40+ Protagonist Examples
What is a Protagonist?
A protagonist is the main character in a story, typically facing challenges and undergoing personal growth throughout the narrative. This central figure drives the plot forward, engages the audience’s empathy, and often embodies the story’s themes. Protagonists can be heroes or antiheroes, and their experiences are crucial to the story’s development and resolution. Their decisions, actions, and interactions are key to understanding the story’s overall message.
Pronunciation of Protagonist
The pronunciation of “protagonist” is broken down phonetically as:
pro·tag·o·nist
This can be heard as:
- pro as in “pro” (rhymes with “no”)
- tag as in “tag”
- o as in “go”
- nist as in “list”
In terms of stress, the emphasis is placed on the first syllable: PRO-ta-go-nist.
Types of Protagonist
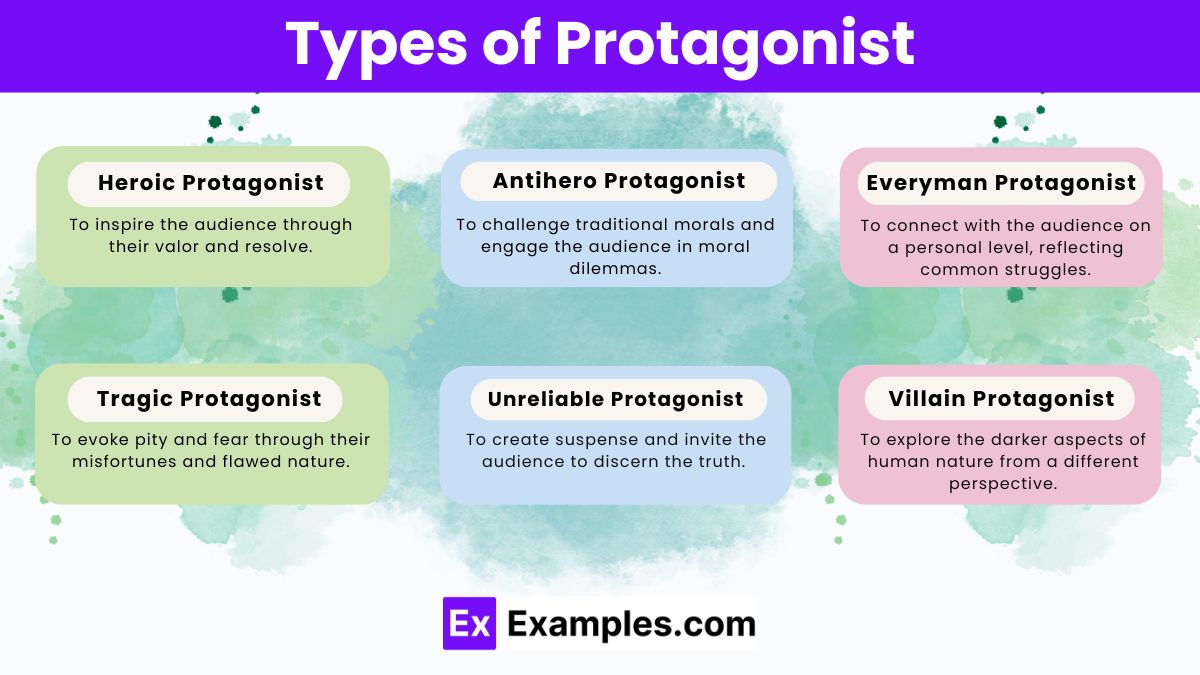
Protagonists are essential figures in literature and media, serving as the central characters around whom stories revolve. Their different types reflect various narrative needs and audience connections. Here are several common types of protagonists:
- Heroic Protagonist
- Traits: Noble, courageous, morally upright.
- Purpose: To inspire the audience through their valor and resolve.
- Example: King Arthur.
- Antihero Protagonist
- Traits: Flawed, complex, often morally ambiguous.
- Purpose: To challenge traditional morals and engage the audience in moral dilemmas.
- Example: Severus Snape from “Harry Potter”.
- Everyman Protagonist
- Traits: Ordinary, relatable, often dealing with everyday challenges.
- Purpose: To connect with the audience on a personal level, reflecting common struggles.
- Example: Arthur Dent from “The Hitchhiker’s Guide to the Galaxy”.
- Tragic Protagonist
- Traits: Characterized by a fatal flaw that leads to their downfall.
- Purpose: To evoke pity and fear through their misfortunes and flawed nature.
- Example: Jay Gatsby from “The Great Gatsby”.
- Unreliable Protagonist
- Traits: Provides a biased or distorted view of the story, which may mislead the audience.
- Purpose: To create suspense and invite the audience to discern the truth.
- Example: Patrick Bateman from “American Psycho”.
- Villain Protagonist
- Traits: Exhibits qualities typical of a villain but plays the central role.
- Purpose: To explore the darker aspects of human nature from a different perspective.
- Example: Alex from “A Clockwork Orange”.
Synonyms & Antonyms of Protagonist
| Synonyms | Antonyms |
|---|---|
| Hero | Antagonist |
| Main character | Adversary |
| Lead | Opponent |
| Central figure | Foe |
| Champion | Enemy |
| Advocate | Rival |
| Proponent | Villain |
Synonyms
- Hero: Often the main character in a story, admired for their bravery, great deeds, or noble qualities.
- Main Character: The central person in a story, around whom the main events occur.
- Lead: Similar to the main character, this is the person who is the focus of the story’s narrative.
- Central Figure: The key person in any event or period, holding significant importance or influence in the story.
- Champion: Someone who fights or argues for a cause or on behalf of someone else.
- Advocate: A person who publicly supports or recommends a particular cause or policy.
- Proponent: Someone who advocates a theory, proposal, or project passionately.
Antonyms
- Antagonist: A character who opposes the protagonist, often presenting conflict in the story.
- Adversary: A person, group, or force that opposes or attacks; an enemy or opponent.
- Opponent: Someone who competes against or fights another in a contest, game, or argument.
- Foe: An enemy or opponent, often used in contexts of dramatic or intense conflict.
- Enemy: A person who is actively opposed or hostile to someone or something.
- Rival: A person or thing competing with another for the same objective or for superiority in the same field.
- Villain: A character whose evil actions or motives are important to the plot, typically opposing the hero or protagonist.
Protagonist vs. Antagonist
| Aspect | Protagonist | Antagonist |
|---|---|---|
| Role in Story | The main character around whom the story revolves. | Often opposes the protagonist, creating conflict. |
| Purpose | Drives the plot forward, often faces challenges and undergoes personal growth. | Challenges the protagonist, helping to reveal key qualities and decisions. |
| Character Traits | Usually portrayed with positive qualities, aiming for the audience’s sympathy. | Typically depicted with traits that oppose the protagonist’s, evoking a range of emotions from the audience. |
| Impact on Plot | Central to the story’s development and resolution. | Essential for introducing and escalating conflict in the narrative. |
| Audience Relation | Designed to earn the audience’s empathy and support. | Often meant to evoke opposition, dislike, or complexity in feelings from the audience. |
Protagonist Personality
A protagonist’s personality is often crafted to be multi-dimensional and relatable, serving as the emotional and moral center of a story. Here are some common traits you might find in a protagonist’s personality:
- Resilience: Protagonists often face significant challenges, and their resilience helps them to overcome adversity and bounce back from setbacks.
- Courage: Many protagonists exhibit courage, whether that means taking on physical dangers, making tough decisions, or standing up for what they believe in.
- Empathy: A key trait that makes protagonists relatable is their ability to understand and share the feelings of others, which drives their actions and decisions.
- Growth: One of the most important aspects of a protagonist’s personality is their capacity for growth. Over the course of the story, they learn, evolve, and change, reflecting the story’s themes and lessons.
- Flawed: Protagonists are rarely perfect; their flaws make them human and relatable. These imperfections contribute to their character development and make their journey more compelling.
- Determination: They are typically very determined, often driven by a goal or a need to change their circumstances, which keeps the story moving forward.
- Leadership: In many stories, the protagonist takes on a leadership role, either by circumstance or by choice, influencing those around them and driving group actions.
Examples of Protagonist in literature
Protagonists are the heart of many literary works, driving the narrative and engaging the reader with their personal journeys. Here are ten examples of famous protagonists in literature:
- Elizabeth Bennet from Pride and Prejudice by Jane Austen – Known for her wit, intelligence, and strong opinions on personal independence and manners.
- Harry Potter from the Harry Potter series by J.K. Rowling – A young wizard who grows from a naive and lonely boy into a courageous and loyal friend, fighting against the dark wizard Voldemort.
- Jane Eyre from Jane Eyre by Charlotte Brontë – An orphaned girl who, despite a difficult upbringing, grows into a strong, independent woman who values morality and equality.
- Holden Caulfield from The Catcher in the Rye by J.D. Salinger – A teenager struggling with the phoniness of the adult world, searching for truth and innocence.
- Frodo Baggins from The Lord of the Rings by J.R.R. Tolkien – A humble hobbit tasked with destroying a powerful ring, his journey is one of immense personal and physical challenge.
- Atticus Finch from To Kill a Mockingbird by Harper Lee – A lawyer in the racially charged American South who stands as a moral hero for his defense of a black man wrongly accused of raping a white woman.
- Sherlock Holmes from the Sherlock Holmes series by Sir Arthur Conan Doyle – A brilliant detective known for his deductive reasoning, keen observation, and intellectual prowess.
- Santiago from The Old Man and the Sea by Ernest Hemingway – An old, seasoned fisherman who battles a giant marlin in the Gulf Stream as a testament to human endurance and spirit.
- Scout Finch from To Kill a Mockingbird by Harper Lee – Known for her curiosity and precociousness, she navigates her childhood in a world filled with prejudice and moral questions.
- Jay Gatsby from The Great Gatsby by F. Scott Fitzgerald – A mysterious millionaire who epitomizes the American dream’s corruption, driven by his love for Daisy Buchanan.
Examples of Protagonist in Sentences
- In the novel, the protagonist faces numerous challenges that test her resilience and ultimately lead to profound personal growth.
- The film’s protagonist, a daring young pilot, embarks on a perilous mission to save his planet from an impending alien invasion.
- Throughout the play, the protagonist’s inner conflicts mirror the tumultuous political landscape of the era.
- As the protagonist navigates the complexities of high school life, she learns valuable lessons about friendship and loyalty.
- The story’s protagonist, an ambitious chef, dreams of opening his own restaurant, despite the skepticism he faces from his family.
- In her journey, the protagonist encounters a wise mentor who helps her unlock her true potential and face her fears.
- The protagonist’s determination to clear his name drives the suspenseful narrative of this crime thriller.
- The novel revolves around the protagonist’s struggle to reconcile her personal ambitions with her responsibilities to her family.
- Desperate to escape his mundane life, the protagonist stumbles upon a mysterious map that leads him on an unexpected adventure.
- The protagonist’s humorous outlook on life adds a light-hearted tone to the otherwise serious storyline.
Examples of Protagonist in Movies
Protagonists in movies often define the narrative and capture the audience’s empathy through their journeys and struggles. Here are examples of well-known protagonists from various films:
- Luke Skywalker in Star Wars – A farm boy who rises to become a key figure in the battle against the oppressive Galactic Empire.
- Ellen Ripley in Alien series – A warrant officer who becomes the central figure in humanity’s battle against a deadly extraterrestrial threat.
- Forrest Gump in Forrest Gump – A man with a low IQ recounts the early years of his life when he finds himself in the middle of key historical events with an extraordinary influence on them.
- Simba in The Lion King – A young lion prince flees his kingdom only to learn the true meaning of responsibility and bravery.
- Andy Dufresne in The Shawshank Redemption – A banker sentenced to life in Shawshank State Penitentiary for the murder of his wife and her lover, despite his claims of innocence.
- Katniss Everdeen in The Hunger Games series – A teenager who volunteers to replace her sister in a brutal televised fight to the death, becoming the symbol of a mass rebellion.
- Tony Stark (Iron Man) in Iron Man series – A wealthy industrialist and genius inventor who creates a powered suit of armor to save his life and fight evil.
- Clarice Starling in The Silence of the Lambs – A young FBI trainee who seeks the advice of the imprisoned Dr. Hannibal Lecter to catch another serial killer.
- Rocky Balboa in Rocky series – An underdog boxer who gets a shot at the world heavyweight championship, depicting his personal and athletic struggles and triumphs.
- Mia Dolan in La La Land – An aspiring actress trying to make her way in Los Angeles, exploring the joys and pains of pursuing dreams in a challenging industry.
Examples of Protagonis for Kids
Protagonists in children’s stories are often designed to inspire, teach, and entertain young readers and viewers. Here are several examples of protagonists from popular children’s media:
- Harry Potter from Harry Potter series by J.K. Rowling – A young wizard who discovers his magical heritage and battles against the dark wizard Voldemort.
- Matilda Wormwood from Matilda by Roald Dahl – A brilliant and kind-hearted girl who uses her intelligence and telekinetic powers to overcome her unkind parents and a cruel headmistress.
- Simba from The Lion King – A lion cub who grows up to reclaim his throne from his usurping uncle, learning valuable life lessons along the way.
- Anne Shirley from Anne of Green Gables by L.M. Montgomery – An imaginative and talkative orphan girl who wins the hearts of everyone in her new home of Avonlea.
- Elsa from Frozen – A queen with the magical ability to create ice and snow, who struggles to control her powers while finding her place as a leader.
- Charlie Bucket from Charlie and the Chocolate Factory by Roald Dahl – A poor boy who wins a tour through the most magnificent chocolate factory in the world, run by Willy Wonka.
- Moana from Moana – A spirited and adventurous girl who sets sail on a daring mission to save her people, discovering her own identity along the way.
- Dora from Dora the Explorer – A young explorer who goes on adventures with her backpack and map, solving puzzles and helping friends with the assistance of the viewers at home.
- George from Curious George – A curious little monkey whose inquisitive nature gets him into trouble, but also leads to important learning experiences.
- Frodo Baggins from The Lord of the Rings – Although originally written for a more general audience, the story of Frodo, a young hobbit tasked with destroying a powerful ring, has been adapted into various formats that appeal to children.
Examples of Protagonist in Psychology
In psychology, the term “protagonist” isn’t used in the same way as in literature or film. Instead, it refers to the central figure in a person’s life narrative or therapeutic contexts. Here are several ways the concept of a protagonist might be applied within the field of psychology:
- Self-Actualization: An individual striving for self-actualization in Maslow’s hierarchy of needs plays the protagonist in their own journey towards achieving personal potential and self-fulfillment.
- Resilience Building: In resilience psychology, the person develops coping mechanisms to bounce back from setbacks, effectively starring as the protagonist overcoming personal adversities.
- Recovery Narrative in Mental Health: Individuals with mental health issues often craft recovery narratives where they are the protagonists actively working towards improving their mental health and well-being.
- Cognitive Restructuring: In cognitive-behavioral therapy, a person actively challenges and changes their own negative thought patterns, positioning themselves as the protagonist who reshapes their mental landscape.
- Identity Formation: Adolescents in developmental psychology are protagonists in their own stories as they navigate through identity crises and the process of establishing a sense of self.
- Life Review Therapy: Older adults often engage in life review therapy, where they recount and reevaluate their life stories, placing themselves as protagonists reflecting on past experiences to enhance their present meaning.
- Assertiveness Training: Individuals learning to become more assertive in therapy sessions take the protagonist role in scenarios designed to practice and reinforce assertive behavior.
- Exposure Therapy: Clients confronting phobias or anxiety disorders through exposure therapy are protagonists who face their fears directly, aiming to reduce their psychological distress.
- Motivational Interviewing: In this therapeutic approach, individuals are motivated to become the protagonist in changing their own behaviors through guided but client-centered counseling.
- Psychological Empowerment: This process involves individuals gaining control over their lives and achieving goals, positioning themselves as protagonists in their journey towards empowerment and personal efficacy.
What Person is Protagonist and Antagonist?
The protagonist is typically the main character in a story, around whom the narrative is primarily centered. This character usually faces challenges and undergoes personal growth throughout the story. The protagonist is often the hero or the central figure the audience is meant to root for, but they can also be more morally complex or even an antihero.
The antagonist, on the other hand, is the character or force that opposes the protagonist. This opposition creates the central conflict for the story. Antagonists are often, but not always, the villain of the story. They can also be a rival, a societal expectation, or an internal struggle within the protagonist, depending on the nature of the story.
Is a Protagonist a Hero or Villain?
A protagonist can be either a hero or a villain. They are the main character, whether they embody heroic qualities or display morally ambiguous or villainous traits
What is a female Protagonist?
A female protagonist is the main character in a story who is female. She is central to the narrative’s development, facing challenges and undergoing personal growth or change throughout the story.


