49+ Journalism Mass Communication Examples
Journalism in mass communication serves as the cornerstone of informed society, blending storytelling with factual reporting to shape public discourse. This comprehensive guide delves into the nuances of journalism within the broad spectrum of mass media, highlighting its crucial role in delivering news, uncovering truths, and holding powers accountable. Through real-world communication examples, we explore various journalism facets, from investigative reporting to digital journalism, and provide insights into effective information dissemination in today’s media-saturated world.
What is Journalism in Mass Communication?
Journalism in mass communication refers to the practice of gathering, assessing, creating, and presenting news and information to the public. It plays a vital role in keeping society informed by reporting on events, issues, and trends. In mass communication, journalism acts as a bridge between the public and information sources, utilizing various media platforms like newspapers, television, and digital media to distribute news widely and efficiently. It’s essential for maintaining an informed public, offering diverse perspectives, and fostering a democratic society.
50 Journalism in Mass Communication Examples
Journalism in mass communication encompasses a wide array of practices, from traditional reporting to modern digital storytelling. This collection showcases 50 unique and distinct examples of journalism, highlighting how it informs, educates, and engages the public through various media formats. These examples illustrate the breadth of journalism, from breaking news coverage to in-depth investigative reports, and demonstrate the essential role journalism plays in providing reliable information and fostering public discourse in our digital media age.
- Front-Page News Report: “City Council Votes for New Environmental Policy.” A front-page story in a major newspaper, covering significant local governmental decisions.
- Television Broadcast of a Political Debate: “Live tonight: Mayoral candidates debate on key city issues.” Televised debates are crucial for presenting political views and policies to a wider audience.
- Investigative Journalism Piece: “Uncovering the Truth Behind Local Factory Pollution.” An investigative report revealing environmental malpractices, influencing public opinion and policy.
- Feature Story in a Magazine: “Life in the Digital Age: How Technology is Shaping Our Daily Lives.” A long-form feature in a magazine, exploring the impact of technology on society.
- Opinion Column in a Newspaper: “Op-Ed: The Need for Educational Reform.” An opinion piece where the writer expresses personal views on current educational challenges.
- Health Crisis Coverage on News Websites: “Breaking: Updates on the Global Health Crisis.” Online news articles providing ongoing coverage and updates on a health crisis.
- Sports Commentary on Radio: “Live commentary: The National Football Championship.” Radio broadcasts offer real-time sports commentary, engaging sports fans nationwide.
- Documentary Journalism: “New documentary explores the lives of refugees.” Documentaries provide in-depth analysis and storytelling on critical social issues.

- Photojournalism in Conflict Zones: “Award-winning photojournalist captures life in war-torn regions.” Photojournalism conveys powerful visual narratives from conflict areas, highlighting humanitarian issues.
- Business News Analysis: “Tech Giant’s Latest Innovation: A Game-Changer?” In-depth analysis of new technological advancements and their industry impact.
- Weather Reporting on TV: “Morning weather forecast: Preparing you for the day ahead.” TV weather reports provide essential information to the public for daily planning.
- Social Media Live Reporting: “Live-tweeting from the scene of the downtown protest.” Journalists use social media for instant reporting from various locations.
- Cultural Reviews in Journals: “Film review: An insight into the new blockbuster.” Cultural reviews offer critiques and perspectives on films, art, and literature.
- Podcast Series on Political Issues: “Our latest podcast episode discusses electoral reforms.” Podcasts are a popular medium for in-depth discussions on political subjects.
- Interviews with Public Figures: “Exclusive interview with the renowned environmental activist.” Interviews in various formats provide insights into the lives and thoughts of influencers.
- Community News in Local Papers: “Local paper highlights community garden initiative success.” Local journalism focuses on community-specific news and events.
- Educational Reporting in Specialized Magazines: “Magazine feature on the impact of digital learning.” Reporting on educational trends and policies in specialized magazines.
- Science and Technology Updates: “Breaking down the latest advancements in renewable energy.” Regular updates on scientific discoveries and technological advancements.

- Economic Reporting in Business Journals: “Quarterly economic report: Analyzing market trends.” Detailed reporting on economic conditions and market trends in business journals.
- Travel Journalism in Blogs: “Exploring hidden gems: A travel blogger’s journey through Asia.” Blogs offer personal travel experiences and recommendations to readers.
- Fashion Journalism in Online Magazines: “The latest fashion trends from Milan’s runway.” Online magazines cover current trends and news in the fashion industry.
- Human Interest Stories on News Portals: “The brave journey of a young entrepreneur.” Human interest stories highlight individual experiences and challenges.
- Radio News Bulletins: “Top of the hour news update: Stay informed.” Radio bulletins provide quick and efficient news updates.
- Infotainment Shows on Television: “Tonight’s show: Exploring science in everyday life.” Infotainment blends entertainment with informative content on TV shows.
- Celebrity News Coverage: “Inside look: Celebrity life under the spotlight.” Coverage of celebrity news, offering insights into the lives of public figures.
- Environmental Reporting in Online Articles: “The impact of climate change on coastal cities.” Reporting on environmental issues to raise awareness and prompt action.
- Legal and Court Reporting: “Courtroom updates: High-profile trial proceedings.” Coverage of legal proceedings, providing transparency and information to the public.
- Historical Journalism in Documentaries: “Documenting the fall of the Berlin Wall.” Documentaries that explore historical events and their impacts.
- Data Journalism and Visualization: “Interactive data visualizations show election results trends.” Data journalism uses visual tools to present complex data effectively.
- Consumer Advocacy Reporting: “Investigating consumer rights in the digital marketplace.” Reporting focused on protecting and informing consumers about their rights.
- Editorial Leadership in Newspapers: “Editorial: Navigating the challenges of modern journalism.” Editorials provide perspectives and direction on current journalistic practices and challenges.
- Newsletters on Current Affairs: “Weekly newsletter: Roundup of global political developments.” Newsletters offer curated content on various topics for regular updates.
- Automotive Journalism in Specialized Media: “The future of electric vehicles: An in-depth look.” Specialized reporting on automotive industry developments and trends.
- Academic Journalism in Scholarly Publications: “Analyzing the impact of media on youth behavior.” Scholarly articles delve into academic research on media-related topics.
- Agricultural Journalism in Trade Publications: “The changing landscape of modern farming techniques.” Coverage of agricultural news and trends in trade publications.
- Lifestyle Journalism on Digital Platforms: “The evolving lifestyle trends in urban living.” Lifestyle journalism explores various aspects of modern living and trends.
- Youth Journalism in Online Forums: “Youth forum: Voices of the next generation.” Platforms where young journalists express their views on current issues.
- Health and Wellness Reporting: “Navigating mental health: Strategies and support.” Reporting on health and wellness topics to inform and educate the public.
- Music Journalism in Online Reviews: “Album review: The resurgence of jazz music.” Reviews and critiques of music albums and artists.
- Political Analysis in Opinion Pieces: “Op-ed: Analyzing the current political landscape.” Opinion pieces offer analysis and viewpoints on political events.
- Art Criticism and Reviews: “Art exhibition review: A fusion of traditional and modern art.” Critiques and reviews of art exhibitions and artists.

- Investigative Reports on Social Issues: “Investigating the rise of homelessness in major cities.” In-depth reporting on critical social issues affecting communities.
- Architectural Journalism in Magazines: “Exploring modern architecture: Trends and sustainability.” Coverage of architectural designs, trends, and sustainability in the industry.
- Gastronomy Journalism in Food Blogs: “Culinary adventures: Exploring world cuisines.” Blogs that explore and review various culinary trends and experiences.
- Children’s News in Specialized Media: “Children’s news show: Making current events accessible to young audiences.” News content tailored specifically for children, making it accessible and informative.
- Entertainment Journalism on Digital Platforms: “The rise of streaming services in the entertainment industry.” Coverage of trends and news in the entertainment sector.
- Sports Journalism in Online Articles: “Analyzing the impact of technology in sports.” Reporting on sports events, trends, and the impact of technology.
- Tech Journalism in Podcasts: “Podcast series: The evolution of artificial intelligence.” Podcasts dedicated to discussing and analyzing technological advancements.
- Academic Analysis in Media Studies Journals: “Journal article: The role of media in shaping public policy.” Scholarly analysis of the media’s influence on public policy and society.
- Virtual Reality in Journalism: “Using virtual reality to immerse audiences in news stories.” Innovative use of VR technology to create immersive journalism experiences.
What is the Role of Journalism in Mass Communication?
Journalism plays a pivotal role in mass communication, serving as the foundation for disseminating information, shaping public opinion, and fostering a well-informed society.

This crucial function of journalism within the broader context of mass communication involves several key aspects:
Informing the Public
- Dissemination of Information: Journalism is the primary conduit for delivering news and information to the public. It plays a crucial role in keeping people informed about local, national, and global events.
- Educational Role: Beyond just reporting news, journalism educates the audience about complex issues, contributing to a more informed public.
Acting as a Watchdog
- Holding Power to Account: One of the most important roles of journalism in mass communication is to act as a watchdog over those in power. This involves investigating and reporting on misconduct, corruption, and misuse of power.
- Promoting Transparency and Accountability: Through investigative reporting and persistent questioning, journalism helps ensure transparency and accountability in public life.
Shaping Public Opinion
- Influencing Perceptions: Journalism has a significant impact on shaping public opinion and societal attitudes. The way stories are reported can influence people’s perceptions and opinions on various issues.
- Reflecting Societal Issues: Journalism mirrors societal problems and debates, highlighting issues that need attention and discussion.
Providing a Platform for Debate and Discussion
- Facilitating Public Discourse: Journalism provides a platform for public debate and discussion, offering diverse viewpoints and analysis.
- Encouraging Civic Engagement: By presenting various perspectives, journalism encourages civic engagement and participation in public life.
Contributing to the Cultural and Social Fabric
- Cultural Reporting: Journalism contributes to the cultural life of a society by covering arts, literature, and entertainment, enriching the social and cultural fabric.
- Social Impact: Stories with strong human interest or social significance can lead to societal changes and reforms.
Adapting to Digital Transformation
- Embracing Digital Media: In the digital age, journalism has evolved to include online reporting, social media, and multimedia content, expanding its reach and impact.
- Staying Relevant: The role of journalism in mass communication has adapted to stay relevant amidst changing technological landscapes and audience preferences.
Journalism is integral to mass communication, serving as a critical tool for informing the public, acting as a watchdog, shaping opinions, fostering public debate, and contributing to the cultural and social dynamics of society. Its evolution in the digital era further emphasizes its adaptability and enduring importance in the mass communication sphere.
What are Types of Mass Communication in Journalism?
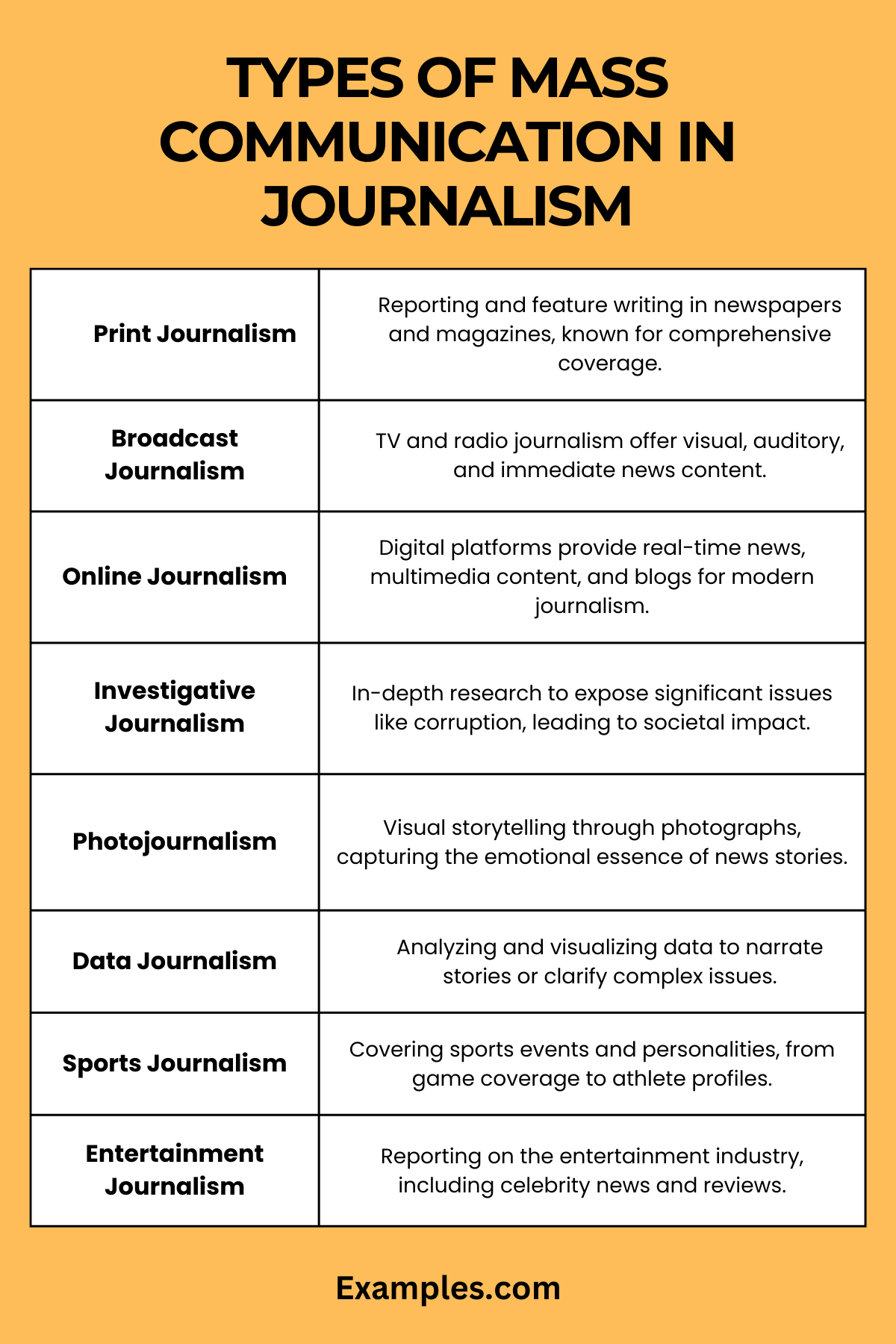
Mass communication in journalism encompasses various types, each serving unique purposes and employing different methods to inform, engage, and influence the public. Understanding these types is essential for comprehending the broad spectrum of journalism within mass communication.
Here, we explore the key types of journalism that contribute significantly to mass communication.
Print Journalism
- Newspapers and Magazines: This traditional form involves reporting news and stories through printed media like newspapers and magazines. It’s known for in-depth, comprehensive coverage of events and issues.
- Feature Writing: Print journalism also includes feature writing, offering detailed insights on specific topics, human interest stories, and in-depth analyses.
Broadcast Journalism
- Television News: TV journalism provides visual and auditory news content, known for its immediacy and wide reach. It includes news bulletins, live reports, and special news shows.
- Radio Journalism: Utilizing the audio medium, radio journalism offers news updates, interviews, and discussions, catering to audiences seeking news on-the-go.
Online Journalism
- Digital News Platforms: In the digital era, online journalism through websites and news portals has become prominent. It offers real-time news updates, multimedia content, and interactive features.
- Blogs and Social Media: Blogging and social media reporting are modern forms of journalism that utilize digital platforms for more personalized, immediate news dissemination.
Investigative Journalism
- In-Depth Reporting: Investigative journalism involves deep research and reporting to uncover truths about significant issues like corruption, scandals, or social injustices. It often leads to public awareness and policy changes.
Photojournalism
- Visual Storytelling: Photojournalism uses photographs to tell news stories, providing a powerful visual representation of events. It’s crucial for documenting and conveying the emotional impact of news stories.
Data Journalism
- Data-Driven Reporting: This type involves analyzing and visualizing data to tell stories or explain complex issues. Data journalism is increasingly important in an era of big data and infographics.
Sports Journalism
- Sports Coverage: Covering sports events, stories, and personalities, sports journalism includes everything from game coverage to in-depth profiles of athletes and analysis of sports trends.
Entertainment Journalism
- Celebrity and Entertainment News: Focusing on the entertainment industry, this type covers celebrity news, entertainment events, film and music reviews, and industry trends.
Business Journalism
- Economic and Financial Reporting: Business journalism focuses on economic, financial, and corporate news, providing analysis and information on business and economic matters.
Political Journalism
- Political Reporting and Analysis: It covers political events, campaigns, government proceedings, and offers analysis of political issues and public policy.
Each type of journalism in mass communication plays a crucial role in informing the public, offering varied perspectives, and addressing different informational needs. From traditional print to dynamic online platforms, the diverse forms of journalism ensure a well-informed and engaged public in today’s interconnected world.
How to Study Journalism and Mass Communication?
Studying journalism and mass communication is a journey that combines academic learning with practical experience, preparing individuals for a dynamic and evolving media landscape. Whether you aspire to be a reporter, a media researcher, or a communication specialist, understanding the steps to study this field effectively is crucial.
Here’s a comprehensive guide to help you navigate the educational pathway in journalism and mass communication.
Choose the Right Degree Program
- Accredited Institutions: Select a college or university with a strong reputation and accreditation in journalism and mass communication.
- Program Focus: Consider programs that align with your interests, whether it’s traditional journalism, digital media, public relations, or broadcast journalism.
Gain Practical Experience
- Internships: Apply for internships in news organizations, media houses, or PR firms to gain hands-on experience.
- Student Media: Participate in student-run newspapers, radio stations, or TV channels for practical learning.
Develop Core Journalism Skills
- Writing and Reporting: Focus on developing strong writing and reporting skills, essential for any journalism career.
- Critical Thinking and Analysis: Sharpen your ability to analyze information critically, a key skill for journalists and communicators.
Understand Media Ethics and Law
- Ethical Standards: Learn about journalistic ethics, including fairness, accuracy, and integrity.
- Media Law: Gain knowledge of media law, understanding the legal considerations and constraints in journalism.
Embrace Multimedia and Technology
- Multimedia Skills: Acquire skills in multimedia storytelling, including video, audio, and digital content creation.
- Technology Proficiency: Stay updated with the latest digital tools and technology used in modern journalism and mass communication.
Network and Build Connections
- Professional Networking: Attend workshops, seminars, and industry events to network with professionals and build connections.
- Mentorship: Seek mentorship opportunities with experienced journalists and media professionals.
Engage in Continuous Learning
- Stay Informed: Keep up with the latest trends, technologies, and changes in the media industry.
- Further Education: Consider advanced studies or specialized training in areas like investigative journalism, media management, or new media.
Research and Independent Projects
- Research Skills: Develop strong research skills to produce well-informed and accurate journalistic content.
- Independent Projects: Undertake independent projects or start a blog to practice and showcase your skills.
Cultivate Soft Skills
- Communication Skills: Enhance your verbal and written communication skills, crucial for effective storytelling.
- Adaptability and Resilience: Build resilience and adaptability to thrive in the fast-paced, often high-pressure world of journalism.
Studying journalism and mass communication is more than just academic learning; it’s about immersing yourself in the field, staying curious, and continuously adapting to the ever-changing media environment. Combining formal education with practical experience and a commitment to ethical standards will pave the way for a successful career in this dynamic field.
In conclusion, journalism and mass communication are vital in shaping informed societies, blending ethical reporting and digital storytelling to convey truth and foster dialogue. This field continuously evolves, adapting to new technologies and audience behaviors, underscoring its enduring importance in our global, interconnected world. Future journalists and communicators are poised to play a pivotal role in this dynamic landscape.



