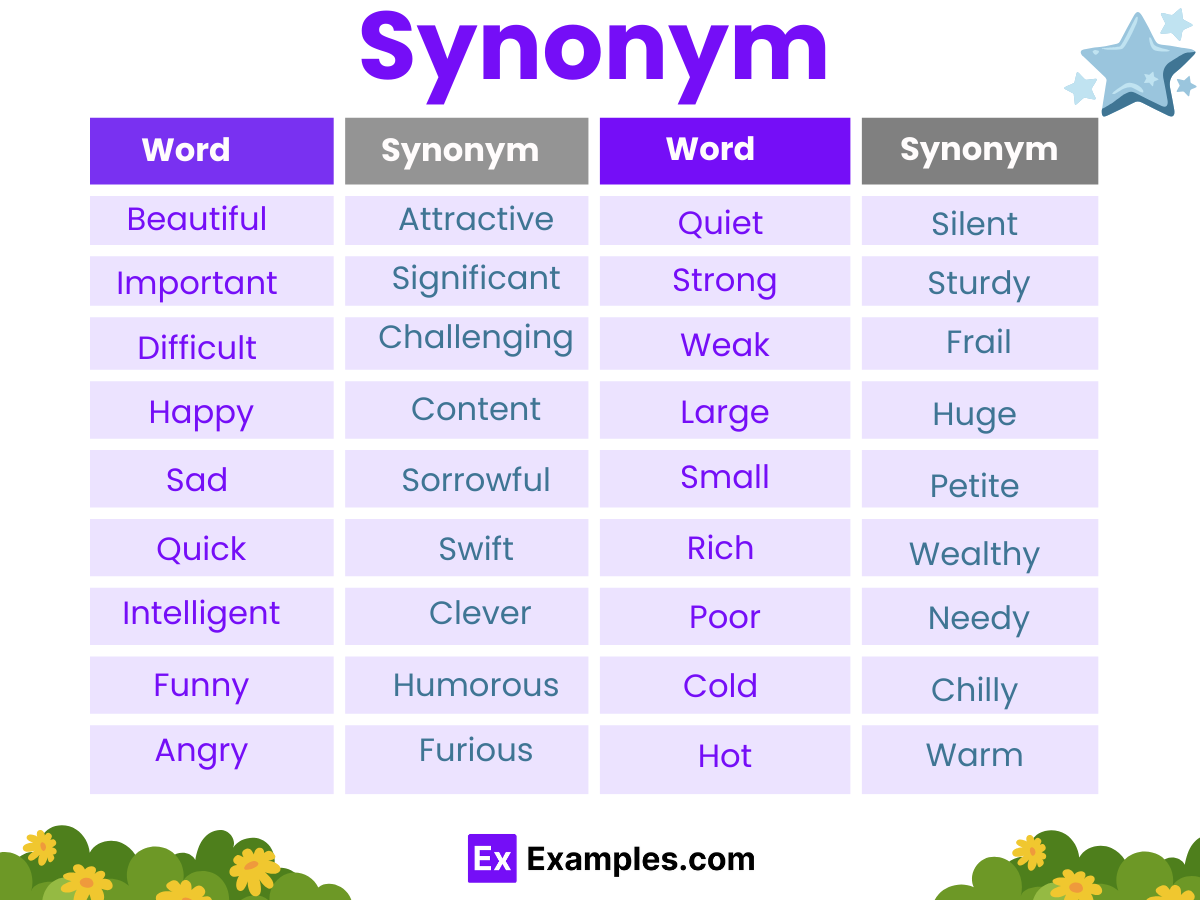
150+ Synonym Examples
The word good has plenty of similar words that mean the same thing. These words are fine, superior, great, acceptable, and virtuous. All of the words above are synonyms of the word good. One can know how Daily Use English Words are similar to each other by looking up their synonyms.
What is a Synonym?
A synonym is a word that has the same or nearly the same meaning as another word in the same language. Synonyms can be used interchangeably in various contexts without significantly altering the meaning of a statement. However, subtle differences in connotation and usage often distinguish synonyms, making them particularly useful for enhancing the richness and precision of language.
40+ Synonym Examples
- Angry – Furious
- Angry denotes a mild or moderate feeling of displeasure.
- Furious implies a more intense, often uncontrollable anger.
- Beautiful – Stunning
- Beautiful refers to pleasing the senses or mind aesthetically.
- Stunning implies an overwhelming beauty that leaves one in awe.
- Big – Massive
- Big refers to something of considerable size.
- Massive indicates an exceptionally large and imposing size.
- Brave – Courageous
- Brave implies facing danger or pain without showing fear.
- Courageous suggests a higher level of bravery, often with a noble purpose.
- Bright – Luminous
- Bright refers to emitting or reflecting a lot of light.
- Luminous implies emitting light in a soft, glowing manner.
- Calm – Serene
- Calm denotes an absence of agitation or excitement.
- Serene suggests a profound peace and tranquility.
- Cheap – Inexpensive
- Cheap implies a low cost, often with a sense of lower quality.
- Inexpensive denotes affordability without necessarily compromising quality.
- Cold – Frigid
- Cold refers to a low temperature.
- Frigid implies an extreme cold that is freezing or intensely cold.
- Confident – Self-assured
- Confident implies a strong belief in one’s own abilities.
- Self-assured suggests a quiet, steady confidence that is not easily shaken.
- Dangerous – Perilous
- Dangerous implies a potential to cause harm or injury.
- Perilous suggests a higher degree of danger, involving serious risk.
- Dark – Obscure
- Dark refers to a lack of light.
- Obscure implies being not well known or difficult to understand.
- Difficult – Arduous
- Difficult implies not easy to do, understand, or deal with.
- Arduous suggests requiring great effort and perseverance.
- Easy – Effortless
- Easy implies simplicity and a lack of difficulty.
- Effortless suggests something done with astonishing ease, almost automatically.
- Fast – Swift
- Fast refers to high speed.
- Swift suggests quickness and rapid movement, often more elegant.
- Funny – Hilarious
- Funny refers to something that causes laughter.
- Hilarious implies a higher degree of humor that causes uproarious laughter.
- Happy – Joyful
- Happy is a general term for feeling pleased or content.
- Joyful implies a deeper, often more expressive level of happiness.
- Hard – Strenuous
- Hard implies a considerable level of difficulty.
- Strenuous suggests requiring great effort and energy.
- Important – Crucial
- Important refers to something of great significance or value.
- Crucial implies something that is critical or pivotal, often decisive in outcome.
- Intelligent – Brilliant
- Intelligent implies having a high mental capacity.
- Brilliant suggests an exceptional sharpness and brightness of mind.
- Interesting – Fascinating
- Interesting implies something that holds attention by its quality.
- Fascinating suggests being intensely interesting or captivating.
- Kind – Benevolent
- Kind refers to a gentle, sympathetic nature.
- Benevolent implies a goodness that is charitable and desires to do good.
- Lazy – Indolent
- Lazy implies a dislike of work or physical exertion.
- Indolent suggests a love of ease and a habitual avoidance of activity.
- Loud – Deafening
- Loud refers to a high volume of sound.
- Deafening implies a volume so loud it can cause hearing loss.
- New – Novel
- New refers to something recently made or acquired.
- Novel implies newness that is original and innovative.
- Old – Ancient
- Old refers to something that has existed for a long time.
- Ancient implies great age, often thousands of years, conferring a sense of history.
- Powerful – Potent
- Powerful implies having great power, strength, or influence.
- Potent suggests a concentrated strength or effect, often more subtle but impactful.
- Rich – Wealthy
- Rich implies having a lot of money or assets.
- Wealthy suggests a substantial accumulation of assets and riches, often more extensive.
- Sad – Melancholy
- Sad refers to feeling sorrow or unhappiness.
- Melancholy implies a deeper, more reflective sadness, often with a poetic quality.
- Smart – Intelligent
- Smart implies being quick-witted or clever.
- Intelligent suggests a capacity for understanding complex ideas and reasoning.
- Weak – Feeble
- Weak implies lacking physical strength or vitality.
- Feeble suggests an even more diminished strength, often due to age or illness.
How to Use Synonym in a Sentence?
synonyms in a sentence involves selecting words that have similar meanings but are best suited to the specific context and tone you want to convey.
- Identify the Key Word: Determine the word in your sentence that you want to replace with a synonym. This is often a word that feels too repetitive or too simplistic for the context.
- Consider the Context: Think about the sentence’s overall meaning and the specific nuance you wish to express. Different synonyms can carry slightly different connotations or levels of intensity.
- Find Synonyms: Use a thesaurus, dictionary, or your knowledge to list possible synonyms for the word you’re replacing.
- Evaluate Suitability: Review the synonyms for their connotations, register (formal, informal, technical, etc.), and how well they fit with the sentence’s tone and meaning.
- Test the Synonym in the Sentence: Place each synonym in the sentence in place of the original word to see which fits best. Read the sentence aloud or in your head to check for flow and appropriateness.
- Ensure Clarity and Accuracy: Make sure the synonym does not alter the intended meaning of the sentence. It’s important that the synonym makes the sentence clearer or more expressive, not less accurate or more confusing.
- Check for Repetition: Ensure that the synonym doesn’t inadvertently repeat a concept or word already used in the surrounding sentences, unless repetition is your specific intent for stylistic reasons.
Example:
Original Sentence: “The scientist explained the procedure clearly.”
- Identify the Key Word: “clearly”
- Consider the Context: The sentence is formal and informative.
- Find Synonyms: “concisely”, “lucidly”, “precisely”
- Evaluate Suitability: “Concisely” might suggest brevity more than clarity, “lucidly” fits the formal and clear tone, and “precisely” implies accuracy but not necessarily clarity of explanation.
- Test the Synonym in the Sentence: “The scientist explained the procedure lucidly.”
- Ensure Clarity and Accuracy: “Lucidly” maintains the original meaning and adds a formal tone.
- Check for Repetition: Assuming no nearby sentence uses “lucidly,” it fits well.
Purpose of Synonyms
- Variety: Synonyms prevent repetition in speech and writing, adding variety and keeping the reader’s or listener’s interest. Using different words for the same concept can make text more engaging and enjoyable to read.
- Precision: They allow speakers and writers to choose the most accurate word for a particular context. Because synonyms often carry slight variations in connotation, selecting the right synonym can convey a precise meaning or emotion.
- Clarity: In certain contexts, one synonym may be clearer or more widely understood than another, making the message more accessible to a broader audience.
- Tone and Register: Synonyms can adjust the tone (e.g., more formal or informal) of communication without changing the underlying meaning. This is crucial in writing for different audiences or purposes.
- Language Development: Learning synonyms is an essential part of language acquisition, expanding both vocabulary and linguistic understanding. It helps learners grasp the nuances of the language and improves their ability to express themselves.
- Cultural Expression: Different cultures or regions may prefer specific synonyms, reflecting cultural identities through language. Understanding these preferences can enhance cross-cultural communication.
- Search Optimization: In the digital realm, synonyms are crucial for search engine optimization (SEO). Using synonyms can help content reach a wider audience by matching with a broader array of search queries.
- Literary Devices: In literature and poetry, synonyms are often used for stylistic reasons, such as to create rhyme, rhythm, or to emphasize a particular theme or emotion.
What are the types of synonyms?
Synonyms can be categorized based on the nuances of their similarity and context of use.
- Absolute Synonyms: These are words that mean exactly the same thing in all or almost all contexts, without any significant difference in usage, connotation, or tone. Absolute synonyms are rare because most synonyms have at least slight differences in connotation or usage.
- Near Synonyms: These words have very similar meanings but differ in nuances, such as connotations, register (formality), or specific contexts in which they are used. Near synonyms make up the majority of synonyms and are what people usually refer to when discussing synonyms. They allow for precision and variety in language use.
- Contextual Synonyms: These are words that function as synonyms in certain contexts but not in others. Their meanings may overlap significantly in specific situations, but in other contexts, their meanings can diverge. Choosing between contextual synonyms requires careful consideration of the specific situation.
- Plesionyms (or Connotative Synonyms): These synonyms are related in meaning but carry different emotional, evaluative, or ideological connotations. The choice among plesionyms can reflect the speaker’s or writer’s attitude toward the subject or the intended emotional impact on the audience.
- Cognitive Synonyms: These are words that share the same semantic field or belong to the same category of thought but may differ in terms of their features or aspects they emphasize. Cognitive synonyms are often used interchangeably in discussions about abstract concepts, theories, or ideas.
- Antonyms (as Opposite Synonyms): While traditionally considered the opposite of synonyms, in a broader linguistic sense, antonyms can be viewed as a type of synonym when discussing the spectrum of meaning. Words can be antonyms in one aspect while sharing semantic similarities in another, providing a nuanced understanding of their relationship.
Difference between Synonyms and Antonym
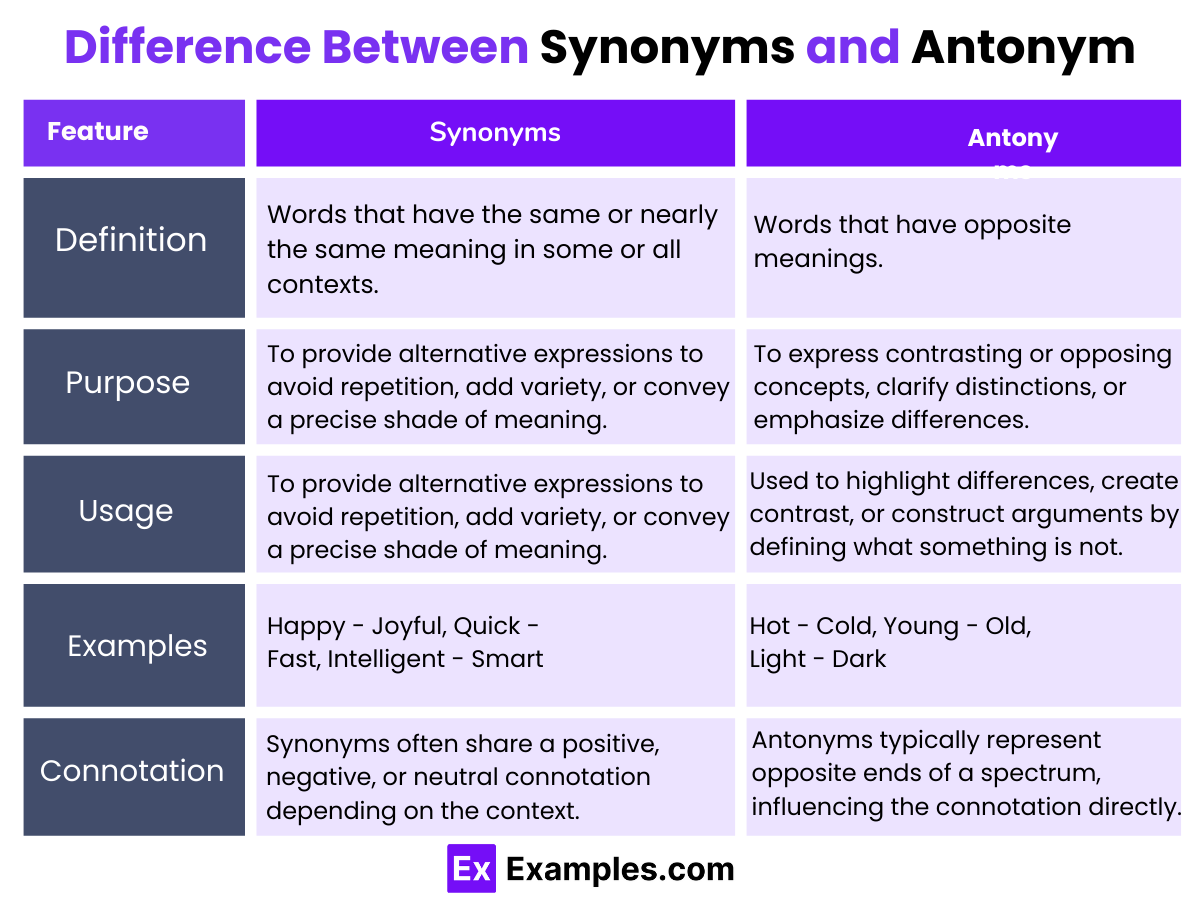
| Feature | Synonyms | Antonyms |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Words that have the same or nearly the same meaning in some or all contexts. | Words that have opposite meanings. |
| Purpose | To provide alternative expressions to avoid repetition, add variety, or convey a precise shade of meaning. | To express contrasting or opposing concepts, clarify distinctions, or emphasize differences. |
| Usage | Used to enrich language, enhance clarity, and adjust the tone of communication. | Used to highlight differences, create contrast, or construct arguments by defining what something is not. |
| Examples | Happy – Joyful, Quick – Fast, Intelligent – Smart | Hot – Cold, Young – Old, Light – Dark |
| Connotation | Synonyms often share a positive, negative, or neutral connotation depending on the context. | Antonyms typically represent opposite ends of a spectrum, influencing the connotation directly. |
| Linguistic Function | Synonyms are crucial for expanding vocabulary and enhancing expressive capacity in language. | Antonyms are vital for teaching and understanding the full range of meaning within a language by setting boundaries. |
Synonyms in Communication
Enhancing Clarity
Synonyms allow speakers and writers to choose words that are most familiar to their audience, thereby avoiding confusion and misunderstanding. By selecting a synonym that is more widely understood or that more accurately reflects the intended meaning, communicators can ensure that their message is clear.
Adding Precision
Different synonyms can carry slightly different nuances. By choosing the most appropriate synonym, communicators can convey their message with greater precision. For example, while “happy,” “elated,” and “content” are synonyms, each suggests a different intensity of happiness. Selecting the right word allows for a more accurate expression of emotion or description.
Avoiding Repetition
Repeated use of the same word can make communication monotonous and less engaging. Synonyms provide a way to avoid repetition, making speech or text more interesting and dynamic. This is particularly useful in writing, where maintaining the reader’s attention is crucial.
Tailoring Language to the Audience
Synonyms allow communicators to adjust their language according to the audience’s level of understanding, cultural background, or preferences. For instance, technical synonyms may be appropriate for a specialist audience, while simpler words might be better for a general audience. This adaptability enhances the effectiveness of communication.
Expressing Subtle Differences
Even closely related synonyms can have different connotations or suggest different degrees of intensity. By choosing among synonyms, communicators can express subtle differences in meaning, mood, or opinion, adding depth and richness to their message.
Enhancing Persuasiveness
In persuasive communication, the choice of words can significantly impact the audience’s response. Synonyms can be strategically chosen to evoke specific emotions or reactions, making the argument more compelling. For example, describing a plan as “innovative” rather than simply “new” can make it more appealing.
Facilitating Cross-Linguistic Communication
For speakers of different languages, synonyms in a shared language can bridge gaps in understanding. When a word in one language has multiple possible translations, knowing synonyms allows for clearer expression and better comprehension across language barriers.
In summary, synonyms are indispensable tools in communication, enriching our language and making our interactions more effective. They enable us to convey our thoughts and feelings with greater accuracy, variety, and appeal, facilitating a deeper connection with our audience
10+ Synonym Examples For Kids
- Happy – Cheerful
- Happy means feeling joy or pleasure.
- Cheerful means showing happiness through actions or expressions.
- Fast – Quick
- Fast means moving with great speed.
- Quick means doing something with speed or in a short time.
- Big – Huge
- Big means of a large size or extent.
- Huge means very big, especially larger than normal.
- Cold – Chilly
- Cold means having a low temperature.
- Chilly means noticeably cold, making you feel slightly cold.
- Easy – Simple
- Easy means not hard to do or understand.
- Simple means easily understood or done, presenting no difficulty.
- Funny – Hilarious
- Funny means causing laughter or amusement.
- Hilarious means extremely funny, causing loud amusement.
- Strong – Powerful
- Strong means having physical power or strength.
- Powerful means having great power or strength, more than just strong.
- Smart – Clever
- Smart means having or showing a quick-witted intelligence.
- Clever means skilled at doing or achieving something; intelligent.
- Sad – Unhappy
- Sad means feeling sorrow or unhappiness.
- Unhappy means not happy or cheerful; sad.
- Small – Tiny
- Small means of a size that is less than normal or usual.
- Tiny means very small, much smaller than usual.
10+ Synonym Example for Grade 1 Students:
- Big – Large
- “Big” means something is really huge.
- “Large” is another way to say something is big or huge.
- Hot – Warm
- “Hot” means something feels very heaty, like the sun.
- “Warm” is a softer heat, like a cozy blanket.
- Cold – Chilly
- “Cold” means something feels like ice or snow.
- “Chilly” is another word to say it’s a little bit cold.
- Happy – Glad
- “Happy” means feeling really good inside, like when you play.
- “Glad” is another way to say you’re feeling happy.
- Sad – Unhappy
- “Sad” means feeling down or not happy.
- “Unhappy” is another word for feeling sad.
- Fast – Quick
- “Fast” means moving really speedy, like a race car.
- “Quick” is another word to say something is fast.
- Slow – Sluggish
- “Slow” means not fast, like a turtle walking.
- “Sluggish” means moving slow or not quick.
- Funny – Silly
- “Funny” means something makes you laugh.
- “Silly” is another word for being funny or goofy.
- Hard – Tough
- “Hard” means something is not easy to do.
- “Tough” is another way to say something is hard.
- Soft – Gentle
- “Soft” means something feels nice to touch, like a pillow.
- “Gentle” is another word to describe something soft or delicate.
10+ Synonym Example for Grade 2 Students:
- Nice – Kind
- Nice means being pleasant or enjoyable.
- Kind is when you are good and caring to others.
- Clean – Spotless
- Clean means there is no dirt or mess.
- Spotless means something is so clean, there’s not even a small spot of dirt.
- Tall – Giant
- Tall means having more height than average.
- Giant means being very tall, like a big tree.
- Short – Little
- Short means not tall or having less height.
- Little is another way to say something is small or short, like a small toy.
- Bright – Shiny
- Bright means having a lot of light or color.
- Shiny means something reflects light, like a sparkling diamond.
- Loud – Noisy
- Loud means making a lot of sound.
- Noisy is when there’s a lot of unwanted sound, like a noisy street.
- Quiet – Silent
- Quiet means making little or no noise.
- Silent means there is no sound at all, like when it’s very quiet at night.
- Good – Great
- Good means something is nice or enjoyable.
- Great means something is even better than good, like a great day at the park.
- Light – Featherlight
- Light means not heavy.
- Featherlight means very light, like a feather.
- Soft – Fluffy
- Soft means easy to press, like a soft pillow.
- Fluffy means something is very soft and light, like a cloud or a fluffy bunny.
10+ Synonym Example for Middle School Students
- Scared – Frightened
- Scared means feeling fear or anxiety.
- Frightened means feeling afraid or anxious about a possible or probable situation.
- Funny – Humorous
- Funny means causing laughter or amusement.
- Humorous means characterized by humor; funny.
- Easy – Simple
- Easy means achieved without great effort; presenting few difficulties.
- Simple means straightforward and uncomplicated.
- Big – Large
- Big means of considerable size or extent.
- Large also means of considerable or relatively great size, extent, or capacity.
- Small – Tiny
- Small means of a size that is less than normal or usual.
- Tiny means very small.
- Angry – Mad
- Angry means feeling or showing strong annoyance, displeasure, or hostility.
- Mad means very angry.
- Tired – Exhausted
- Tired means in need of sleep or rest; weary.
- Exhausted means drained of one’s physical or mental resources; very tired.
- Neat – Tidy
- Neat means arranged in an orderly, tidy way.
- Tidy means arranged neatly and in order.
- Strong – Powerful
- Strong means having the power to move heavy weights or perform other physically demanding tasks.
- Powerful means having great power or strength.
- Weak – Frail
- Weak means lacking the power to perform physically demanding tasks; lacking physical strength and energy.
- Frail means physically weak and delicate.
10+ Synonym Example for High School Students
- Understand – Comprehend
- Understand means to grasp the meaning of something.
- Comprehend implies a deeper level of understanding, often including the ability to analyze and integrate knowledge.
- Explain – Elucidate
- Explain means to make something clear or easy to understand.
- Elucidate suggests providing a very clear, detailed explanation that makes complex ideas understandable.
- Study – Investigate
- Study refers to the act of learning about a subject, usually by reading or practicing.
- Investigate implies a more in-depth examination or research to discover facts or truths.
- Difficult – Challenging
- Difficult implies something is not easy to do, requiring effort.
- Challenging suggests that, although something is difficult, it is engaging and can be overcome with effort and determination.
- Teacher – Educator
- Teacher refers to someone who instructs students in a school.
- Educator suggests a broader role, including both teaching and other aspects of guiding and inspiring students in their learning and personal development.
- Homework – Assignment
- Homework refers to tasks assigned to students by their teachers to be completed outside of class.
- Assignment can refer to any task or work given to someone as part of their job or studies, not just homework.
- Test – Examination
- Test is a general term for a set of questions or exercises evaluating a student’s knowledge or skills.
- Examination suggests a more formal or comprehensive test, often covering a broader subject area.
- Idea – Concept
- Idea refers to a thought or suggestion as to a possible course of action.
- Concept suggests a more developed idea, often abstract and part of a larger theoretical framework.
- Class – Course
- Class refers to a group of students who meet at set times to study a subject.
- Course refers to the entire program of study covering a specific subject or topic, often over a semester or an academic year.
- Project – Endeavor
- Project usually refers to a piece of school work or research that requires planning and is designed to achieve a particular aim.
- Endeavor suggests a serious attempt or effort to achieve something, often something new or challenging.
10+ Synonym Example for College Students
- Analyze – Scrutinize
- Analyze means to examine something in detail to understand it better or to draw conclusions.
- Scrutinize implies a more thorough or critical examination, often to find faults or key details.
- Thesis – Dissertation
- Thesis generally refers to a major piece of written work required for a degree, especially at the master’s level.
- Dissertation is typically used to describe a lengthy, formal document that argues in defense of a particular thesis, especially for a doctoral degree.
- Lecture – Presentation
- Lecture refers to an educational talk to an audience, especially students in a university or college.
- Presentation can imply any form of introduction of information to an audience, often involving digital media support and not limited to academic settings.
- Seminar – Workshop
- Seminar usually refers to a class at a college or university in which a topic is discussed by a teacher and a small group of students.
- Workshop implies a more interactive session focusing on practical work or discussion in a particular field or subject.
- Internship – Apprenticeship
- Internship refers to a temporary position with an emphasis on on-the-job training rather than merely employment, often for students or recent graduates.
- Apprenticeship is a system of training a new generation of practitioners of a trade or profession with on-the-job training and often some accompanying study.
- Scholarship – Grant
- Scholarship is financial support awarded to a student, based on academic achievement or other criteria, to pursue further education.
- Grant generally refers to a sum of money given by an organization, especially a government, for a particular purpose such as research or education.
- Curriculum – Syllabus
- Curriculum refers to the overall content taught in an educational system or a course.
- Syllabus outlines the subjects or topics covered in a course or at an educational institution.
- Tutor – Mentor
- Tutor typically means someone who gives individual, or in some cases small group, instruction.
- Mentor implies a more experienced person guiding someone less experienced, often in a broader developmental sense beyond academic instruction.
- Degree – Qualification
- Degree refers to the rank conferred by a college or university after the completion of a course of study or after having achieved an academic achievement.
- Qualification generally means the attainment of a certain standard or level, especially in terms of job requirements, which can include degrees but also encompasses certificates, diplomas, or professional titles.
- Research – Inquiry
- Research refers to the systematic investigation into and study of materials and sources to establish facts and reach new conclusions.
- Inquiry often means a process of asking questions to gain information, with a broader scope that can include but is not limited to formal research.
Importance of Synonyms
Synonyms are words or phrases that mean exactly or nearly the same as another word or phrase in the same language. They play a crucial role in the English language and communication overall. Understanding and using synonyms effectively can enrich language skills, enhance writing, and improve comprehension. Here are several reasons why synonyms hold significant importance:
Enriches Vocabulary
Using synonyms expands one’s vocabulary. A rich vocabulary allows for more precise and varied expression. It enables individuals to communicate more effectively, as they can choose words that best fit the context of their message.
Enhances Writing
- Avoids Repetition: Synonyms help avoid repetition in writing, making content more engaging and readable. Instead of using the same word repeatedly, one can use synonyms to introduce variety.
- Improves Style and Tone: The choice of words can significantly affect the style and tone of writing. Synonyms allow writers to adjust their language to suit different audiences and purposes.
Facilitates Clear Communication
Different contexts and audiences may require different levels of language. Synonyms enable speakers and writers to tailor their language appropriately, ensuring that their message is understood clearly. This is especially important in diverse settings where clarity and precision are crucial.
Aids in Learning and Teaching
For educators and students, synonyms are valuable tools. They help in teaching language and comprehension skills, assisting students in understanding that words can have similar meanings but slight differences in connotation and usage.
Boosts Creative Expression
In creative writing and poetry, synonyms are essential for evoking specific feelings, images, or ideas. They enrich the text, making it more vivid and expressive.
Improves Reading Comprehension
Understanding synonyms enhances reading comprehension. It enables readers to grasp the meaning of texts more fully, as they can recognize the significance of similar words used in different contexts.
Essential for SEO and Digital Content Creation
In the digital age, synonyms are vital for search engine optimization (SEO). Using various keywords that mean the same thing can help content rank higher on search engine results pages, making it more likely to be seen by the target audience.
How to Use a Synonym in Paraphrasing
Paraphrasing is a very important process a writer or a researcher must do to prevent any issues in the reviewing process. If you need various examples of synonyms or lists of synonyms, you may use the list above to help you out.
Step 1: Outline and Break the Sentence Down To its Elements
Begin choosing a sentence you want to paraphrase and create a sentence outline with all its elements. Be sure to dissect and break down each part of the sentence and figure out each part’s purpose.
Step 2: Try to Check Which Words You Want to Paraphrase
After you have broken down and outlined the overall sentence structure, you must now decide which words and parts of the sentence you will paraphrase. You can highlight each word you want to change and keeps to prevent confusion during the paraphrasing process.
Step 3: Paraphrase the Words with Synonyms
Each word has a synonym associated with the word, so be sure to paraphrase each word with the closest synonym possible under the correct context, tone, or theme. You may also alter the form of the word and swap the positions of each part of the sentence.
Step 4: Paraphrase the Sentence
After you have chosen the proper synonyms of the words you want to change in the sentence, completely paraphrase the whole sentence structure. If you want to paraphrase more than one sentence, you may repeat steps 1 to 4 until you are satisfied with the results.
FAQs
When Should Synonyms Be Used?
Synonyms should be used to avoid repetition, enhance vocabulary, adjust the tone, and ensure clarity in writing and speaking. They are especially useful in creative writing, academic papers, and digital content to engage the audience more effectively and improve SEO.
Synonym vs. antonym; what is the difference between a synonym and an antonym?
Synonyms are words that have definitions, meanings, or symbolism related to a specific word the person chooses. The antonym is the literal juxtaposition and antithesis of the synonym having the opposite definition, meaning, or symbolism of a word.
Why do researchers and technical writers need to know how to use synonyms in their writing?
Plagiarism is a very serious issue that people can face when they write for a living. Synonyms will allow the person to write a statement with a similar or the same thought without the risk of plagiarism or obtaining a plagiarism strike and are considered a hard skill that people must include in their skill pool.
What Are 10 Examples of Synonyms Words?
- Happy – Joyful: Both express a state of being pleased or content.
- Sad – Melancholy: These words describe feelings of sorrow or unhappiness.
- Fast – Quick: Both indicate high speed or rapid movement.
- Easy – Simple: These synonyms convey the lack of difficulty.
- Hard – Difficult: Both words describe something that requires a lot of effort.
- Big – Large: Used to describe something of considerable size.
- Small – Tiny: Both terms refer to something of minimal size.
- Smart – Intelligent: Describe someone who is quick to learn or understand.
- Begin – Commence: Both mean to start something.
- End – Conclude: These words are used to indicate the cessation of an action or event.
What is a thesaurus, and how does it relate to synonyms?
A thesaurus is a type of book that allows the person to look up various synonyms of a word the person is unfamiliar with. Not only will the thesaurus act as a handy physical or digital reference for synonyms, but this book will also include the antonyms of the chosen word.
Synonyms are words that have the same or similar meanings to a word the person is searching for. Proper usage of synonyms will allow the person to create varied statements that can relay the same information but have different words and sentence structures. If one wants to augment and improve their writing skills, then one should learn how to utilize synonyms in their work.