11+ Secondary Source Examples to Download
According to the scientific method, academics must study and write scientific publications that are supported by evidence and have a strong scientific basis. The author provides the necessary citations for linked material and references that set out the structural scientific underpinning. These citations, linked materials, and references are examples of secondary sources the researcher uses in their research.
1. Primary and Secondary Sources
2. Primary Secondary Source Sort
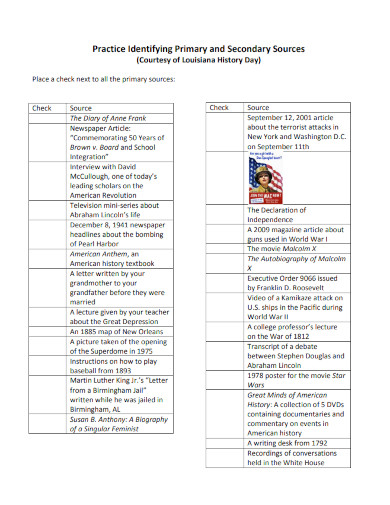
3. Practice Identifying Primary and Secondary Sources
4. Teaching Primary and Secondary Sources
5. Evaluating Primary and Secondary Sources
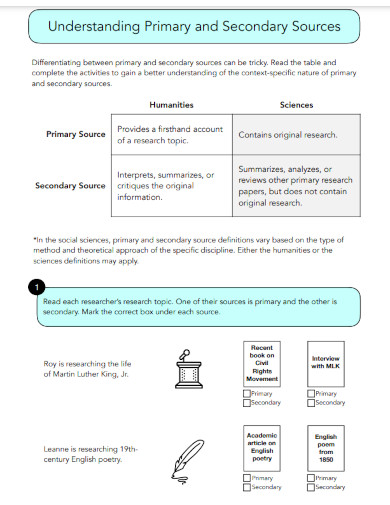
6. Understanding Primary and Secondary Sources
7. Working Primary and Secondary Sources
8. Identifying Primary and Secondary Sources
9. Secondary Source Analysis Worksheet
10. Incorporating Primary and Secondary Sources
11. Guidelines for Primary Source Literacy
12. Designing Case Studies from Secondary Sources
What Is a Secondary Source
A secondary source is a type of source that acts as the instrument of the researcher’s understanding of the data set provided by the primary source. Not only that but the secondary source is also used to help code and explain the data obtained through the primary source.
How To Research and Obtain Secondary Sources
Secondary sources are readily available and can be sourced through various methods and actions. If you want to have a reference of how a secondary source looks you may read the articles named Working Primary and Secondary Sources, Practice Identifying Primary and Secondary Sources, and Teaching Primary and Secondary Sources on the links above, which will help with your overall understanding of both a primary and a secondary source.
Step 1: Select A Subject or Scientific Niche You Are Investigating
If you have not selected a subject or research question that you are tackling for your research paper, then you must first choose, create, or select the research topic you are going to write about. Be sure to write about something that you are wholly interested in as the writing process for the research topic is very arduous and time-consuming.
Step 2: Search Through an Online Catalog
One of the easiest ways to research and obtain secondary sources is via the act of searching and sifting through an online database or catalog. An example of an online catalog you can use is Google Scholar, which allows you to quickly search research topics to obtain any adjacent related literature.
Step 3: Use References Stated in the Reference or Bibliography of Other Research Articles
Another way you can obtain more references is through the utilization of the reference or bibliography section of any research paper you are citing and referencing. This will allow you to also glean information and data past researchers obtain throughout their research.
Step 4: Consult Experts Related to The Chosen Subject
You may also consult experts who are well-versed in the specific subject or niche you are choosing to tackle for your research paper. Not only will they be able to give you reliable data, but the experts can also be used to help out in the coding of the data obtained from the primary source.
FAQs
What is the difference between a primary and a secondary source?
A primary source is a type of data source used in a research paper or scientific report that comes from first-hand experience and reliable gathered statistical data. Examples of this type of data source include survey questions or surveys, interview transcripts, and case studies. A secondary source, on the other hand, is a data source that the researcher uses to explain and interpret the dataset provided by the primary source. These types of sources come in the form of related literature, books, and other scholarly works used in the research process. Therefore the relationship between a primary and a secondary source is a very important concept to learn.
How do you identify secondary sources?
People can easily differentiate and identify primary and secondary sources from each other. This is mainly because the dataset the primary source provides originates from the research they are writing, whilst the secondary source comes from a source outside of the research article or paper. Not only that but the dataset from the secondary source also comes from the literature that the author will cite in the body of the research paper or article.
Why are secondary sources important?
Secondary sources allow the author, scholar, and writer to synthesize and extrapolate the information obtained and gathered from the primary source. This means that the secondary source is the instrument the researcher will use to code and analyze all the datasets and statistics from the primary source.
A secondary source is a type of reference and data source that the researchers use to explain and extrapolate the data obtained from the primary source. These often manifest themselves in the research paper as related literature, books, and other scholarly sources adjacent to the overall subject matter of the research. A well-researched scientific article will need the researcher, scholar, or author to obtain reliable and valid secondary sources to succinctly explain and support their data.