Which food is a rich source of Vitamin C?
Bananas
Oranges
Rice
Bread
Embark on a culinary expedition with our comprehensive guide to food sources. From the sun-drenched fields where grains wave in the breeze to the deep, nutrient-rich waters teeming with fish, this guide explores the myriad ways nature provides for us. Delving into both common and exotic sources, it illuminates how each food item travels from its origin to our plates, emphasizing nutritional benefits and environmental impact. Tailored for food enthusiasts, environmentalists, and health-conscious individuals, this introduction sets the stage for a deeper understanding of our food’s journey and its significance in sustaining a healthy body and planet.
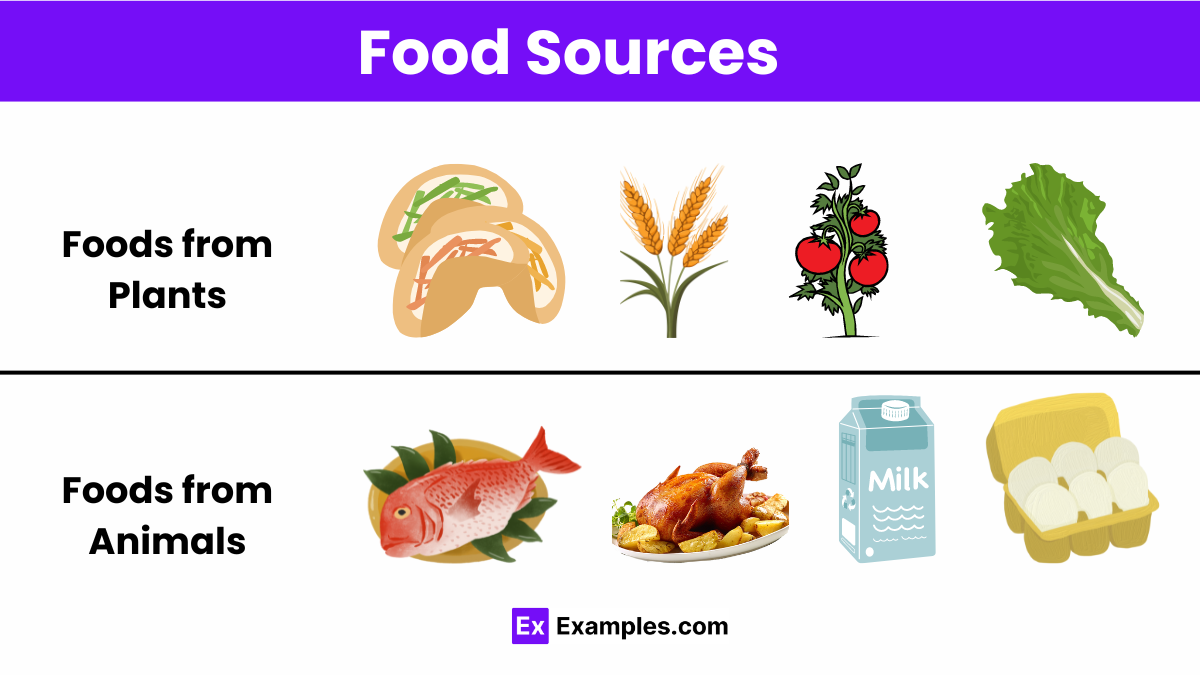
Food sources encompass a diverse range of substances that provide nutritional support for organisms, primarily humans. These sources can be classified into various categories based on the type of nutrients they offer, such as carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals. Each category plays a crucial role in maintaining health, growth, and vitality. Here’s a closer look at these categories.
Foods derived from plants are essential components of the human diet, providing a wide range of nutrients, including carbohydrates, vitamins, minerals, proteins, and fats, as well as dietary fiber. Plant-based foods come from various parts of plants, including fruits, vegetables, grains, nuts, seeds, and legumes.
Plant-based foods not only provide essential nutrients for human health but also have environmental benefits. Producing plant-based foods generally requires less water, land, and energy and emits fewer greenhouse gases compared to producing animal-based foods. As a result, incorporating more plant-based foods into the diet is recommended for both health and environmental sustainability.
Animal-based foods are derived from various animals and include meat, dairy products, eggs, and honey, among others. These foods are important sources of protein, fats (including essential fatty acids), vitamins (such as B12 and D), and minerals (including iron, zinc, and calcium).
here are approximately 20,000 edible plant species on Earth, offering a vast diversity of food sources for human consumption.
Different parts of plants used as food include leaves, fruits, seeds, roots, stems, and flowers, each offering unique nutritional benefits.
The main components of food are carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals, and water, essential for human health and survival
The Nitrogen Cycle is a fundamental ecological process, recycling nitrogen through the atmosphere, soil, and living organisms. It supports life by converting nitrogen into usable forms, aiding plant growth and thus sustaining the food chain. Human activities, however, have disrupted this cycle, necessitating sustainable practices to restore its balance and ensure environmental health.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
Which food is a rich source of Vitamin C?
Bananas
Oranges
Rice
Bread
Which of the following is a good source of protein?
Apples
Carrots
Chicken
Lettuce
Which food is a primary source of carbohydrates?
Fish
Bread
Spinach
Cheese
Which of the following is a good source of dietary fiber?
Beans
Eggs
Milk
Yogurt
Which food is a rich source of calcium?
Oranges
Spinach
Cheese
Chicken
Which of the following foods is a good source of Omega-3 fatty acids?
Apples
Potatoes
Beef
Salmon
Which food is a good source of iron?
Bananas
Rice
Carrots
Spinach
Which of the following is a good source of Vitamin A?
Rice
Carrots
Bread
Cheese
Which food is a primary source of healthy fats?
Apples
Avocado
Lettuce
Chicken
Which food source is high in magnesium?
White bread
Brown rice
Milk
Broccoli
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

