Mass Communication vs Communication Studies – 19+ Examples
Exploring the realms of Mass Communication and Communication Studies reveals distinct yet interconnected fields within the media landscape. While Mass Communication focuses on the dissemination of information across various platforms to a wide audience, Communication Studies delves deeper into the theoretical and practical aspects of human communication. This comparison sheds light on their unique focuses, methodologies, and career paths, guiding those interested in pursuing a future in the expansive world of media and communication.
What is the Difference Between Mass Communication and Communication Studies?
Understanding the nuances between Mass Communication and Communication Studies is crucial for students and professionals navigating the media and communication sectors. This table provides a detailed comparison with different aspects:
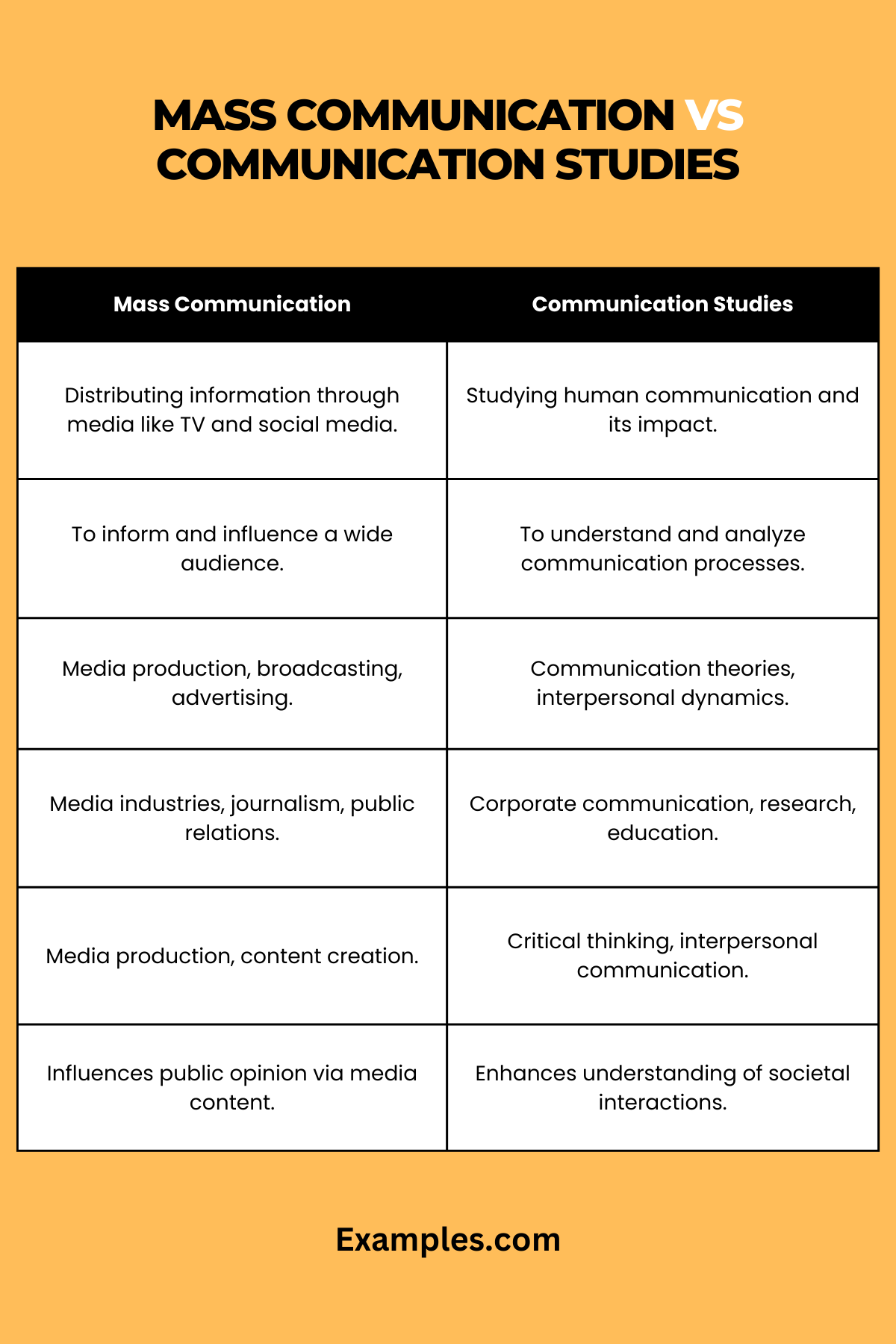
| Aspect | Mass Communication | Communication Studies |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Focused on distributing information through media to large, diverse audiences. | Concentrated on understanding all aspects of human communication. |
| Key Disciplines | Includes broadcasting, journalism, advertising, and public relations. | Encompasses interpersonal, nonverbal, organizational, and cross-cultural communication. |
| Skill Development | Develops skills in media production, campaign planning, and audience engagement. | Builds competencies in communication analysis, rhetoric, and effective dialogue. |
| Research Areas | Research typically involves audience metrics, media impact, and content analysis. | Focuses on communication theory, sociolinguistics, and discourse analysis. |
| Practical Application | Practical applications in news media, advertising firms, and corporate PR. | Applicable in various fields like human resources, conflict resolution, and counseling. |
| Educational Content | Coursework includes media ethics, digital media, and media writing. | Coursework covers communication theory, persuasion, and group dynamics. |
| Technological Integration | High emphasis on digital media tools, broadcasting equipment, and social media. | Includes the study of communication technology’s impact on society and behavior. |
| Career Outcomes | Careers in media houses, marketing agencies, and digital content creation. | Careers in communication training, research, consultancy, and organizational development. |
| Audience Engagement | Focuses on mass audience targeting and engagement strategies. | Involves understanding interpersonal dynamics and audience segmentation. |
| Content Creation | Involves creating content for mass consumption like news stories and advertisements. | Teaches creation of effective communication strategies for varied audiences. |
| Global Perspective | Often discusses global media trends, international broadcasting, and cultural impacts. | Studies global communication patterns, cultural communication, and international relations. |
| Ethical Framework | Addresses ethical considerations in media production and dissemination. | Explores ethics in personal and organizational communication contexts. |
This table illustrates that Mass Communication is geared towards media-centric skills and industry practices, while Communication Studies provides a broader understanding of communication in various personal and professional contexts. Each field has its unique focus, preparing individuals for different roles within the broader spectrum of communication.
10 Mass Communication Examples
Here are 10 examples of Mass Communication, each illustrating the diverse ways information and entertainment are disseminated to a broad audience. These instances highlight the scope and impact of mass communication in various formats.
- National Television Broadcasts:
Channels like NBC and BBC broadcast a variety of programs nationwide, reaching millions. They epitomize mass communication, offering news, entertainment, and educational content. - Major Newspapers:
Newspapers like The Guardian and The Washington Post provide widespread news coverage and editorial content, crucial for informed public discourse and opinion shaping. - Commercial Radio Stations:
Stations like KISS FM broadcast music, news, and talk shows to a large audience, serving as classic examples of audio mass communication. - Online News Portals:
Platforms like CNN.com and HuffingtonPost.com deliver real-time news globally, representing the digital evolution of mass communication with widespread accessibility. - Social Media Networks:
Platforms such as Facebook and Twitter facilitate the rapid dissemination of information and news, highlighting the role of social media in modern mass communication. - Cinema and Film Distribution:
Hollywood movies distributed globally are a form of mass communication, influencing culture and entertainment across different societies. - Advertising Campaigns on Multiple Media:
Large-scale advertising campaigns, especially those spread across various media channels, are prime examples of mass communication, aiming to reach a diverse audience. - Public Service Announcements:
Broadcast on television and radio, PSAs communicate important social messages to the wider public, embodying the informative role of mass communication. - Digital Streaming Services:
Platforms like Netflix and Hulu, offering a wide range of content, exemplify the modern face of mass communication, reaching audiences worldwide. - Podcasts and Webinars:
With their rising popularity, podcasts and webinars have become significant tools in mass communication, providing information and entertainment to a global audience.
10 Communication Studies Examples
Delve into the world of Communication Studies with these examples, illustrating the diverse applications and impact of effective communication practices across various contexts. These instances highlight the importance of understanding and mastering communication skills.
- Interpersonal Communication Analysis:
Studies focusing on interpersonal dynamics, such as family or workplace communication, explore how individuals exchange information and emotions, crucial for relationship building and conflict resolution. - Organizational Communication Strategies:
Examining communication within businesses and organizations, these studies assess how internal communication affects productivity and employee morale, essential for effective management and teamwork. - Cross-Cultural Communication Research:
This area explores how cultural differences impact communication, vital for global business strategies, diplomacy, and multicultural understanding in an increasingly interconnected world. - Public Speaking and Rhetoric Courses:
Courses teaching public speaking skills, including rhetoric and persuasive techniques, are key for individuals aiming to excel in leadership, advocacy, or public-facing roles. - Health Communication Campaigns:
Studies in health communication examine how information about health and wellness is conveyed to the public, highlighting the importance of clear, accessible communication in healthcare. - Political Communication Analysis:
Analyzing how politicians and governments communicate with the public, these studies are crucial for understanding political campaigns, policy promotion, and public engagement strategies. - Media Literacy Education:
Programs that teach media literacy help individuals critically assess and interpret various media messages, an essential skill in the digital age for combating misinformation. - Corporate Crisis Communication:
Case studies of corporate crisis management reveal how effective communication can mitigate damage and maintain trust during challenging times, a key skill for public relations professionals. - Nonverbal Communication Research:
Studies focusing on nonverbal cues, such as body language and facial expressions, provide insights into the subtleties of human interaction, important for personal and professional relationships. - Communication Technology Trends Analysis:
Researching emerging communication technologies, like social media and virtual reality, offers insights into their societal impact, shaping the future of how we connect and interact.
Comparison Between Mass Communication and Communication Studies
The fields of Mass Communication and Communication Studies, while intertwined, cater to different academic and professional pursuits. Here’s an alternative table format that provides a fresh perspective on how these two disciplines compare:
| Comparison Criteria | Mass Communication Attributes | Communication Studies Attributes |
|---|---|---|
| Educational Focus | Centers on media channel utilization, content creation, and audience dynamics. | Emphasizes the study of interpersonal, cultural, and organizational communication. |
| Typical Coursework | Includes subjects like media ethics, broadcast journalism, and digital media. | Covers topics like communication theory, rhetoric, and conflict resolution. |
| Skill Set Emphasis | Focuses on technical skills in media production, writing, and strategic communication. | Highlights interpersonal skills, analytical thinking, and effective messaging. |
| Career Pathways | Leads to roles in media houses, advertising agencies, and corporate communication. | Opens opportunities in fields like education, counseling, and human resources. |
| Research Orientation | Involves studying audience behavior, media effects, and advertising impact. | Focuses on research in communication behaviors, persuasion, and media influence. |
| Industry Applications | Relevant in broadcasting, journalism, PR, and advertising sectors. | Applicable in various sectors, including corporate, non-profit, and academia. |
| Content Production | Oriented towards producing mass media content for wide dissemination. | Involves developing communication strategies for diverse settings. |
| Technological Aspects | Heavily reliant on evolving media technologies and digital platforms. | Considers the impact of communication technologies on individual and group interaction. |
| Societal Impact | Aims to inform, entertain, and influence public opinion on a mass scale. | Aims to enhance personal and organizational communication effectiveness. |
| Ethical Considerations | Focuses on ethics related to media production, distribution, and journalism. | Explores ethical communication practices in personal and professional environments. |
| Global Perspective | Discusses the role and impact of media in a global context. | Studies global communication patterns and the impact of cultural differences. |
| Interactivity | Ranges from broadcast media with limited interactivity to interactive digital media. | Emphasizes the importance of interactive skills in various communication contexts. |
This comparison illustrates that while Mass Communication is geared towards media production and dissemination to large audiences, Communication Studies offers a more in-depth exploration of the nature, theories, and applications of communication in various contexts. Each discipline equips students with distinct skills and knowledge, suited to different career paths in the broad field of communication.
The comparison between Mass Communication and Communication Studies uncovers distinct yet complementary disciplines. While Mass Communication is centered on media dissemination and audience reach, Communication Studies delves into the intricacies of human interaction across various contexts. Understanding these differences is key for those navigating media-related careers, offering insights into choosing the path that aligns best with their interests and professional goals.



