Types of Mass Communication – Examples
Mass communication is a dynamic and expansive field, encompassing various types that cater to diverse audiences and purposes. This comprehensive guide explores the key types of mass communication, each illustrated with practical examples. From traditional forms like newspapers and television to digital platforms such as social media and blogs, the guide offers insights into how each type functions and its impact on the audience. Including communication examples, this guide is an essential resource for anyone interested in media studies, marketing, or understanding the landscape of modern communication.
What are Types of Mass Communication?
Mass communication refers to the process of conveying information and messages to a large group of people, typically through various media channels. It plays a crucial role in disseminating news, entertainment, education, and advertisements to the public.
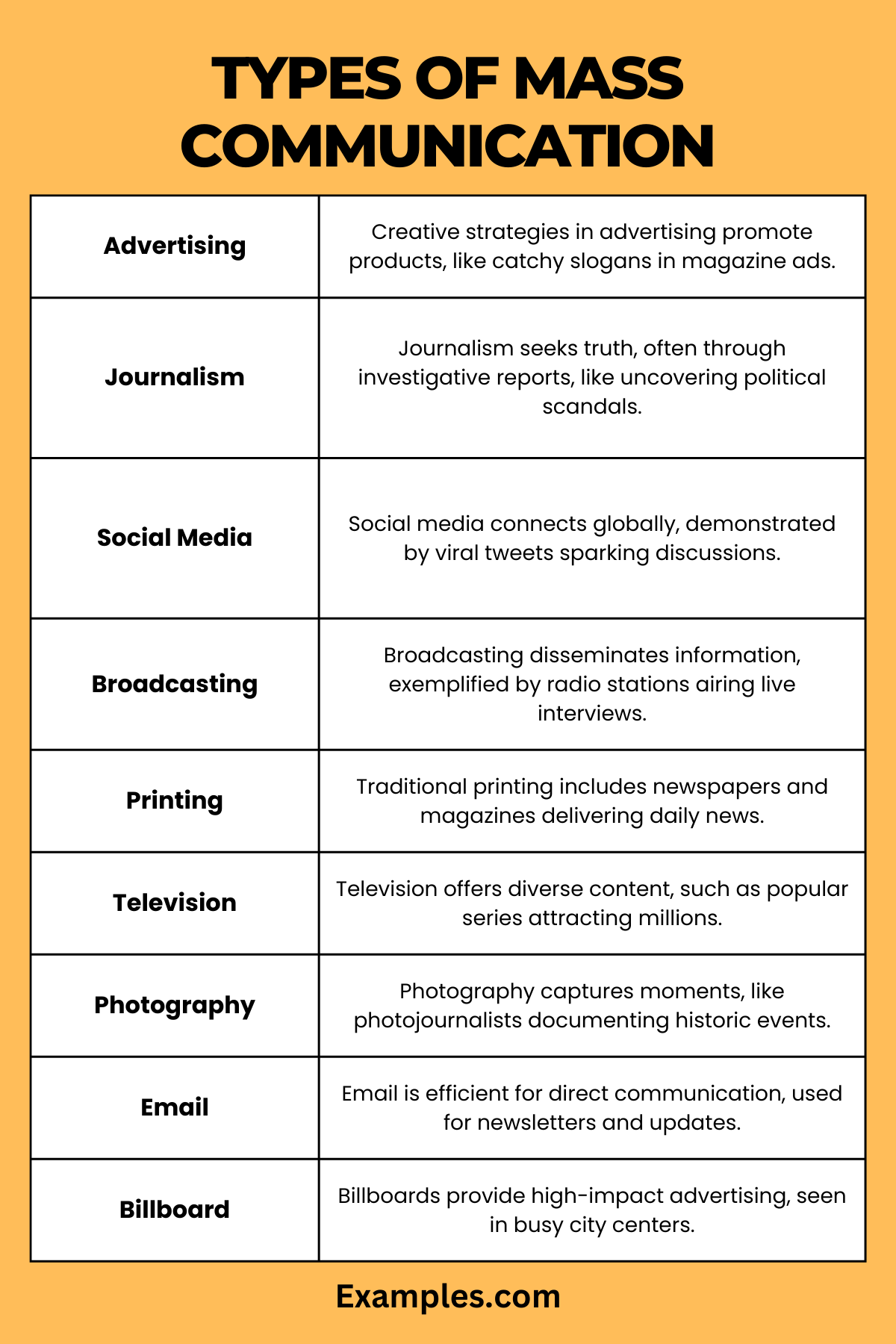
Here are the primary types of mass communication:
Advertising
Advertising is a strategic communication process designed to persuade an audience to take action, typically in the context of buying products or services. It blends creative visuals and compelling narratives to capture attention and drive consumer engagement.
Examples: A captivating online ad campaign for a smartphone, a memorable TV commercial for a fast-food chain, or an eye-catching print ad in a fashion magazine.
Journalism
Journalism is the practice of collecting, analyzing, and presenting news and information. It serves as a cornerstone of informed society, providing unbiased reporting on current events and issues.
Examples: Investigative reporting on political corruption, a daily news podcast covering global events, or a local newspaper article about community developments.

Social Media
Social Media platforms are digital spaces for sharing, networking, and content creation, revolutionizing how individuals and businesses communicate. They facilitate real-time interaction and wide content dissemination.
Examples: A brand’s promotional campaign on Facebook, an influencer’s lifestyle posts on Instagram, or a viral Twitter hashtag movement.
Broadcasting
Broadcasting disseminates audio or visual content to a wide audience via electronic mass communication media, notably radio and television. It’s integral for news, entertainment, and education.
Examples: A national radio program discussing societal issues, a live broadcast of a major sports event, or an educational TV series for children.

Printing
Printing encompasses the production of text and images on paper, playing a significant role in distributing written material. It remains a vital medium for literature, news, and advertising.
Examples: Monthly lifestyle magazines, daily printed newspapers, or promotional flyers for a local event.
Television
Television is a powerful medium for delivering diverse content, including news, drama, documentaries, and more. It combines visual and auditory elements to inform, educate, and entertain.
Examples: A popular reality TV show, an international news channel’s coverage, or an educational children’s cartoon series.
Photography
Photography captures moments and stories through still images. It’s a versatile medium used in art, journalism, advertising, and personal expression.
Examples: A photojournalist’s visual coverage of a protest, a fashion brand’s photoshoot for a new collection, or a nature photographer’s gallery exhibition.
Film
Film is an influential artistic medium known for its storytelling prowess, combining elements like script, acting, sound, and cinematography. Films range from blockbuster hits to independent documentaries.
Examples: An award-winning Hollywood drama, an independent documentary about climate change, or an international film festival’s short film selection.
Email is a widely-used digital communication tool for personal, professional, and marketing purposes. It allows for direct, efficient, and versatile exchanges of information.
Examples: A company’s weekly newsletter to its customers, a professional’s email correspondence with clients, or a marketing email announcing a new product launch.

Billboard
Billboards are large outdoor advertising structures, offering high visibility for promotional messages in public spaces. They are effective for brand exposure and marketing campaigns.
Examples: A highway billboard advertising a new car model, a digital billboard in a city center promoting a concert, or a public service billboard about health awareness.
Public Relations
Public Relations (PR) involves managing the spread of information between an organization and the public. It’s crucial for maintaining a positive image and effective communication.
Examples: A PR campaign for a product launch, crisis management PR for a company in turmoil, or a charity’s PR efforts to raise awareness for a cause.
Each type of mass communication serves distinct purposes and reaches audiences in unique ways, making them integral to the fabric of contemporary society.
What are Types of Research Methods in Mass Communication?
Mass communication research is pivotal in understanding the effects, reach, and dynamics of various media forms on the audience. Different research methods provide insights into how media influences public opinion, behaviors, and societal trends. Below, we delve into these methods, offering a comprehensive guide on each type’s purpose and application.
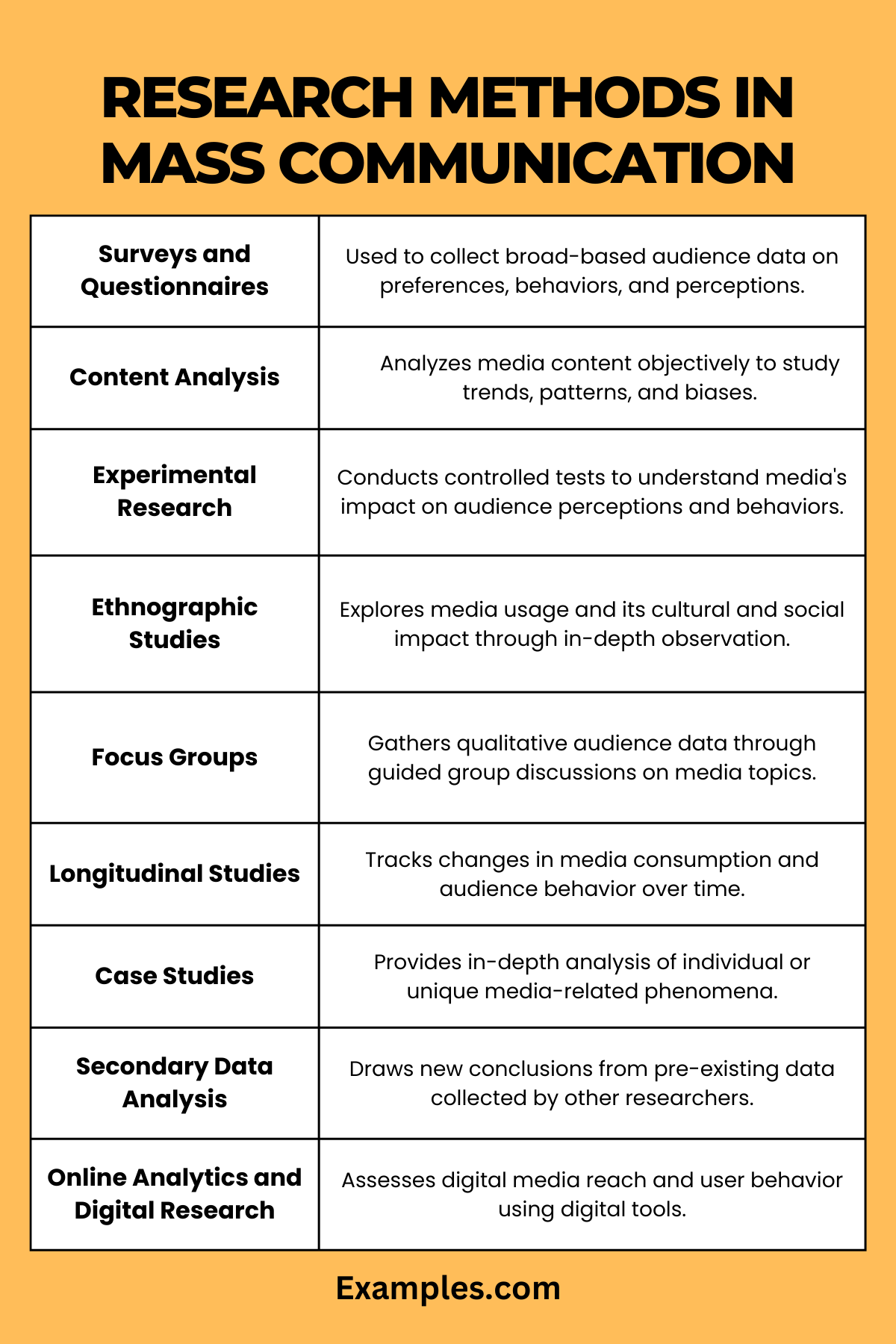
Surveys and Questionnaires
Surveys and questionnaires are fundamental tools in mass communication research, used for collecting quantitative data from a large audience.
- Purpose: To gather broad-based information on audience preferences, behaviors, and perceptions.
- Application: Typically used in audience analysis, measuring media effects, and evaluating viewer or reader demographics.
Content Analysis
Content analysis is a systematic approach to analyzing the content of media messages.
- Purpose: To objectively and quantitatively analyze the content of communication.
- Application: Commonly used to study trends, patterns, biases in news media, advertising, TV shows, and social media content.
Experimental Research
Experimental research in mass communication involves controlled testing to understand the cause-and-effect relationships.
- Purpose: To determine the impact of specific media content or formats on audience perceptions and behaviors.
- Application: Ideal for testing new media products, advertising techniques, or understanding viewer response.
Ethnographic Studies
Ethnographic studies offer an in-depth look at the audience’s media consumption in their natural environment.
- Purpose: To explore media usage and its impact on culture and social behavior.
- Application: Used in studying subcultures, media usage in different demographic groups, and user experience.
Focus Groups
Focus groups involve guided discussions on a media topic with a selected group of individuals.
- Purpose: To collect qualitative data on audience attitudes, feelings, and responses to media content.
- Application: Useful in pre-testing media content, advertising messages, or gathering detailed viewer feedback.
Longitudinal Studies
Longitudinal studies track changes in media patterns or audience behavior over time.
- Purpose: To observe and record long-term effects and shifts in media consumption.
- Application: Suitable for studies on the lifelong impact of media or changing audience habits.
Case Studies
Case studies offer a detailed examination of individual or group experiences with media.
- Purpose: To provide an in-depth analysis of specific media-related phenomena.
- Application: Used in exploring unique instances, such as a groundbreaking advertising campaign or a significant media event.
Secondary Data Analysis
Secondary data analysis involves analyzing existing data collected by others.
- Purpose: To draw new conclusions from previously gathered data.
- Application: Useful when primary data collection is not feasible, like analyzing historical media trends.
Online Analytics and Digital Research
This method utilizes digital tools to analyze user behavior and interactions in digital environments.
- Purpose: To assess digital media reach, engagement, and user behavior.
- Application: Ideal for studying website traffic, social media engagement, and online content consumption patterns.
Audience Measurement Systems
Audience measurement systems quantify the size and composition of a media audience.
- Purpose: To provide data on how many people are consuming different media forms.
- Application: Essential in television ratings, radio listenership metrics, and online viewership statistics.
Each research method offers unique insights and has its place in the broad spectrum of mass communication research. By understanding and applying these methods appropriately, researchers can obtain a comprehensive view of the media’s role in society and its effects on audiences.
In conclusion, understanding the types of mass communication is crucial in today’s media-centric world. From traditional mediums like newspapers and television to modern digital platforms such as social media and podcasts, each type serves a unique purpose in disseminating information and shaping public opinion. Grasping these varied forms empowers individuals and organizations to communicate effectively and adapt to the evolving landscape of mass communication.



