20+ Closed Loop Communication in Medical Examples
Dive into the critical world of Closed Loop Communication in Medical settings with this detailed guide. Understand through various communication examples how this method revolutionizes patient care and team coordination. This guide illuminates the structured, repetitive approach of closed-loop communication, emphasizing its necessity in healthcare for reducing errors and enhancing patient outcomes. Learn the key components, benefits, and real-world applications in medical scenarios.
Download Closed Loop Communication Training in Medical Simulation PDF
What is Closed Loop Communication in Medical? – Meaning
Closed Loop Communication in Medical contexts refers to a communication strategy where information is not only conveyed but also acknowledged, repeated, and then confirmed by the original sender. This method ensures that messages are understood accurately and carried out correctly, crucial in high-stakes environments like healthcare. It’s a systematic approach to verbal exchanges that significantly reduces errors, clarifies instructions, and enhances overall patient safety and team efficiency.
What is the Best Example of Closed Loop Communication in Medical?
A prime example of Closed Loop Communication in Medical practice is during surgical procedures. Imagine a surgeon requesting an instrument: “Please pass the scalpel.” The nurse acknowledges by repeating, “Passing the scalpel,” and once handed over, the surgeon confirms, “Scalpel received.” This cycle of instruction, repetition, and confirmation ensures that the right actions are taken promptly and accurately, minimizing the risk of errors and ensuring the patient’s safety and the team’s coordinated effort. This example demonstrates how vital closed-loop communication is in maintaining high standards of care and safety in medical environments.
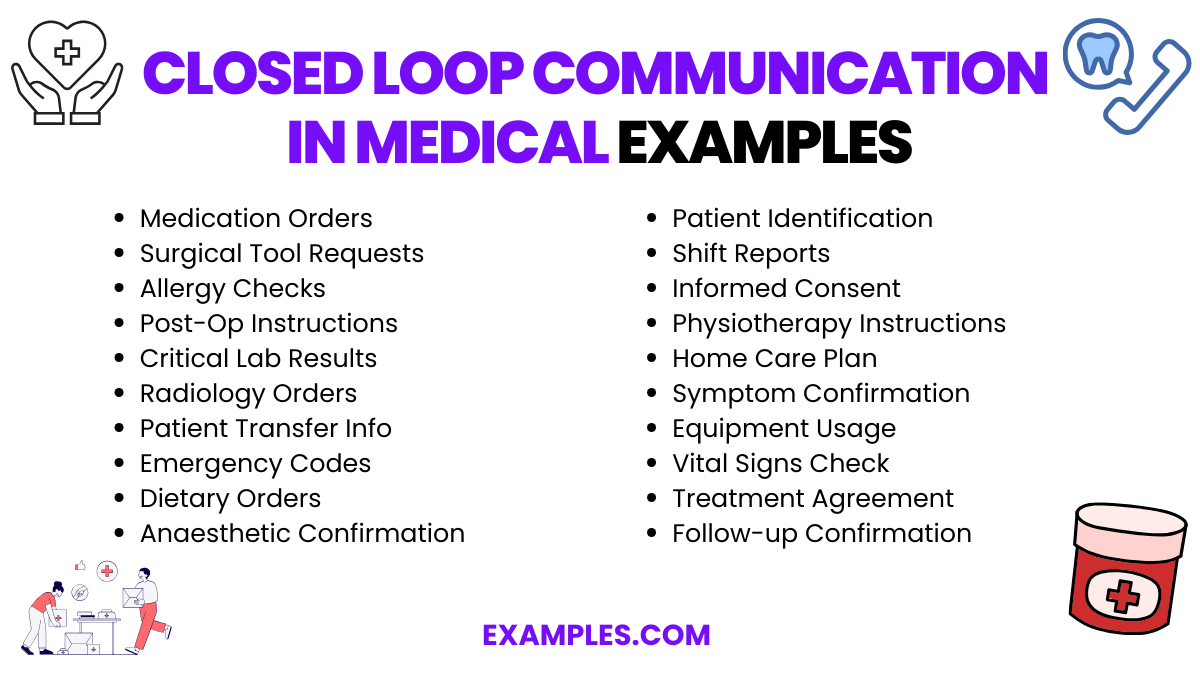
20 Closed Loop Communication in Medical Examples
Explore 20 pivotal examples of Closed Loop Communication in medical settings, a cornerstone for ensuring accuracy and patient safety. This guide showcases various scenarios where closed-loop communication methods are applied, highlighting their role in preventing errors and promoting effective team collaboration. From routine check-ups to complex surgeries, understand the Essential Actions for Closed Loop Communication and how each step contributes to a safer, more efficient healthcare system. Each example not only illustrates the application of Closed Loop Communication but also emphasizes how its integration into every step of patient care – from admission to discharge – is fundamental. These scenarios show the Closed Loop Communication Steps and Closed Loop Communication in Healthcare in action, providing a blueprint for medical professionals to enhance communication, reduce errors, and improve patient outcomes.
- Medication Orders: Doctor orders medication dosage; nurse repeats and confirms back before administration. What is Closed Loop Communication? It ensures the correct medication and dosage.
- Surgical Tool Requests: Surgeon requests a tool, assistant repeats the request and confirms upon delivery. This prevents any surgical mishaps.
- Allergy Checks: Before administering medication, the nurse confirms any allergies with the patient and reconfirms with the medical records.
- Post-Op Instructions: Doctor gives post-operative care instructions, which the patient or nurse repeats back to confirm understanding.
- Critical Lab Results: Lab technician communicates critical results to a physician, who repeats and documents the information, ensuring no misunderstanding.
- Radiology Orders: Radiologist details the scan needed, and the technician repeats back the type and area of the scan for accuracy.
- Patient Transfer Information: When transferring a patient, one nurse communicates the status and needs, and the receiving nurse repeats and confirms.
- Emergency Codes: In emergencies, staff announce codes clearly and repeat them to ensure everyone understands the situation and responds appropriately.
- Dietary Orders for Patients: Dietary staff confirm and reconfirm special meal requirements with nursing staff before preparing patient meals.
- Anaesthetic Dosage Confirmation: Anesthesiologist states the dosage, nurse repeats it, and the anesthesiologist confirms before administration.
- Patient Identification: Before any procedure, staff confirm the patient’s identity by having them state their name and DOB, which is then confirmed with their wristband or chart.
- End-of-Shift Report: Nurses provide detailed patient reports at shift change, and the incoming nurse repeats key information to ensure continuity of care.
- Informed Consent Process: Doctor explains the procedure and risks, patient or family repeats understanding, ensuring informed consent is accurately obtained.
- Physiotherapy Instructions: Therapist details exercises, patient repeats back to confirm understanding of the routine.
- Home Care Plan: Before discharge, patient or family repeats back understanding of the home care plan to ensure clarity.
- Symptom Description and Confirmation: Patient describes symptoms, doctor repeats and clarifies to ensure an accurate diagnosis.
- Equipment Usage: When introducing new equipment, the user repeats the steps as instructed by the trainer to confirm correct usage.
- Vital Signs Check: Nurse announces patient’s vital signs, another healthcare worker acknowledges and confirms by repeating the numbers.
- Treatment Plan Agreement: Doctor details a treatment plan, patient or other medical staff repeat to confirm agreement and understanding.
- Follow-up Appointment Confirmation: Before the patient leaves, the date and time of the next appointment are repeated and confirmed to ensure attendance.
Closed Loop Communication in Medical Training
Mastering Closed Loop Communication is a vital component of medical training, engraining precision and patient safety in budding healthcare professionals. This detailed segment explores how medical training programs incorporate Closed Loop Communication, emphasizing the Importance of Closed Loop Communication and its role in preventing errors. Through these examples, witness how medical trainees learn the art of clear, concise, and effective communication, particularly focusing on Closed Loop Communication in Nursing and Closed Feedback Loop Communication.
- Drug Administration Simulation: Trainees practice administering medication, verbally confirming the drug and dose as they administer it.
- How to Communicate: “Administering 5mg of Drug X now.” “Confirming, 5mg of Drug X administered.”
- Emergency Response Drills: Students participate in mock codes, practicing urgent communication and role-specific responses.
- How to Communicate: “I need an IV line set up immediately!” “Setting up an IV line now!”
- Patient Handover Training: Trainees practice exchanging crucial patient information during shift changes, ensuring nothing is missed.
- How to Communicate: “Patient is allergic to penicillin and due for medication at 2100.” “Understood, allergic to penicillin, medication due at 2100.”
- Surgical Procedure Walkthroughs: Future surgeons and nurses practice calling out and confirming each step of a procedure.
- How to Communicate: “Clamp ready for the incision.” “Clamp handed and ready.”
- Interdisciplinary Communication Exercises: Trainees from different medical fields practice collaborating and communicating on patient cases.
- How to Communicate: “The patient needs a chest X-ray before the procedure.” “I’ll arrange for the chest X-ray immediately.”
What is the Significance of Closed Loop Communication in Medical Settings, and How Does it Impact Patient Safety?
Closed Loop Communication is fundamental in medical settings, directly impacting patient safety and care quality. This method ensures information is accurately exchanged, reducing errors and enhancing team coordination.
- Error Reduction: By confirming information, Closed Loop Communication minimizes misunderstandings and mistakes in patient care.
- Efficiency in Care: Speedy, accurate exchanges lead to more efficient diagnosis, treatment, and patient management.
- Team Accountability: Each member is accountable for their part of the communication, ensuring a collective responsibility towards patient safety.
- Patient Involvement: Patients become active participants in their care, leading to better outcomes and satisfaction.
- Cultural Competency: Facilitates clearer understanding in diverse medical settings, accommodating different languages and cultural communication styles.
What are the Key Components of a Closed Loop Communication Protocol in Medical Contexts, and Why Are They Important?
Closed Loop Communication in medical contexts is composed of several key components, each vital for maintaining clear and effective dialogue among healthcare professionals. Incorporating Open Loop vs Closed Loop Communication strategies allows healthcare teams to compare and choose the most effective communication method for each situation. The implementation of Closed Loop Communication for Patients and Nurses ensures that the medical team, including the frontline nursing staff, operates with a shared understanding, leading to better patient care and safety. Each component plays a crucial role in creating a robust communication network within healthcare settings, ultimately contributing to reduced errors and improved patient outcomes.
- Message Delivery: The initial conveyance of information, instructions, or questions clearly and concisely.
- Acknowledgment: The receiver verbally acknowledges the message, indicating that it was heard.
- Clarification: The receiver asks for clarification if any part of the message was unclear or if additional information is needed.
- Confirmation/Feedback: The receiver repeats the message back to the sender to confirm understanding, and the sender provides feedback to ensure accuracy.
- Documentation: Finally, Important Communications are documented in the patient’s Medical Record for future reference and continuity of care.
How Does Technology Influence Closed Loop Communication in Medical?
Technology enhances Closed Loop Communication in medical settings by providing reliable, fast, and clear channels for exchanging critical information, leading to increased accuracy and efficiency.
How is Closed Loop Communication Integrated into Medical Training to Enhance Communication Skills?
Closed Loop Communication is integrated into medical training through simulations, role-playing, and feedback exercises, ensuring that future healthcare professionals develop precise and effective communication habits.
Why Do We Need Closed Loop Communication in Medical?
Closed Loop Communication is crucial in medical settings for reducing errors, ensuring patient safety, and enhancing the quality of care by confirming that vital information is accurately shared and understood.
In conclusion, Closed Loop Communication is indispensable in medical settings, providing a systematic approach to reduce errors and enhance patient safety. Its implementation, through clear, structured dialogue, is key to improving healthcare outcomes. Understanding and applying this communication method effectively ensures a higher standard of care, fostering trust and efficiency in the fast-paced medical environment.