Business Communication vs Personal Communication: : Difference Between, Examples, PDF
In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the contrasting worlds of Business Communication and Personal Communication. Business Communication is a structured, goal-oriented approach used within a professional setting, involving communication examples like formal reports, emails, and business meetings. Personal Communication, in contrast, occurs in informal, personal contexts and is often spontaneous, encompassing conversations with friends and family. Understanding the key differences in these communication styles is crucial for effective interactions in both personal and professional life. This guide aims to provide practical examples, illustrate the effects of each communication style, and offer solutions to common communication challenges.
Download Business Communication PDF
Download Personal Communication PDF
Difference Between Business Communication and Personal Communication
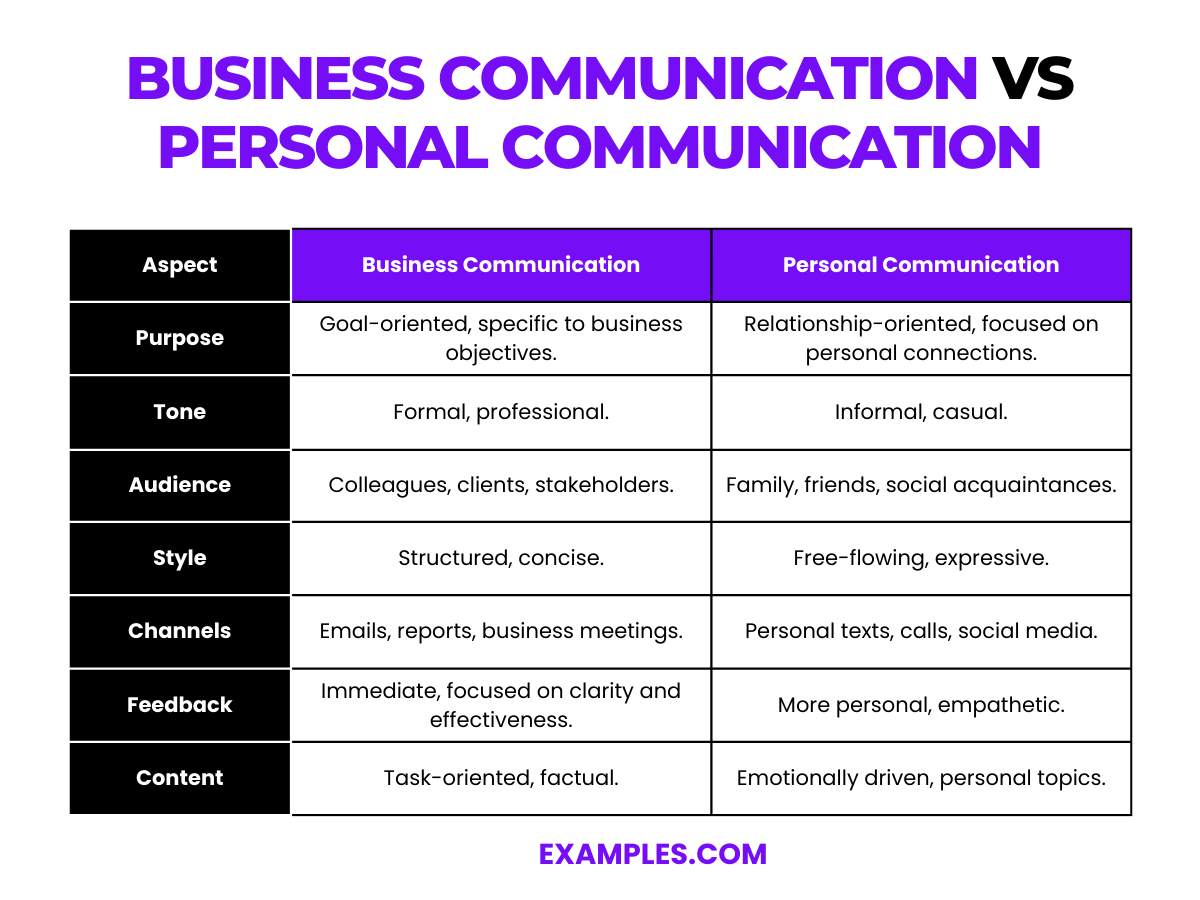 Business Communication and Personal Communication are two distinct realms of interaction, each with its own unique characteristics and contexts. Business Communication is typically formal, structured, and goal-oriented, occurring within professional settings and focused on efficient information exchange and decision-making. Personal Communication, on the other hand, is informal, often spontaneous, and revolves around personal relationships and casual interactions. It is flexible and emotionally driven. This comparison highlights the fundamental differences in purpose, style, tone, audience, and the typical channels used in each form of communication. Understanding these differences is crucial for navigating both personal and professional spheres effectively.
Business Communication and Personal Communication are two distinct realms of interaction, each with its own unique characteristics and contexts. Business Communication is typically formal, structured, and goal-oriented, occurring within professional settings and focused on efficient information exchange and decision-making. Personal Communication, on the other hand, is informal, often spontaneous, and revolves around personal relationships and casual interactions. It is flexible and emotionally driven. This comparison highlights the fundamental differences in purpose, style, tone, audience, and the typical channels used in each form of communication. Understanding these differences is crucial for navigating both personal and professional spheres effectively.
| Aspect | Business Communication | Personal Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Goal-oriented, specific to business objectives. | Relationship-oriented, focused on personal connections. |
| Tone | Formal, professional. | Informal, casual. |
| Audience | Colleagues, clients, stakeholders. | Family, friends, social acquaintances. |
| Style | Structured, concise. | Free-flowing, expressive. |
| Channels | Emails, reports, business meetings. | Personal texts, calls, social media. |
| Feedback | Immediate, focused on clarity and effectiveness. | More personal, empathetic. |
| Content | Task-oriented, factual. | Emotionally driven, personal topics. |
| Flexibility | Generally rigid, adheres to business norms. | Highly flexible, adapts to individual relationships. |
| Boundaries | Defined by professional roles and relationships. | Defined by personal boundaries and preferences. |
| Regulation | Guided by company policies and professional etiquette. | Guided by social norms and personal rapport. |
This table outlines the fundamental differences between Business Communication and Personal Communication, highlighting their distinct purposes, styles, and contexts. Understanding these differences is key to effective communication in both professional and personal settings.
10 Business Communication Examples
Business Communication is essential in professional settings, facilitating clear and effective exchange of information. Here are 10 examples along with causes and fixes:
- Emails: Efficient for quick communication but can cause misunderstandings. Clarity and conciseness are key.
- Meetings: Essential for collaboration, yet can be time-consuming. Effective planning and agenda-setting can fix this.
- Reports: Provide detailed information but can be overwhelming. Summarization and clear data presentation help.
- Presentations: Effective for conveying ideas, but poor design can distract. Focus on simplicity and relevance.
- Business Letters: Formal communication method, can be perceived as impersonal. Personalizing content can improve this.
- Memos: Quick and informative, but might be ignored. Ensuring relevance and brevity can enhance effectiveness.
- Corporate Newsletters: Great for updates, risk becoming monotonous. Engaging content and visuals can keep interest.
- Conference Calls: Facilitates remote communication, yet technical issues can hinder. Regular checks and preparedness are solutions.
- Social Media Posts: Good for branding, but can misinterpret. Clear, audience-appropriate language is essential.
- Feedback Sessions: Important for improvement, yet can be taken negatively. Constructive, balanced feedback is crucial.
10 Personal Communication Examples
Personal Communication encompasses a variety of everyday interactions that are informal, spontaneous, and often emotional. This type of communication is crucial for building and maintaining personal relationships, expressing feelings, and sharing experiences. Here are 10 examples of Personal Communication:
- Casual Conversations: Spontaneous talks with friends or family.
- Personal Emails: Informal written communication with close ones.
- Text Messaging: Quick, informal chats.
- Social Media Interactions: Engagements on platforms like Facebook or Instagram.
- Phone Calls: Voice conversations for personal matters.
- Video Calls: Virtual face-to-face interactions.
- Letters: Handwritten, personalized communication.
- Personal Blogs: Sharing personal stories and experiences online.
- Gestures and Non-verbal Cues: Body language in personal interactions.
- Personal Meetings: In-person gatherings with friends or family.
Comparison Between Business Communication and Personal Communication
The comparison between Business Communication and Personal Communication highlights key differences in their approach, audience, and purpose. Business Communication is formal, structured, and focused on clear, concise information exchange in a professional context. It involves interactions like meetings, formal emails, and reports, aimed at achieving specific organizational goals. Personal Communication, on the other hand, is more informal and spontaneous, focusing on building and maintaining personal relationships. It includes casual conversations, text messages, and social media interactions. Understanding these differences is crucial for effective communication in both personal and professional life.
- Purpose: Business Communication aims at specific organizational goals, while Personal Communication focuses on building personal relationships.
- Tone: Formal and professional in Business Communication; informal and casual in Personal Communication.
- Content: Factual and task-oriented in Business Communication; emotional and varied in Personal Communication.
- Medium: Emails, reports, and meetings for Business Communication; texts, calls, and social media for Personal Communication.
- Feedback: More direct and immediate in Business Communication; often empathetic and open-ended in Personal Communication.
- Audience: Colleagues and clients in Business Communication; friends and family in Personal Communication.
- Boundaries: Strict professional etiquette in Business Communication; more relaxed and personal in Personal Communication.
- Privacy Level: Business Communication is often public or semi-public; Personal Communication is usually private.
- Record Keeping: Business Communication often requires record keeping; Personal Communication does not.
- Regulation: Business Communication is regulated by organizational policies; Personal Communication is guided by social norms.
Relationship Between Business Communication and Personal Communication
The relationship between Business Communication and Personal Communication is complex and multifaceted, as these two forms of communication often influence and intersect with each other:
- Skill Transfer: Skills developed in personal communication, like empathy and active listening, can enhance business communication.
- Professional and Personal Balance: Effective business communicators often maintain a balance between professionalism and personal touch.
- Influence on Relationships: How one communicates in business can impact personal relationships and vice versa.
- Adaptability: The ability to switch between these communication styles is crucial in various contexts.
- Cultural Influences: Personal communication styles can influence professional interactions, especially in multicultural settings.
- Feedback Learning: Feedback mechanisms in personal communication can be applied to business contexts for improved interactions.
- Conflict Resolution: Techniques used in personal communication can be effective in resolving business disputes.
- Technological Impact: Technology used in personal communication often crosses over to business environments.
- Emotional Intelligence: Skills like understanding and managing emotions are crucial in both realms.
- Network Building: Personal communication skills can aid in building professional networks.
Understanding how these two communication types relate and influence each other is key to effective overall communication skills.
In conclusion, this article has explored the key differences and relationships between Business Communication and Personal Communication. It highlights how each form has its unique examples, effects, and solutions. Understanding these differences is crucial for effective communication in both professional and personal spheres. Recognizing the signs of communication issues and knowing how to address them can lead to improved interactions in all areas of life.


