Mass Communication vs Strategic Communication – 19+ Examples
In the ever-evolving world of media, understanding the distinction between Mass Communication and Marketing Communication is crucial. While both disciplines are essential in reaching and engaging audiences, they serve different purposes and employ varied strategies. Mass Communication focuses on disseminating information to a broad audience, whereas Marketing Communication strategically targets specific groups to promote products or services. This comparison offers insights into their unique roles, techniques, and impacts in the landscape of modern communication.
What is the Difference Between Marketing and Mass Communications?
Understanding the differences between marketing and mass communications is key to navigating the complex world of media and communication. Here’s a detailed comparison in a table format, highlighting their distinct characteristics and functions:
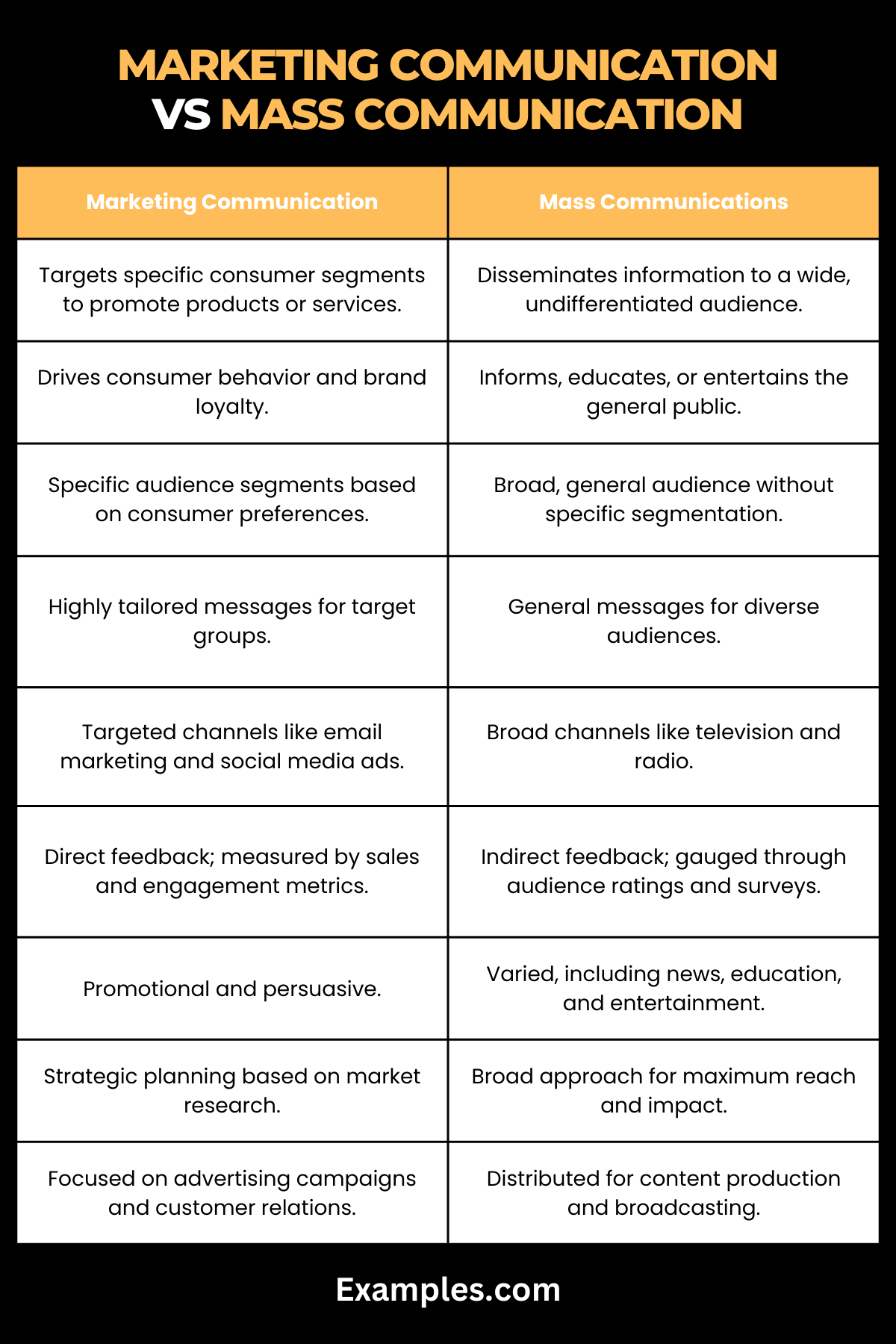
| Aspect | Marketing Communication | Mass Communications |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Marketing communication involves strategies to promote products or services and engage with specific consumer segments. | Mass communications is the process of disseminating information to a wide, undifferentiated audience. |
| Primary Objective | The main goal is to drive consumer behavior, such as encouraging purchases or building brand loyalty. | Aimed at informing, educating, or entertaining a broad public audience. |
| Target Audience | Focuses on specific audience segments based on consumer behavior and preferences. | Targets a general, wide-ranging audience with no specific segmentation. |
| Message Customization | Messages are highly tailored to resonate with the targeted consumer group. | Messages are more general, catering to a diverse and broad audience. |
| Channels Used | Utilizes targeted channels like email marketing, social media ads, and direct mail. | Employs broad-reaching channels such as television, radio, and newspapers. |
| Feedback and Measurement | Emphasizes direct feedback mechanisms and measures success through sales figures, conversion rates, and customer engagement. | Feedback is indirect, often gauged through audience ratings, surveys, or viewership numbers. |
| Content Style | Content is promotional and persuasive, aiming to highlight the benefits of products or services. | Content varies widely, including news, educational material, and entertainment. |
| Tactical Approach | Involves strategic planning focusing on market research, consumer behavior, and sales tactics. | Broad and inclusive in approach, aiming for maximum reach and impact. |
| Resource Allocation | Resources are allocated for market research, advertising campaigns, and customer relationship management. | Resources are distributed for content production, broadcasting, and publication. |
| Outcome Measurement | Success is measured by market penetration, customer acquisition, and ROI. | Success is often measured by reach, audience engagement, and public influence. |
| Flexibility and Adaptation | Highly adaptable and responsive to market trends and consumer feedback. | More fixed in scheduling but adaptable in content based on current events and trends. |
| Impact Assessment | Assesses impact based on consumer response, brand recognition, and market share. | Impact is evaluated based on audience size, public perception, and societal influence. |
While marketing communication and mass communications overlap in their use of media channels, they differ significantly in their objectives, target audiences, content, and measurement of success. Marketing communication is more focused and tailored, aiming to influence consumer behavior, whereas mass communications is broader, seeking to inform or entertain a wide audience.
10 Mass Communication Examples
Mass communication is a powerful tool that encompasses various forms for disseminating information, shaping opinions, and providing entertainment. Here are 10 examples, each illustrating a different facet of mass communication:
- Television News Broadcasts: As a staple in Broadcasting Mass Communication, television news broadcasts offer real-time updates on global events, significantly influencing public perception and knowledge.
- Social Media Platforms: Platforms like Facebook and Twitter exemplify Social media Mass Communication, transforming how news is shared and consumed, and facilitating instant public discourse.
- Radio Programs: Radio, an enduring medium in Broadcasting Mass Communication, provides a mix of news, talk shows, and music, accessible to a wide and varied audience.
- Newspapers and Magazines: These traditional forms of Printing Mass Communication continue to offer in-depth analysis and diverse perspectives, despite the rise of digital media.
- Online News Portals: Portals like CNN represent Digital Age Mass Communication, providing immediate access to global news and facilitating a more informed public.
- Public Service Announcements (PSAs): PSAs are crucial in Mass Communication in Advertising, delivering vital information about health, safety, and social welfare to the public.
- Documentaries and Educational Programs: Often found on television and online platforms, these are key in Journalism Mass Communication, offering detailed insights on a variety of topics.
- Advertising Campaigns: Through Television Mass Communication and online channels, advertising campaigns shape consumer preferences and drive market trends.
- Podcasts: Emerging as a popular medium in Digital Age Mass Communication, podcasts offer diverse and accessible content, from educational material to entertainment.
- Corporate Press Releases: Used in Public Relations Mass Communication, press releases are essential for companies to disseminate important information and manage their public image.
10 Marketing Communication Examples
Exploring various examples of marketing communication showcases its versatility and effectiveness. From cutting-edge digital campaigns to impactful traditional methods, these instances demonstrate how companies successfully engage with their audience through innovative marketing strategies. Each example underscores the use of specific marketing techniques, reflecting the dynamic and diverse nature of this field.
- Social Media Campaigns:
Leveraging platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter, these campaigns create engaging content to boost brand interaction. They often utilize influencer partnerships and user-generated content, enhancing brand loyalty and online presence. - Email Marketing:
Involves sending personalized messages to a segmented audience, offering promotions and updates. It’s an effective strategy for sustaining customer relationships and driving sales, making the most of direct and personal communication channels. - SEO Content:
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) content is designed to improve online visibility. Brands use SEO strategies in their articles and blogs to rank higher in search engine results, attracting more organic traffic and enhancing digital footprints. - Pay-Per-Click Advertising:
PPC ads, a model where advertisers pay for each click, are used on search engines and social media. It targets specific audience segments, efficiently driving traffic to websites and increasing online visibility. - Content Marketing:
This strategy focuses on creating and distributing valuable, relevant content to attract and retain a defined audience. It establishes expertise, enhances brand awareness, and keeps businesses in the consumer’s mind. - Influencer Marketing:
Utilizes individuals with significant online followings to promote products or services. This method effectively reaches specific demographics and leverages the trust influencers have with their audience. - Direct Mail Advertising:
Direct mail involves sending physical marketing materials to potential customers. This traditional method remains effective in reaching target audiences and creating tangible brand impressions. - Trade Shows and Exhibitions:
Participating in trade shows allows businesses to directly showcase their offerings, often in a B2B context. These events provide opportunities for direct engagement and networking. - Branded Merchandise:
Companies use branded items like pens or t-shirts as marketing tools. These items keep the brand visible, enhancing recall and loyalty. - Public Relations Campaigns:
Aim to manage public perception and brand image. These campaigns involve media releases and community initiatives, fostering a positive public image and managing reputation.
What is the Relationship Between Marketing and Mass Communication?
Understanding the relationship between marketing and mass communication is crucial in the field of media and communications. While they are distinct disciplines, their interplay is significant in shaping media content and audience perception. Here’s a detailed exploration of their relationship presented in a table format:
| Aspect | Relationship Aspect | Explanation and Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Content Creation | Marketing influences content in mass communication. | Marketing strategies often dictate the content style and subject matter in mass communication channels, aiming to align with audience preferences and trends. |
| Audience Engagement | Mass communication expands marketing reach. | Mass communication platforms like television and social media extend the reach of marketing campaigns, effectively engaging a broader audience. |
| Brand Perception | Interdependent impact on brand image. | Marketing shapes brand perception through targeted campaigns, while mass communication amplifies and solidifies this perception among the general public. |
| Communication Channels | Shared use of media platforms. | Both marketing and mass communication utilize similar channels, such as social media and broadcasting, to disseminate messages and advertisements. |
| Feedback Mechanisms | Mutual reliance on audience feedback. | Marketing relies on feedback for consumer insights, while mass communication uses audience feedback to gauge content effectiveness and relevance. |
| Technological Advancements | Co-evolution with digital media. | Innovations in digital technology impact both fields, with marketing adopting new tactics in digital platforms and mass communication expanding its reach and interactivity. |
| Message Customization | Marketing tactics influence mass communication. | Marketing’s focus on audience segmentation and message customization influences how mass communication tailors its content to different audience groups. |
| Public Relations | Synergy in brand messaging and public image. | Effective public relations, a key aspect of marketing, often requires support from mass communication to enhance brand reputation and manage public perception. |
| Crisis Management | Collaborative approach in managing crises. | In crisis situations, marketing strategies adjust to align with the broad, informative messaging typically conveyed through mass communication channels. |
| Audience Analysis | Shared reliance on audience data and insights. | Both disciplines analyze audience data to understand preferences, behaviors, and trends, leading to more effective communication strategies. |
| Ethical Considerations | Shared responsibility in ethical messaging. | Both fields face ethical challenges in message creation and delivery, and must navigate these responsibly to maintain public trust and credibility. |
| Globalization | Enhanced global reach and influence. | The globalization of media has expanded the scope of both marketing and mass communication, creating a more interconnected and diverse audience base. |
The relationship between marketing and mass communication is characterized by a complex interplay of content creation, audience engagement, and shared use of media channels. While they have distinct objectives and methods, their collaboration is essential in shaping media landscapes, audience perceptions, and brand images in today’s digital world.
What is the Comparison Between Marketing and Mass Communication?
Understanding the comparison between marketing and mass communication is essential for professionals navigating the media landscape. This detailed guide presents a comprehensive comparison in a table format, elucidating their distinct approaches, goals, and methodologies:
| Aspect | Marketing | Mass Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Marketing involves strategies to promote and sell products or services, focusing on customer engagement and conversion. | Mass communication is the process of disseminating information, news, or entertainment to a broad audience. |
| Primary Goal | The primary goal is to influence consumer behavior, driving sales and brand loyalty. | Aims to inform, educate, or entertain a wide and diverse audience. |
| Target Audience | Targets specific consumer segments, tailored to their behaviors and preferences. | Addresses a broad, general audience, often without specific segmentation. |
| Content Strategy | Content in marketing is promotional, persuasive, and geared towards showcasing product or service benefits. | Mass communication content is diverse, including news, educational content, and entertainment. |
| Channels and Mediums | Utilizes targeted mediums like digital advertising, social media marketing, and direct mail. | Employs a wide range of channels, such as television, radio, newspapers, and online platforms. |
| Feedback Mechanism | Direct and immediate feedback through customer interactions, sales data, and market research. | Indirect feedback gathered from audience ratings, surveys, and viewership data. |
| Measurement of Success | Success is measured by marketing metrics like conversion rates, sales figures, and ROI. | Success is evaluated based on audience reach, impact, and engagement levels. |
| Message Customization | Highly customized and personalized messages aimed at specific consumer needs and desires. | Generalized messages designed to appeal to the interests of a wide audience. |
| Tactical Execution | Involves strategic planning, market analysis, and targeted campaign development. | Focused on content creation, broadcasting, and wide dissemination. |
| Resource Allocation | Resources are allocated for market research, advertising campaigns, and promotional activities. | Distributed across content production, media buying, and broadcasting infrastructure. |
| Adaptability | Highly adaptable to market trends, consumer feedback, and changing preferences. | Adaptable in terms of content, aligning with current events, trends, and audience interests. |
| Impact Assessment | Assesses impact based on market share, customer loyalty, and brand positioning. | Measures impact through audience size, societal influence, and public perception. |
Marketing and mass communication, while interconnected in the media field, exhibit clear differences. Marketing is more focused on consumer engagement and sales, employing targeted strategies, whereas mass communication aims to reach a wide audience with a variety of content, focusing on informing and entertaining. This comparison underscores their unique roles in the world of communication and media.
The contrast between Mass Communication and Marketing Communication is pivotal in the media landscape. Mass Communication broadly disseminates information, while Marketing Communication strategically targets specific audiences. Understanding these differences is essential for crafting effective communication strategies, whether to inform a wide audience or to drive targeted consumer engagement and brand loyalty. This guide offers key insights into navigating these two distinct yet interconnected fields.



