10+ Future Tense Examples, Excercises
Future Tense refers to a grammatical tense primarily used to describe events that have not yet occurred or will occur in the future. It can be formed using auxiliary verbs like “will” or “shall” along with the base form of the main verb.
What is Future Tense?
Future Tense is a grammatical category used to describe actions or events that have not yet happened but are expected to occur in the future. It often involves the use of auxiliary verbs such as “will” or “shall,” combined with the base form of the verb to indicate actions that are anticipated to happen. In English, the future tense can also be expressed through the use of modal verbs like “might,” “could,” or “should,” the “going to” construction, or even the present progressive tense, depending on the context and the degree of certainty about the future event.
Examples:
- I will travel to France next year.
- She is going to start her new job on Monday.
Types of the Future Tense
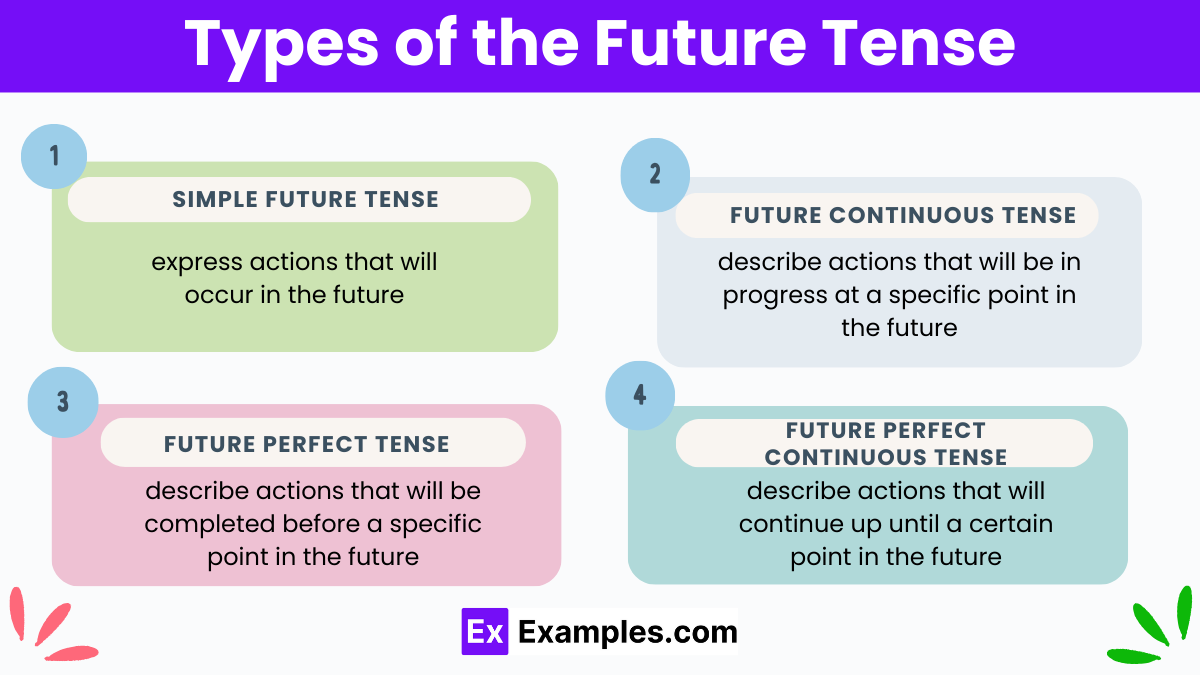
In English grammar, the future tense is used to talk about actions or events that have not yet occurred but are expected or planned to occur in the future. There are 4 types of future tenses that vary based on the action’s timing, duration, or completion. Here’s a breakdown.
- Simple Future Tense
- Future Continuous Tense
- Future Perfect Tense
- Future Perfect Continuous Tense
1. Simple Future Tense
The Simple Future Tense is used to express actions that will occur in the future. It doesn’t reflect any continuation or completion of the action.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | A verb form used to denote an action that will happen in the future. |
| General Formula | Subject + will/shall + V1 + Object |
| Examples | I will write articles on different topics.<br>Robert will read various kinds of books. They will play football in that field. |
2. Future Continuous Tense
The Future Continuous Tense is used to describe actions that will be in progress at a specific point in the future. This tense emphasizes the duration of the action.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Used to express an action that will be ongoing at a certain point in the future. |
| General Formula | Subject + will be + present participle + Object |
| Examples | Tomorrow at noon, I will be meeting with the manager. He will be studying at the library. |
3. Future Perfect Tense
The Future Perfect Tense is used to describe actions that will be completed before a specific point in the future. This tense often goes with time expressions.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Indicates an action that will be completed before a specific time in the future. |
| General Formula | Subject + will have + past participle + Object |
| Examples | By next month, I will have finished this book. She will have traveled to New York by the time we get there. |
4. Future Perfect Continuous Tense
The Future Perfect Continuous Tense is used to describe actions that will continue up until a certain point in the future. It focuses on the duration before something in the future and often emphasizes cause or reason.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Describes an action that will continue up until a point in the future. |
| General Formula | Subject + will have been + present participle + Object |
| Examples | By next year, I will have been working here for a decade. They will have been driving for five hours by sunset. |
Structure of the Future Tense
| Future Tense Type | Structure | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Simple Future Tense | Subject + Auxiliary verb (will) + Base form of the verb + the rest of the sentence | He will leave for New York tomorrow morning. |
| Future Continuous Tense | Subject + Helping Verb (will) + Be + Main verb + ing + the rest of the sentence | They will be playing soccer at the park this weekend. |
| Future Perfect Tense | Subject + Helping Verb (will) + Have + Past participle form of the verb + the rest of the sentence along with the time frame | She will have finished her homework by dinner time. |
| Future Perfect Continuous Tense | Subject + Helping verb (will) + Have + been + Main verb + ing + the rest of the sentence | I will have been working here for three years by the end of next month. |
1. Simple Future Tense
Structure: Subject + Auxiliary verb (will) + Base form of the main verb + the rest of the sentence
Example: He will leave for New York tomorrow morning.
2. Future Continuous Tense
Structure: Subject + Helping Verb (will) + Be + Main verb + ing + the rest of the sentence
Example: They will be playing soccer at the park this weekend.
3. Future Perfect Tense
Structure: Subject + Helping Verb (will) + Have + Past participle form of the main verb + the rest of the sentence along with the time frame
Example: She will have finished her homework by dinner time.
4. Future Perfect Continuous Tense
Structure: Subject + Helping verb (will) + Have + been + Main verb + ing + the rest of the sentence
Example: I will have been working here for three years by the end of next month.
Structure of Sentences in Future Tense
| Sentence Type | Structure | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Positive | Subject + Will + Base form of the verb | They will visit their grandparents next weekend. |
| Negative | Subject + Will not/Won’t + Base form of the verb | She won’t attend the party tonight. |
| Interrogative | Will + Subject + Base form of the verb | Will you join us for dinner tomorrow? |
| Negative Interrogative | Won’t + Subject + Base form of the verb | Won’t they come to the meeting? |
Examples of the Future Tense
- She will visit the new art gallery tomorrow.
- They will buy a new car next month.
- I will be attending a conference next week.
- We will be traveling to Europe during the summer holidays.
- By 2025, he will have graduated from university.
- They will have completed the construction by the end of this year.
- By next month, I will have been working at this company for ten years.
- She will have been living in London for two years by the time we visit.
- Tomorrow at this time, they will be celebrating their team’s victory.
- He will start his new job on Monday.
Exercises of the Future Tense
Exercise 1: Fill in the blanks with the correct form of the verb in parentheses.
- I __________ (travel) to London next week.
- By 2023, she __________ (complete) her degree.
- They __________ (not, stay) at the hotel we recommended.
- __________ (you, cook) dinner tonight?
- __________ (he, not, work) on the project by next month?
Answers:
- I will travel to London next week.
- By 2023, she will have completed her degree.
- They will not stay at the hotel we recommended.
- Will you cook dinner tonight?
- Won’t he be working on the project by next month?
Exercise 2: Choose the correct future tense form to complete the sentences.
- This time next week, I __________ (will be flying/will fly) to New York.
- By the end of the year, he __________ (will have been/will be) teaching here for a decade.
- She __________ (will not have finished/won’t have been finishing) the report by tomorrow.
- __________ (Will they be staying/Are they staying) at your place next weekend?
- __________ (Will she have been working/Has she worked) here for three years by April?
Answers:
- This time next week, I will be flying to New York.
- By the end of the year, he will have been teaching here for a decade.
- She will not have finished the report by tomorrow.
- Will they be staying at your place next weekend?
- Will she have been working here for three years by April?
FAQ’s
Can “shall” and “will” be used interchangeably in the Future Tense?
Traditionally, “shall” is formal and used with “I” and “we” for simple future; “will” is more common today.
What is the difference between “will” and “going to” in Future Tense?
“Will” is for decisions at the moment of speaking; “going to” is for planned actions or strong intentions.



