Oral Communication vs Written Communication – 9+ Examples
Navigating the realms of communication often leads to a comparison between Oral Communication and written communication. This guide offers a comprehensive understanding of these two pivotal forms of interaction, enriched with practical examples. While Oral Communication thrives in immediacy and personalization, written communication stands out for its permanence and detail-oriented nature. Each form holds distinct advantages and scenarios of effectiveness, crucial for both personal and professional settings. Our exploration not only contrasts these methods but also delves into how they can complement each other, enhancing overall communication skills. Stay tuned for an insightful journey through the dynamics of oral and written communication.
Differences between Oral Communication vs Written Communication
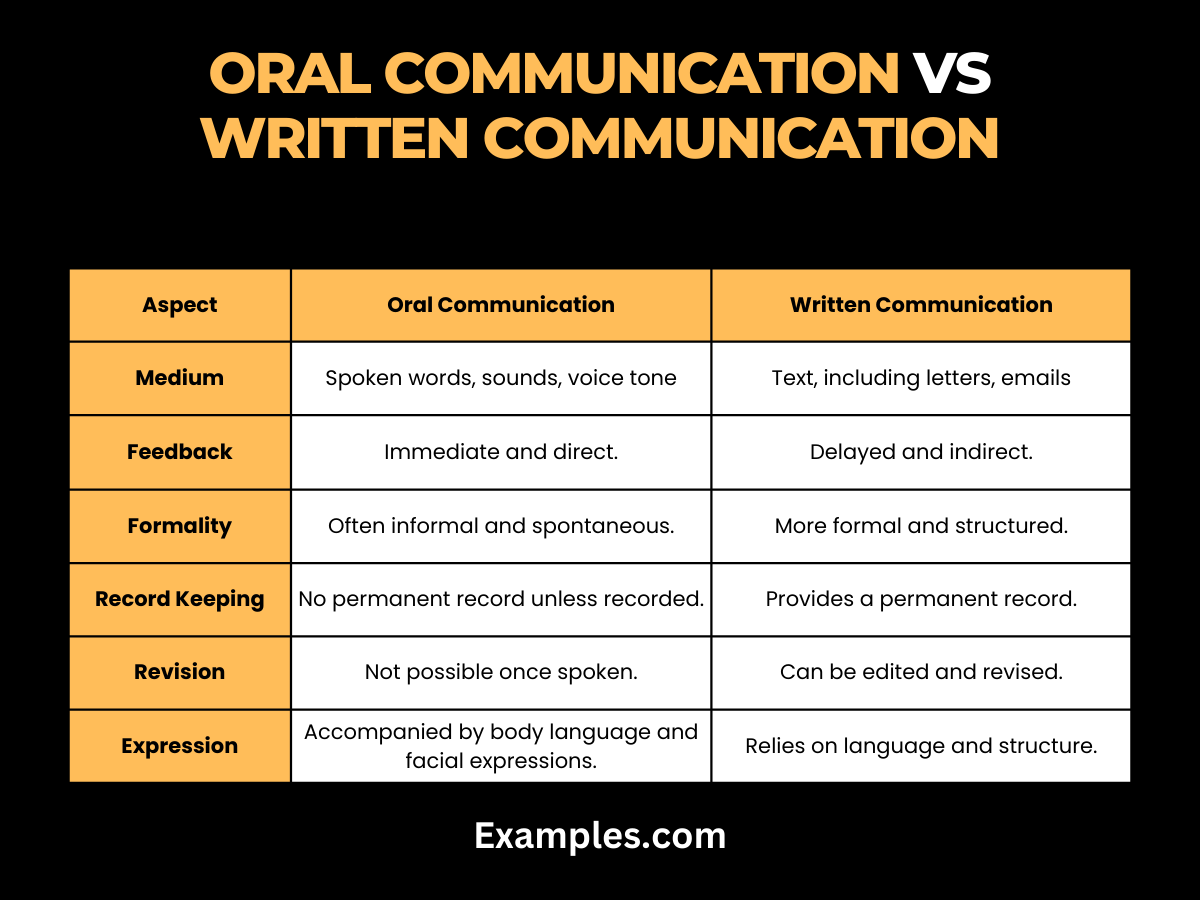
| Aspect | Oral Communication | Written Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Medium | Spoken words, sounds, voice tone, and pitch. | Text, including letters, emails, and reports. |
| Feedback | Immediate and direct. | Delayed and indirect. |
| Formality | Often informal and spontaneous. | More formal and structured. |
| Record Keeping | No permanent record unless recorded. | Provides a permanent record. |
| Revision | Not possible once spoken. | Can be edited and revised. |
| Expression | Accompanied by body language and facial expressions. | Relies on language and structure. |
| Accessibility | Requires the presence of both parties. | Can be accessed at any time. |
| Audience Reach | Limited to those present. | Can reach a wider audience. |
| Clarity | Depends on the speaker’s clarity and articulation. | Clearly articulated if well-written. |
| Correction | Immediate clarification possible. | Corrections require additional communication. |
10 Oral Communication Skills
Oral communication skills are essential in effectively conveying messages and engaging in meaningful conversations. These skills range from active listening to persuasive speaking, each playing a crucial role in personal and professional interactions. Here are 10 key oral communication skills, accompanied by examples and explanations.
- Active Listening: Focusing attentively on the speaker.
Example: Nodding and responding with, “I understand your point, please go on.” - Clear Articulation: Speaking clearly to ensure understanding.
Example: “Our meeting is scheduled for 10 AM tomorrow in the conference room.” - Confidence: Conveying your message with self-assurance.
Example: “I am confident that our strategy will lead to success.” - Empathy: Showing understanding and concern in your speech.
Example: “I can see how that situation would be frustrating for you.” - Persuasive Speaking: Convincingly presenting your ideas.
Example: “Investing in this technology now will benefit us long term.”

- Non-Verbal Cues: Using body language to complement your words.
Example: Smiling when talking about positive outcomes. - Effective Questioning: Asking questions that provoke thought and clarification.
Example: “How do you think this will impact our project timeline?” - Feedback Giving: Providing constructive feedback.
Example: “Your report was well-written, but adding more data would enhance it.” - Adaptability: Adjusting your communication style to your audience.
Example: Using simpler terms when explaining technical concepts to non-experts. - Storytelling: Engaging your audience with relevant stories.
Example: “Let me share an experience that illustrates this point perfectly.”
10 Written Communication Skills
Written communication skills are vital for conveying information clearly and effectively in a variety of contexts. These skills include everything from proper grammar to persuasive writing. Below are 10 key written communication skills, with examples and brief explanations.
- Clarity and Conciseness: Writing clearly and to the point.
Example: “Please submit the report by Monday, including all statistical analyses.” - Proper Grammar and Punctuation: Using correct language mechanics.
Example: “The meeting’s agenda includes: budget review, project updates, and team feedback.” - Professional Tone: Maintaining a formal and respectful tone.
Example: “I am writing to request your assistance with the upcoming project.” - Persuasive Writing: Convincing the reader with your argument.
Example: “Investing in renewable energy now will yield significant long-term benefits.” - Organized Structure: Structuring your writing for easy understanding.
Example: “Firstly, we will discuss the budget, followed by project updates.” - Attention to Detail: Paying attention to specifics in your writing.
Example: “The total cost, including taxes, comes to $1,050.” - Adaptability to Audience: Tailoring your writing to your reader.
Example: Using more technical language in a report for industry experts. - Effective Email Communication: Writing emails that are clear and actionable.
Example: “Please find attached the document for your review. I look forward to your feedback.”

- Editing and Proofreading: Ensuring your writing is error-free.
Example: Reviewing a document multiple times before submission. - Creative Writing: Using creativity to make your writing engaging.
Example: “In a world dominated by technology, our company remains committed to human-centric solutions.”
These examples illustrate how effective oral and written communication skills can be applied in various contexts, enhancing clarity, engagement, and understanding in interactions.
Importance of Oral and Written Communication for Students
Effective communication skills, encompassing both oral and written communication, are essential tools for students in today’s dynamic world. Here are ten points highlighting their importance:
- Enhances Learning Experience: Proficiency in oral communication enables students to actively participate in classroom discussions, leading to a deeper understanding of academic concepts.
- Boosts Confidence: Mastering written and oral communication builds confidence, essential for student presentations and group collaborations.
- Critical Thinking Development: Engaging in oral communication activities like debates helps in honing critical thinking skills, a crucial aspect for academic success.
- Improves Academic Writing: Proficiency in written communication is vital for crafting essays, reports, and research papers, reflecting a student’s grasp of the subject matter.
- Facilitates Effective Collaboration: Effective oral and written communication skills are key to successful group projects and teamwork, fostering a cooperative learning environment.
- Career Preparation: These skills prepare students for future careers, where oral communication and writing abilities are highly valued in the workplace.
- Enhances Persuasion Skills: Persuasive oral communication is crucial for debates and persuading others, while written skills are essential for convincing arguments in essays.
- Supports Problem Solving: Clear communication, both oral and written, is fundamental in identifying and articulating solutions to complex problems.
- Promotes Global Understanding: In a multicultural world, effective communication skills help students understand and connect with diverse cultures and viewpoints.
- Technology Integration: With the rise of digital communication, students must adeptly navigate between oral and written communication mediums, from classroom discussions to online forums and emails.
Developing these skills not only aids in academic growth but also lays the foundation for a successful professional life, underscoring their crucial role in a student’s holistic development.
What is the Relationship Between Oral and Written Communication?
Here’s a table summarizing the relationship between Oral and Written Communication:
| Aspect | Relationship |
|---|---|
| Medium | Both use language to convey messages, but in different forms. |
| Feedback | Oral provides immediate interaction, influencing written forms. |
| Formality | Oral’s informality complements written’s structured nature. |
| Record Keeping | Oral’s transient nature is balanced by written’s permanence. |
| Revision | Oral’s spontaneity contrasts with written’s editability. |
| Expression | Both employ different methods to convey emotions and emphasis. |
| Accessibility | Oral’s immediacy is complemented by written’s lasting access. |
| Audience Reach | Oral’s immediate audience vs. written’s broader distribution. |
| Clarity | Both aim for clarity, adapting to their mediums’ strengths. |
| Correction | Oral’s quick corrections contrast with written’s formal revisions. |
This table illustrates how Oral and Written Communication are interrelated and how each form complements and influences the other.
Both oral and written communication are indispensable, each serving distinct purposes. Oral communication excels in immediacy and emotional expression, while written communication shines in permanence and detail. Understanding when to use each form effectively is key to successful communication, be it in personal connections, academic pursuits, or professional engagements.
For a deeper understanding of the nuances and effective strategies in oral communication, resources such as Harvard University’s tips on public speaking can be immensely valuable. Similarly, for honing written communication skills, especially in academic contexts, the Purdue Online Writing Lab (OWL) offers comprehensive guides and resources that cater to a wide range of writing needs. Leveraging these high-quality resources can significantly enhance one’s communication skills, ultimately leading to more successful and meaningful exchanges in various aspects of life.
By embracing both oral and written communication, individuals can navigate the complexities of modern communication, making their interactions more effective and fulfilling. Whether it’s a face-to-face conversation, a digital communication, or a formal document, the ability to articulate thoughts clearly and effectively in both spoken and written form is a skill that will always stand in good stead.



