.
Clarity in Language: Simplify language, avoid jargon, and use straightforward communication for transparent dialogue.
Visual Tools for Comprehension: Incorporate visual aids like diagrams to supplement verbal communication and enhance understanding.
Encourage Patient Engagement: Create an open environment for questions and concerns, fostering dialogue and overcoming barriers.
Technological Integration: Embrace technology judiciously, providing guidance for digital tools while respecting preferences.
Language Services and Cultural Competency: Utilize language services and cultural competency training to bridge linguistic and cultural gaps.
Collaborative Healthcare Teams: Promote teamwork for seamless communication, ensuring a cohesive approach to patient care.
Follow-Up and Improvement: Establish robust follow-up procedures, seeking patient feedback for continuous communication improvement.
In conclusion, understanding and addressing communication barriers with patients is vital for fostering effective healthcare interactions. This comprehensive guide, enriched with real-world examples, equips healthcare providers with practical strategies. By embracing clear communication, active listening, and cultural competence, professionals can navigate challenges, build trust, and enhance the overall quality of patient care.