20 Intercultural Business Communication Examples
In the globalized business world, Intercultural Business Communication is key to success. This complete guide, brimming with diverse communication examples, provides insights into navigating the complex landscape of cross-cultural corporate interactions. It covers everything from developing global business communication strategies to understanding cultural diversity in corporate communication. Whether you’re dealing with international communication in business or fostering multicultural workplace communication, this guide offers valuable techniques and examples for effective global engagement.
Download Importance of Intercultural Business Communication PDF
What is Intercultural Business Communication?
Intercultural Business Communication refers to the exchange of information and ideas between individuals or groups from different cultural backgrounds within a business context. It’s about understanding and navigating the varied cultural norms, values, and practices that influence how people communicate in a professional setting. This type of communication is crucial in today’s globalized business world, as it enables companies to effectively interact with diverse clients, partners, and employees, fostering mutual respect and successful international collaborations.
What is the Best Example of Intercultural Business Communication?
A prime example of Intercultural Business Communication can be seen in multinational companies like Coca-Cola. With operations in over 200 countries, Coca-Cola exemplifies how to effectively communicate across diverse cultural landscapes. They tailor their marketing strategies, product offerings, and communication styles to resonate with local cultures while maintaining their global brand identity. For instance, their advertising campaigns often feature local languages, cultural symbols, and values specific to each region, demonstrating an understanding and respect for cultural nuances. This approach not only enhances customer engagement but also strengthens their global presence by building a deep, culturally-sensitive connection with diverse audiences worldwide. This strategy showcases the importance of adapting communication styles to different cultural contexts, a cornerstone of successful intercultural business communication.
20 Intercultural Business Communication Examples
In the realm of Intercultural Business Communication, understanding cultural nuances is vital. Example of Miscommunications often arise from differences in cultural norms, language barriers, non-verbal cues, and business etiquettes. Acknowledging and adapting to these differences is key to fostering effective global interactions.
- Language Barrier:
- Cause: Misinterpretation due to language differences.
- Fix: Use clear, simple language and consider professional translation services.
- Non-Verbal Misunderstandings:
- Cause: Varied meanings of gestures across cultures.
- Fix: Research and respect non-verbal cues of other cultures.
- Different Communication Styles:
- Cause: Direct vs. indirect communication preferences.
- Fix: Adapt your style to match your counterpart’s preference.
- Varied Decision-Making Processes:
- Cause: Some cultures decide by consensus, others by hierarchy.
- Fix: Understand and align with their decision-making style.
- Contrasting Negotiation Tactics:
- Cause: High-context vs. low-context negotiation styles.
- Fix: Be aware of and adapt to different negotiation norms.
- Email Etiquette Differences:
- Cause: Varying norms for formality and tone in emails.
- Fix: Observe and mirror the other party’s email style.
- Time Perception Variations:
- Cause: Different attitudes towards punctuality and deadlines.
- Fix: Clarify and respect time-related expectations.
- Hierarchy and Authority Differences:
- Cause: Diverse attitudes towards power distance.
- Fix: Be aware of hierarchical structures and act accordingly.
- Cultural Stereotyping:
- Cause: Preconceived notions about a particular culture.
- Fix: Educate yourself and avoid assumptions.
- Meeting Miscommunications:
- Cause: Differing approaches to conducting meetings.
- Fix: Align meeting styles and agendas in advance.
- Differing Work-Life Balance Expectations:
- Cause: Varied importance placed on work-life balance.
- Fix: Respect individual preferences and norms.
- Holiday and Work Schedule Conflicts:
- Cause: Overlooking international holidays and work schedules.
- Fix: Plan with awareness of global calendars.
- Virtual Communication Challenges:
- Cause: Misinterpretations in remote interactions.
- Fix: Use video conferencing and instant messengers effectively.
- Project Management Misalignments:
- Cause: Different project management styles.
- Fix: Use project management tools to synchronize efforts.
- Assumptions about Familiarity:
- Cause: Assuming similar business practices.
- Fix: Research and ask questions to understand practices.
- Feedback Interpretation Variations:
- Cause: Different approaches to giving and receiving feedback.
- Fix: Be clear and sensitive in feedback sessions.
- Social Interaction Misunderstandings:
- Cause: Different norms for socializing in a business context.
- Fix: Observe and adapt to social customs.
- International Marketing Missteps:
- Cause: Overlooking cultural sensitivities in marketing.
- Fix: Customize marketing strategies to local cultures.
- Diverse Conflict Resolution Styles:
- Cause: Varied approaches to handling conflicts.
- Fix: Understand and respect different conflict resolution methods.
- Global Team Collaboration Hurdles:
- Cause: Coordinating across time zones and cultures.
- Fix: Utilize collaboration tools and schedule considerately.
Intercultural Communication in International Business
In the dynamic landscape of International Business, effective Intercultural Communication is a cornerstone for success. It’s about understanding diverse cultural values and norms to navigate global markets skillfully. This involves more than just language proficiency; it’s about cultural empathy, adaptability, and awareness in business interactions. Here are 10 distinct examples showcasing the essence of intercultural communication in international business:
- Negotiating with Japanese Clients:
- Explanation: Japanese business culture values politeness and indirect communication.
- How to Communicate: “I believe we can find a mutually beneficial agreement, let’s explore this further.”
- Presenting to a German Audience:
- Explanation: Germans appreciate directness and detailed presentations.
- How to Communicate: “Let me provide you with a detailed overview and specific data to support our proposal.”
- Collaborating with Indian Teams:
- Explanation: Indian culture often values a hierarchical approach and respect for seniority.
- How to Communicate: “I would value your guidance on this matter and your team’s insights.”
- Discussing Contracts with American Businesses:
- Explanation: American business culture is results-oriented and values straightforwardness.
- How to Communicate: “Let’s focus on the key outcomes and efficiencies we can achieve together.”
- Partnering with Brazilian Companies:
- Explanation: Brazilian business culture is relationship-oriented with an emphasis on personal connections.
- How to Communicate: “I’m looking forward to building a strong partnership based on trust and collaboration.”
- Emailing a British Colleague:
- Explanation: The British often prefer politeness and understatement in communication.
- How to Communicate: “I would be most grateful if you could review the attached document at your earliest convenience.”
- Setting a Meeting with Middle Eastern Partners:
- Explanation: In Middle Eastern cultures, personal relationships are vital, and discussions often go beyond just business.
- How to Communicate: “I am looking forward to our meeting and the opportunity to learn more about your esteemed company.”
- Negotiating with Chinese Suppliers:
- Explanation: Chinese business culture values respect, patience, and long-term relationships.
- How to Communicate: “I respect your business practices and am keen to develop a long-lasting business relationship.”
- Networking with French Professionals:
- Explanation: French business culture appreciates formality and high-context communication.
- How to Communicate: “I am impressed by your expertise and would appreciate your insights on this matter.”
- Conducting Business in South Africa:
- Explanation: South African business culture is diverse and values both personal connections and professionalism.
- How to Communicate: “I am excited to work together, embracing both our professional goals and the rich diversity of our teams.
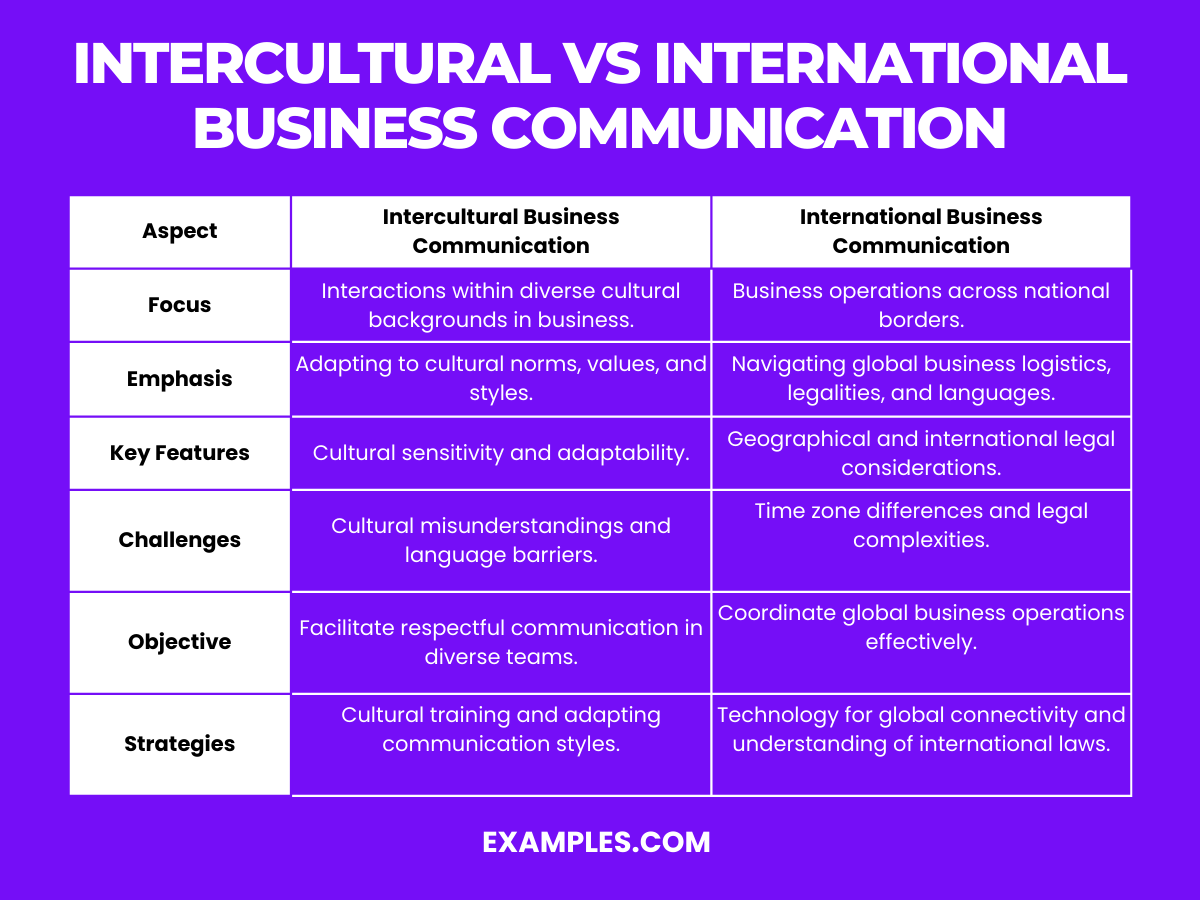
Difference between Intercultural and International Business Communication
| Aspect | Intercultural Business Communication | International Business Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Interaction between individuals from different cultural backgrounds within a business setting. | Business operations and communication across national borders. |
| Emphasis | Understanding and adapting to cultural norms, values, and communication styles. | Dealing with logistical, legal, and linguistic aspects of global business. |
| Key Features | Cultural sensitivity, adaptability, and awareness. | Geographical considerations, international laws, and cross-border logistics. |
| Challenges | Cultural misunderstandings, language barriers, and non-verbal communication differences. | Time zone differences, legal complexities, and international market dynamics. |
| Objective | To facilitate effective and respectful communication among diverse team members. | To manage and coordinate business operations effectively on a global scale. |
| Strategies | Cultural education, awareness training, and adapting communication styles. | Use of technology for global connectivity, understanding international business laws, and cultural research. |
| Examples | Adapting marketing messages to local cultures, using culturally appropriate negotiation tactics. | Setting up international offices, managing global supply chains, dealing with international regulations. |
| Outcome | Enhanced collaboration and productivity within a culturally diverse team. | Successful international business operations and global market expansion. |
| Tools | Cultural training programs, language translation services, intercultural communication workshops. | Global project management tools, international legal advisors, translation and localization services. |
| Impact | Improved internal team relations and better understanding of diverse markets. | Expanded business reach, increased market share, and competitive advantage in global markets |
Tips for Effective Intercultural Business Communication
Navigating Intercultural Business Communication effectively is crucial in the global business landscape. Here are essential strategies to enhance your interactions across diverse cultures:
1. Cultural Awareness and Sensitivity
- Understand and respect the diverse cultural backgrounds you interact with. Educate yourself about the customs, communication styles, and business etiquettes of these cultures.
- Engage in cultural training or workshops for deeper insights.
2. Active Listening
- Focus on understanding the context and nuances of conversations. It’s not just about the words, but the meaning behind them.
- Show engagement by asking clarifying questions and summarizing key points.
3. Clarity in Communication
- Avoid complex language, idioms, and jargon that might be confusing. Ensure your message is straightforward and easily understandable.
- Confirm understanding to ensure your message is received as intended.
4. Understanding Non-Verbal Cues
- Be aware that non-verbal communication can differ significantly across cultures. What’s acceptable in one culture might not be in another.
- Research and observe the non-verbal norms of your international colleagues.
5. Adaptability
- Be prepared to adjust your communication style as needed. Being adaptable is key when dealing with cross-cultural interactions.
- Change your approach based on feedback and reactions from your audience.
6. Embracing Language Diversity
- Recognize that not everyone is comfortable with English. Be patient and accommodating with non-native speakers.
- Learn key phrases in the languages of your main business partners to show respect and effort.
7. Relationship Building
- Many cultures place a high value on building personal relationships in a business context. Focus on establishing trust and understanding.
- Invest time in getting to know your international colleagues and business partners beyond just work-related conversations.
Implementing effective Intercultural Business Communication Strategies is crucial in today’s globalized business environment. These strategies involve understanding and respecting cultural differences, enhancing communication skills, and adapting to various business practices worldwide. Key strategies include:
- Cultural Awareness Training: Implement training programs for employees to understand different cultural norms and values.
- Language Skills Development: Encourage language learning to break down communication barriers.
- Customized Communication Styles: Adapt communication styles to suit different cultural contexts, including variations in negotiation, decision-making, and conflict resolution.
- Utilization of Technology: Leverage technology like video conferencing and instant messaging platforms to facilitate smoother cross-cultural communication.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Establish feedback channels to understand and address any cultural misunderstandings.
- Regular Cultural Audits: Conduct regular audits to assess and improve the effectiveness of communication strategies
Importance of Intercultural Communication for Business
In today’s globalized economy, the importance of Intercultural Business Communication cannot be overstated. It plays a pivotal role in bridging cultural gaps, enhancing mutual understanding, and fostering productive international business relationships. Here’s a detailed look at why intercultural communication is so crucial for businesses:
- Facilitates Global Expansion: Understanding and respecting cultural differences are essential when expanding into new international markets. Effectivebusiness communication helps businesses to adapt their strategies to local customs and consumer preferences, making global expansion more seamless and successful.
- Improves Team Collaboration: With the rise of multinational corporations and diverse workforces, effective intercultural communication ensures that all employees, regardless of their cultural background, can collaborate efficiently. This leads to a more harmonious and productive workplace.
- Enhances Customer Relations: Being culturally aware enables businesses to communicate more effectively with a diverse client base. This sensitivity can lead to stronger customer relationships and loyalty, as customers feel understood and valued.
- Reduces Misunderstandings: Miscommunication can lead to conflicts, errors, and inefficiencies. By prioritizing intercultural communication, businesses can minimize these risks, leading to smoother operations and better problem-solving.
- Boosts Innovation and Creativity: Exposure to multiple cultural perspectives can spark new ideas and innovative approaches to business challenges. This diversity of thought is a valuable asset in the rapidly changing business world.
- Builds a Positive Corporate Reputation: Companies that excel in intercultural communication are often seen as more respectful and socially responsible. This enhances their brand image and can lead to increased business opportunities and partnerships.
- Supports Effective Leadership: Leaders who are skilled in intercultural communication can manage and motivate a diverse workforce more effectively. This ability is crucial for inspiring teams and driving them towards common business goals.
- Aids in Risk Management: Understanding cultural nuances can help businesses anticipate and mitigate risks associated with international business transactions and negotiations.
- Encourages Respect and Inclusivity: Promoting intercultural communication within an organization fosters an environment of respect and inclusivity. This not only benefits employee morale but also attracts talent from a wide range of backgrounds.
- Drives Competitive Advantage: Ultimately, businesses that are adept at intercultural communication are better positioned to succeed in the global marketplace. They can navigate international challenges more effectively and capitalize on opportunities that others may miss.
The article from Walden University offers four essential tips for effective intercultural business communication. These tips emphasize the importance of considering different perspectives, conducting thorough research on cultural differences, being observant in communication situations, and the value of education in developing intercultural communication skills. It highlights that understanding and adapting to diverse communication styles is key for successful interactions in today’s global business environment.