100+ Domestic Animal Names: Meaning, Types, Importance, PDF
Embark on a delightful exploration of domestic animal names, where each name holds a tale of companionship, utility, and love. From the soft purrs of a cat to the loyal gaze of a dog, the bustling barnyards with cows and chickens, to the serene presence of aquarium fish, this guide illuminates the diverse array of animals that have been domesticated to share our lives. Uncover the familiar and the unexpected, deepening your bond with these integral members of our daily existence.
Download List of Domestic Animal Names - PDF
List of Domestic Animal Names
Domestic animals are integral to human societies around the globe, offering companionship, labor, and resources such as food and clothing. These animals have been selectively bred and adapted over generations to live alongside humans, each serving a unique role within agricultural, therapeutic, or household settings. From the loyal dog, often referred to as ‘man’s best friend’, to the industrious farm animals like cows and chickens that are pivotal in providing sustenance, domestic animals are diverse and multifaceted. They not only fulfill practical needs but also enrich our lives, contributing to emotional and psychological well-being. The bond between humans and domestic animals is a testament to the interdependent relationship that has evolved over millennia, highlighting the complexity and depth of our connection to the natural world
| Dog | Cat | Chicken | Cow |
| Sheep | Goat | Horse | Pig |
| Duck | Rabbit | Turkey | Goldfish |
| Parrot | Hamster | Bee | Donkey |
| Guinea Pig | Llama | Alpaca | Canary |
| Finch | Pigeon | Quail | Goose |
| Koi | Betta | Guppy | Molly |
| Platy | Shrimp | Snail | Crab |
| Lobster | Octopus | Clownfish | Seahorse |
| Jellyfish | Starfish | Sea Urchin | Sea Cucumber |
| Silkworm | Butterfly | Ladybug | Ant |
| Fruit Fly | Beetle | Moth | Dragonfly |
| Grasshopper | Firefly | Bee | Wasp |
| Hornet | Caterpillar | Cockroach | Mosquito |
| Fly | Bumblebee | Cicada | Ferret |
| Gerbil | Chinchilla | Mink | Rat |
| Squirrel | Buffalo | Yak | Camel |
| Oyster | Mussel | Barnacle | Scallop |
| Peafowl | Emu | Ostrich | Sparrow |
| Dove | Hawk | Eagle | Owl |
| Parakeet | Finch | Canary | Pigeon |
| Quail | Goose | Swan | Turkey |
| Duck | Chicken | Hen | Rooster |
| Bull | Heifer | Calf | Steer |
| Ewe | Ram | Lamb | Mare |
| Stallion | Colt | Foal | Gelding |
| Sow | Boar | Piglet | Hog |
| Budgerigar | Billy Goat | Nanny Goat | Filly |
| Cockatiel | Lovebird | Budgerigar | Macaw |
| Angelfish | Tetra | Discus | Siamese Fighting Fish |
| Zebrafish | Gourami | Swordtail | Pleco |
| Corydoras | Goldfish | Koi Carp | Neon Tetra |
| Oscar | Molly | Guppy | Betta |
| Shrimp | Snail | Lobster | Crab |
| Octopus | Squid | Cuttlefish | Jellyfish |
| Starfish | Sea Urchin | Sea Cucumber | Sea Anemone |
| Clam | Scallop | Mussel | Oyster |
| Barnacle | Krill | Plankton | Algae |
Types of Domestic Animals
Domestic animals, integral to human societies, can be broadly categorized based on their roles and relationships with humans. Here’s an overview:
1. Pets/Companion Animals
Pets, often known as companion animals, enrich our lives with joy and companionship. These loyal and affectionate beings provide emotional support, reduce stress, and enhance our daily routines. Ideal for teaching empathy and responsibility, pets make excellent educational tools in classroom settings.
- Dog: A loyal and protective companion known for its ability to bond with humans.
- Cat: An independent and often affectionate pet with a playful side.
- Parrot: A colorful bird known for its ability to mimic human speech.
- Goldfish: A low-maintenance aquatic pet, popular for its peaceful nature.
- Hamster: A small, nocturnal rodent, ideal as a child’s first pet due to its size and care requirements.
- Rabbit: Known for their gentle and quiet nature, rabbits are sociable pets that require space to roam.
- Guinea Pig: A friendly and vocal rodent, guinea pigs are known for their social nature.
- Turtle: Long-lived reptiles that require specific habitats; known for their calm demeanor.
- Ferret: Playful and curious, ferrets are small carnivorous mammals that enjoy human interaction.
- Budgerigar: A small, brightly colored bird, valued for its singing and ability to learn words.
2. Livestock
Livestock animals are pivotal in agriculture, providing a range of products from food to clothing materials. These animals are integral to sustainable farming practices, aiding in land management and contributing to a balanced ecosystem.
- Cow: A key source of milk, meat, and leather; essential in dairy and beef industries.
- Sheep: Valued for wool, meat, and milk; plays a crucial role in textile and food sectors.
- Pig: Provides a significant source of protein through pork; known for their intelligence.
- Goat: Offers milk, meat, and sometimes fiber; adaptable to various climates.
- Hen: A primary source of eggs and poultry meat; integral to food security.
- Turkey: Raised for its meat, especially in festive seasons; known for its distinctive gobble.
- Duck: Produces eggs and meat; valued for their down feathers as well.
- Horse: Beyond working roles, horses are raised for meat in some cultures.
- Bee: Essential for pollination and honey production; critical to agriculture.
- Rabbit: Raised for meat and fur; known for their rapid reproduction rate.
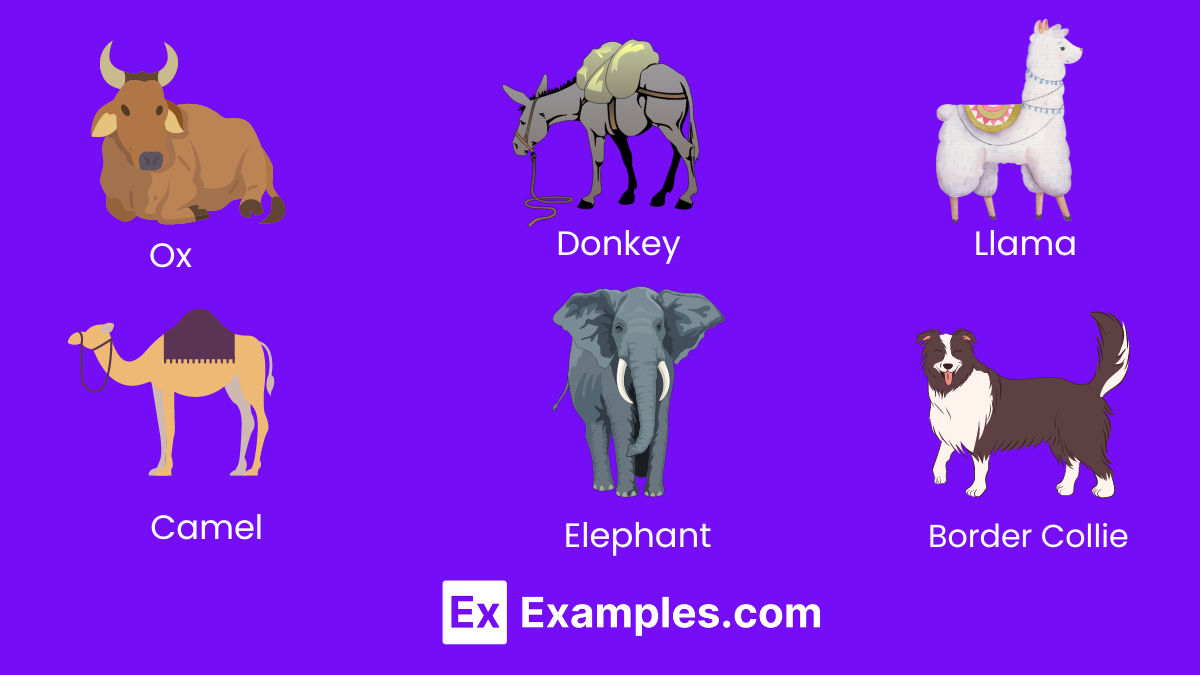
3. Working Animals
Working animals play critical roles in various industries, from agriculture to law enforcement. These animals are trained to perform specific duties, showcasing remarkable intelligence and adaptability.
- Ox: Traditional beasts of burden, oxen are used for plowing fields and transporting goods.
- Donkey: Known for their endurance and ability to carry heavy loads in difficult terrains.
- Mule: A hybrid of a horse and a donkey, mules are valued for their strength and resilience.
- Camel: Adapted to desert climates, camels are used for transport and as pack animals.
- Elephant: Employed in forestry for their ability to move large objects; also used in ceremonial roles in some cultures.
- K-9 Police Dog: Trained for law enforcement duties, including search and rescue, and detecting substances.
- Border Collie: Renowned for their intelligence, used primarily for herding livestock.
- Falcon: Used in the sport of falconry and for controlling pest populations in certain areas.
- Horse: Employed in a variety of tasks from transportation to ceremonial duties.
- Llama: Used as pack animals in rugged terrains and also for their wool
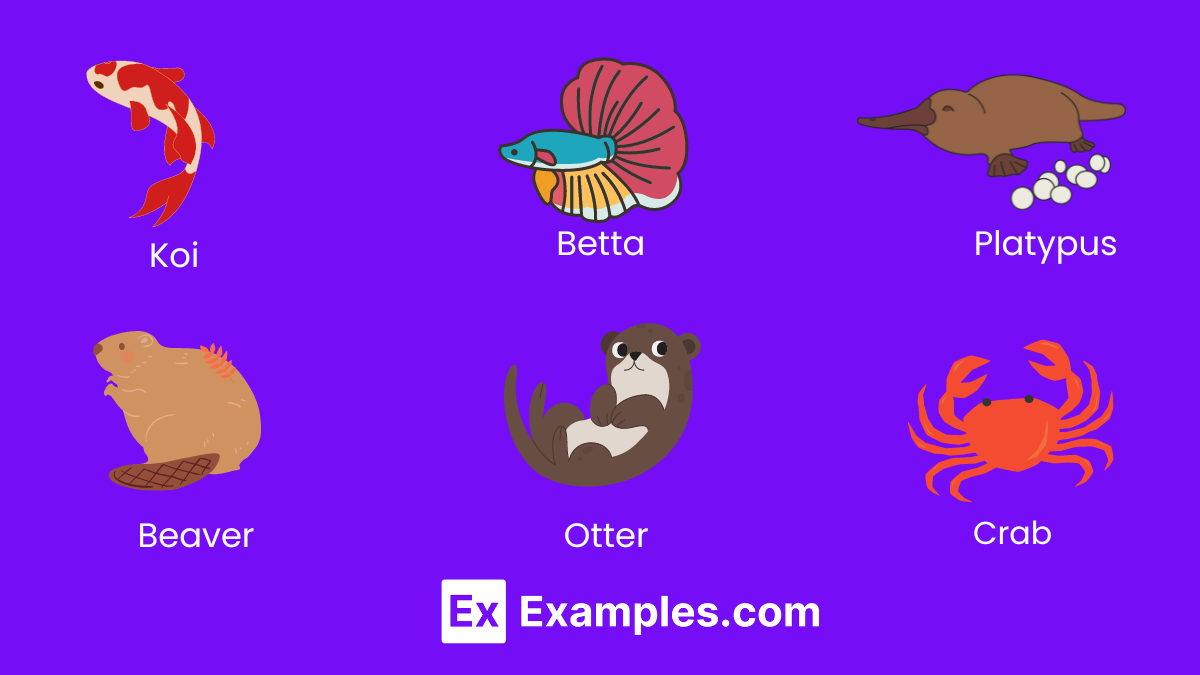
4. Aquatic and Semi-Aquatic Animals
Aquatic and semi-aquatic animals thrive in water environments, ranging from freshwater lakes to the vast ocean. These creatures, adapted to life in or near water, play vital roles in aquatic ecosystems, contributing to the biodiversity and health of their habitats. Ideal for teaching about aquatic life and ecosystems, they offer a glimpse into the diverse life forms our planet hosts.
- Goldfish: A popular pet fish known for its vibrant colors and ease of care.
- Koi: Ornamental fish celebrated for their beauty in outdoor ponds and water gardens.
- Betta: Known for their vivid colors and elaborate fins; thrive in small tanks.
- Turtle: Reptiles that live in or around water, known for their hard protective shells.
- Frog: Amphibians that live part of their lives in water and part on land.
- Duck: Waterfowl known for their ability to live in both aquatic and terrestrial environments.
- Platypus: A unique mammal native to Australia, known for its duck-bill and webbed feet.
- Beaver: Known for building dams, lodges, and canals in freshwater habitats.
- Otter: Playful mammals adapted for swimming, known for their sleek, streamlined bodies.
- Crab: Aquatic and semi-aquatic creatures known for their sideways walk and strong pincers.
5. Insects
Insects, the most diverse group of organisms on Earth, play crucial roles in our ecosystems, including pollination, decomposition, and as a food source for other animals. Studying insects offers insights into biodiversity, adaptation, and the ecological balance, making them fascinating subjects for educational exploration.
- Butterfly: Known for their colorful wings and metamorphosis from caterpillars.
- Bee: Crucial for pollination, bees are known for producing honey and beeswax.
- Ant: Social insects known for their complex colonies and ability to work together.
- Ladybug: Recognized by their red and black spotted appearance; beneficial for controlling pests.
- Dragonfly: Known for their long bodies and agile flying; predators of mosquitoes.
- Grasshopper: Recognizable by their powerful hind legs used for jumping.
- Firefly: Known for their bioluminescent ability to produce light in the dark.
- Moth: Close relatives of butterflies, known for their nocturnal activity and diverse species.
- Cicada: Known for their loud calls and emerging in large numbers every few years.
- Cockroach: Notorious for their resilience and adaptability to various environments.
Importance of Domestic Animals
Domestic animals hold a crucial place in human societies, extending far beyond their initial roles in agricultural and domestic settings. Their significance spans cultural, emotional, economic, and environmental realms, making them indispensable to human life.
1. Agricultural and Economic Contributions: Domestic animals like cows, goats, and chickens are pivotal in agriculture, providing meat, milk, eggs, and wool, which are essential for human nutrition and clothing. The economic impact of livestock farming is substantial, supporting the livelihoods of millions of people worldwide, particularly in rural areas.
2. Environmental Stewardship: Certain domestic animals play significant roles in maintaining ecological balance. For example, bees are critical for pollination, contributing to the health of ecosystems and aiding in the production of a large portion of the food crops consumed by humans.
3. Companion and Service Roles: Pets such as dogs and cats offer companionship, reducing loneliness and promoting mental well-being. Service animals, including guide dogs, provide invaluable assistance to individuals with disabilities, enhancing their independence and quality of life.
4. Educational and Therapeutic Uses: Domestic animals are also utilized in educational settings to teach responsibility and empathy. Animal-assisted therapy has been recognized for its therapeutic benefits, aiding in the treatment of psychological and emotional disorders.
5. Cultural Significance: Many domestic animals hold cultural and religious significance in various societies, symbolizing traits such as strength, fertility, and prosperity. They are often integral to rituals, traditions, and celebrations.
6. Biodiversity and Genetic Resources: Through the domestication process, a diverse array of breeds has been developed, contributing to genetic diversity. This genetic reservoir is vital for breeding programs aimed at improving resistance to diseases and adapting to changing environmental conditions.
Which animals are commonly considered as domestic pets?
Commonly considered domestic pets include a variety of animals that people keep for companionship, enjoyment, and sometimes for their ability to perform tasks around the home. These pets typically have traits such as a pleasant demeanor, loyalty, and the ability to interact with humans. Here are some of the most popular ones:
- Dogs: Often referred to as “man’s best friend,” dogs are valued for their loyalty, companionship, and ability to be trained for various tasks.
- Cats: Known for their independent nature and affectionate behavior towards their owners, cats are one of the most common household pets.
- Fish: Aquarium fish, such as goldfish, bettas, and guppies, are popular for their diverse colors and the tranquil environment they create.
- Birds: Parrots, canaries, and budgerigars are favored for their beauty, song, and in some cases, the ability to mimic human speech.
- Rabbits: Appreciated for their gentle nature, rabbits can be affectionate and interactive pets.
- Hamsters: Small and low-maintenance, hamsters are often chosen as pets for children, teaching them responsibility.
- Guinea Pigs: Known for their docile nature and the tendency to vocalize, making them interactive pets.
- Turtles: Some species of turtles are kept as pets for their interesting behaviors and longevity.
- Ferrets: Playful and curious, ferrets are popular for their entertaining antics.
- Reptiles: Certain reptiles like bearded dragons, geckos, and certain species of snakes are kept for their unique appearance and behaviors.
How are domestic animals used by humans?
Domestic animals serve humans in a multitude of ways, reflecting the depth and diversity of the relationships formed over thousands of years of domestication. These uses can be categorized into several broad areas:
1. Companionship:
- Pets like dogs, cats, birds, and rabbits provide companionship, love, and emotional support to their owners. They are often considered part of the family.
2. Agriculture and Livestock Production:
- Animals such as cows, pigs, sheep, goats, and chickens are raised for their meat, milk, eggs, and wool, contributing significantly to the global food supply and textile industries.
3. Work and Transportation:
- Horses, donkeys, and camels have historically been used for transportation, carrying loads, and helping with agricultural tasks like plowing fields.
4. Service and Assistance:
- Service animals, such as guide dogs for the blind, therapy animals, and police or military dogs, are trained to perform specific tasks to assist humans in their daily lives and in special operations.
5. Sports and Recreation:
- Horses are used in competitive sports like racing, show jumping, and dressage. Dogs participate in shows, agility competitions, and hunting.
6. Pest Control:
- Cats are often kept to control rodent populations, while certain dog breeds are used to manage vermin.
7. Research and Education:
- Animals like mice, rats, and rabbits are used in scientific research to advance medical and biological knowledge. Educational farms and petting zoos use domestic animals to teach about agriculture, biology, and responsible animal care.
8. Conservation and Ecological Contributions:
- Bees are kept for pollination, which is essential for the growth of many crops and the health of ecosystems.
9. Clothing and Accessories:
- Sheep are sheared for wool, and certain breeds of goats are raised for cashmere and mohair. Leather and fur are other products obtained from domestic animals like cows and rabbits.
10. Cultural and Religious Roles:
- In many cultures, certain animals hold symbolic meanings and are part of religious ceremonies and traditions.
In conclusion, domestic animals are an integral part of human life, offering companionship, sustenance, and assistance across various aspects of society. From the loyal dog to the industrious bee, each species holds a unique place in our hearts and homes, underscoring the importance of understanding and respecting the diverse roles these remarkable creatures play in our world.