10+ Object Examples
In grammar, an object is a part of a sentence that is acted upon by the subject. There are two main types of objects: direct objects and indirect objects. A direct object receives the action of the verb directly, while an indirect object receives the action indirectly, often preceded by prepositions like “to” or “for.” Identifying objects helps clarify the relationships between the elements of a sentence and provides depth to its meaning. Understanding objects is crucial for constructing clear and coherent sentences in any language.
What is an Object?
An object in grammar is a component of a sentence that receives the action of the verb. There are two types: direct objects, which receive the action directly, and indirect objects, which receive it indirectly. Identifying objects clarifies sentence structure and enhances communication. Understanding their roles is essential for constructing coherent sentences.
Functions of an Object
In grammar, an object serves several functions within a sentence. It primarily receives the action of the verb, whether directly or indirectly. The main functions of an object include:
- Receiving Action: Objects serve as the recipients of the action performed by the subject of the sentence. For example, in the sentence “She ate an apple,” “an apple” is the object receiving the action of eating performed by “she.”
- Direct Object: A direct object directly receives the action of the verb without any intermediary. It answers the question “what” or “whom” after the verb. In the sentence “He kicked the ball,” “the ball” is the direct object, receiving the action of being kicked.
- Indirect Object: An indirect object receives the action indirectly and is often preceded by prepositions like “to” or “for.” It answers the questions “to whom,” “for whom,” “to what,” or “for what” after the verb. For example, in the sentence “She gave a gift to her friend,” “her friend” is the indirect object, receiving the gift indirectly.
- Enhancing Clarity: Identifying objects helps clarify the relationships between different sentence elements. It provides additional context and detail, making the sentence clearer and more understandable. Without objects, sentences may lack specificity and precision.
- Structural Role: Objects play a crucial role in the structure and coherence of sentences. They contribute to the overall grammatical structure, helping to organize and convey the intended meaning effectively. Understanding the functions of objects is essential for constructing grammatically correct and meaningful sentences in any language.
Importance of Object
Objects play a crucial role in the structure and meaning of sentences. Understanding their importance is essential for effective communication and language comprehension. Here’s why objects matter:
- Clarity and Precision: Objects provide specificity and clarity to the action performed in a sentence. They answer questions like “what” or “whom” the action is directed towards, adding precision to the message conveyed. Without objects, sentences may lack detail and appear vague.
- Completeness of Action: Objects complete the action initiated by the subject of the sentence. They receive the action of the verb, ensuring that the sentence expresses a complete thought. Without objects, sentences may feel incomplete or lacking in substance.
- Structural Integrity: Objects contribute to the grammatical structure and coherence of sentences. They help organize the components of a sentence in a logical manner, enhancing readability and comprehension. Understanding the role of objects aids in constructing well-structured and coherent sentences.
- Variety in Expression: Objects allow for a diverse range of expressions and sentence structures. By modifying the object, writers can convey different nuances of meaning and emphasis. This versatility adds depth and richness to language usage.
- Contextual Clues: Objects provide valuable contextual clues that aid in interpretation and understanding. They help clarify the relationships between different elements of a sentence, guiding readers to comprehend the intended message accurately.
Types of Objects
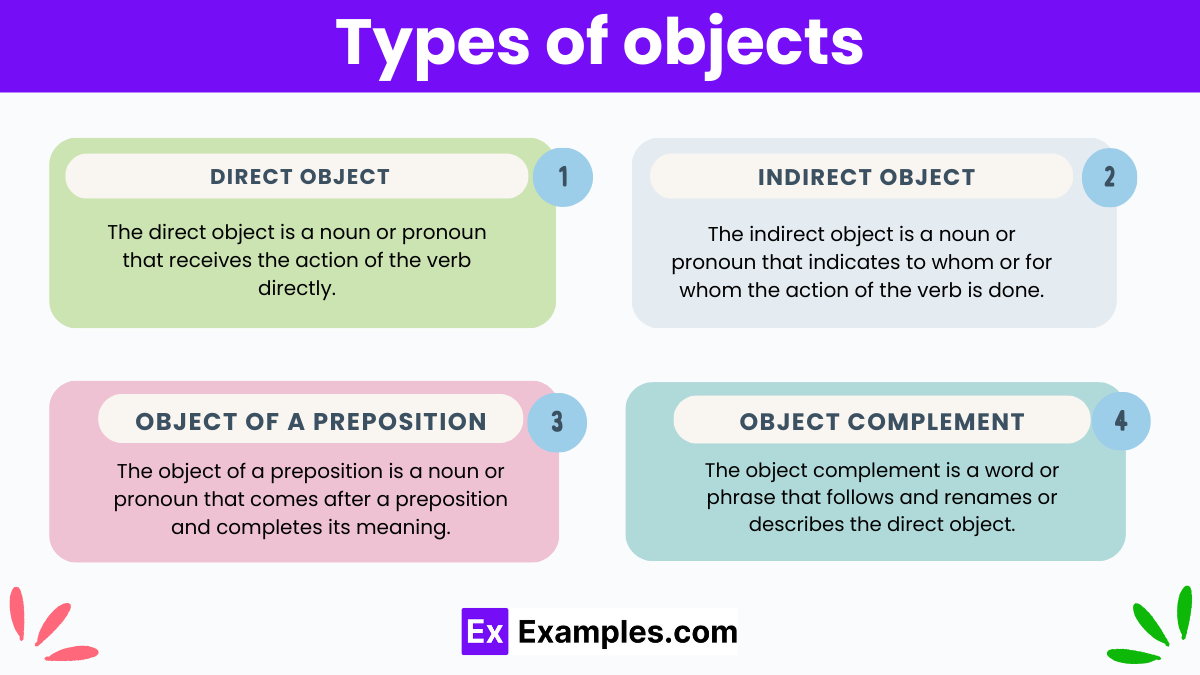
In grammar, objects are essential components that receive the action of the verb in a sentence. Understanding the different types of objects is key to mastering sentence construction. Here are the main types:
1. Direct Object:
- The direct object is a noun or pronoun that receives the action of the verb directly.
- It answers the question “What?” or “Whom?” after the verb.
- Example: “She ate an apple.” (The direct object “an apple” receives the action of the verb “ate.”)
2. Indirect Object:
- The indirect object is a noun or pronoun that indicates to whom or for whom the action of the verb is done.
- It often comes before the direct object and answers the questions “To whom?” or “For whom?”.
- Example: “He gave his sister a gift.” (The indirect object “his sister” receives the gift.)
3. Object of a Preposition:
- The object of a preposition is a noun or pronoun that comes after a preposition and completes its meaning.
- It provides additional information about location, direction, time, or possession.
- Example: “She sat on the chair.” (The object of the preposition “on” is “the chair.”)
4. Object Complement:
- The object complement is a word or phrase that follows and renames or describes the direct object.
- It provides additional information about the direct object, often renaming it or stating its condition.
- Example: “They named the puppy Max.” (The object complement “Max” renames the direct object “the puppy.”)
Pronouns for objects
Pronouns are versatile tools in language that replace nouns to avoid repetition and streamline communication. When used as objects in sentences, pronouns maintain clarity and readability. Let’s explore two types of pronouns serving as objects:
- Direct Object Pronouns:
- Example: “She loves him.”
- In this sentence, “him” acts as the direct object pronoun, replacing the noun “John.” Instead of saying “She loves John,” the pronoun “him” efficiently communicates the same idea while avoiding redundancy.
- Indirect Object Pronouns:
- Example: “He gave her a book.”
- In this example, “her” functions as the indirect object pronoun, replacing the noun “Sarah.” Instead of repeating “He gave Sarah a book,” the pronoun “her” simplifies the sentence structure while conveying the same meaning.
Observations about Objects
- Role in Sentence Structure: Objects play a vital role in sentence structure by receiving the action of the verb. They provide essential information about what or whom the action is directed towards.
- Two Main Types: There are two main types of objects in grammar: direct objects and indirect objects. Direct objects receive the action of the verb directly, while indirect objects receive the action indirectly.
- Clarity and Precision: Identifying objects in a sentence enhances clarity and precision in communication. They help specify the recipient of the action, making the sentence more informative.
- Variety in Usage: Objects can vary in form and function, providing flexibility in sentence construction. They can be nouns, pronouns, or even phrases, depending on the context.
- Importance in Language Learning: Understanding objects is essential for language learners as they form the backbone of sentence construction. Mastery of objects leads to improved proficiency in grammar and communication skills.
- Contextual Interpretation: Objects provide valuable context for interpreting the meaning of a sentence. They help establish relationships between different elements of the sentence, aiding in comprehension.
Synonyms and Antonyms for Object
| Synonyms | Antonyms |
|---|---|
| Item | Subject |
| Thing | Purpose |
| Entity | Aim |
| Article | Goal |
| Element | Intention |
| Artifact | Desire |
| Matter | Mission |
| Entity | Objective |
Examples of Object in Sentences
- She ate an apple.
- He read a book.
- They watched the movie.
- I bought a new car.
- She gave him a present.
- They built a sandcastle.
- He fixed the broken chair.
- She painted a beautiful picture.
- They visited the Eiffel Tower.
- I planted flowers in the garden.
What is the Object of a Preposition?
The object of a preposition is the noun, pronoun, or noun phrase that follows a preposition and completes its meaning by indicating its relationship to another word in the sentence.
What is an Object and Subject?
- An object in grammar is a noun, pronoun, or noun phrase that receives the action of the verb in a sentence.
- A subject, on the other hand, is a noun, pronoun, or noun phrase that performs the action of the verb.
How do I use Object to in a Sentence?
o use “object to” in a sentence, you can follow this structure: [Subject] + [Verb] + object to + [noun or gerund phrase representing what is objected to].
For example:
- She objects to the proposal.
- They objected to his decision.
- He objects to swimming in cold water.



