29+ Priming Theory in Mass Communication Examples
Delve into the intriguing world of Priming Theory in Mass Communication, a fundamental concept shaping media effects and audience perception. This complete guide, enriched with relatable examples, illustrates how media primes audiences to interpret subsequent information. Essential for students, educators, and professionals, it offers practical insights into utilizing priming in Mass Communication Scenarios/Situations, enhancing the impact of media messages.
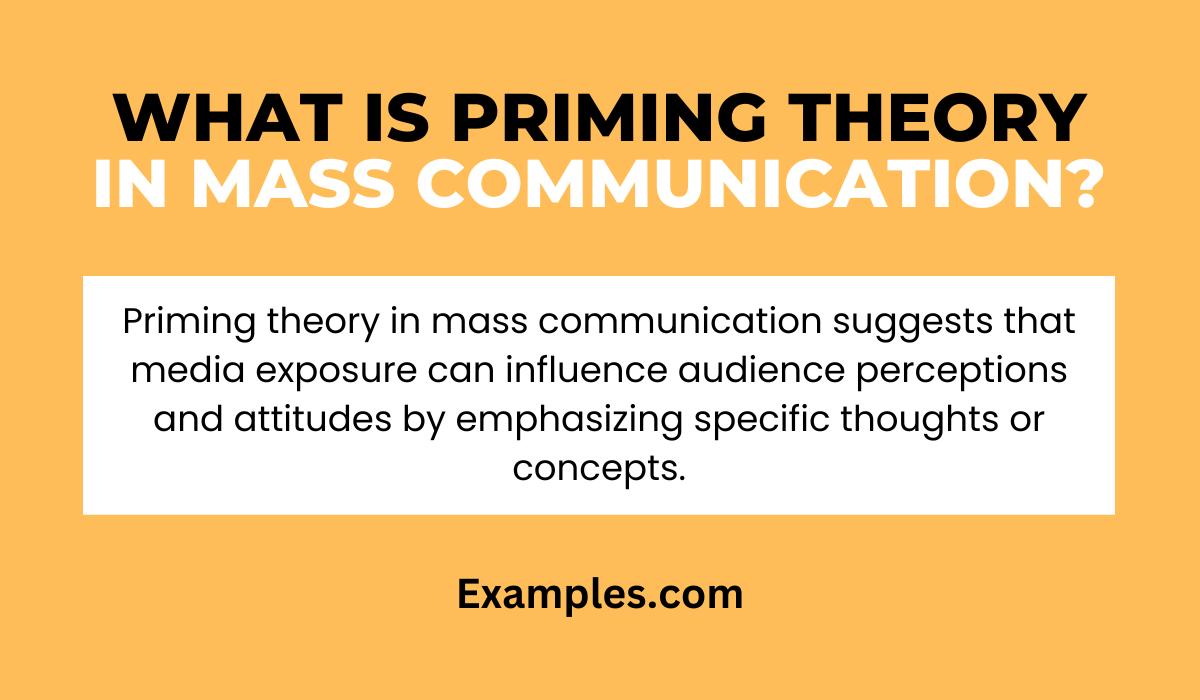
What is Priming Theory in Mass Communication?
Priming Theory in Mass Communication is a psychological concept explaining how media exposure influences the audience’s subsequent thoughts and behaviors. When people are exposed to certain stimuli in media, like words, images, or scenarios, it ‘primes’ them to later respond in specific ways. For example, if a news report frequently discusses crime, viewers might later interpret ambiguous situations as more dangerous. Priming can shape public opinion and attitudes, playing a crucial role in Mass Communication in Real Life and Mass Media Campaigns.
History of Priming Theory in Mass Communication
Priming Theory, as it relates to Mass Communication, has evolved significantly since its inception. Initially, it was closely linked with cognitive psychology, focusing on how exposure to one stimulus influences responses to a subsequent stimulus. However, it soon found its place in communication studies, particularly in understanding media effects.
In the early stages, researchers explored how media content could prime thoughts about public issues or personal traits, subsequently influencing judgments and decisions. This was particularly evident in the realm of political Mass Communication, where news coverage could prime voters to prioritize certain issues over others during elections. Over time, the theory expanded to include not just cognitive responses but emotional and attitudinal effects as well, making it a comprehensive tool for analyzing the influence of mass media in various spheres, including Social Media Mass Communication and Broadcasting Mass Communication.
What is the Best Example of Priming Theory in Mass Communication?
Priming theory, a significant concept in mass communication, primarily focuses on how media exposure can subtly influence people’s perceptions, beliefs, and behaviors. One of the best examples of priming theory in action is its application in political campaigns and news coverage.
In the context of an election, media coverage can ‘prime’ viewers by emphasizing certain issues or characteristics of candidates. For instance, if news outlets persistently focus on a candidate’s economic policies, viewers are more likely to judge the candidate based on these policies. This focus can overshadow other aspects of the candidate’s profile, such as foreign policy expertise or moral values.
A detailed case of this occurred during the 2008 U.S. Presidential elections. Extensive media coverage was given to the economic crisis prevailing at that time. This constant focus led voters to prioritize economic issues over others when evaluating candidates. Barack Obama, who consistently presented strong and relatable economic policies, benefitted from this priming. The media, by concentrating on economic issues, inadvertently influenced voters to place more weight on this criterion, which played a crucial role in Obama’s victory.

30 Examples of Priming Theory in Mass Communication
Priming Theory plays a pivotal role in mass communication, shaping how audiences perceive and process information. This theory suggests that media exposure can influence an individual’s later thoughts or actions by “priming” certain ideas or associations. Understanding the intricacies of Priming Theory is essential in fields like public relations mass communication and journalism mass communication, where message framing significantly impacts public opinion and behavior.

- News Report on Healthcare Policy: A news segment focuses on the struggles of uninsured individuals, subtly encouraging viewers to support healthcare reforms.
- This primes the audience to think favorably about policy changes.
- Advertising Campaign for Green Products: An ad series highlights the environmental benefits of using green products, priming consumers to prioritize eco-friendly purchases.
- It subtly influences consumer behavior towards sustainability.
- Political Debate Coverage: Media outlets emphasizing a candidate’s economic policies can prime the audience to consider economic issues as most crucial.
- This shifts public focus towards economic agendas.

- Social Media Campaign on Road Safety: Posts and videos about road accidents due to texting prime viewers to be more conscious while driving.
- It creates an awareness that leads to safer driving habits.
- Educational Program on TV: A television program showcasing successful entrepreneurs inspires students to consider entrepreneurship.
- This primes students to value and aspire towards entrepreneurial careers.
- Documentary on Climate Change: Documentaries highlighting the impacts of climate change prime viewers to be more environmentally conscious.
- It motivates actions towards reducing one’s carbon footprint.
- Celebrity Endorsements in Ads: Featuring celebrities in health-related ads primes audiences to associate health products with glamour and success.
- This can increase the product’s appeal and perceived value.
- Crime Reports in Newspapers: Continuous reporting of urban crimes can prime readers to perceive cities as unsafe.
- This can affect their decisions about travel or residence.
- Public Service Announcements on Smoking: PSAs showing the adverse effects of smoking prime viewers to associate smoking with negative outcomes.
- It can lead to a reduction in smoking prevalence.
- Blog Articles on Fitness Trends: Blogs discussing new fitness regimes prime readers to try out these trends.
- This influences health and lifestyle choices.
- Mass Email Campaigns for Fundraising: Emails highlighting the struggles faced by a community can prime recipients to donate.
- It evokes empathy and prompts action.
- Billboard Advertising for Tourism: Billboards showing exotic destinations prime viewers to consider those places for their next vacation.
- It influences travel decisions and preferences.
- Television Commercials on Investment Products: Commercials that focus on the security of investment products prime viewers to think about their financial future.
- This can lead to more cautious financial planning.
- Social Media Posts on Voting: Posts encouraging voting behavior prime users to be more politically active.
- It increases voter turnout during elections.
- Broadcasting of Sports Events: Broadcasting major sports events can prime viewers to take up or follow a particular sport.
- It impacts sports culture and participation.
- Radio Shows Discussing Mental Health: Shows focusing on mental health issues prime listeners to be more aware and empathetic towards such conditions.
- This promotes a more understanding and supportive society.
- Magazine Articles on Healthy Eating: Articles emphasizing the benefits of a healthy diet prime readers to make better food choices.
- It influences eating habits and lifestyle.
- Online Forums on Tech Innovations: Discussions about new technology prime users to be more receptive to adopting new gadgets.
- It drives technology trends and consumer behavior.
- Movie Themes on Social Issues: Films that tackle social issues prime viewers to think and discuss these topics more actively.
- This can lead to increased social activism.
- Newsletters on Personal Development: Newsletters focusing on self-improvement techniques prime subscribers to work on their personal growth.
- It influences self-development practices.
- Podcasts on Entrepreneurship: Podcasts discussing successful business stories prime listeners to consider starting their own businesses.
- It inspires entrepreneurial ventures.
- YouTube Videos on DIY Projects: Videos that showcase do-it-yourself projects prime viewers to engage in creative activities.
- This boosts creativity and practical skills.
- Press Releases on Corporate Social Responsibility: Press releases that highlight a company’s CSR initiatives prime the public to view the company favorably.
- It shapes corporate reputation and public relations.
- Educational Videos on Recycling: Videos teaching the importance of recycling prime viewers to be more environmentally responsible.
- This encourages sustainable living practices.
- Book Reviews in Magazines: Reviews focusing on a book’s educational value can prime readers to seek more knowledge-based literature.
- It influences reading choices and intellectual development.

- Infographics on Health Statistics: Infographics showing health statistics prime viewers to be more health-conscious.
- It can lead to healthier lifestyle choices.
- Radio Advertisements for Local Events: Ads about local events prime listeners to participate in community activities.
- This enhances community engagement.
- Television Series on Historical Events: Series that accurately depict historical events prime viewers to take an interest in history.
- It fosters educational interest and historical awareness.
- Twitter Campaigns on Social Movements: Hashtag campaigns about social movements prime users to support or learn more about these causes.
- It amplifies social awareness and activism.
- E-books on Financial Literacy: E-books focusing on financial management skills prime readers to be more financially literate.
- This promotes sound financial decision-making.
Role of Symbolic Interactionism in Mass Communication
- Influencing Public Opinion and Behavior: Media content can set the agenda for what audiences think about, subtly guiding their opinions and behaviors. This is especially evident in how news coverage can shape public perception on issues like immigration, healthcare, or crime.
- Election Campaign Strategies: Political campaigns often use media to prime voters. By focusing on particular issues or traits of a candidate, media can influence what criteria voters use to make their decisions.
- Advertising and Marketing: In advertising, priming is used to create associations between a product and certain feelings or values. For instance, a car advertisement might focus on safety, priming viewers to prioritize safety when considering a car purchase.
- Perception of Social Issues: Media can shape how people interpret and understand social issues. For example, continuous coverage of violent crimes can prime viewers to perceive the world as more dangerous than it is, influencing public policy and personal behavior.
- Cultural Influence and Stereotyping: Media can reinforce stereotypes by consistently linking certain groups with specific attributes or behaviors. This form of priming can have long-term effects on societal attitudes and prejudices.
- Media Literacy and Critical Thinking: Understanding the role of priming can enhance media literacy, encouraging audiences to be more critical of the information they consume and aware of the potential for subtle influence.
Importance of Priming Theory in Mass Communication
Priming Theory plays a pivotal role in the realm of Mass Communication. This theory delves into how exposure to media content can influence an individual’s subsequent perceptions and behaviors. Here are some key aspects highlighting its importance:
- Influence on Public Perception: Priming can significantly shape public opinion, especially in politically charged environments. By emphasizing certain topics, media can manipulate the salience of these topics in the public’s mind.
- Impact on Audience Behavior: Exposure to specific media content can subtly guide audience behavior. For instance, news reports focusing on crime can lead to increased public concern about safety.
- Role in Advertising and Marketing: In advertising, priming is used to create a predisposition towards a product or brand. This often leads to increased consumer responsiveness to subsequent marketing messages.
- Educational Applications: Priming is also utilized in educational mass communications, where certain themes are emphasized to enhance learning and retention.
- Cultural Influence: Through repeated exposure to specific themes or narratives, priming contributes to shaping cultural norms and values.
- Political Communication: In political mass communication, priming is used to influence public opinion on policy issues, candidates, and political parties.
- Crisis Management: During crises, the media’s focus on specific aspects can influence public response and behavior, making priming a crucial tool in crisis communication strategies.
How to Use Priming Theory in Mass Communication
Utilizing Priming Theory effectively in Mass Communication involves strategic planning and execution. Here are detailed steps and points on how to apply this theory:
- Identify Key Concepts: Start by identifying the core concepts or messages you want to prime. These could range from brand attributes in advertising to social issues in news reporting.
- Content Creation: Develop content that subtly incorporates these concepts. The content should be engaging and relevant to ensure audience attention and absorption.
- Repetition is Key: For priming to be effective, the key concepts need to be repeated across various communication channels. This could include television Mass Communication, social media, or blog Mass Communication.
- Contextual Relevance: Ensure that the priming elements are contextually relevant to the audience. This increases the likelihood of the primed concepts being activated in the audience’s memory.
- Leverage Multimedia: Utilize a mix of text, images, and videos to reinforce the primed concepts. Different formats can appeal to various audience segments.
- Monitor Audience Response: Keep track of how the audience is responding to the primed content. This can be through social media engagement, surveys, or behavioral analysis.
- Adjust Strategies Accordingly: Based on audience feedback, adjust your priming strategies. This might involve changing the content, the frequency of repetition, or the communication channels used.
- Ethical Considerations: Always consider the ethical implications of priming. Avoid manipulative or deceptive practices that could mislead or harm the audience.
- Integration with Other Theories: Combine priming with other mass communication theories like the Agenda-Setting Theory or Framing Theory for a more comprehensive approach.
- Continual Learning and Adaptation: Stay updated with the latest research in priming and mass communication to refine and evolve your strategies.
The Priming Theory is a powerful tool in Mass Communication, influencing public opinion, behavior, and cultural norms. Its effective use requires strategic planning, ethical consideration, and continual adaptation to changing audience dynamics and media landscapes.