Mass Communication vs Visual Communication – 19+ Examples
In the diverse realm of media, distinguishing between Mass Communication and Visual Communication is pivotal. While Mass Communication encompasses a broad spectrum of media forms to disseminate information to large audiences, Visual Communication specifically focuses on conveying messages and ideas through visual elements. This exploration delves into how each field operates, their unique methodologies, and their impact in the digital age, highlighting the distinct yet complementary roles they play in the world of communication.
What is the Difference between Mass Communication and Visual Communication?
The distinction between Mass Communication and Visual Communication is crucial in the field of media studies. Below is a detailed comparison presented in a table format, highlighting their unique attributes and roles:
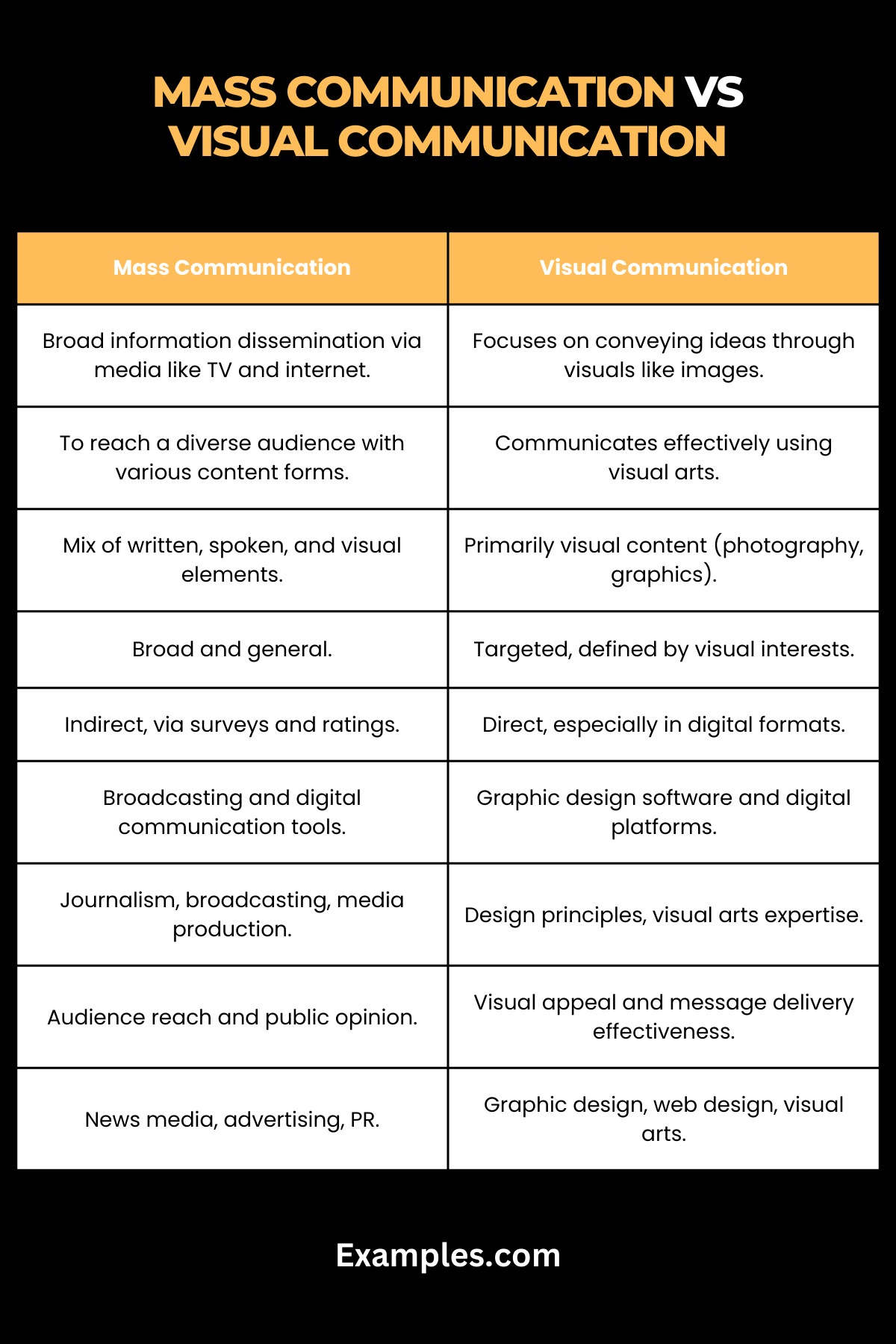
| Aspect | Mass Communication | Visual Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Involves disseminating information broadly through channels like television, radio, newspapers, and the internet. | Focuses on conveying information and ideas primarily through visual elements like images, graphics, and videos. |
| Primary Objective | To reach and influence a wide, diverse audience with various forms of content. | To communicate messages effectively using visual art forms and design principles. |
| Content Nature | Includes written, spoken, and visual content, depending on the medium. | Primarily visual content, including photography, illustration, and graphic design. |
| Communication Approach | Often a one-to-many approach, targeting general audiences. | Can be both one-to-one and one-to-many, with a focus on visual engagement and interpretation. |
| Target Audience | Broad and general, aiming to cater to diverse demographics. | Specific target audiences, often defined by visual preferences and understanding. |
| Feedback Mechanism | Feedback is generally indirect, gauged through audience ratings, surveys, and viewership. | Direct and immediate feedback is possible, especially in digital mediums, through user interaction and engagement. |
| Technological Utilization | Utilizes a range of technologies for broadcasting and digital communication. | Heavily reliant on graphic design software, imaging technology, and digital platforms. |
| Skillset and Expertise | Requires skills in journalism, writing, broadcasting, and media production. | Demands expertise in design principles, visual arts, and often, digital design tools. |
| Impact Measurement | Measured by reach, audience size, and impact on public opinion. | Assessed by visual appeal, user engagement, and effectiveness in visual message delivery. |
| Industry Applications | Applied in news media, advertising, public relations, and digital content creation. | Used in graphic design, advertising, web design, and visual art installations. |
| Message Customization | Generalized to appeal to a broad audience across different mediums. | Highly tailored to create visual impact and resonance with specific audience groups. |
| Role in Communication | Aims to inform, persuade, or entertain on a mass scale. | Aims to engage, inform, and captivate through visual storytelling and design. |
This table illustrates that while Mass Communication covers a wide range of communication forms to a general audience, Visual Communication is more focused on conveying messages through visual mediums. Both play distinct yet complementary roles in the communication landscape.
10 Mass Communication Examples
Discover the diverse and impactful world of Mass Communication through these ten examples. Each showcases the power of mass media in reaching and influencing wide audiences, demonstrating the variety and depth of communication strategies in this dynamic field.
- National Television Broadcasts:
National TV broadcasts deliver news, entertainment, and educational content to millions. They play a key role in shaping public opinion and cultural trends. - Radio Talk Shows:
Radio talk shows provide a platform for discussion on various topics, reaching audiences during commutes. They blend entertainment with information, making them a staple in mass communication. - Newspaper Publications:
Newspapers have been a traditional form of mass media, offering in-depth news, editorials, and features. They are crucial for informed public discourse and community engagement. - Online News Portals:
With the digital shift, online news portals have become a primary news source. They offer real-time updates and interactive content, appealing to the digitally savvy audience. - Social Media Platforms:
Platforms like Facebook and Twitter facilitate rapid information dissemination, influencing public opinion. Their viral nature makes them powerful tools in mass communication. - Advertising Campaigns on Billboards:
Billboard advertising captures the attention of a wide audience, especially in high-traffic areas. It’s a visual strategy in mass communication for brand promotion. - Public Service Announcements (PSAs):
PSAs are used to educate and inform the public on important issues like health and safety. They leverage mass media for societal welfare. - Corporate Press Releases:
Press releases are essential for companies to communicate with the public and stakeholders. They are a formal tool to announce news or changes. - Magazine Features:
Magazines cater to specific interests, yet they reach a broad audience. They blend entertainment with informative content, influencing trends and opinions. - Documentary Broadcasts on Television:
Documentaries on television channels educate and engage viewers on various topics. They combine visual storytelling with factual reporting, appealing to a wide audience.
10 Visual Communication Examples
Explore the realm of Visual Communication with these ten compelling examples. Each showcases the effectiveness of conveying messages through visual means, highlighting the significance and impact of visual elements in communication.
- Infographics:
Infographics combine data and design to present complex information clearly and engagingly. They are widely used in digital marketing to simplify and visualize data. - Brand Logos:
A well-designed brand logo communicates a company’s identity and values visually. It’s an essential element in branding, instantly recognizable and evoking brand association. - Architectural Designs:
Architectural designs communicate ideas and concepts through blueprints and 3D models. They are vital in conveying the vision and functionality of a space. - User Interface (UI) Design of Websites and Apps:
UI design plays a key role in how users interact with websites and apps. Good design enhances user experience and facilitates easy navigation. - Photography in Advertising:
Advertising heavily relies on photography to capture attention and convey messages. Effective photographs can evoke emotions and drive consumer engagement. - Film and Video Production:
Film and video production combines visual storytelling with auditory elements. It’s a powerful medium for narrative communication, widely used in entertainment and marketing. - Social Media Visual Content:
Visual content on platforms like Instagram and Pinterest dominates social media. It’s crucial for engagement, brand presence, and viral marketing campaigns. - Public Art and Installations:
Public art, like murals and installations, communicates cultural narratives and social messages. It’s an expressive form of visual communication accessible to a broad audience. - Product Packaging Design:
Packaging design not only protects products but also communicates brand identity and information visually. It influences consumer perceptions and buying decisions. - Animated Explainer Videos:
Animated videos explain concepts using engaging visuals and narratives. They are effective in educational content, product demonstrations, and storytelling.
Comparison Between Mass Communication and Visual Communication
The fields of Mass Communication and Visual Communication play distinct yet interconnected roles in the media world. Here’s an expanded comparison in table format, highlighting more aspects to illuminate their differences:
| Aspect | Mass Communication | Visual Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Core Principle | Broadly transmitting information and ideas through a mix of media to a wide audience. | Focused on conveying messages primarily through visual elements like images and design. |
| Key Methods | Utilizes diverse methods such as broadcasting, print media, and digital content. | Emphasizes visual techniques like graphic design, illustration, and videography. |
| Content Diversity | Offers a variety of content including news, educational material, and entertainment. | Specializes in visually-driven content, often used in advertising, art, and design. |
| Audience Engagement | Seeks to reach and influence a broad public audience with general or specific messages. | Engages audiences through visual appeal and creative design, often targeting specific demographics. |
| Technology Utilization | Integrates various technological platforms, from traditional media to digital channels. | Heavily reliant on the latest visual technology, software, and digital mediums. |
| Interactivity | Varies from one-way broadcasting to interactive digital media platforms. | Often interactive, especially in digital formats, allowing audience participation and feedback. |
| Narrative Style | Uses a combination of storytelling techniques, including textual, audio, and visual. | Leverages visual storytelling, employing imagery and artistic elements to convey narratives. |
| Impact on Audience | Aims for wide reach and influence, impacting public opinion and behavior. | Focuses on creating an immediate visual impact and lasting impression on viewers. |
| Professional Skillset | Requires skills in journalism, writing, media production, and communication strategies. | Demands expertise in visual arts, graphic design, color theory, and visual aesthetics. |
| Application in Marketing | Used in advertising and public relations to reach a broad customer base. | Essential in brand identity, product design, and creating visually appealing marketing materials. |
| Educational Focus | Covers a broad spectrum of media studies, communication theories, and media ethics. | Concentrates on design principles, visual theory, and practical skills in visual media creation. |
| Cultural Influence | Reflects and shapes societal values, norms, and trends through widespread media. | Influences cultural aesthetics and visual literacy, often leading trends in design and art. |
This detailed comparison reveals that Mass Communication is about reaching and engaging a diverse audience through various media forms, while Visual Communication is centered around the power of visuals to convey messages and ideas. Each field employs distinct methods and techniques, shaping the way information and ideas are presented and perceived in the media landscape.
Which Has More Job Opportunities, Visual Communication or Mass Communication?
In today’s media-rich landscape, both Visual Communication and Mass Communication offer a wealth of job opportunities, each with its own unique prospects. Evaluating which field has more job opportunities depends on various factors including industry demand, technological advancements, and evolving communication trends.
Job Opportunities in Mass Communication
Mass Communication encompasses a broad range of media platforms – from traditional broadcasting and journalism to newer forms like digital media and online content creation. This diversity opens up numerous career paths:
- Journalism: Opportunities in reporting, editing, and news analysis.
- Broadcasting: Roles in television and radio, such as producers, presenters, and technical support.
- Public Relations: Positions in corporate communication, brand image management, and crisis communication.
- Advertising: Career paths in creative development, campaign management, and media planning.
- Digital Media: Expanding opportunities in content creation, social media management, and digital marketing.
The digital transformation has significantly broadened the scope of Mass Communication, making it an ever-evolving field with a steady demand for professionals.
Job Opportunities in Visual Communication
Visual Communication focuses on conveying messages through visual elements, offering opportunities in various sectors:
- Graphic Design: Roles in branding, advertising, and digital content creation.
- Web and UI/UX Design: Designing user-friendly and visually appealing digital interfaces.
- Photography and Videography: Opportunities in commercial, journalistic, and artistic photography/videography.
- Animation and Motion Graphics: Careers in animation studios, advertising agencies, and film production.
- Art Direction: Leading creative visual projects in advertising, publishing, and film.
With the increasing importance of visual aesthetics in branding and communication, Visual Communication professionals are in high demand, especially in industries prioritizing digital and visual content.
Comparison and Trends
- Demand Dynamics: Both fields have strong demands but in different sectors. Mass Communication is broader and more traditional, while Visual Communication is more niche and specialized.
- Impact of Digitalization: The digital age has amplified opportunities in both fields, with a notable increase in digital and social media roles.
- Skills and Specialization: Visual Communication often requires more specialized skills in design and art, whereas Mass Communication covers a wider range of skills from writing to production.
Both Mass Communication and Visual Communication present vast and varied job opportunities, shaped by industry needs and technological advancements. Whether one pursues the diverse and expansive field of Mass Communication or the specialized, creative realm of Visual Communication, each offers a unique set of career paths. Your choice should align with your skills, interests, and the evolving trends in the dynamic world of media and communication.



