60+ Past Participle Examples
The past participle is a verb forms typically ending in “-ed,” “-d,” “-t,” “-en,” or “-n” and used in perfect tenses, passive voice, and as adjectives. Examples include “eaten,” “played,” and “driven.” It often pairs with auxiliary verbs like “has,” “have,” or “had.” For instance, in “She has finished her work,” “finished” is the past participle of “finish.”
What Is a Past Participle?
The past participle is a verb form used in perfect tenses and passive voice. For regular verbs, it typically ends in -ed (e.g., “walked”), while irregular verbs have various endings (e.g., “gone,” “written”). It combines with auxiliary verbs like “has,” “have,” and “had” to form perfect tenses and is used in passive constructions.
When Do We Use the Past Participle?
The past participle is a verb form that is used in several grammatical contexts in English. Here are the main situations in which you use the past participle:
1. Perfect Tenses
The past participle is used to form the perfect tenses, which describe actions that are completed at the time of speaking or by a specified time.
Present Perfect
Used to describe actions that have been completed at some point in the past but are relevant to the present. Example:
- I have finished my homework.
- She has visited Paris several times.
Past Perfect
Used to describe an action that was completed before another action in the past.
Example:
- By the time he arrived, we had already left.
- She had finished the exam before the timer went off.
Future Perfect
Used to describe an action that will be completed before a specified time in the future.
Example:
- By next year, I will have graduated from college.
- They will have finished the project by tomorrow.
2. Passive Voice
The past participle is used to form the passive voice, where the focus is on the action or the recipient of the action rather than the doer.
Example:
- The book was written by George Orwell.
- The cookies have been baked.
3. As Adjectives
The past participle can function as an adjective, describing a noun or pronoun.
Example:
- The broken vase lay on the floor.
- He felt exhausted after the long run.
4. Past Participial Phrases
Past participial phrases can be used to provide additional information about a noun, often functioning as adjectives.
Example:
- The girl, surprised by the sudden noise, jumped back.
- The car, damaged in the accident, was towed away.
How to form Past Participles
Past participles can be formed in two main ways: regular and irregular forms. Here’s a guide on how to create them:
1. Regular Verbs
For most regular verbs, the past participle is formed by adding “-ed” to the base form of the verb.
Examples:
- Play: play -> played
- Work: work -> worked
- Visit: visit -> visited
2. Irregular Verbs
Irregular verbs do not follow a single pattern, so their past participles must be memorized.
Examples:
- Go: go -> gone
- Eat: eat -> eaten
- Take: take -> taken
- Write: write -> written
- Break: break -> broken
Past Participle Examples in Sentences
Perfect Tenses
Present Perfect:
- She has completed her assignment.
- They have visited the museum several times.
Past Perfect:
- By the time the show started, we had found our seats.
- She had finished her homework before dinner.
Future Perfect:
- By next month, I will have saved enough money for the trip.
- They will have left by the time you arrive.
Passive Voice
- The cake was baked by my grandmother.
- The book has been read by millions of people.
- The new policy was implemented last year.
As Adjectives
- The broken vase lay on the floor.
- She handed me a written note.
- The painted fence looks new.
Past Participial Phrases
- Exhausted from the long day, he went straight to bed.
- The car, damaged in the accident, was towed away.
- The letter, signed by the president, confirmed the new policy.
Irregular Verbs in Sentences
- He has gone to the store.
- They had written their reports before the deadline.
- She has seen that movie twice.
- The bell has rung already.
- The treasure was hidden in the cave.
Regular Verbs in Sentences
- I have walked this path many times.
- They had finished their meal before the meeting started.
- She has learned a lot this semester.
- The room was decorated beautifully.
- The documents were printed and ready for distribution.
Past Participle with Prepositions Examples
Past participles are often used with prepositions to form phrases that describe conditions, reasons, or results. Here are some examples:
1. Interested in
- “She is interested in learning new languages.”
- “They were interested in the latest technology.”
2. Known for
- “The town is known for its beautiful scenery.”
- “He is known for his generosity.”
3. Committed to
- “They are committed to improving the community.”
- “She is committed to her job.”
4. Worried about
- “He is worried about his exam results.”
- “She is worried about the future.”
5. Excited about
- “The children are excited about the trip.”
- “She is excited about starting her new job.”
6. Satisfied with
- “They are satisfied with the service.”
- “He is satisfied with his progress.”
7. Tired of
- “She is tired of waiting.”
- “They are tired of the constant noise.”
8. Surprised by
- “We were surprised by the news.”
- “She was surprised by his reaction.”
9. Covered with
- “The ground was covered with snow.”
- “The cake was covered with frosting.”
10. Filled with
- “The room was filled with laughter.”
- “Her eyes were filled with tears.”
Verb tenses that use the Past Participle
The past participle is used in several English verb tenses, primarily in perfect tenses and the passive voice. Here’s a guide to the verb tenses that use the past participle:
1. Present Perfect
- Form: Has/Have + Past Participle
- Example: “She has finished her homework.”
- Usage: Describes actions that occurred at an unspecified time before now or began in the past and continue to the present.
2. Past Perfect
- Form: Had + Past Participle
- Example: “He had left before she arrived.”
- Usage: Describes actions that were completed before another past action.
3. Future Perfect
- Form: Will Have + Past Participle
- Example: “By next week, they will have completed the project.”
- Usage: Describes actions that will be completed before a specified time in the future.
4. Present Perfect Continuous
- Form: Has/Have Been + Present Participle (Note: While this tense primarily uses the present participle, the auxiliary verb “been” is the past participle of “be.”)
- Example: “She has been studying for hours.”
- Usage: Describes actions that began in the past and continue into the present with a focus on the duration.
5. Past Perfect Continuous
- Form: Had Been + Present Participle (Again, “been” is the past participle of “be.”)
- Example: “He had been waiting for two hours before she arrived.”
- Usage: Describes actions that were ongoing in the past up until another past action, with a focus on the duration.
6. Future Perfect Continuous
- Form: Will Have Been + Present Participle (Again, “been” is the past participle of “be.”)
- Example: “By next year, she will have been working here for a decade.”
- Usage: Describes actions that will be ongoing up until a point in the future, with a focus on the duration.
7. Passive Voice
- Form: Form of “Be” (is, am, are, was, were, be, being, been) + Past Participle
- Examples:
- “The cake was baked by my grandmother.”
- “The project is completed every year.”
- Usage: Used to indicate that the subject of the sentence is acted upon by someone or something else.
Past Participles of Regular Verbs
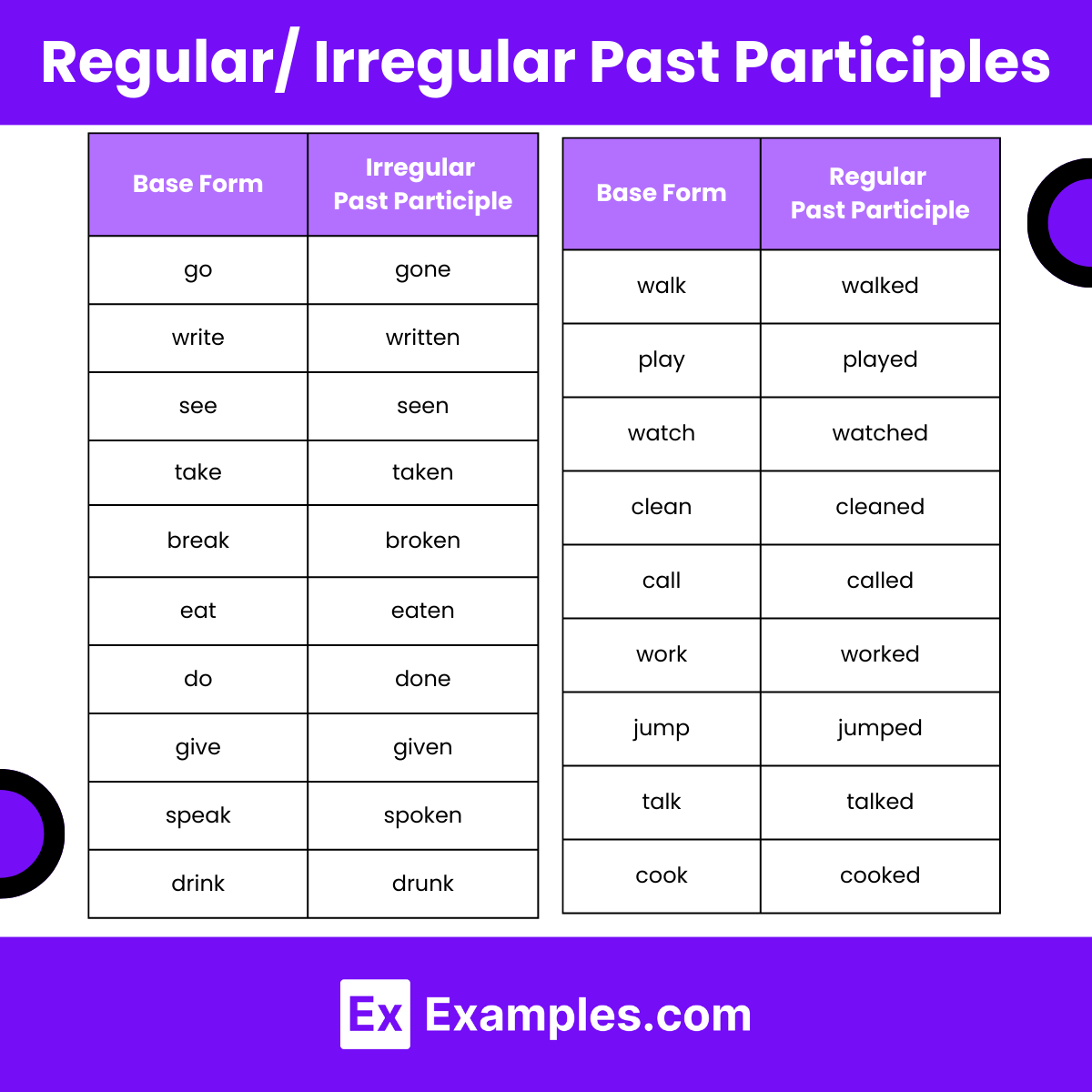
Regular verbs in English form their past participles by adding “-ed,” “-d,” or occasionally “-t” to the base form of the verb. Here are examples of regular verbs with their past participles:
Examples:
| Base Form | Past Participle |
|---|---|
| accept | accepted |
| arrive | arrived |
| bake | baked |
| call | called |
| clean | cleaned |
| close | closed |
| dance | danced |
| decide | decided |
| enjoy | enjoyed |
| help | helped |
| join | joined |
| jump | jumped |
| learn | learned |
| like | liked |
| listen | listened |
| love | loved |
| move | moved |
| need | needed |
| open | opened |
| play | played |
| rain | rained |
| start | started |
| talk | talked |
| touch | touched |
| use | used |
| walk | walked |
| want | wanted |
| watch | watched |
| work | worked |
Past Participle of Irregular Verbs
Irregular verbs do not follow a consistent pattern when forming their past participles. Each irregular verb has a unique past participle form that must be memorized. Here are examples of common irregular verbs with their past participles:
Examples:
| Base Form | Past Simple | Past Participle |
|---|---|---|
| arise | arose | arisen |
| be | was/were | been |
| become | became | become |
| begin | began | begun |
| bite | bit | bitten |
| break | broke | broken |
| bring | brought | brought |
| build | built | built |
| buy | bought | bought |
| choose | chose | chosen |
| come | came | come |
| do | did | done |
| drink | drank | drunk |
| drive | drove | driven |
| eat | ate | eaten |
| fall | fell | fallen |
| feel | felt | felt |
| find | found | found |
| fly | flew | flown |
| forget | forgot | forgotten |
| get | got | gotten |
| give | gave | given |
| go | went | gone |
| grow | grew | grown |
| have | had | had |
| hear | heard | heard |
| hold | held | held |
| keep | kept | kept |
| know | knew | known |
| leave | left | left |
| lose | lost | lost |
| make | made | made |
| meet | met | met |
| pay | paid | paid |
| read | read | read |
| ride | rode | ridden |
| ring | rang | rung |
| run | ran | run |
| say | said | said |
| see | saw | seen |
| sell | sold | sold |
| send | sent | sent |
| sing | sang | sung |
| sit | sat | sat |
| sleep | slept | slept |
| speak | spoke | spoken |
| stand | stood | stood |
| take | took | taken |
| teach | taught | taught |
| tell | told | told |
| think | thought | thought |
| understand | understood | understood |
| wear | wore | worn |
| write | wrote | written |
Using a Past Participle as an Adjective
Past participles can function as adjectives to describe noun or pronoun. When used this way, they often describe a state or condition resulting from an action. Here are some examples and explanations:
Examples:
- Broken
- Sentence: “The broken vase lay on the floor.”
- Explanation: “Broken” describes the state of the vase after it has been damaged.
- Excited
- Sentence: “The excited children ran towards the playground.”
- Explanation: “Excited” describes the children’s emotional state.
- Baked
- Sentence: “We enjoyed the freshly baked bread.”
- Explanation: “Baked” describes the bread that has been cooked in the oven.
- Closed
- Sentence: “The closed door prevented us from entering.”
- Explanation: “Closed” describes the door that is shut.
- Written
- Sentence: “She handed me the written report.”
- Explanation: “Written” describes the report that has been prepared in writing.
- Tired
- Sentence: “After the long hike, everyone felt tired.”
- Explanation: “Tired” describes the state of feeling fatigue.
- Fried
- Sentence: “We had fried chicken for dinner.”
- Explanation: “Fried” describes the chicken that has been cooked in oil.
- Burned
- Sentence: “The burned toast tasted awful.”
- Explanation: “Burned” describes the toast that has been overcooked.
- Fallen
- Sentence: “The fallen leaves covered the ground.”
- Explanation: “Fallen” describes the leaves that have dropped from the trees.
- Known
- Sentence: “She is a well-known author.”
- Explanation: “Known” describes the author’s level of recognition.
Other Uses of the Past Participle
Past participles are versatile and have several uses beyond forming perfect tenses. They can also be used in passive voice constructions, as adjectives, and in certain phrases. Here are the various uses of the past participle:
1. Perfect Tenses
Past participles are used to form perfect tenses, indicating completed actions or states.
- Present Perfect: “She has eaten dinner.”
- Past Perfect: “They had finished the project before the deadline.”
- Future Perfect: “By tomorrow, I will have completed the assignment.”
2. Passive Voice
In passive voice constructions, the past participle is used with a form of the verb “to be” to indicate that the subject is acted upon.
- Present Passive: “The book is written by the author.”
- Past Passive: “The cake was baked by my grandmother.”
- Future Passive: “The results will be announced tomorrow.”
3. As Adjectives
Past participles can function as adjectives to describe nouns, often indicating a completed action or condition.
- “The broken vase lay on the floor.”
- “We need to fix the damaged roof.”
- “She looked at the written report.”
4. Perfect Infinitive
The perfect infinitive form combines “to have” with the past participle to indicate a completed action.
- “She is happy to have finished her work.”
- “He claimed to have seen the movie already.”
5. Participle Phrases
Participle phrases provide additional information about a noun and can be used to create complex sentences.
- “The man, known for his kindness, helped the elderly woman.”
- “The students, exhausted from the exam, went home early.”
6. Conditionals and Hypotheticals
Past participles are used in conditional sentences to describe hypothetical or contrary-to-fact situations.
- “If I had known, I would have acted differently.”
- “She would have come if she had been invited.”
7. Reported Speech
Past participles are sometimes used in reported speech, particularly in indirect statements.
- “He said that the package had been delivered.”
- “She mentioned that the work was completed.”
Examples in Sentences:
- Present Perfect: “They have gone to the store.”
- Past Passive: “The letter was written by John.”
- As Adjective: “The painted fence looked beautiful.”
- Perfect Infinitive: “She seems to have forgotten the meeting.”
- Participle Phrase: “The child, covered in mud, smiled at his mother.”
- Conditional: “If she had studied, she would have passed the test.”
- Reported Speech: “He confirmed that the task was completed.”
Past tense vs. Past Participle
The past tense and past participle are both forms of verbs, but they are used in different contexts and have different functions. Here’s a table comparing the two:
| Aspect | Past Tense | Past Participle |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Indicates an action that occurred in the past. | Used in perfect tenses, passive voice, and as adjectives. |
| Usage | Describes completed actions or states. | Forms perfect tenses, passive constructions, and functions as adjectives. |
| Examples | “She walked to school.” | “She has walked to school.” “The letter was written.” “The broken vase lay on the floor.” |
| Formation (Regular Verbs) | Base form + “-ed” Example: “play” -> “played” | Usually the same as past tense for regular verbs Example: “play” -> “played” |
| Formation (Irregular Verbs) | No fixed pattern, must be memorized Example: “go” -> “went” | No fixed pattern, must be memorized Example: “go” -> “gone” |
| Key Difference | Directly describes past actions or conditions. | Used with auxiliary verbs (e.g., has, have, had) and in passive voice. |
What is a past participle?
A past participle is a verb form typically ending in -ed, -d, -t, -en, or -n used to form perfect tenses and passive voice.
How is the past participle formed?
Regular verbs form the past participle by adding -ed to the base form (e.g., “walk” becomes “walked”). Irregular verbs have unique forms (e.g., “go” becomes “gone”).
Can you give examples of past participles?
Yes, examples include “walked,” “written,” “eaten,” “broken,” and “gone.”
What is the function of past participles?
Past participles are used in perfect tenses (e.g., “have eaten”) and passive voice (e.g., “was written”).
Are past participles and past tense the same?
No, past tense indicates completed actions (e.g., “I walked”), while past participle forms are used with auxiliary verbs (e.g., “I have walked”).
What are irregular past participles?
Irregular past participles do not follow a fixed pattern (e.g., “write” becomes “written,” “go” becomes “gone”).
How do past participles function in passive voice?
In passive voice, past participles follow forms of “to be” (e.g., “The book was written by the author”).
Can past participles be used as adjectives?
Yes, past participles can describe nouns (e.g., “broken window,” “cooked food”).
What is the difference between past participle and present participle?
Past participles indicate completed actions (e.g., “eaten”), while present participles indicate ongoing actions and end in -ing (e.g., “eating”).
How are past participles used in perfect tenses?
Past participles combine with “have,” “has,” or “had” to form perfect tenses (e.g., “She has finished her work”).



