100+ Herbivorous Animal Names: Meaning, Types, PDF
Domestic animals, the loyal and indispensable companions of humanity, grace our homes, farms, and landscapes with their presence. From the faithful dogs that guard our homes to the diligent cows that grace our pastures, these animals form an integral part of our daily lives and cultures. This diverse group not only includes beloved pets like cats and rabbits but also encompasses hardworking livestock such as chickens and goats, each contributing uniquely to human society.
Download List of Herbivorous Animal Names - PDF
List of Herbivorous Animal Names
Herbivorous animals play a pivotal role in ecosystems around the globe, thriving on a plant-based diet. These creatures, ranging from the majestic African elephants that roam the savannah to the gentle deer in wooded forests, contribute significantly to the ecological balance. They act as natural landscapers, controlling plant growth and spreading seeds, which helps in the regeneration of plant life. Their feeding habits also create habitats for other wildlife, maintaining biodiversity. In agricultural contexts, domestic herbivores like cows and sheep are vital for human sustenance, providing dairy, wool, and meat, and supporting economies. Moreover, the existence of these animals is crucial for scientific research and education, offering insights into evolutionary biology, animal behavior, and conservation efforts. Protecting their natural habitats is essential for preserving biodiversity and ensuring the health of our planet. As we delve into the diverse world of herbivores, it’s clear that their survival is intricately linked with our environmental stewardship and conservation efforts.
| Giraffe | Elephant | Zebra | Bison |
| Cow | Goat | Sheep | Deer |
| Kangaroo | Panda | Gorilla | Hippopotamus |
| Horse | Donkey | Camel | Llama |
| Rabbit | Guinea Pig | Tortoise | Iguana |
| Parrot | Koala | Sloth | Antelope |
| Gazelle | Wallaby | Capybara | Rhinoceros |
| Elk | Moose | Reindeer | Gaur |
| Okapi | Saiga | Tapir | Chinchilla |
| Hamster | Jerboa | Lemur | Manatee |
| Galapagos Tortoise | Green Sea Turtle | Howler Monkey | Orangutan |
| Wombat | Alpaca | Yak | Red Panda |
| Chameleon | Crested Porcupine | Dik-dik | Eland |
| Impala | Kudu | Muntjac | Nene |
| Quokka | Ruffed Lemur | Sika Deer | Takin |
| Uakari | Vicuña | Warthog | Xerus |
| Yellow-Footed Tortoise | Zebu | Aoudad | Barbary Sheep |
| Cuscus | Duiker | Echidna | Fallow Deer |
| Galápagos Land Iguana | Hare | Indian Rhinoceros | Javan Rhino |
| Kinkajou | Langur | Marmoset | Nilgai |
| Oribi | Pika | Quagga | Rhea |
| Sable Antelope | Tahr | Urial | Vole |
| Waterbuck | Xantusia | Yellow-backed Duiker | Zorilla |
| Addax | Bongo | Caribou | Dugong |
| Emu | Flying Squirrel | Gila Monster | Hutia |
| Ibis | Jackrabbit | Klipspringer | Lemming |
| Meerkat | Numbat | Opossum | Porcupine |
| Quokka | Rock Hyrax | Springbok | Tenrec |
| Uinta Ground Squirrel | Vaquita | Woolly Monkey | Yellow Mongoose |
Types of Herbivorous Animal Names
Herbivorous animals, those that feed exclusively on plant matter, come in various forms and sizes, adapting to diverse ecosystems around the world. Here’s a breakdown of different types of herbivores based on their primary food sources and habits:
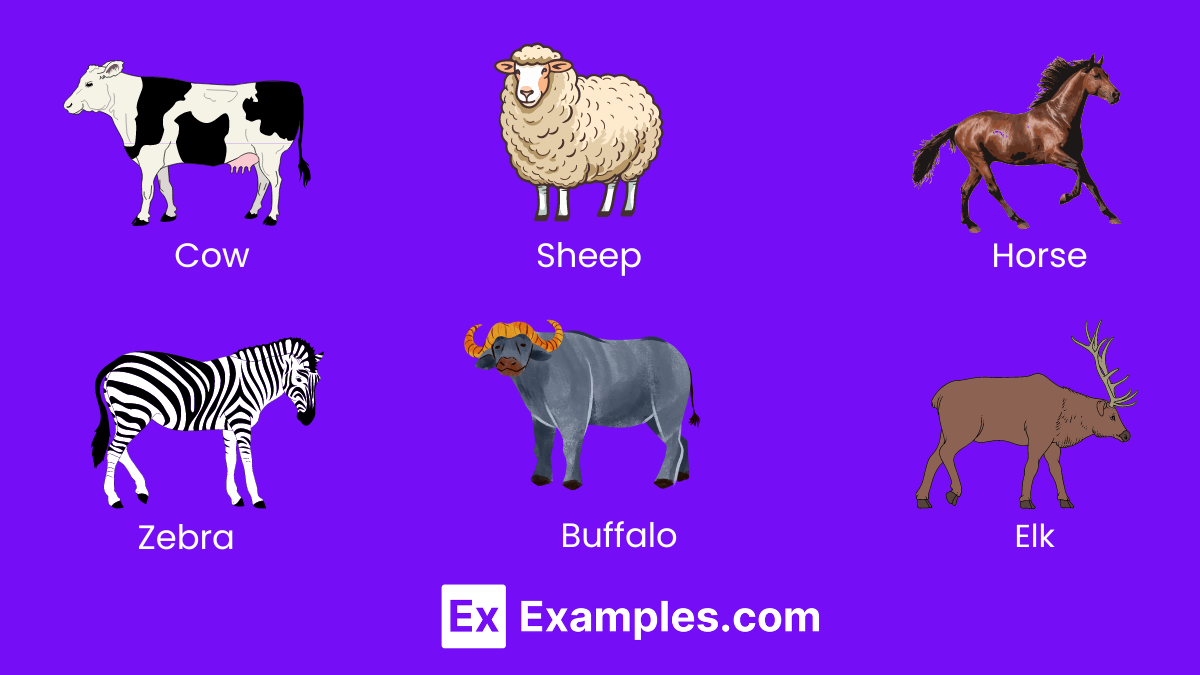
1. Grazers
Grazers thrive on grasses and low-lying vegetation, shaping the landscape and maintaining healthy grasslands. Their grazing patterns can prevent wildfires and promote biodiversity, making them essential for ecosystem balance. Grazers often have specialized digestive systems to break down tough plant fibers, contributing significantly to nutrient cycling within their habitats.
- Cow: Domesticated for dairy and beef, cows are quintessential grazers.
- Sheep: Valued for wool and meat, sheep graze on a variety of grasses.
- Horse: Grazes on grasslands, playing a role in habitat maintenance.
- Zebra: Wild grazers known for their distinctive striped coats.
- Buffalo: Key species in grassland ecosystems, buffalo graze in herds.
- Elk: Large deer species that graze in forests and meadows.
- Wildebeest: Migrate in large herds across African savannas to graze.
- Rabbit: Small mammals that graze on grass and clover.
- Guinea Pig: Domesticated version often grazes on fresh grass.
- Yak: Adapted to high altitudes, yaks graze on alpine vegetation.
2. Browsers
Browsers selectively feed on leaves, twigs, and higher vegetation, often shaping the structure of forests and woodlands. Their feeding habits encourage new plant growth and maintain the health of forested areas. Browsers are adapted to reach diverse plant parts, contributing to their ecosystems by controlling plant overgrowth and aiding in seed dispersal.
- Giraffe: With long necks, giraffes browse on tree leaves and shoots.
- Deer: Prefer leaves, shoots, and occasionally bark from trees.
- Moose: Largest of the deer family, moose browse on aquatic vegetation.
- Okapi: Forest dwellers that browse on tree leaves and fruits.
- Koala: Feeds almost exclusively on eucalyptus leaves.
- Panda: While mainly eating bamboo, pandas are considered browsers.
- Antelope: Many species browse on shrubs and trees in savannas.
- Mountain Gorilla: Primarily browsers, feeding on leaves and stems.
- Black Rhinoceros: Browses on twigs, leaves, and bushes.
- Bushbaby: Small primates that browse on leaves and insects.
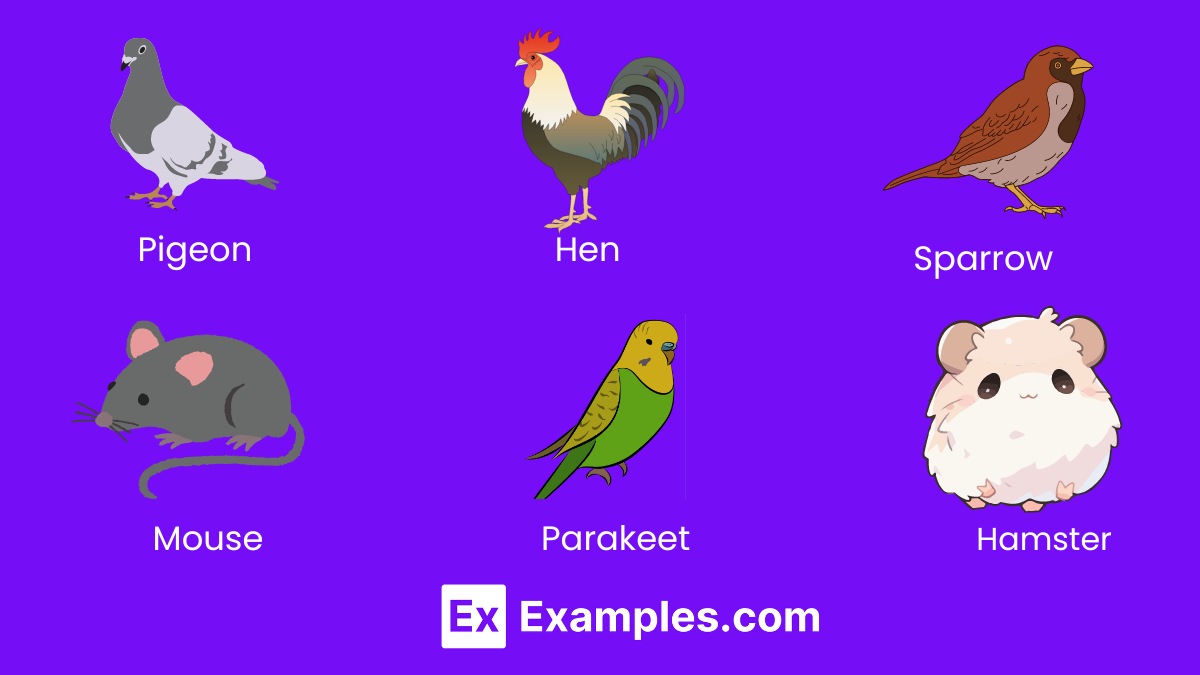
3. Granivores
Granivores are specialized feeders that consume seeds and grains, playing a key role in seed dispersal and the control of plant populations. Their dietary habits can influence the composition and distribution of plant species within their habitats, making them vital for maintaining the balance between different plant communities.
- Pigeon: Urban and wild pigeons consume a variety of seeds.
- Hen : Domesticated hens peck at seeds and grains.
- Sparrow: Small birds that feed extensively on seeds.
- Mouse: Many mouse species forage for seeds as a primary food source.
- Parakeet: Prefer seeds as part of their diet, especially in captivity.
- Hamster: In the wild, hamsters hoard seeds for consumption.
- Quail: Ground-dwelling birds that feed on seeds and grains.
- Dove: Known for eating seeds from a variety of plants.
- Finch: Small birds with a diet rich in seeds.
- Grouse: Consume seeds, especially during winter months.
4. Frugivores
Frugivores predominantly feed on fruit, aiding in the dispersal of seeds through their digestive tracts. This feeding behavior is crucial for the regeneration of plant populations and the maintenance of diverse ecosystems. Frugivores often have colorful, appealing appearances, attracting them to the fruits they consume and ensuring the continuation of plant species.
- Orangutan: Primarily frugivores, they play a role in seed dispersal.
- Fruit Bat: Night-time foragers that distribute tropical fruit seeds.
- Toucan: Known for their large beaks, toucans feed on a variety of fruits.
- Parrot: Many species enjoy fruits as a significant part of their diet.
- Chimpanzee: Consume fruit, aiding in forest regeneration.
- Hornbill: Tropical birds that feed on fruits and assist in seed dispersal.
- Manatee: Aquatic frugivores that consume water vegetation and fruits.
- Lemur: Primarily frugivorous, contributing to seed dispersal in forests.
- Flying Fox: Large bats that feed on fruit, aiding in pollination.
- Fig Bird: Consumes figs and other fruits, distributing seeds.
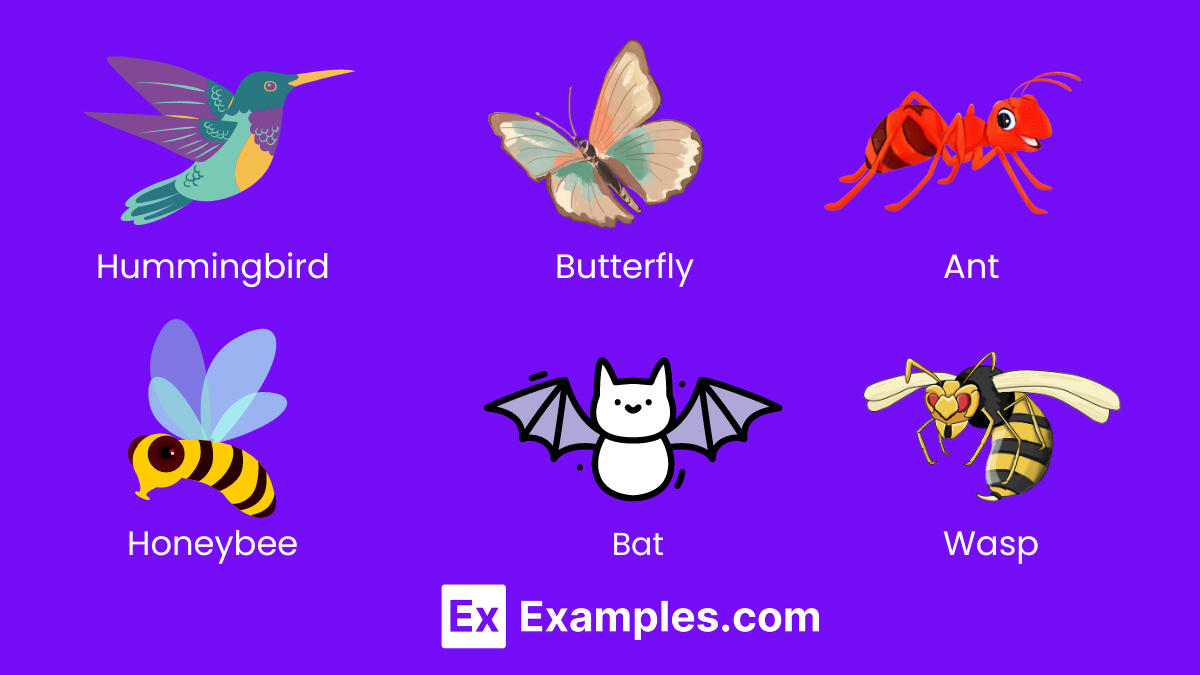
5. Nectarivores
Nectarivores specialize in consuming nectar from flowers, playing a crucial role in pollination and thus in the reproduction of many plant species. Their adaptations, such as long beaks or specialized tongues, allow them to access the nectar, while their feeding habits contribute to the cross-pollination of flowers, aiding in biodiversity and ecosystem health.
- Hummingbird: Vibrant birds with rapid wingbeats, adapted to hover near flowers.
- Butterfly: Delicate insects with long proboscises for reaching into flowers.
- Sunbird: Small, brightly colored birds, similar to hummingbirds in behavior.
- Honeybee: Essential for pollination, bees collect nectar to produce honey.
- Bat: Certain species have adaptations for nocturnal nectar feeding.
- Lorikeet: Parrots with brush-tipped tongues for feeding on nectar.
- Moth: Many species, like the hawk moth, are adapted for nectar feeding.
- Ant: Some ant species are known to consume nectar directly from plants.
- Wasp: Certain wasps consume nectar, contributing to pollination.
- Hoverfly: Mimics bees and wasps; larvae consume pests, adults feed on nectar.
6. Folivores
Folivores are herbivores that feed primarily on leaves, which are abundant but often low in nutrition and hard to digest. These animals have specialized digestive systems to extract necessary nutrients from leaves, playing a significant role in controlling plant growth and contributing to the cycling of nutrients within their habitats.
- Chameleons: There are folivorous reptiles known for their ability to change color and primarily feed on leaves.
- Sloth: Slow-moving tree-dwellers that feed on leaves.
- Giraffe: Their long necks allow them to browse high tree leaves.
- Panda: Although known for bamboo, they are technically folivores.
- Orangutan: Primarily consume fruit but also eat leaves.
- Gorilla: Mountain gorillas have a diet rich in leaves.
- Okapi: Forest dwellers that feed on tree leaves and buds.
- Howler Monkey: Known for consuming a variety of leaves.
- Iguana: Green iguanas are primarily folivorous, feeding on leaves.
- Tortoise: Many species are folivores, consuming a range of leaves.
7. Aquatic Herbivores
Aquatic Herbivores play a vital role in aquatic ecosystems, feeding on water plants and algae. They help maintain healthy waterways by controlling algae blooms and aquatic plant growth, ensuring biodiversity and the stability of aquatic habitats. These herbivores range from small fish to large mammals, each adapted to their unique aquatic environment.
- Manatee: Gentle giants known as “sea cows,” feeding on sea grasses.
- Dugong: Similar to manatees, they graze on underwater vegetation.
- Green Sea Turtle: Feeds on a variety of sea grasses and algae.
- Hippos: While semi-aquatic, they consume large amounts of aquatic plants.
- Aquatic Snail: Many species feed on algae and decaying plant matter.
- Cichlid Fish: Some species are adapted to graze on algae.
- Beaver: Known for constructing dams, they feed on aquatic plants.
- Mallard Duck: Feeds on aquatic vegetation, small fish, and insects.
- Koi Carp: Ornamental fish that graze on pond algae and plants.
- Tadpole: The larval stage of frogs, primarily feeding on algae.
List of Herbivorous Animal Names from A-Z
Herbivorous Animals Starting with A
| Animal Name | Animal Name |
|---|---|
| Antelope | Alpaca |
| Aoudad | Agouti |
| Axis Deer | African Buffalo |
| Addax | Anoa |
| Arabian Oryx | Argali |
Herbivorous Animals Starting with B
| Animal Name | Animal Name |
|---|---|
| Bison | Blackbuck |
| Bighorn Sheep | Barbary Sheep |
| Blue Wildebeest | Bongo |
| Bushbuck | Black Rhinoceros |
| Bonobo | Brazilian Tapir |
Herbivorous Animals Starting with C
| Animal Name | Animal Name |
|---|---|
| Camel | Capybara |
| Chamois | Collared Peccary |
| Cottontail Rabbit | Chital |
| Cape Buffalo | Capuchin Monkey |
| Common Eland | Crested Porcupine |
Herbivorous Animals Starting with D
| Animal Name | Animal Name |
|---|---|
| Deer | Dik-dik |
| Duiker | Dromedary Camel |
| Desert Tortoise | Dormouse |
| Damara Zebra | Dorcas Gazelle |
| Dusky Langur | Drill (Monkey) |
Herbivorous Animals Starting with E
| Animal Name | Animal Name |
|---|---|
| Elephant | Elk |
| Eastern Grey Kangaroo | Echidna |
| Ethiopian Wolf | European Bison |
| Edible Dormouse | Eastern Lowland Gorilla |
| Emu | Eurasian Beaver |
Herbivorous Animals Starting with F
| Animal Name | Animal Name |
|---|---|
| Fallow Deer | Fruit Bat |
| Forest Buffalo | Flying Squirrel |
| Fennec Fox | Fin Whale |
| Florida Manatee | Fossa |
| François’ Langur | Four-horned Antelope |
Herbivorous Animals Starting with G
| Animal Name | Animal Name |
|---|---|
| Giraffe | Gazelle |
| Giant Panda | Galápagos Tortoise |
| Gaur | Guanaco |
| Gerenuk | Gelada |
| Green Sea Turtle | Grant’s Zebra |
Herbivorous Animals Starting with H
| Animal Name | Animal Name |
|---|---|
| Horse | Hippopotamus |
| Howler Monkey | Hanuman Langur |
| Hartebeest | Himalayan Tahr |
| Hirola | Hog Deer |
| Hyrax | Huemul |
Herbivorous Animals Starting with I
| Animal Name | Animal Name |
|---|---|
| Impala | Indian Rhinoceros |
| Ibex | Indian Elephant |
| Iguana | Indian Flying Fox |
| Italian Crested Porcupine | Indian Bison |
| Indri | Indian Muntjac |
Herbivorous Animals Starting with J
| Animal Name | Animal Name |
|---|---|
| Javan Rhinoceros | Jersey Cattle |
| Javan Deer | Jabiru |
| Japanese Macaque | Javan Langur |
| Junglefowl | Jackson’s Chameleon |
| Juniper Hairstreak (Butterfly) | Javan Rusa |
Herbivorous Animals Starting with K
| Animal Name | Animal Name |
|---|---|
| Kangaroo | Koala |
| Kudu | Klipspringer |
| Key Deer | Kirk’s Dik-dik |
| Kiang | Komodo Dragon |
| Kakapo | Kinkajou |
Herbivorous Animals Starting with L
| Animal Name | Animal Name |
|---|---|
| Llama | Langur |
| Lemur | Lesser Kudu |
| Lowland Tapir | Leafcutter Ant |
| Lar Gibbon | Luzon Bleeding-heart |
| Long-tailed Chinchilla | Lynx |
Herbivorous Animals Starting with M
| Animal Name | Animal Name |
|---|---|
| Moose | Manatee |
| Mountain Gorilla | Mule Deer |
| Muskox | Macaque |
| Mountain Zebra | Marsh Deer |
| Muntjac | Markhor |
Herbivorous Animals Starting with N
| Animal Name | Animal Name |
|---|---|
| Nilgai | Nubian Goat |
| Nyala | Northern Giraffe |
| Nutria | Nene (Hawaiian Goose) |
| Nubian Ibex | Northern White Rhinoceros |
| Nabarlek | Nilgiri Tahr |
Herbivorous Animals Starting with O
| Animal Name | Animal Name |
|---|---|
| Okapi | Orangutan |
| Oryx | Olive Baboon |
| Ocelot | Onager |
| Orca (as a rare exception, eats fish) | Opossum (opportunistic) |
| Owl Monkey | Ox |
Herbivorous Animals Starting with P
| Animal Name | Animal Name |
|---|---|
| Panda | Pronghorn |
| Proboscis Monkey | Porcupine |
| Pangolin | Pygmy Hippopotamus |
| Parrot | Pudu |
| Peccary | Philippine Tarsier |
Herbivorous Animals Starting with Q
| Animal Name | Animal Name |
|---|---|
| Quokka | Quagga (extinct) |
| Queen Alexandra’s Birdwing (Butterfly) | Quetzal |
Herbivorous Animals Starting with R
| Animal Name | Animal Name |
|---|---|
| Reindeer | Red Panda |
| Ring-tailed Lemur | Rhinoceros |
| Rock Hyrax | Roosevelt Elk |
| Red Kangaroo | Red River Hog |
| Ruffed Lemur | Rabbits |
Herbivorous Animals Starting with S
| Animal Name | Animal Name |
|---|---|
| Sheep | Squirrel |
| Saiga Antelope | Sloth |
| Springbok | Sumatran Elephant |
| Sika Deer | Spectacled Bear |
| Swamp Deer | Sun Bear |
Herbivorous Animals Starting with T
| Animal Name | Animal Name |
|---|---|
| Tapir | Tortoise |
| Thomson’s Gazelle | Tahr |
| Takin | Tamarin |
| Tree Kangaroo | Tamandua |
| Tufted Capuchin | Toco Toucan |
Herbivorous Animals Starting with U
| Animal Name | Animal Name |
|---|---|
| Uakari (Monkey) | Ugandan Kob |
| Urial | Uinta Ground Squirrel |
| Ulysses Butterfly | Umbrella Bird |
| Unau (Two-toed Sloth) | Urutu |
| Upland Sandpiper |
Herbivorous Animals Starting with V
| Animal Name | Animal Name |
|---|---|
| Vicuña | Vervet Monkey |
| Vietnamese Pot-bellied Pig | Vaquita |
| Vampire Bat (feeds on blood, a unique case) | Velvet Worm |
| Vole | Vine Snake (primarily eats eggs) |
| Visayan Warty Pig | Venezuelan Red Howler |
Herbivorous Animals Starting with W
| Animal Name | Animal Name |
|---|---|
| Wallaby | Warthog |
| White Rhinoceros | Wildebeest |
| Water Buffalo | Wombat |
| Woolly Mammoth (extinct) | Wood Bison |
| Western Lowland Gorilla | White-tailed Deer |
Herbivorous Animals Starting with X
| Animal Name | Animal Name |
|---|---|
| Xerus (Squirrel) | Xenopus (a primarily insectivorous frog, but included for the sake of completion) |
Herbivorous Animals Starting with Y
| Animal Name | Animal Name |
|---|---|
| Yak | Yellow-backed Duiker |
| Yapok (Water Opossum, mainly feeds on aquatic organisms but included for completion) | Yucatan Squirrel |
Herbivorous Animals Starting with Z
| Animal Name | Animal Name |
|---|---|
| Zebra | Zebu |
| Zokor | Zorilla (though primarily carnivorous, included for completion) |
In conclusion, Our exploration of herbivorous animal names from A to Z showcases the incredible diversity of Earth’s plant-eating creatures. From the majestic African Elephant to the humble Zebra, each animal plays a vital role in maintaining ecological balance. This journey highlights the importance of understanding and conserving these species, as they contribute significantly to the health and sustainability of our planet’s ecosystems