Although vs Even though – Meanings, Examples, Differences, Usage
In essence, while “Although” and “Even though” are often interchangeable, subtle differences exist in their formality and positioning within sentences. “Although” tends to be more formal and is typically placed at the beginning of a sentence, whereas “Even though” can appear at the beginning or within the sentence and is considered less formal than “Although”. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for effective communication, allowing writers to convey their ideas with clarity and precision. Whether navigating formal writing or casual conversation, grasping the subtleties between “although” and “even though” empowers effective communication across various contexts.
Although and Even though – Meanings
- “Although” is a conjunction used to introduce a contrast or concession in a sentence. It indicates that the statement following it contrasts with or acknowledges an unexpected or contrary fact to the preceding clause. “Although” is commonly employed to express a concession, presenting an idea that runs counter to the expectation set by the main clause. It signifies a relationship of opposition or contradiction between two clauses, often highlighting unexpected outcomes or circumstances in discourse.
- “Even though” also functions as a conjunction, serving a similar purpose to “although.” It introduces a subordinate clause that presents a contrast or concession to the main clause of the sentence. “Even though” emphasizes the persistence or strength of the concession, implying that despite the acknowledged contrary fact, the main clause remains true or valid. This conjunction conveys a sense of resilience or determination in the face of opposing circumstances, indicating that despite challenges or obstacles, the main statement still holds true.
Summary
How To Pronounce Although and Even though
- “Although” is pronounced as /ɔːlˈðoʊ/ with the stress on the first syllable, rhyming with “all-tho.”
- “Even though” is pronounced as /ˈiːvən ðoʊ/ with the stress on the first syllable of “even,” and “though” pronounced as /ðoʊ/, rhyming with “even tho.”
Differences Between Although and Even though
| Aspect | Although | Even though |
|---|---|---|
| Position in sentence | Typically used at the beginning of a sentence. | Can be used at the beginning or in the middle. |
| Formality | Considered more formal. | Slightly less formal than “although.” |
| Strength of concession | Standard level of concession. | Emphasizes persistence despite contrary facts. |
| Frequency of use | Commonly used in formal writing and speech. | More commonly used in informal contexts. |
| Flexibility | Less flexible in terms of placement within a sentence. | Offers more flexibility in placement. |
| Tone | May convey a slightly more formal or academic tone. | Often conveys a slightly less formal or conversational tone. |
How to Remember the Differences Between “Although” and”Even though”
- At the Beginning: “Although” is typically placed at the beginning of a sentence, while “Even though” can appear at the beginning or in the middle.
- Elegance vs. Flexibility: “Although” is often considered more formal, conveying a sense of elegance, while “Even though” offers more flexibility and can be used in informal contexts.
- Focus on Emphasis: “Even though” emphasizes persistence despite contrary facts, making it ideal for situations where resilience is highlighted.
When to use Although and Even though
Usage of “Although”:
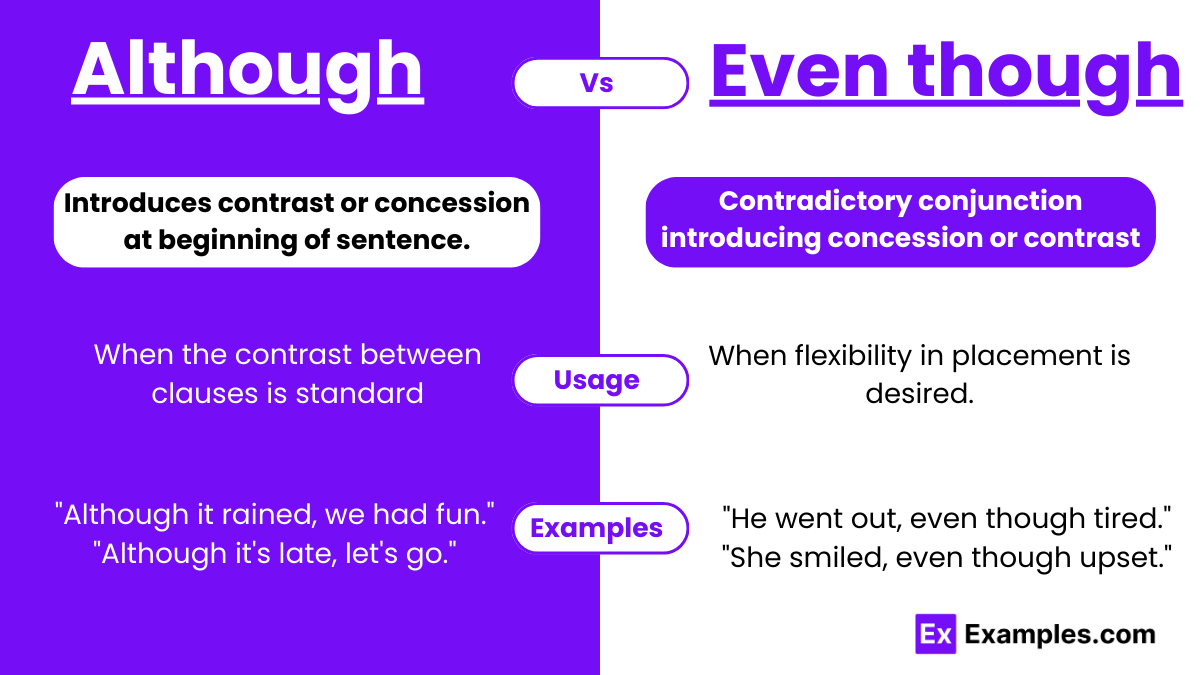
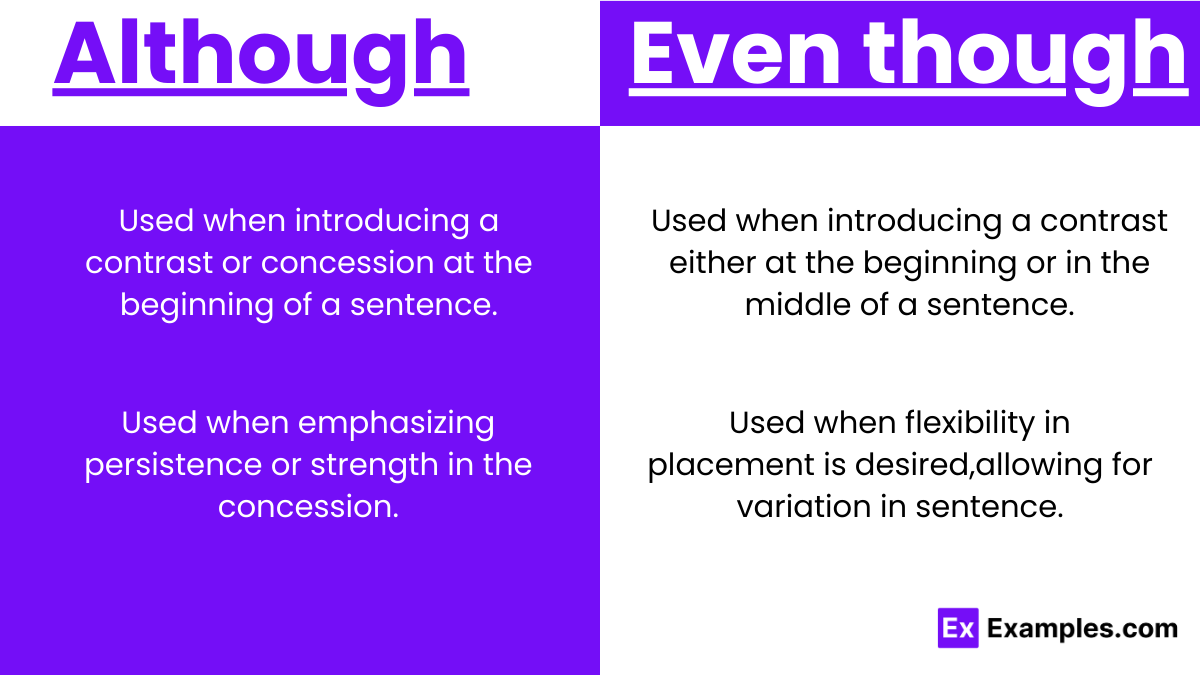
- When introducing a contrast or concession at the beginning of a sentence, especially in formal writing or speech.
- When aiming for a more formal tone or conveying a sense of elegance in the expression of contradictory ideas.
- When the contrast between clauses is standard or expected, without a need for additional emphasis on persistence or resilience.
Usage of “Even though”:
- When introducing a contrast or concession either at the beginning or in the middle of a sentence, suitable for both formal and informal contexts.
- When flexibility in placement is desired, allowing for variation in sentence structure and rhythm.
- When emphasizing persistence or strength in the concession, particularly in situations where resilience despite contrary facts is a key focus.
Although and Even though – Examples
 https://images.examples.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/Althought-vs-Even-though-5.png
https://images.examples.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/Althought-vs-Even-though-5.png
Examples of “Although”
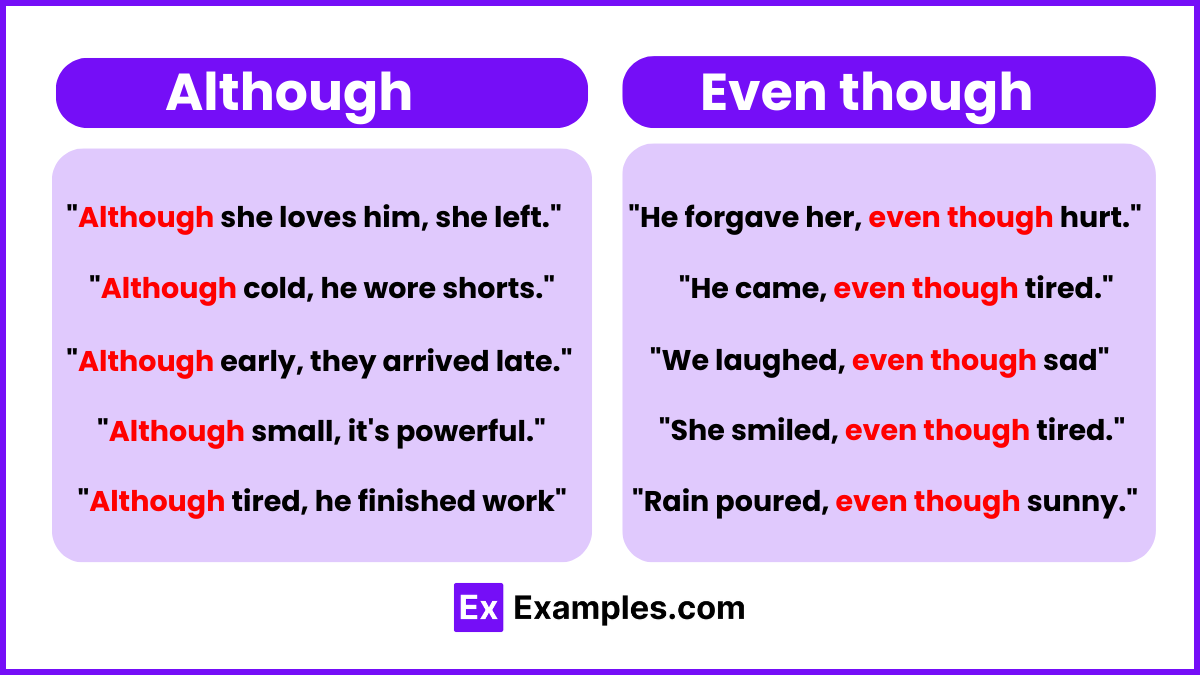
- Although it was raining, they decided to go for a hike.
- Although she was tired, she stayed up late to finish her project.
- Although the restaurant was crowded, they managed to find a table.
- Although he studied hard, he didn’t perform well on the exam.
- Although she had reservations, she agreed to attend the event.
Examples of “Even though”
- Even though it was his day off, he went into work to finish the project.
- He decided to go for a run, even though it was raining heavily.
- Even though she was afraid of heights, she went skydiving.
- Even though they missed the train, they still managed to arrive on time.
- She decided to pursue her dream career, even though it meant taking a pay cut.
Synonyms For Although and Even though
| “Although” | “Even though” |
|---|---|
| Though | Despite |
| Even if | In spite of |
| Notwithstanding | Even when |
| While | Regardless |
| Granted | Despite the fact that |
| However | Even in the event that |
| Yet | Albeit |
| Nevertheless | Despite the fact |
| Nonetheless | Even |
| In spite of that | Notwithstanding the fact that |
Exercise
Instructions: Fill in the blanks with the appropriate phrase, “Although” or “Even though,” to complete each sentence correctly.
- _______________ it was raining, they decided to go for a hike.
- _______________ it was his day off, he went into work to finish the project.
- _______________ she was tired, she stayed up late to finish her project.
- The restaurant was crowded. _______________, they managed to find a table.
- He studied hard. _______________, he didn’t perform well on the exam.
Answers:
- Although
- Even though
- Although
- Even though
- Although
FAQ’S
What is the rule for even though?
Always put ‘even though’ at the beginning of the subordinate clause.
Is there any difference between Although and Even though?
The word ‘although’ means in spite of something. The word ‘even though’ means despite the fact
What comes before even though?
“Even though” usually begins a dependent or subordinate clause.
Is there a comma after Although?
“Although” is a subordinating conjunction. If there’s another clause before “although,” you should put a comma before it.