7 Forms of Mass Communication Examples
Exploring the diverse forms of mass communication reveals the dynamic ways in which information and ideas are transmitted to large audiences. From traditional platforms like newspapers and television to digital realms encompassing social media and online news portals, each form offers unique advantages in disseminating information. Understanding these various forms helps us appreciate the complexity and impact of mass communication in our rapidly evolving, interconnected world. This exploration underscores the pivotal role mass communication plays in shaping public discourse and opinion.
How is Mass Communication Different from Other Forms of Communication?
Mass communication is a distinct and influential form of communication that differs significantly from other types. Understanding these differences is key to grasping its unique role in society.

Broad Audience Reach
Unlike personal or interpersonal communication, which are limited to individual or small group interactions, mass communication is designed to reach a large audience, often spanning across various demographics and geographical locations. This wide reach is facilitated through mediums like television, radio, newspapers, and the internet.
One-way Communication Flow
Mass communication typically involves a one-way flow of information. The sender (such as a news organization) broadcasts a message to the audience without direct feedback. In contrast, other forms of communication, like interpersonal communication, are two-way, with both parties able to respond and engage in a dialogue.
Message Standardization
In mass communication, the message is often standardized and not tailored to specific individuals. This contrasts with personal communication, where messages are often personalized and adapted based on the relationship and interaction between the individuals involved.
Professional Content Creation
Content in mass communication is usually created by professionals, ensuring it is well-researched, structured, and presented. This level of professionalism is typically absent in casual forms of communication.
Technology and Infrastructure
Mass communication relies heavily on technology and infrastructure, such as broadcasting networks, printing presses, and digital platforms. These technologies enable the dissemination of messages to a large audience, a feature that is not intrinsic to other forms of communication.
Influence on Public Opinion
Due to its broad reach and professional content, mass communication has a significant impact on public opinion and societal norms. It plays a crucial role in shaping cultural narratives, influencing trends, and informing the public about important issues.
Regulation and Ethics
Mass communication is often subject to regulations and ethical considerations due to its potential impact on society. This includes adherence to journalistic standards, respect for copyright laws, and sensitivity to cultural and social norms.
What are the Forms of Mass Communication Courses?
Mass communication courses offer an extensive range of educational paths, each focusing on different aspects of media and communication. These courses are designed to equip students with the necessary skills and knowledge to excel in various media-related professions. Understanding the diverse forms of mass communication courses is crucial for aspiring media professionals to find their niche in this dynamic field.
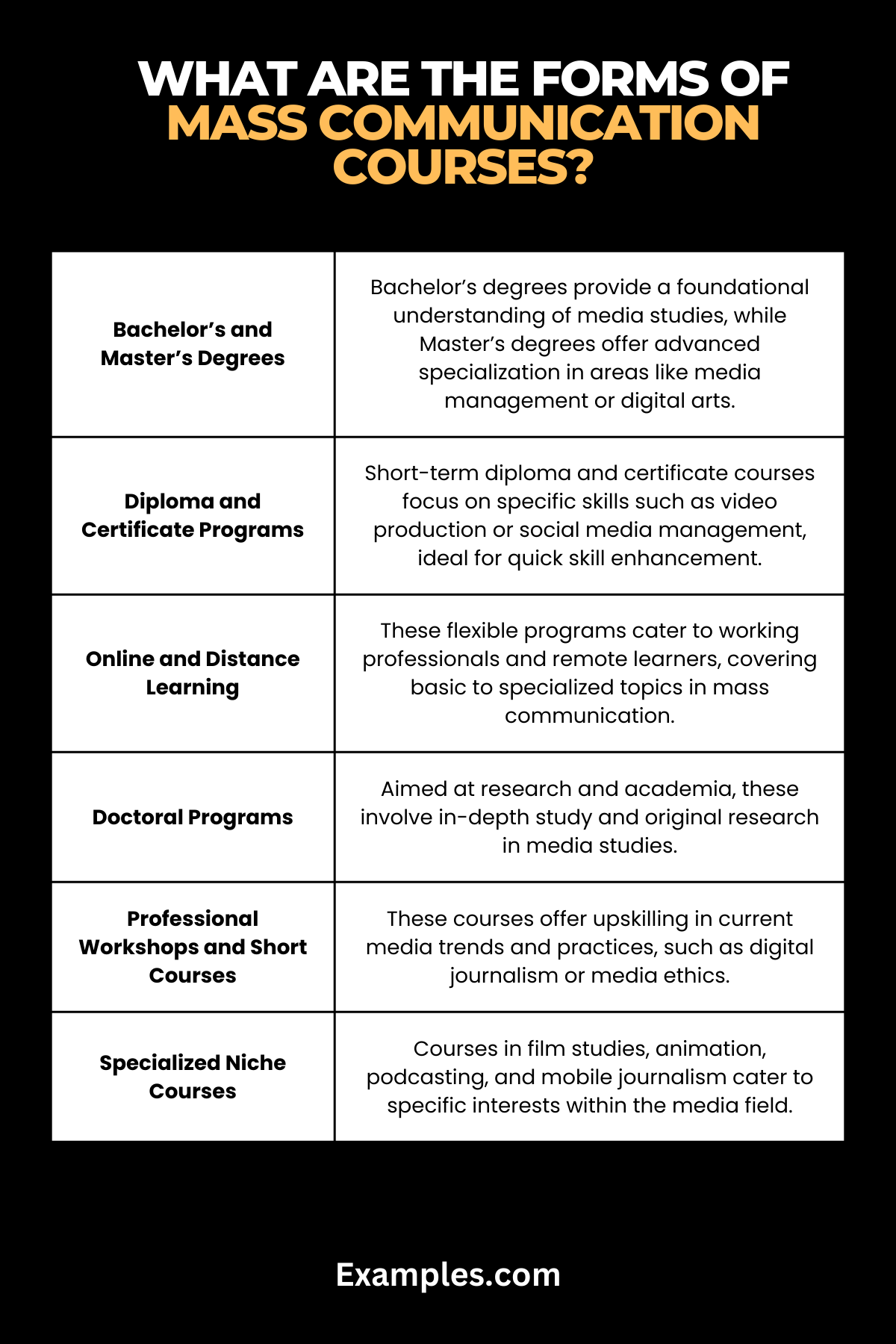
Bachelor’s Degree in Mass Communication
A Bachelor’s degree in Mass Communication provides a comprehensive foundation in media studies. It covers various aspects like journalism, broadcasting, public relations, and digital media. This program typically spans four years, offering both theoretical knowledge and practical skills.
Master’s Degree in Mass Communication
For those seeking advanced expertise, a Master’s degree in mass communication delves deeper into specialized areas like media management, strategic communication, or digital media arts. These programs usually last two years and are ideal for career advancement and in-depth research opportunities.
Diploma and Certificate Courses
Diploma and certificate courses in mass communication are shorter, focusing on specific skills like video production, social media management, or graphic design. These programs are practical and skill-oriented, ideal for those looking to quickly enter the workforce or specialize in a particular area.
Online and Distance Learning Programs
Online and distance learning programs in mass communication offer flexibility and accessibility. They cover various topics, from basic media studies to specialized subjects like digital marketing or media law, catering to working professionals and remote learners.
Doctoral Programs in Mass Communication
Doctoral programs are for those aiming at research and academia in the field of mass communication. These rigorous programs involve in-depth study and original research, contributing new knowledge to the field of media studies.
Professional Workshops and Short Courses
Professional workshops and short courses in mass communication focus on upskilling and staying updated with the latest trends in the media industry. Topics might include digital journalism, media ethics, or emerging technologies in communication.
Specialized Courses in Niche Areas
There are also specialized courses focusing on niche areas of mass communication like film studies, animation, podcasting, or mobile journalism. These courses are tailored to the needs of specific media sectors.
What Forms of Communication are Considered Mass Media?
Mass media encompasses a wide range of communication forms designed to reach a large, diverse audience. This guide delves into the various types of mass media, each playing a unique role in disseminating information and shaping public perception.
Traditional Print Media
- Newspapers: Offer daily or weekly publications covering a wide range of topics, from news to opinion pieces.
- Magazines: Provide in-depth coverage on specific interests, lifestyles, and industries.
Broadcast Media
- Television: A dominant form of mass media, offering news, entertainment, and educational content through various channels.
- Radio: Known for its accessibility and wide reach, radio broadcasts news, music, talk shows, and other audio content.
Digital Media
- Online News Portals: Websites and apps that deliver breaking news, feature stories, and multimedia content.
- Blogs and E-zines: Digital platforms for sharing opinions, reviews, and specialized content.
Social Media
- Platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram: Facilitate user-generated content and news sharing, significantly impacting how information is spread and consumed.
Film and Cinema
- Movies and Documentaries: Offer storytelling and documentary-style content, influencing cultural narratives and public opinion.
Outdoor Media
- Billboards and Public Displays: Visible in public spaces, these convey advertising messages or public information.
Understanding the diverse forms of mass communication is crucial in today’s interconnected world. This guide has provided insights into various media types and practical tips for effective communication. Embracing these forms enhances our ability to convey messages broadly and impactfully, highlighting the significant role of mass communication in shaping public discourse and societal trends.