40+ Proper Noun Examples
A proper noun refers to the name of a specific individual, place, organization, or thing. Unlike common nouns, proper nouns are always capitalized. This distinct grammatical category includes personal names such as “Sarah” or “Michael,” geographical locations like “France” or “Mount Everest,” and institutional names such as “Microsoft” or “Harvard University.” Proper nouns are unique identifiers that distinguish one particular entity from others of a similar type, making them essential for clear communication. They help to provide exact references in speech and writing, ensuring that listeners and readers can identify specific subjects with precision.
What is a Proper Noun?
A proper noun is a specific name used for an individual, place, or organization. It stands out from common nouns by always being capitalized. Examples include ‘Egypt,’ ‘Juliet,’ and ‘Google.’ Proper nouns uniquely identify entities, providing clarity in communication.
Pronunciation of Proper Noun
The pronunciation of the phrase “proper noun” is straightforward. It can be phonetically broken down as follows:
- Proper: /ˈprɑː.pɚ/
- Noun: /naʊn/
The emphasis is on the first syllable of “proper,” which sounds like “prah,” with the ‘a’ as in “father.” The second syllable is softer, sounding like “per” with the ‘e’ resembling the ‘u’ in “supper.”
For “noun,” the word rhymes with “down,” where the ‘ou’ sounds like the ‘ou’ in “found.”
Together, “proper noun” is pronounced as /ˈprɑː.pɚ naʊn/.
Types of Proper Noun
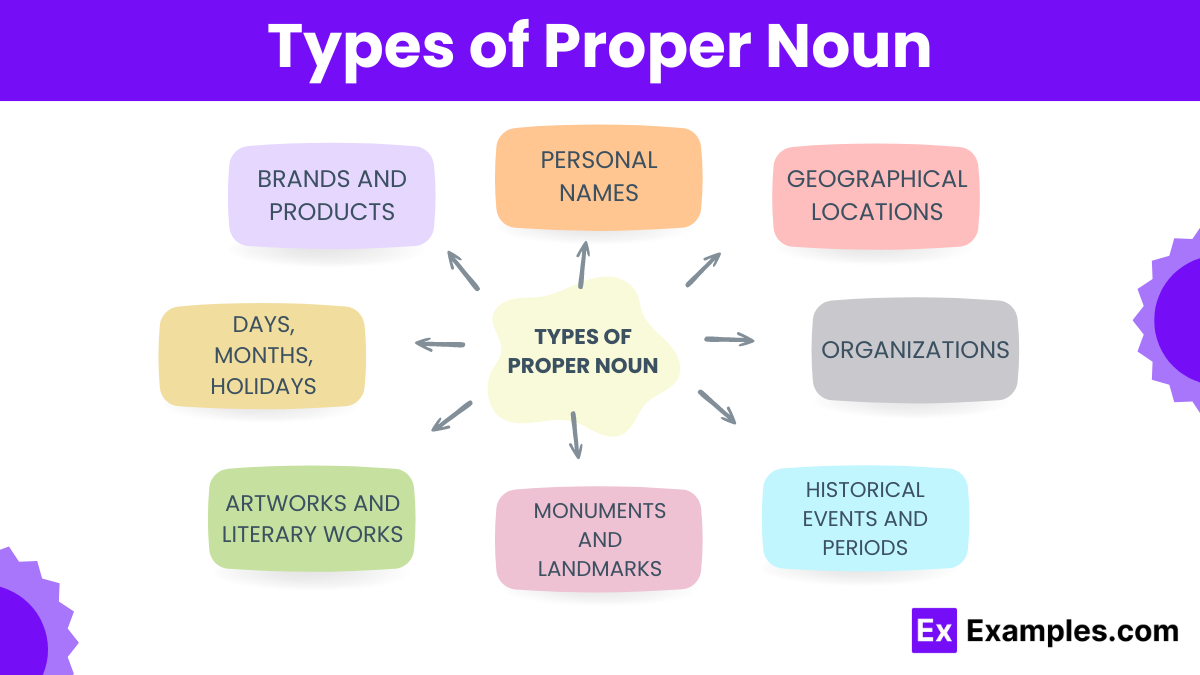
Proper nouns are specific names given to particular people, places, or things to distinguish them from others of a similar kind. Here are distinct types of proper nouns:
- Personal Names: Names given to individual people, such as Emma, John, or Mohammed.
- Geographical Locations: Names of specific places like Paris, Mount Everest, Amazon River, or Africa.
- Organizations: Names of specific companies, institutions, government bodies, etc., such as Google, United Nations, or Harvard University.
- Historical Events and Periods: Names of significant times or events in history like World War II, The Renaissance, or The Great Depression.
- Monuments and Landmarks: Specific names of notable structures or places, such as The Statue of Liberty, The Eiffel Tower, or Stonehenge.
- Artworks and Literary Works: Titles of specific books, movies, paintings, or sculptures like The Mona Lisa, Hamlet, or Star Wars.
- Days, Months, Holidays: Specific days, months, or recognized holidays, including Monday, July, Christmas, or Thanksgiving.
- Brands and Products: Specific names of products or brands that are trademarked or otherwise distinguished from general types, such as Nike, Coca-Cola, or iPhone.
Proper Noun vs. Common Noun
| Aspect | Proper Noun | Common Noun |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Names a specific individual, place, organization, or event. | Refers to a general category or class of people, places, things, or ideas. |
| Capitalization | Always capitalized. | Not capitalized unless it begins a sentence. |
| Examples | Michael, Paris, Microsoft, Olympics. | man, city, company, sports event. |
| Purpose | Identifies unique entities, distinguishing them from others of the same type. | Represents a generic member of a group or class. |
| Variability | Less variable; usually remains the same. | Highly variable depending on context and usage. |
| Modification | Generally stands alone without modifiers unless specifying further (e.g., Old King Cole). | Often modified by adjectives to specify attributes (e.g., large dog). |
Synonyms & Antonyms for Proper Noun
Synonyms
- Specific name
- Personal name
- Unique identifier
- Proper name
- Named entity
Antonyms
- Common noun
- General noun
- Generic name
- Non-specific name
- Collective noun
Capitalization rules of Proper Nouns
Capitalizing proper nouns correctly is essential for accurate and professional writing. Here are the main rules to follow:
- Personal Names: Always capitalize the first and any middle names of people. For example, John Edgar Hoover.
- Geographical Names: Capitalize the names of mountains, rivers, seas, and geographical areas. Examples include Mount Everest, Mississippi River, and South America.
- Buildings and Monuments: Names of significant buildings, monuments, and other landmarks should be capitalized. Examples: Statue of Liberty, Eiffel Tower.
- Days, Months, and Holidays: Capitalize the days of the week, months of the year, and holidays, but not the seasons. For example, Monday, July, Christmas; contrast with “autumn”.
- Institutions and Organizations: The full names of institutions, organizations, businesses, and governmental bodies should be capitalized. For instance, Harvard University, Coca-Cola, Federal Bureau of Investigation.
- Events and Periods: Historical periods and significant events are capitalized. Examples include The Renaissance, The Great Depression, World War II.
- Titles and Specific Roles: When titles such as King, President, or Captain are used as part of a proper name, they should be capitalized. For example, President Lincoln; however, do not capitalize these words when they are used generally (e.g., “the president spoke”).
- Brands and Products: Names of brands and specific products should be capitalized. For instance, Apple, iPhone.
How to Use Proper Nouns?
Proper nouns are essential for specific identification in both writing and speech. Here’s a guide on how to use proper nouns effectively:
- Capitalization: Always capitalize proper nouns, regardless of where they appear in a sentence. This distinguishes a specific name from a general one.
- No Articles: Generally, do not use definite or indefinite articles (the, a, an) before proper nouns. However, there are exceptions, such as “the United States” or “the Netherlands.”
- Use Sparingly: Overuse of proper nouns can clutter your writing or speech. Use them when they are necessary to specify what or whom you are talking about, but replace them with pronouns or other identifiers where appropriate to avoid repetition.
- Appropriate Context: Use proper nouns when you need to name specific entities like people, places, organizations, and sometimes dates and events. This adds clarity and specificity to your descriptions.
- Adjective Forms: When derived from proper nouns, adjectives remain capitalized. For example, “Shakespearean drama” or “Victorian architecture.”
- Consistency: Maintain consistency when referring to a proper noun multiple times in the same piece. Ensure the spelling and formality level are consistent throughout the document.
- Avoid Modifications: Typically, avoid adding unnecessary modifiers to proper nouns. If modification is necessary, such as describing a location within a broader geographical context, make sure it maintains clarity, e.g., “Paris, France.”
Examples of Proper Noun in Sentences
- Sarah plans to visit New York City next summer.
- Microsoft recently launched a new version of its Windows operating system.
- Mount Kilimanjaro is one of the most famous mountains in Africa.
- The Great Wall of China attracts millions of tourists every year.
- Dr. Johnson will be speaking at the conference held at Harvard University.
- We celebrated Thanksgiving with our relatives in Boston last year.
- Leonardo DiCaprio starred in Titanic, which became one of the highest-grossing films of all time.
- Amazon has become one of the world’s largest online retailers.
- The Taj Mahal is recognized as a symbol of love around the world.
- President Lincoln is often cited for his leadership during the American Civil War.
Examples of Proper Noun For kids
Proper nouns are the specific names of people, places, and things. Here are some kid-friendly examples of proper nouns, perfect for helping children understand how they are used:
- Mickey Mouse lives in Disneyland.
- Mrs. Thompson is my favorite teacher at Lincoln Elementary School.
- We went to McDonald’s for lunch last Saturday.
- Harry Potter is a character in books written by J.K. Rowling.
- The Pacific Ocean is the largest ocean in the world.
- Christmas is my favorite holiday because I get to visit Grandma and Grandpa.
- My best friend Lucy has a dog named Rex.
- I love watching SpongeBob SquarePants on Nickelodeon.
- We visited The Statue of Liberty on our trip to New York.
- Mount Rushmore has the faces of four American presidents carved into it.
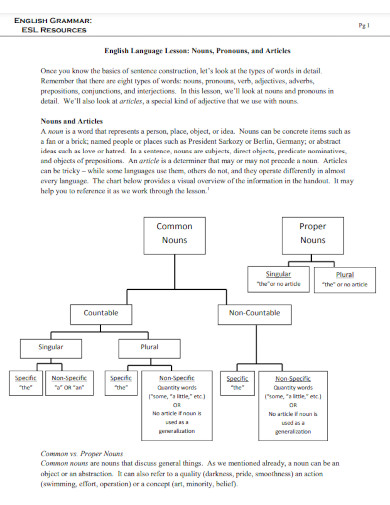
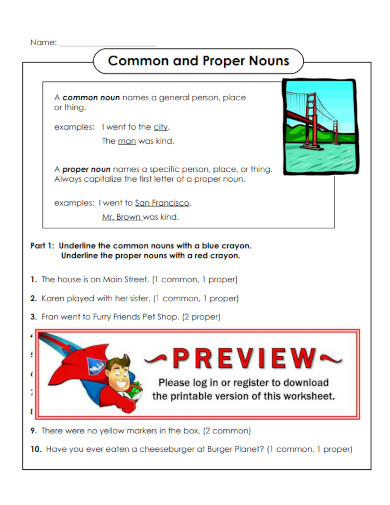
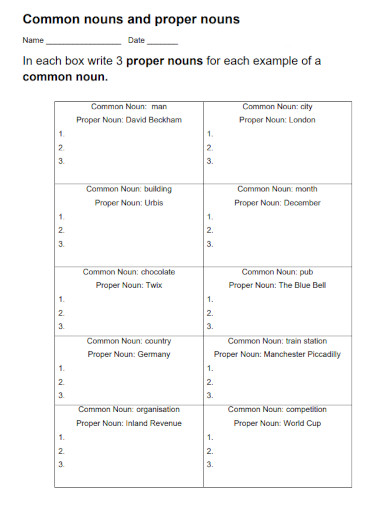
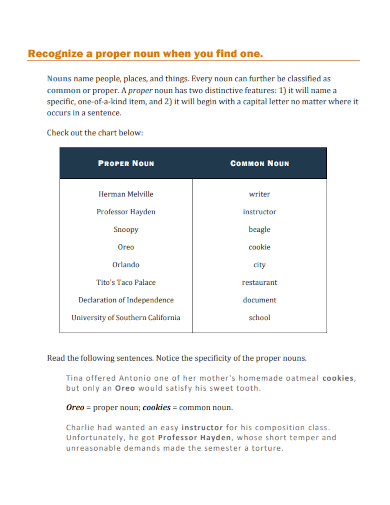
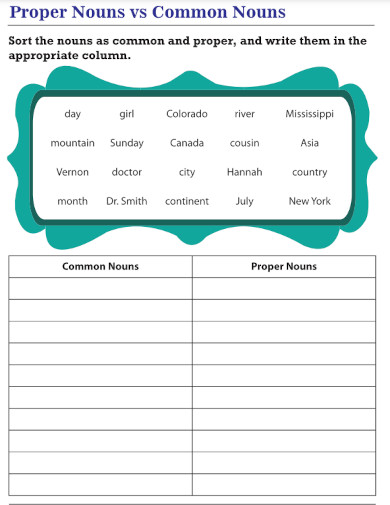
1. Proper Nouns Common Nouns
2. Common and Proper Nouns
3. Proper vs Common Nouns Worksheet
4. Common Proper Collective Abstract Types of Noun
5. E2E3 Common Nouns and Proper Nouns
6. The Proper Noun Template
7. Common and Proper Nouns Definition
8. Proper Nouns and Capitalization
9. Building a Proper Noun Database
10. Common Nouns and Proper Nouns Worksheet
11. Sorting Common and Proper Nouns
12. ELA-Common and Proper Nouns
Examples of Proper Noun for Students
Proper nouns are essential for accurately naming and identifying specific entities in both academic writing and daily communication. Here are examples suitable for students to help them understand and use proper nouns effectively:
- William Shakespeare wrote many plays and poems during the Elizabethan era.
- Harvard University is one of the most prestigious universities in the United States.
- The Great Pyramid of Giza is the oldest of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World.
- Africa is the second largest continent after Asia.
- Amazon started as an online bookstore and has grown into a global e-commerce giant.
- World War II ended in 1945 with significant impacts across Europe and Asia.
- Mount Everest is the highest mountain in the world, located in the Himalayas.
- Taylor Swift released her debut album in 2006 and quickly became a global music icon.
- The Grand Canyon is one of the most visited natural attractions in the United States.
- NASA, the National Aeronautics and Space Administration, is responsible for the civilian space program as well as for aeronautics and aerospace research.
Examples of Proper Noun of Things
Proper nouns aren’t just for people and places; they also name specific things. Here are examples of proper nouns that refer to specific things, which can help illustrate this concept:
- The Mona Lisa is one of the most famous paintings in the world, displayed in the Louvre Museum.
- The Titanic was a British passenger liner that sank in 1912 during its maiden voyage.
- Coca-Cola is one of the most popular soft drinks globally.
- iPhone is a series of smartphones designed and marketed by Apple Inc.
- The Declaration of Independence is an important document in American history.
- Windows 10 is an operating system developed by Microsoft.
- The Great Wall of China is an ancient series of walls and fortifications located in northern China.
- Ferrari is renowned for its luxury sports cars.
- Big Ben refers to the Great Bell of the clock at the north end of the Palace of Westminster in London.
- The Harry Potter Series are books written by J.K. Rowling that have become global bestsellers.
How to Identify a Proper Noun from a Common Noun
Common and proper nouns are widely used in our vocabulary and literature. To prevent miscommunications or misdiagnosis of nouns, it is very important for the person to understand the concept of proper nouns and how to use them. If you want to practice using proper nouns you may use the templates, exercises, and worksheets available on the links above.
Step 1: Check for Capitalization
Not all capitalized nouns are proper nouns, but all proper nouns are capitalized. A common noun can be capitalized if it is at the start or beginning of the sentence or is used in a different context. For example “My Dad likes cooking vegetables, but he doesn’t like eating them.” Dad in the example is both capitalized and is not located at the beginning of the statement, but it is still a common noun. This means that one can discern if the noun is proper by checking the capitalization, but one shouldn’t assume all capitalized nouns are proper.
Step 2: Check If the Noun is Used to Describe a Specific Thing or Group of Things
One of the most important things to remember is that nouns are labels for a specific thing or group of things. A proper noun has the same function but it refers to a specific unique object or entity. Check if the noun refers to something specific, as most of the time it is considered a proper noun.
Step 3: Research if the Proper Noun is Unique to the Object or Person it Refers
In the example above the noun, “Dad” is capitalized and is used as a stand-in for a proper noun. The context will allow this to occur as the person using the sentence uses “Dad” to refer to their father. The reason why we consider the word “Dad” as a common noun is that this word can be used to refer to other fathers that are not included in the discussion. You must research whether or not the proper noun refers to something unique, a single group of objects, or entities.
Step 4: Understand the Context of the Sentence
The context of the sentence can affect the nouns used in a specific sentence. Therefore it is very important for the person to understand and discern the context that is used in the sentence.
FAQs
What is the difference between a proper and a common noun?
There are primarily two ways of categorizing nouns. The first category is based on the amount or number of the object, person, or group the noun specifies while the second category focuses if the noun describing something general or specific. People have categorized proper and common nouns under the second category. A proper noun refers to an object, place, or entity that is very specific and is most of the time unique to the referred object, place, or entity. For example, Golden Gate Bridge is a proper noun that people use to refer to a specific landmark in San Francisco. A common noun refers to the label of a general object, place, or entity. Using a similar example, a bridge is the common form of the Golden Gate Bridge, this common noun is very general and requires a specific context to discern its usage. This highlights the difference between proper and common nouns.
How do you turn proper nouns into proper adjectives?
Some proper nouns can be used as proper adjectives, some of which are subjectively or objectively understood. To transform or convert a proper noun into a proper adjective is to add specific suffixes to the end of the proper noun. For example, if we want to explain or describe something’s appearance that gives or evokes a feeling of Roman architecture and aesthetics, we can transform the proper noun Roman into a proper adjective by attaching -esque or -like at the end of the proper noun. This will produce the proper adjective of Romanesque or Roman-like. Other suffixes one can use to convert proper nouns into proper adjectives include -like, -esque, -ian, -an, -istic, and -ese. The usage of the suffix will depend on the proper noun that the person will convert into a proper adjective.
Can a proper noun be a verb?
Yes, a proper noun can be used as a verb. But the usage of this is very subjective and is highly dependent on the social context and pop culture. For example, Google is now often used to indicate one’s active search for a specific topic or subject on a search engine. Most of the time, the proper noun will replace a specific activity that is somehow associated with the proper noun. Another example of a proper noun used as a verb is the utilization of Instagram as the specific action of taking a photo or video of something and posting it on Instagram. A person can use the proper verb Instagram as this “Alexa likes to Instagram photos of her Gunpla collection.”
A proper noun is a type of noun that refers to a specific person, landmark, place, animal, and object. This type of noun is more specific and refers to the label that is only unique to it. Proper nouns are used a lot in our everyday dialogues and readings. Therefore it is important to know how to distinguish this type of noun from common nouns from proper nouns.