99+ Adverb Examples
An adverb, an essential pillar of English grammar, dynamically modifies verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs, infusing sentences with precision and flair. By answering questions like “how?”, “when?”, and “where?”, adverbs add layers of meaning, enhancing clarity. Dive deep into the realm of adverbs with this guide, exploring its types, understanding its usage through Adverb examples, and mastering the art of incorporating them effectively in your writing. This comprehensive resource is your key to unlocking the dynamic world of adverbs.
What is an Adverb? – Definition
An adverb is a part of speech that modifies (describes) verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. Essentially, it provides additional information about how, when, where, why, or to what extent an action is performed.
What is an example of an Adverb?
Consider the sentence: “She sang beautifully.” Here, “beautifully” is an adverb because it describes how she sang, modifying the verb “sang“.
100 Adverb Examples

Adverbs infuse depth and detail into our sentences, painting a clearer picture of the actions or states they describe. From manner and frequency to place and degree, adverbs diversify our expression palette, making communication vivid and precise. Dive into the captivating world of adverbs with these illustrative examples.
- Quickly – He ran quickly to catch the bus.
- Softly – She whispered softly in his ear.
- Early – The flowers bloomed early this year.
- Rarely – He rarely eats sweets.
- Lazily – The cat sat lazily on the windowsill.
- Abruptly – The movie ended abruptly.
- Gracefully – She dances gracefully.
- Annually – They visit their grandparents annually.
- Gently – The water flows gently down the stream.
- Attentively – The child listened attentively to the story.
- Beautifully – She sings beautifully.
- Rapidly – The news spread rapidly.
- Always – They always have dinner at seven.
- Often – She is often late for meetings.
- Brightly – The sun shines brightly in the summer.
- Sadly – The story was sadly true.
- Correctly – He answered the question correctly.
- Unexpectedly – The train arrived unexpectedly early.
- Longingly – He looked at her longingly.
- Happily – They lived happily ever after.
- Sweetly – The bird sang sweetly.
- Nearly – He nearly missed the flight.
- Heavily – The rain fell heavily last night.
- Hard – She works hard to support her family.
- Relentlessly – The athlete trained relentlessly.
- Seldom – He seldom reads novels.
- Quietly – She quietly entered the room.
- Loudly – The fireworks exploded loudly.
- Easily – He easily solved the puzzle.
- Daily – The mail arrives daily.
- Freely – They freely expressed their opinions.
- Persistently – The cat meowed persistently.
- Carefully – He carefully handled the delicate artifact.
- Smoothly – The car drives smoothly.
- Politely – She politely declined the offer.
- Biannually – The event occurs biannually.
- Gently – The tree swayed gently in the wind.
- Angrily – He responded angrily to the criticism.
- Sometimes – She sometimes forgets her keys.
- Fiercely – The wind howled fiercely.
- Privately – They discussed the matter privately.
- Exceptionally – The team played exceptionally well.
- Elegantly – She dressed elegantly for the party.
- Wonderfully – The flowers smelled wonderfully.
- Slowly – The door opened slowly.
- Blankly – He stared blankly at the wall.
- Continuously – The clock ticks continuously.
- Unexpectedly – The letter arrived unexpectedly.
- Fluently – She spoke fluently in five languages.
- Eagerly – The students answered eagerly.
- Divinely – The dessert tasted divinely.
- Boldly – He boldly voiced his disagreement.
- Impatiently – She impatiently waited for her turn.
- Endlessly – The river flows endlessly.
- Successfully – He completed the marathon successfully.
- Firmly – She firmly believed in her dreams.
- Highly – The bird flew highly above the clouds.
- Softly – The music played softly in the background.
- Clearly – He clearly stated the instructions.
- Joyfully – They celebrated joyfully.
- Silently – He silently disagreed.
- Brightly – The stars shone brightly.
- Briskly – She briskly walked through the park.
- Silently – The snow fell silently.
- Constantly – The phone rang constantly.
- Deeply – He looked deeply into her eyes.
- Suddenly – The car stopped suddenly.
- Locally – They lived locally.
- Tragically – The novel ended tragically.
- Secretly – She secretly admired him.
- Automatically – The process works automatically.
- Loudly – They cheered loudly for the team.
- Violently – The waves crashed violently against the shore.
- Regularly – He regularly exercises.
- Peacefully – The old man peacefully passed away.
- Naturally – She naturally has curly hair.
- Enthusiastically – They enthusiastically participated.
- Passionately – The singer performed passionately.
- Simply – She simply couldn’t understand.
- Knowledgeably – The teacher spoke knowledgeably.
- Loudly – The baby cried loudly.
- Sincerely – She sincerely apologized.
- Punctually – The guests arrived punctually.
- Seriously – He seriously considered the offer.
- Previously – They previously met in Paris.
- Mysteriously – The wind whispered mysteriously.
- Generally – He generally wakes up early.
- Perfectly – The computer works perfectly.
- Obviously – She obviously knew the answer.
- Definitely – The party was definitely fun.
- Instantly – He instantly regretted his words.
- Fully – They fully support the cause.
- Completely – The room was completely dark.
- Barely – She barely recognized him.
- Wildly – They danced wildly.
- Proudly – She proudly displayed her medal.
- Especially – The dessert was especially good.
- Doubtfully – She looked at him doubtfully.
- Directly – He walked directly to his room.
- Delightfully – The room was delightfully decorated.
Adverb Clause Examples

An adverb clause is a group of words that functions as an adverb in a sentence. It often starts with a subordinating conjunction and provides details about the main clause, like when, where, or why something happened. Here are unique examples:
- Although she studied hard – Although she studied hard, she didn’t pass the exam.
- Before the sun rises – He starts working before the sun rises.
- Whenever it rains – Whenever it rains, she feels sad.
- Unless you study – You will fail unless you study.
- As long as she lives – She’ll remember this moment as long as she lives.
Adverb Examples Sentences

Adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs to provide more detail or clarity. These words help specify how, when, or where an action is performed. See more adverb sentence examples
- Tomorrow – We will go to the museum tomorrow.
- Frequently – Sarah frequently visits her grandmother.
- Downstairs – The kids ran downstairs.
- Too – The coffee was too hot.
- Almost – She almost missed the bus.
Conjunctive Adverb Examples

Conjunctive adverbs connect two independent clauses, showing the relationship between them, like contrast, sequence, or cause-and-effect.
- However – She wanted to join the team; however, she had a conflicting schedule.
- Therefore – He didn’t study; therefore, he failed.
- Moreover – The book is thrilling; moreover, it’s a true story.
- Otherwise – Finish your work; otherwise, you’ll be punished.
- Meanwhile – She started making dinner; meanwhile, he set the table.
Adverbial Phrase Examples

Adverbial phrases are groups of words that act as adverbs, modifying verbs to tell when, where, how, or to what extent an action is performed.
- With great enthusiasm – She accepted the offer with great enthusiasm.
- In a hurry – He left in a hurry.
- Every single day – He practices piano every single day.
- At a snail’s pace – The meeting progressed at a snail’s pace.
- With all her heart – She sang with all her heart.
Adjectives and Adverbs Examples

Adjectives describe or modify nouns and pronouns, whereas adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. It’s essential to distinguish between them. See more Adjective & Verbs Examples
- Beautiful (Adjective) – That is a beautiful painting. Beautifully (Adverb) – She sang beautifully.
- Loud (Adjective) – The loud music hurt my ears. Loudly (Adverb) – He spoke loudly.
- Quick (Adjective) – He has a quick mind. Quickly (Adverb) – She runs quickly.
- Happy (Adjective) – They look so happy. Happily (Adverb) – Kids played happily outside.
- Flawless (Adjective) – Her performance was flawless. Flawlessly (Adverb) – The software runs flawlessly.
Adverbial Manner Examples

Adverbs of manner describe how an action is performed. They often answer the question ‘how?’
- Carefully – He placed the vase carefully on the shelf.
- Loudly – The audience clapped loudly.
- Gracefully – The dancer moved gracefully across the stage.
- Rudely – He interrupted rudely during the discussion.
- Efficiently – The team worked efficiently to meet the deadline.
Adverb of Place Examples

Adverbs of place describe where the action is happening. They answer the question ‘where?’
- Here – Come sit here.
- Everywhere – There were papers scattered everywhere.
- Anywhere – I can’t find my glasses anywhere.
- Outside – The children are playing outside.
- Underground – The subway runs underground.
Adverb of Purpose Examples

Adverbs of purpose explain why an action is done. They usually come after the main clause and are introduced by conjunctions like so, so that, in order that.
- So that – She woke up early so that she could catch the bus on time.
- In order to – He saved money in order to buy a new car.
- Lest – They whispered lest they should wake the baby.
- For fear that – He locked the door for fear that thieves might enter.
- So – She studied hard so she could pass the exam.
Adverb of Frequency Examples

Adverbs of frequency describe how often something occurs. They answer the question ‘how often?’
- Always – He always drinks coffee in the morning.
- Sometimes – I sometimes read before bed.
- Rarely – She rarely eats chocolate.
- Often – They often go for a walk in the park.
- Never – He never smokes.
Adverb of Time Examples

Adverbs of time provide information about when a certain action took place. They answer the question ‘when?’
- Now – I need the report now.
- Yesterday – She arrived yesterday.
- Later – We can discuss it later.
- Soon – The movie will start soon.
- Today – He will call you today.
Adverb Prepositional Phrase Examples

These are prepositional phrases that function as adverbs, answering questions like ‘how?’, ‘when?’, ‘where?’, etc.
- In a hurry – She left in a hurry.
- At midnight – Ghosts appear at midnight.
- With a smile – He greeted me with a smile.
- For a while – Stay with me for a while.
- On time – She always arrives on time.
Adverbials of Time Examples

Adverbials of time specify the timing of the action in the sentence. They can be single words, phrases, or even clauses.
- In the evening – We relax in the evening.
- During the summer – They visited us during the summer.
- Before sunset – Be home before sunset.
- After the rain stops – We’ll leave after the rain stops.
- Once a year – We visit the theme park once a year.
Relative Adverb Examples

Relative adverbs introduce relative clauses and often refer to a time, place, or reason.
- When – Do you remember the day when we first met?
- Where – This is the house where I grew up.
- Why – The reason why she left remains a mystery.
Examples of Adverbs and Verbs

Here are Examples of Adverbs & Verbs, the adverb modifies the verb, giving more information about the action.
- Whispered – He whispered softly in her ear.
- Runs – She runs quickly.
- Writes – He writes neatly.
- Danced – She danced gracefully.
- Spoke – He spoke loudly to be heard.
Adverb Examples for Kids

These are basic adverbs for kids that are suitable for introducing the concept to children.
- Fast – He runs fast.
- Loud – The dog barks loud.
- Here – Come sit here.
- Now – Do it now.
- Always – I always brush my teeth.
Adverb Examples for 3rd Grade

These are slightly more advanced than the basic examples but still quite simple and straightforward. See more Adverb Examples for 3rd Grade.
- Quietly – She reads quietly in the corner.
- Sometimes – I sometimes eat cereal for breakfast.
- Outside – Let’s play outside.
- Today – We have a test today.
- Often – He often visits his grandmother.
Adverb Examples for 4th Grade

4th grade level adverbs can be a bit more varied, offering more depth to sentences.
- Rarely – She rarely watches TV.
- Eagerly – He eagerly opened his present.
- Nearly – We nearly missed the bus.
- Slowly – The turtle moved slowly.
- Yesterday – I saw him yesterday at the park.
Adverb Examples for 5th Grade

By 5th grade, students can handle more complex adverbs that provide a richer understanding of actions. See more Adverb Examples for 5th Grade
- Frequently – She visits the library frequently.
- Desperately – He desperately wanted to win.
- Eventually – I’ll finish my homework eventually.
- Suddenly – It started raining suddenly.
- Probably – We’ll probably go to the zoo tomorrow.
Adverb Sentence Examples with Underline

Here, the adverbs with underline for clarity.
- She sings beautifully.
- The students always listen to the teacher.
- He never forgets his keys.
- The bird flew upward.
- They often travel during the summer.
Types of Adverbs
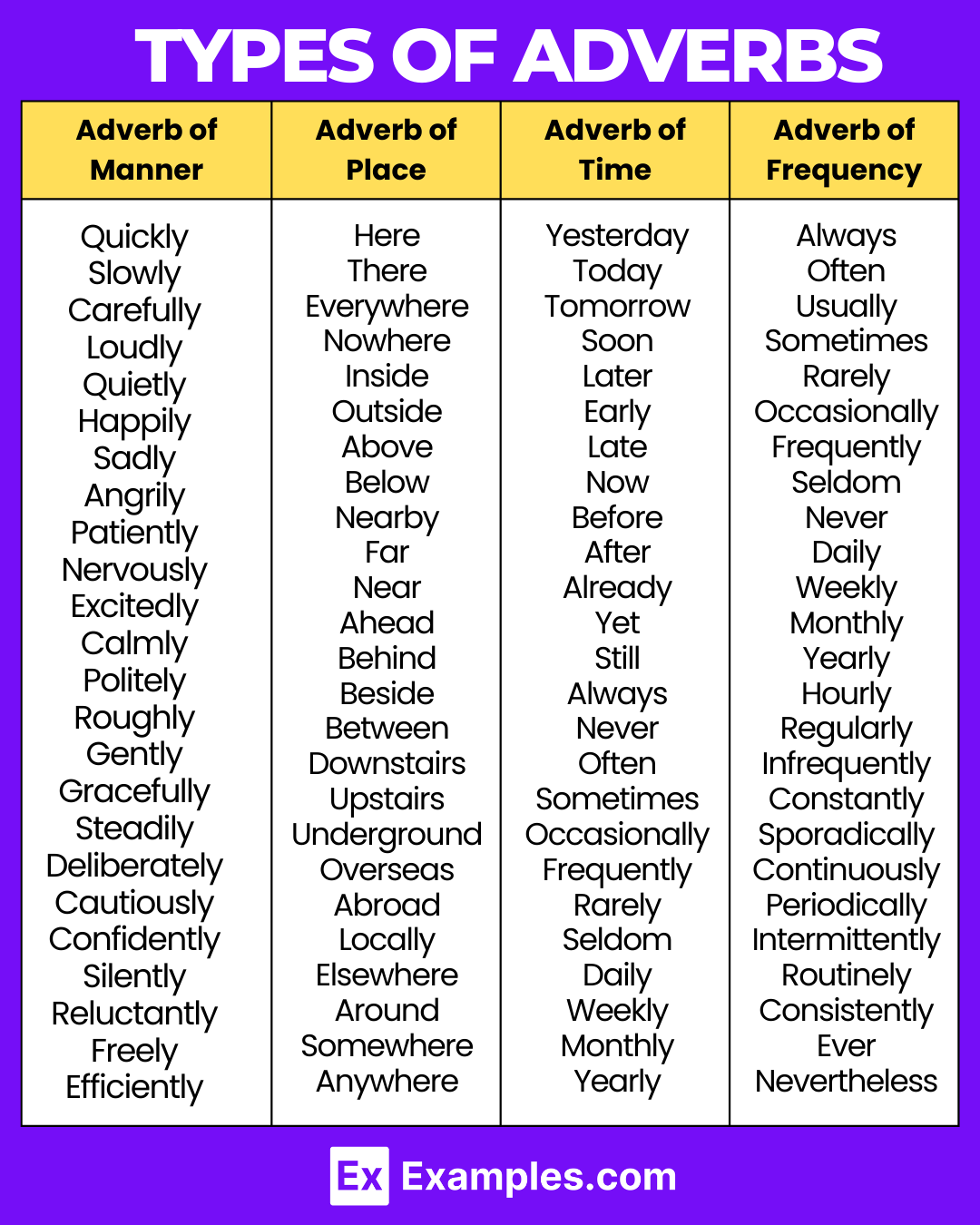
Adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs, providing greater detail to the action or quality they describe. They are essential components in English grammar. Let’s delve into the main types:
- Adverbs of Manner – Answer the question “how?”
- Examples: quickly, softly, loudly, smoothly.
- Sentence: She sang beautifully.
- Adverbs of Frequency – Answer the question “how often?”
- Examples: always, often, sometimes, rarely, never.
- Sentence: He rarely eats meat.
- Adverbs of Time – Answer the question “when?”
- Examples: now, today, yesterday, soon, late.
- Sentence: We will meet tomorrow.
- Adverbs of Place – Answer the question “where?”
- Examples: here, there, everywhere, nowhere, somewhere.
- Sentence: The cat is hiding somewhere.
- Adverbs of Degree – Modify adjectives or adverbs, indicating intensity or degree.
- Examples: very, too, quite, almost, absolutely.
- Sentence: The movie was too long.
- Adverbs of Certainty – Express how sure we are about an action or event.
- Examples: definitely, probably, certainly, possibly.
- Sentence: He will probably come to the party.
Adverbs Vs Adjectives
While both adverbs and adjectives describe more about a word, their functions and applications differ. Let’s break down these differences:
- Function:
- Adverbs: They modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. They provide more information about how, when, where, or to what extent an action is performed.
- Adjectives: They describe or modify nouns or pronouns. They give more information about a person, place, thing, or idea.
- Questions Answered:
- Adverbs: How? When? Where? To what extent?
- Adjectives: What kind? Which one? How many?
- Examples:
- Adverbs: She runs quickly. (Describes how she runs)
- Adjectives: She has a quick mind. (Describes the noun – mind)
- Position:
- Adverbs: They can be placed at the beginning, middle, or end of a sentence.
- Example: Sometimes we watch movies. / We sometimes watch movies. / We watch movies sometimes.
- Adjectives: Typically positioned before the noun or pronoun they modify.
- Example: She wore a beautiful dress.
- Adverbs: They can be placed at the beginning, middle, or end of a sentence.
- Form:
- Adverbs: Many adverbs are formed by adding “-ly” to an adjective.
- Example: quick (adjective) becomes quickly (adverb)
- Adjectives: They don’t have a specific ending. Some common adjective endings include -ous, -ful, -ish, -al, but many don’t follow a pattern.
- Adverbs: Many adverbs are formed by adding “-ly” to an adjective.
- Comparatives and Superlatives:
- Adverbs: Not all adverbs can have comparative and superlative forms. Those that do often use ‘more’ and ‘most’.
- Example: efficiently, more efficiently, most efficiently
- Adjectives: They can be in the positive, comparative, or superlative degree.
- Example: happy, happier, happiest
- Adverbs: Not all adverbs can have comparative and superlative forms. Those that do often use ‘more’ and ‘most’.
By understanding the distinctions between adverbs and adjectives, you can ensure that you’re using each word type appropriately and effectively in your sentences.
What is the Function of an Adverb?
At its core, an adverb is a modifier that provides additional meaning to a verb, another adverb, an adjective, or an entire sentence. The main functions of adverbs include:
- Describing Action: They give more information about how an action is performed.
- Example: She reads quietly.
- Indicating Frequency: They explain how often an action occurs.
- Example: I always drink coffee in the morning.
- Highlighting Time: They reveal when an action happened.
- Example: He will leave tomorrow.
- Describing Place: They illustrate where an action occurs.
- Example: The cat is sitting upstairs.
- Modifying Adjectives: They can intensify or weaken an adjective.
- Example: The movie was incredibly boring.
- Modifying Other Adverbs: They can adjust or modify another adverb.
- Example: He runs very quickly.
- Expressing Certainty or Doubt: They can convey the degree of certainty concerning an action.
- Example: She will probably come to the party.
How to Identify an Adverb
Identifying an adverb in a sentence can sometimes be challenging, but here are steps to assist you:
- Look for Common Endings: Many adverbs end in “-ly”, like quickly, softly, and loudly.
- Ask the Right Questions: Determine if a word answers “how?”, “when?”, “where?”, “in what manner?”, or “to what extent?”.
- Check If It Modifies a Verb, Adjective, or Another Adverb: If it does, it’s likely an adverb.
- Look for Words that Talk About Frequency: Words like always, often, sometimes, rarely, etc.
- Identify Adverbs of Certainty: Words like probably, definitely, and possibly can also be adverbs.
How to Use Adverb (When and Where) – Step by Step Guide
Using adverbs effectively can enrich your writing and speech. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to properly use them:
- Determine the Need for an Adverb: Before you use an adverb, ask yourself if it’s necessary. Does it add meaningful information or clarity to the sentence?
- Place It Close to the Word It Modifies: For clarity, the adverb should be close to the verb, adjective, or adverb it’s modifying.
- Example: She gently closed the door.
- Avoid Redundancy: Ensure the adverb isn’t just repeating information.
- Avoid: She whispered quietly. (Here, “whispered” already implies a quiet action.)
- Use Adverbs to Convey Emotion or Tone: They can help in expressing the emotional context of a statement.
- Example: I am completely thrilled with the news!
- Placement for Adverbs of Frequency: Typically, they should be placed before the main verb but after auxiliary verbs.
- Example: She always sings. BUT She has always been singing.
- Adverbs Modifying Adjectives or Other Adverbs: Place them right before the word they modify.
- Example: It’s an incredibly exciting game.
- Avoid Overuse: While adverbs can be powerful, overusing them can weaken your writing or speech. Ensure each adverb serves a purpose.
By understanding and practicing the use of adverbs, you can make your sentences more detailed and expressive, adding depth to your communication.
How to Pronounce Adverbs
Adverbs are a diverse category, and their pronunciation is influenced by their roots, suffixes, and the regional accents in which they’re spoken. However, when dealing specifically with adverbs that derive from adjectives (particularly those ending in “-ly”), there are some patterns and tips that can help:
- Endings in “-ly”:
- Most adverbs formed from adjectives end in “-ly”. In general, this “-ly” is pronounced as “lee” or just “li”.
- Example: Quickly is pronounced as ‘kwik-lee’.
- Stress the Base:
- The stress typically falls on the base adjective rather than the “-ly” ending.
- Example: In beautifully, the stress is on ‘beaut-‘ and not on ‘-ly’.
- Transition Sounds:
- For adjectives ending in “-y”, replace the “y” with “-ily”.
- Example: Happy becomes happily, where “happ-” remains stressed.
- Practice with Audio Tools:
- Utilize pronunciation websites or apps like Forvo, HowToPronounce, or PronounceItRight. They provide native speaker a, which can be invaluable.
- Replicate Native Speakers:
- Listen to podcasts, movies, or music in English. Try to mimic the pronunciation of adverbs you hear. This not only helps with pronunciation but also with intonation and rhythm.
Tips for Using Adverbs in English
Adverbs can enrich your sentences, but they must be used judiciously to ensure clarity and prevent redundancy. Here are some tips:
- Position Matters:
- Adverbs can be placed at the beginning, middle, or end of a sentence, but the position can change the emphasis or even the meaning.
- Example: Sometimes, I eat ice cream (general statement) vs. I eat ice cream sometimes (specific habit).
- Avoid Overuse:
- Don’t clutter your sentences with unnecessary adverbs. A well-chosen verb can often stand on its own.
- Example: Instead of “He ran quickly,” consider “He sprinted.“
- Choose Specific Adverbs:
- The more precise your adverb, the clearer your meaning will be.
- Example: Instead of saying “She sang nicely,” you might say, “She sang melodiously.”
- Adverb vs. Adjective:
- Ensure you’re using an adverb, not an adjective. Remember, adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, and other adverbs, while adjectives modify nouns.
- Common Mistake: “She feels badly” should be “She feels bad.”
- Comparative and Superlative Forms:
- Be cautious when using comparative (more, less) and superlative (most, least) forms with adverbs.
- Example: “She sings more beautifully” is correct, but “She sings more prettily” sounds awkward.
- Split Infinitives:
- Traditional grammar rules say not to split infinitives with an adverb (e.g., “to boldly go”). However, in modern English, this rule is more flexible. Ensure the sentence flows well and retains clarity.
- Interact with Native Speakers:
- The best way to get a feel for adverb usage is to communicate with native English speakers, whether through conversation exchange platforms, language classes, or travel.
- Reading is Fundamental:
- Engage with diverse reading materials. Notice how authors use adverbs in literature, newspapers, and articles.
- Seek Feedback:
- If you’re learning English, ask teachers, peers, or language exchange partners for feedback on your adverb usage.
Remember, adverbs add color and depth to your sentences. With practice and attention to these guidelines, you’ll master the art of using them effectively in English.


