80+ Interpersonal Skills Examples
Interpersonal skills, often referred to as people skills or soft skills, are essential for effective communication and interaction in various environments. These skills encompass abilities such as active listening, empathy, teamwork, and conflict resolution. Effective interpersonal skills facilitate positive relationships in both personal and professional settings, enhancing collaboration and understanding. Developing these skills can lead to better job performance, improved relationships, and a more successful career trajectory.
What are Interpersonal Skills?
Interpersonal skills are essential for effective communication and collaboration with others. They include strong verbal and non-verbal communication abilities, enabling individuals to excel in personal and professional interactions. People with these skills are adept at managing relationships and are often regarded as personable and effective communicators.
Best Examples of Interpersonal Skills
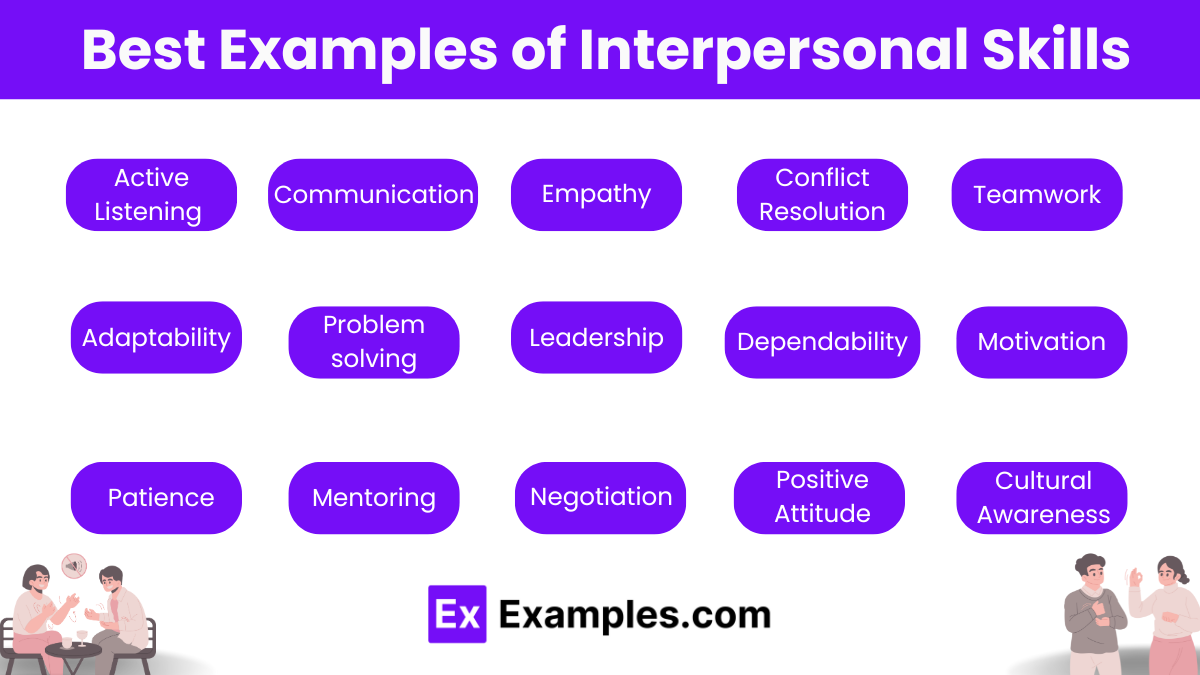
Interpersonal skills are crucial for building relationships and achieving success in both personal and professional settings. Here are key examples:
- Active Listening – Fully concentrating, understanding, responding, and remembering what is being said.
- Communication – Conveying information clearly and effectively through both verbal and non-verbal means.
- Empathy – Understanding and sharing the feelings of others, which helps in building rapport and trust.
- Conflict Resolution – Effectively managing and resolving disagreements in a constructive manner.
- Teamwork – Collaborating effectively with others to achieve common goals and outputs.
- Adaptability – Adjusting to new conditions and effectively handling changes or challenges.
- Problem-solving – Identifying issues and making decisions to find the best solution.
- Leadership – Inspiring and guiding individuals or groups to achieve personal and collective goals.
- Dependability – Being reliable and trustworthy in fulfilling commitments and responsibilities.
- Motivation – Inspiring oneself and others to take action and achieve goals.
- Patience – Handling delays or problems without becoming annoyed or anxious.
- Mentoring – Guiding and supporting the developmental journey of others.
- Negotiation – Reaching agreements between parties with differing perspectives.
- Positive Attitude – Maintaining a hopeful and optimistic outlook, which can influence the work environment.
- Cultural Awareness – Understanding and respecting cultural differences and acting appropriately in a variety of social context.
Importance of Interpersonal Skills
Interpersonal skills are vital for successful communication and collaboration in both personal and professional settings. These skills, including effective communication, empathy, and conflict resolution, enhance relationships and workplace efficiency. Strong interpersonal abilities facilitate career advancement, improve leadership effectiveness, and increase adaptability in diverse environments. Additionally, they contribute significantly to personal satisfaction and better customer interactions, underscoring their importance across various aspects of life.
Here’s why they are so important:
- Enhanced Communication: Strong interpersonal skills improve the ability to express ideas and message clearly and effectively in both personal and professional contexts.
- Better Relationships: These skills facilitate stronger connections with others, enhancing personal and work relationships through better mutual understanding and empathy.
- Conflict Resolution: Effective interpersonal skills enable individuals to handle disputes constructively, without creating or escalating conflicts.
- Improved Teamwork: They are essential for working effectively in team settings, ensuring that group dynamics remain productive and collaborative.
- Career Advancement: Employers value interpersonal skills highly, often placing them on par with technical abilities, as they are key to leadership and managerial roles.
- Networking Opportunities: Good interpersonal skills expand networking capabilities, providing greater career and personal opportunities through broader social interactions.
- Leadership Abilities: Strong interpersonal abilities are foundational for effective leadership, as they help in motivating, inspiring, and guiding others.
- Customer Relations: In roles involving customer interaction, interpersonal skills are crucial for satisfying clients and building loyalty.
- Cultural Sensitivity: With global interactions increasing, the ability to navigate and respect cultural differences is more important than ever.
- Personal Satisfaction: Mastering interpersonal skills also contributes to personal happiness and satisfaction, as it improves one’s ability to socialize and engage in meaningful relationships.
How to Use Interpersonal Skills
Interpersonal skills are essential for navigating social interactions and achieving success in both personal and professional environments. Here’s how you can effectively use these skills:
- Active Listening:
- Focus fully on the speaker, avoiding distractions.
- Show you’re listening through nods and affirmative sounds.
- Reflect back what is said to confirm understanding.
- Effective Communication:
- Use simple, clear language tailored to your audience.
- Employ both verbal and non-verbal cues effectively.
- Ensure your message is understood by asking for feedback.
- Feedback Provision:
- Deliver feedback in a constructive, non-confrontational manner.
- Focus on the action, not the person, to avoid defensiveness.
- Be specific and clear about what improvements are needed.
- Feedback Reception:
- Listen to feedback without interrupting.
- Ask questions to clarify points you do not understand.
- Use feedback as a tool for personal or professional growth.
- Empathy Demonstration:
- Try to understand others’ feelings and viewpoints.
- Acknowledge their feelings, even if you don’t agree.
- Respond with compassion and understanding.
- Conflict Management:
- Address conflicts early before they escalate.
- Strive to understand all sides and find common ground.
- Maintain calm and propose constructive solutions.
- Team Collaboration:
- Share information and resources willingly.
- Recognize and appreciate each team member’s contributions.
- Encourage open communication and group decision-making.
- Reliability:
- Keep your promises and commitments.
- Be punctual and prepared for meetings and appointments.
- Consistently meet deadlines and quality expectations.
- Encouragement:
- Praise others for their efforts and achievements.
- Support colleagues during challenging times.
- Inspire positivity and confidence in those around you.
- Negotiation Skills:
- Prepare thoroughly, understanding both your needs and the other party’s.
- Aim for outcomes that offer mutual benefits.
- Maintain a respectful and professional demeanor throughout negotiations.
- Respect for Others:
- Treat everyone with equal respect, regardless of their position or background.
- Listen openly to different perspectives and treat all contributions as valuable.
- Avoid biases and judgments in your interactions.
- Building Rapport:
- Engage in friendly, meaningful conversations.
- Find common interests to strengthen connections.
- Be genuine and sincere in your interactions.
- Adaptability:
- Remain open to changing environments and new information.
- Quickly adjust your approach based on situational demands.
- Embrace change as an opportunity for growth.
- Problem Solving:
- Identify key issues clearly and without bias.
- Brainstorm multiple solutions to find the most effective one.
- Implement solutions decisively and evaluate their effectiveness.
- Leadership:
- Inspire trust and respect through integrity and transparency.
- Motivate and guide others toward achieving common goals.
- Provide clear direction and support to your team.
- Patience:
- Remain calm and understanding when delays or frustrations arise.
- Take a step back to assess situations objectively.
- Allow processes to unfold naturally without forcing issues.
- Cultural Awareness:
- Educate yourself about different cultures and their norms.
- Show respect for cultural differences in communication and behavior.
- Adapt your approach to be inclusive of diverse perspectives.
- Persuasion Skills:
- Understand the needs and motivations of others.
- Present arguments that resonate with those needs.
- Communicate benefits clearly and persuasively.
- Social Skills:
- Be approachable and open in social settings.
- Maintain good manners and a friendly demeanor.
- Engage in active listening during conversations.
- Self-awareness:
- Reflect on your own behavior and its impact on others.
- Recognize your emotional triggers and manage your responses.
- Continuously seek feedback and opportunities for self-improvement.
Types of Interpersonal Skills
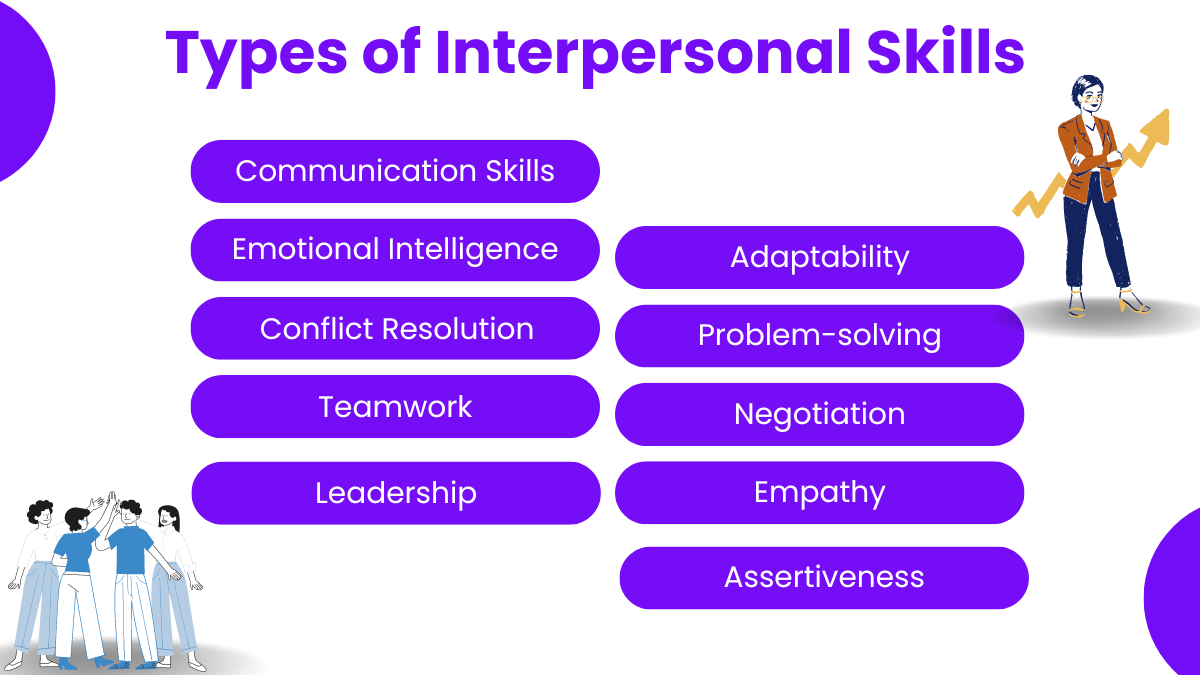
Interpersonal skills are essential for effective communication and interaction with others. Here are several types of interpersonal skills:
- Communication Skills: This includes verbal and non-verbal communication, active listening, and clarity in expressing ideas and thoughts.
- Emotional Intelligence: The ability to understand and manage one’s emotions, as well as empathize with others, is crucial for building strong relationships.
- Conflict Resolution: Being able to navigate conflicts and disagreements peacefully and constructively is a valuable interpersonal skill.
- Teamwork: Working collaboratively with others towards a common goal requires skills such as cooperation, compromise, and the ability to contribute positively to group dynamics.
- Leadership: Effective leadership involves inspiring and motivating others, delegating tasks, and providing guidance and direction.
- Adaptability: The capacity to adapt to changing situations and environments, as well as being open to new ideas and perspectives, is essential for interpersonal effectiveness.
- Problem-solving: Being able to identify, analyze, and solve problems collaboratively with others demonstrates strong interpersonal skills.
- Negotiation: Negotiating skills involve finding mutually beneficial solutions and reaching agreements through communication and compromise.
- Empathy: Understanding and sharing the feelings of others, as well as showing compassion and support, is key to building meaningful connections.
- Assertiveness: Being able to express opinions, needs, and boundaries in a respectful and confident manner is an important interpersonal skill.
Signs of Good Interpersonal Skills
Good interpersonal skills are evident through various observable signs that indicate effective communication and interaction with others. Here are several signs of good interpersonal skills:
- Active Listening: Demonstrating genuine interest in others’ perspectives and actively engaging in conversations by listening attentively.
- Empathy: Showing understanding and compassion towards others’ feelings and experiences, and expressing empathy through words and actions.
- Effective Communication: Communicating clearly and concisely, expressing ideas and thoughts articulately, and being able to convey messages in a way that is easily understood by others.
- Conflict Resolution: Resolving conflicts and disagreements calmly and constructively, seeking mutually beneficial solutions, and promoting harmony and cooperation.
- Adaptability: Being flexible and adaptable in various situations, demonstrating openness to new ideas and perspectives, and adjusting communication style as needed.
- Positive Body Language: Using positive body language such as maintaining eye contact, smiling, and having open and welcoming gestures, which contribute to building rapport and trust.
- Teamwork: Collaborating effectively with others, contributing to group goals, and supporting team members to achieve collective success.
- Respectful Communication: Treating others with respect and consideration, valuing their opinions and contributions, and avoiding judgmental or dismissive behavior.
- Problem-solving Skills: Approaching challenges with a solution-oriented mindset, analyzing problems critically, and seeking creative and collaborative solutions.
- Assertiveness: Asserting one’s opinions, needs, and boundaries confidently and respectfully, while also being receptive to feedback and differing viewpoints.
Signs of Good Interpersonal Skills
Good interpersonal skills are evident through various observable signs that indicate effective communication and interaction with others. Here are several signs of good interpersonal skills:
- Active Listening: Demonstrating genuine interest in others’ perspectives and actively engaging in conversations by listening attentively.
- Empathy: Showing understanding and compassion towards others’ feelings and experiences, and expressing empathy through words and actions.
- Effective Communication: Communicating clearly and concisely, expressing ideas and thoughts articulately, and being able to convey messages in a way that is easily understood by others.
- Conflict Resolution: Resolving conflicts and disagreements calmly and constructively, seeking mutually beneficial solutions, and promoting harmony and cooperation.
- Adaptability: Being flexible and adaptable in various situations, demonstrating openness to new ideas and perspectives, and adjusting communication style as needed.
- Positive Body Language: Using positive body language such as maintaining eye contact, smiling, and having open and welcoming gestures, which contribute to building rapport and trust.
- Teamwork: Collaborating effectively with others, contributing to group goals, and supporting team members to achieve collective success.
- Respectful Communication: Treating others with respect and consideration, valuing their opinions and contributions, and avoiding judgmental or dismissive behavior.
- Problem-solving Skills: Approaching challenges with a solution-oriented mindset, analyzing problems critically, and seeking creative and collaborative solutions.
- Assertiveness: Asserting one’s opinions, needs, and boundaries confidently and respectfully, while also being receptive to feedback and differing viewpoints.
How to Improve Interpersonal Skills
Improving interpersonal skills is essential for enhancing communication and building stronger relationships. Here are several effective strategies for developing and honing interpersonal skills:
- Practice Active Listening: Pay close attention to what others are saying, show interest through verbal and non-verbal cues, and avoid interrupting. Practice summarizing and paraphrasing to demonstrate understanding.
- Develop Empathy: Put yourself in others’ shoes, strive to understand their perspectives and emotions, and show empathy through supportive and compassionate responses.
- Enhance Communication Skills: Work on expressing yourself clearly and concisely, using appropriate body language and tone of voice, and seeking clarification when needed. Practice effective communication in both verbal and written forms.
- Seek Feedback: Actively solicit feedback from others about your communication style and interpersonal interactions. Use constructive criticism as an opportunity for growth and improvement.
- Practice Conflict Resolution: Learn and apply conflict resolution techniques such as active listening, identifying underlying issues, and seeking win-win solutions. Practice remaining calm and respectful during disagreements.
- Build Self-Awareness: Reflect on your own thoughts, feelings, and behaviors in interpersonal situations. Identify strengths and areas for improvement, and work on managing emotions and reactions effectively.
- Develop Flexibility: Be open to different perspectives, ideas, and approaches. Practice adapting your communication style and behavior to suit the preferences and needs of others.
- Participate in Team Activities: Engage in group projects, team sports, or community activities that require collaboration and teamwork. Practice effective communication, cooperation, and leadership skills within a group setting.
- Take Interpersonal Skills Training: Attend workshops, seminars, or online courses focused on interpersonal communication, conflict resolution, emotional intelligence, and related topics. Apply the skills and techniques learned in real-life situations.
- Seek Role Models: Observe and learn from individuals who demonstrate strong interpersonal skills. Identify role models in your personal or professional life and emulate their communication style, empathy, and relationship-building strategies.
Interpersonal Skills vs. Communication Skills
| Aspects | Interpersonal Skills | Communication Skills |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Revolve around interactions and relationships | Focus on transmitting messages and information |
| Components | Include empathy, emotional intelligence | Emphasize clarity, articulation, and effective expression |
| Purpose | Facilitate building relationships and trust | Aid in conveying information and fostering understanding |
| Understanding Others | Emphasize understanding others’ perspectives | Highlight active listening and providing constructive feedback |
| Conflict Resolution | Help in conflict resolution and collaboration | Assist in expressing ideas clearly and persuasively |
| Teamwork and Cooperation | Involve teamwork, cooperation, and adaptability | Enhance non-verbal communication and interpreting cues |
| Assertiveness and Adaptability | Include assertiveness and adaptability | Focus on both verbal and written expression and comprehension |
| Importance | Important for leadership, teamwork, and relationship-building | Vital for public speaking, presentations, and written communication |
Interpersonal Skills for Jobs
Interpersonal skills are essential in various job roles across industries. Here are some examples of how interpersonal skills are valued in different professions:
- Customer Service:
- Communicate effectively with customers
- Address their concerns and build rapport
- Ensure positive interactions and customer satisfaction
- Sales:
- Establish connections with clients
- Understand their needs and guide them through the purchasing process
- Drive sales and foster client relationships
- Management:
- Lead teams and delegate tasks
- Provide feedback and resolve conflicts
- Create a supportive and productive work environment
- Healthcare:
- Empathize with patients and deliver compassionate care
- Collaborate with colleagues and other healthcare professionals
- Ensure effective communication and quality care delivery
- Teaching:
- Engage students and explain concepts clearly
- Manage classroom dynamics and cultivate a positive learning environment
- Promote student success and development
- Human Resources:
- Conduct interviews and mediate employee disputes
- Facilitate communication between departments
- Foster a positive organizational culture and value diversity
- Leadership:
- Inspire and motivate teams
- Communicate vision and goals
- Build trust among team members and navigate challenges
- Team Collaboration:
- Foster collaboration and teamwork
- Work effectively with colleagues and share ideas
- Resolve conflicts and achieve common objectives
Examples of Interpersonal Skills for Resume
Interpersonal skills are valuable attributes that employers look for when reviewing resumes. Here are 15 examples of interpersonal skills that can enhance your resume:
- Communication: Clear and effective communication skills, both verbal and written.
- Active Listening: Ability to listen attentively and understand others’ perspectives.
- Empathy: Capacity to understand and empathize with the emotions and experiences of others.
- Teamwork: Collaboration and cooperation within a team to achieve common goals.
- Leadership: Inspiring and guiding others towards achieving objectives and leading by example.
- Conflict Resolution: Skill in resolving conflicts and disagreements in a constructive manner.
- Adaptability: Flexibility and openness to change and new ideas.
- Problem-Solving: Analytical and critical thinking skills to identify and solve problems.
- Negotiation: Ability to negotiate and find mutually beneficial solutions in various situations.
- Time Management: Efficient use of time and prioritization of tasks to meet deadlines.
- Networking: Building and maintaining relationships with colleagues, clients, and industry professionals.
- Decision Making: Making informed and timely decisions based on available information and analysis.
- Cultural Sensitivity: Respect and understanding for diverse cultures, backgrounds, and perspectives.
- Stress Management: Coping mechanisms and strategies to handle stress and pressure effectively.
- Public Speaking: Confidence and proficiency in delivering presentations or speeches to various audiences.
Examples of Interpersonal Skills for Interview
During interviews, showcasing interpersonal skills is crucial to demonstrate your ability to work effectively with others and contribute positively to the team. Here are several examples of interpersonal skills to highlight during interviews:
- Communication: Articulate your thoughts clearly and concisely, demonstrating effective verbal and non-verbal communication skills.
- Active Listening: Show attentiveness and engage with the interviewer by actively listening to their questions and responding thoughtfully.
- Empathy: Display empathy by acknowledging and understanding the perspectives and feelings of others, including the interviewer.
- Teamwork: Provide examples of successful collaborations and your ability to work well within a team, emphasizing your contributions to group projects or initiatives.
- Leadership: Discuss instances where you took on leadership roles or demonstrated leadership qualities, such as motivating others or resolving conflicts.
- Conflict Resolution: Describe situations where you successfully resolved conflicts or disagreements with colleagues or team members in a professional and constructive manner.
- Adaptability: Highlight your flexibility and ability to adapt to changing situations or environments, showcasing your resilience and versatility.
- Problem-Solving: Share examples of how you identified problems, analyzed options, and implemented effective solutions, demonstrating your analytical and problem-solving skills.
- Negotiation: Discuss experiences where you negotiated agreements or compromises, showcasing your ability to find mutually beneficial solutions in challenging situations.
- Time Management: Explain how you effectively manage your time and prioritize tasks to meet deadlines and achieve goals, demonstrating your organizational skills and efficiency.
- Networking: Mention your efforts in building and maintaining professional relationships, both within and outside the workplace, highlighting your networking abilities.
- Decision Making: Provide examples of instances where you made important decisions based on thorough analysis and consideration, showcasing your decision-making abilities.
- Cultural Sensitivity: Express your respect for diversity and inclusion, emphasizing your ability to work harmoniously with individuals from diverse backgrounds and cultures.
- Stress Management: Describe how you handle stressful situations and maintain composure under pressure, showcasing your resilience and ability to stay focused and productive.
- Public Speaking: If relevant to the role, discuss your experience and confidence in delivering presentations or speeches, highlighting your communication and presentation skills.
Plenty of businesses have agreements and partnerships with other companies and businesses to create a network. Successful partnerships hinge on the interpersonal skills of the people conducting the meetings.
1. Interpersonal Skills Template
2. Interpersonal Skills at Work
3. Interpersonal Skills Tutorial
4. Communication and Interpersonal Skills
5. Interpersonal Skills Summary Report
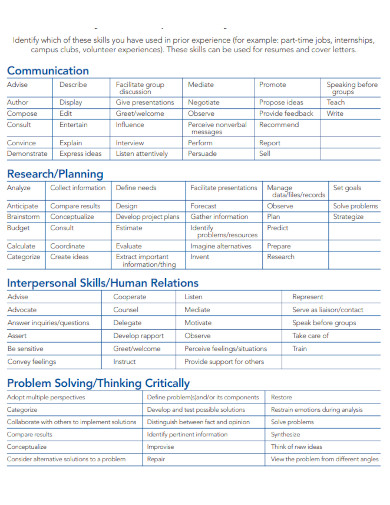
6. Identifying Interpersonal Skills
7. Interpersonal Skills Example
8. Effective Library Interpersonal Skills
9. Interpersonal Effectiveness Skills
10. Interpersonal Skills for Effective Collaboration
11. Interpersonal Skills Workshop
12. Education Interpersonal Skills
13. Interpersonal Studies Template
14. Interpersonal Skills and Conflict Management
15. Improving Interpersonal Skills Communication
16. Psychosocial and Interpersonal Skills
17. Interpersonal Skills for Teachers Trainees
18. Interpersonal Soft Skills
19. Building Effective Interpersonal Communication Skills
20. Interpersonal Resume Skills Checklist
21. Developing Interpersonal Skills
22. Foundations of Interpersonal Skills Communication
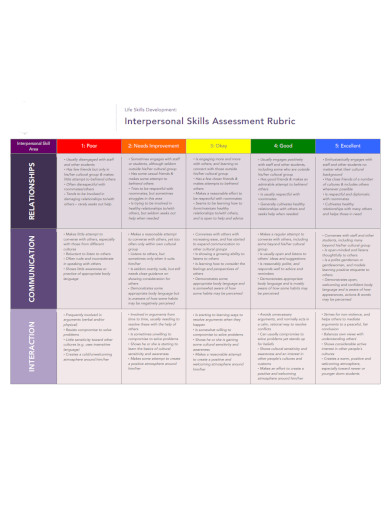
23. Interpersonal Skills Self-Assessment
24. Interpersonal Skills Assessment Rubric
How to Practice Your Interpersonal Skills
Interpersonal skills are soft skills that will take some time to develop and practice as it hinges more on the practical aspect of communication. Before you begin practicing and developing your interpersonal skills, you should conduct a self-assessment to determine how developed your skills are. You can further improve or train your soft skills by attending an interpersonal skill workshop.
1.) Practice Maintaining Relationships
You can develop your interpersonal skills through everyday interactions with the people around you. The best way to do this is to maintain the relationships you have created with the people you care about. You don’t have to limit yourself to your friends, family, or significant other you may also extend this to your workmates or groupmates.
2.) Work on Communication
It’s hard to communicate your thought and feelings to someone you think is significant in your life. Practice communication by talking to yourself in the mirror and conducting self-reflection exercises. Not only that, but you can also practice controlling your emotions.
3.) Practice and Improve Empathy
If you want to improve your interpersonal skills, then you must practice empathic listening. This means that you must be able to get on the same emotional level as the person you are talking to or listening to. Empathy will improve both your interpersonal and inter-relational skills.
4.) Learn How to Conduct Active Listening
Active listening is a skill that allows the person to be engaged in the conversation and will signal to the other person that you are listening to them. You can practice this skill by staying focused on the conversation and showing the other person that you are listening.
Examples of Interpersonal Skills for Students
Interpersonal skills are essential for students to succeed academically and socially. Here are some examples of interpersonal skills that students can develop:
- Communication: Ability to express thoughts and ideas clearly, both verbally and in writing.
- Active Listening: Capacity to listen attentively and understand others’ perspectives and instructions.
- Teamwork: Collaborating effectively with classmates on group projects and assignments.
- Leadership: Taking initiative and guiding peers towards common goals in group activities or extracurriculars.
- Conflict Resolution: Resolving conflicts and disagreements with peers in a constructive and respectful manner.
- Empathy: Understanding and empathizing with the feelings and experiences of others, fostering positive relationships.
- Adaptability: Adjusting to changes in academic environments or schedules and embracing new challenges.
- Problem-Solving: Analyzing problems, brainstorming solutions, and implementing effective strategies.
- Negotiation: Finding compromises and solutions in group settings or discussions.
- Time Management: Managing time efficiently to balance academic responsibilities, extracurricular activities, and personal commitments.
- Networking: Building relationships with peers, teachers, and professionals to support academic and career goals.
- Decision Making: Making informed decisions based on thorough consideration of options and consequences.
- Cultural Sensitivity: Respecting and appreciating cultural differences and perspectives within diverse student populations.
- Stress Management: Developing coping mechanisms to handle academic pressure and stress effectively.
- Public Speaking: Confidence in delivering presentations or participating in class discussions.
Examples of Interpersonal Skills for in the Workplace
nterpersonal skills, vital for fostering positive workplace relationships and effective communication, are highly valued by employers. Here are some examples, with transition words enhancing clarity and readability:
- Communication: Articulating ideas clearly and actively listening to others are essential components of effective communication in the workplace. This skill facilitates smooth collaboration and ensures that information is conveyed accurately.
- Active Listening: Paying full attention to what others are saying is the cornerstone of active listening. By asking clarifying questions and demonstrating empathy, misunderstandings can be minimized, fostering a cohesive work environment.
- Teamwork: Collaboration with colleagues is integral to achieving common goals and enhancing productivity. Contributing ideas and supporting team members not only strengthens team dynamics but also promotes a sense of camaraderie.
- Leadership: Inspiring and motivating others is a hallmark of effective leadership. By providing guidance and direction, leaders empower their teams to achieve success while fostering a culture of accountability.
- Conflict Resolution: Addressing conflicts calmly and diplomatically is key to maintaining a harmonious workplace. By finding mutually acceptable solutions, tensions can be diffused, allowing teams to focus on their objectives.
- Empathy: Understanding the emotions and perspectives of coworkers builds trust and rapport. By demonstrating empathy, individuals can foster a supportive work environment conducive to collaboration and innovation.
- Adaptability: Flexibility in adapting to changing work environments is essential for navigating evolving priorities and demands. Remaining open to new ideas and approaches enables individuals to thrive in dynamic workplaces.
- Problem-Solving: Analyzing problems collaboratively and developing effective solutions promotes innovation and efficiency. By fostering a problem-solving mindset, teams can overcome challenges and achieve their goals.
- Negotiation: Negotiating terms and agreements requires diplomacy and compromise. By seeking mutually beneficial outcomes, conflicts can be resolved amicably, preserving relationships and promoting cooperation.
- Time Management: Prioritizing tasks and managing deadlines efficiently is essential for meeting organizational goals. By allocating time effectively, individuals can optimize their productivity and minimize stress.
- Networking: Building and maintaining professional relationships expands opportunities and supports career growth. By cultivating a strong network, individuals can access resources and expertise to further their professional development.
- Decision Making: Making well-informed decisions based on available information is crucial for effective leadership. By weighing alternatives and considering potential impacts, leaders can steer their teams toward success.
- Cultural Sensitivity: Respecting and valuing diversity fosters an inclusive workplace culture. By understanding cultural differences and adapting communication accordingly, organizations can create an environment where all employees feel valued and respected.
- Stress Management: Coping with work-related stressors effectively is essential for maintaining well-being. By practicing stress management techniques and seeking support when needed, individuals can navigate challenges with resilience.
- Public Speaking: Confidently delivering presentations engages audiences and conveys ideas persuasively. By honing public speaking skills, individuals can effectively communicate their message and influence others positively.
Examples of Interpersonal Skills In Business
Interpersonal skills are indispensable in the business world, facilitating effective communication, collaboration, and relationship-building. Here are some examples of how interpersonal skills manifest in a business context:
- Communication: Clear and concise communication is fundamental in business interactions. Whether conveying ideas in meetings, negotiating deals, or addressing client concerns, effective communication ensures clarity and understanding among stakeholders.
- Active Listening: Active listening is essential for comprehending clients’ needs, understanding colleagues’ perspectives, and resolving conflicts. By listening attentively and empathetically, businesses can build trust and rapport with clients and colleagues alike.
- Teamwork: Collaborating effectively with colleagues and across departments is vital for achieving business objectives. Teamwork involves sharing ideas, providing support, and leveraging each team member’s strengths to drive success.
- Leadership: Strong leadership is characterized by the ability to inspire and motivate teams toward shared goals. Leaders foster a positive work culture, empower employees to take initiative, and guide them through challenges with confidence and resilience.
- Conflict Resolution: Conflict is inevitable in business, but effective conflict resolution skills can turn challenges into opportunities for growth. By addressing conflicts promptly and diplomatically, businesses can preserve relationships and maintain productivity.
- Empathy: Empathy is crucial for understanding clients’ concerns, anticipating their needs, and providing personalized solutions. In business, empathy fosters stronger client relationships, leading to increased satisfaction and loyalty.
- Adaptability: Business environments are dynamic and constantly evolving, requiring individuals to adapt quickly to changes. Adaptability involves embracing new technologies, processes, and market trends to stay competitive and relevant.
- Problem-Solving: Businesses encounter various challenges, from logistical issues to strategic dilemmas. Effective problem-solving skills enable businesses to identify root causes, explore innovative solutions, and implement strategies that drive growth and profitability.
- Negotiation: Negotiation skills are essential for securing favorable deals, resolving disputes, and building mutually beneficial partnerships. Successful negotiation involves active listening, strategic compromise, and finding win-win solutions for all parties involved.
- Time Management: Time is a precious resource in business, and effective time management skills are essential for maximizing productivity and meeting deadlines. By prioritizing tasks, delegating responsibilities, and minimizing distractions, businesses can achieve optimal efficiency.
- Networking: Building and maintaining professional networks is critical for business growth and development. Networking involves forging connections with clients, industry peers, and potential collaborators to access new opportunities and resources.
- Decision Making: Sound decision-making skills are fundamental to business success. Business leaders must weigh options, analyze risks, and make informed decisions that align with organizational goals and values.
- Cultural Sensitivity: In a globalized business landscape, cultural sensitivity is essential for navigating diverse markets and working with international clients and partners. Understanding cultural norms, customs, and communication styles fosters respect and enhances business relationships.
- Stress Management: Business environments can be fast-paced and high-pressure, necessitating effective stress management techniques. By practicing self-care, maintaining work-life balance, and seeking support when needed, individuals can mitigate stress and maintain well-being.
- Public Speaking: Public speaking skills are valuable for delivering persuasive presentations, pitching ideas, and representing the business in public forums. Confident and articulate public speakers can captivate audiences, convey messages effectively, and enhance the business’s reputation and credibility.
Examples of Interpersonal Skills in Nursing
In nursing, interpersonal skills are essential for providing compassionate care, fostering trust with patients, and collaborating effectively with colleagues. Here are some examples of interpersonal skills in nursing:
- Communication: Nurses must communicate effectively with patients, their families, and other healthcare professionals. Clear and empathetic communication helps ensure patients understand their care plans and feel heard and supported.
- Active Listening: Actively listening to patients’ concerns, fears, and preferences is crucial for building trust and rapport. By listening attentively, nurses can address patients’ needs and provide personalized care.
- Empathy: Empathy allows nurses to understand and connect with patients on an emotional level. Showing empathy can ease patients’ anxiety, increase their comfort levels, and enhance their overall healthcare experience.
- Compassion: Compassionate care involves treating patients with kindness, respect, and dignity. Compassionate nurses provide emotional support, alleviate suffering, and advocate for their patients’ well-being.
- Teamwork: Collaboration with other healthcare professionals is essential for delivering comprehensive patient care. Nurses work alongside doctors, therapists, and other team members to coordinate treatments, share information, and ensure continuity of care.
- Leadership: Nursing leadership involves guiding and supporting other team members, advocating for patients, and promoting best practices in patient care. Strong nursing leaders inspire confidence, foster teamwork, and drive positive outcomes.
- Patient Advocacy: Nurses serve as advocates for their patients, ensuring their voices are heard and their rights are respected. Advocating for patients’ needs and preferences helps promote patient-centered care and improve outcomes.
- Conflict Resolution: Conflict may arise in healthcare settings, and nurses must effectively resolve disputes while maintaining professionalism and patient safety. Skilled conflict resolution ensures a harmonious work environment and optimal patient care.
- Cultural Competence: Cultural competence enables nurses to provide culturally sensitive care to patients from diverse backgrounds. Understanding cultural differences in beliefs, values, and healthcare practices promotes respect and enhances patient outcomes.
- Critical Thinking: Nurses must critically analyze patient data, assess symptoms, and make informed decisions about patient care. Strong critical thinking skills help nurses identify potential problems, implement effective interventions, and improve patient outcomes.
- Stress Management: Nursing can be emotionally and physically demanding, requiring nurses to manage stress effectively. Practicing self-care, seeking support from colleagues, and utilizing stress management techniques are essential for maintaining well-being.
- Patient Education: Educating patients and their families about their health conditions, treatment options, and self-care practices empowers them to take an active role in their healthcare. Effective patient education promotes adherence to treatment plans and improves health outcomes.
- Professionalism: Professionalism encompasses integrity, accountability, and ethical conduct in nursing practice. Maintaining professional boundaries, upholding patient confidentiality, and adhering to professional standards are essential for building trust and credibility.
- Adaptability: Nursing requires adaptability to respond effectively to changing patient needs, unexpected situations, and evolving healthcare environments. Being flexible and adaptable allows nurses to deliver high-quality care in diverse settings and circumstances.
- Attention to Detail: Paying attention to detail is essential for accurate documentation, medication administration, and monitoring patients’ conditions. Thoroughness and precision in nursing practice help prevent errors and ensure patient safety.
FAQs
What are the four most important Interpersonal Skills?
The four most important interpersonal skills are communication, empathy, teamwork, and adaptability. Effective communication fosters understanding, while empathy builds rapport. Teamwork promotes collaboration, and adaptability enables individuals to navigate diverse situations and relationships successfully.
What is Interpersonal Skills at Work?
Interpersonal skills at work refer to the ability to effectively communicate, collaborate, and interact with others in a professional environment. These skills include communication, teamwork, empathy, conflict resolution, leadership, and adaptability, essential for building positive relationships and achieving common goals within the workplace.
How Do You Show Interpersonal Skills?
You can demonstrate interpersonal skills by actively listening, communicating clearly, collaborating effectively, showing empathy, resolving conflicts constructively, being adaptable, and exhibiting leadership qualities. These actions foster positive relationships and productive interactions in various settings.
How can I improve my Interpersonal Skills?
Practice active listening, empathize with others, communicate clearly, collaborate effectively, and seek feedback to enhance your interpersonal skills.
What are examples of Interpersonal Skills?
Examples include communication, teamwork, empathy, conflict resolution, leadership, adaptability, problem-solving, negotiation, time management, and cultural sensitivity.
How do Interpersonal Skills benefit workplaces?
Interpersonal skills promote cooperation, reduce conflicts, enhance productivity, foster innovation, improve morale, and contribute to a positive work environment.
Can interpersonal skills be learned?
Yes, interpersonal skills can be developed through practice, self-awareness, feedback, and ongoing learning and improvement efforts.
How do I demonstrate interpersonal skills?
Show empathy, communicate effectively, collaborate with others, resolve conflicts constructively, lead by example, and adapt to different situations and personalities.
Are interpersonal skills the same as communication skills?
While communication is a key component of interpersonal skills, they also encompass other abilities like empathy, teamwork, and conflict resolution.
What role do interpersonal skills play in leadership?
Interpersonal skills are crucial for effective leadership, enabling leaders to communicate vision, inspire teams, resolve conflicts, and build strong relationships.