30+ Present Tense Examples
The present tense in English is primarily used to describe actions or conditions occurring at the current moment, but it can also refer to general truths, habits, and scheduled events. This tense is categorized into four forms: simple present (I walk), present continuous (I am walking), present perfect (I have walked), and present perfect continuous (I have been walking). Each form serves a different function, helping to convey various types of actions or states that are happening in the present.
What is the Present Tense?
The present tense in English describes actions or conditions at the current moment and encompasses general truths, habits, and schedules. It includes four forms: simple present (I walk), present continuous (I am walking), present perfect (I have walked), and present perfect continuous (I have been walking), each used for different aspects of current and ongoing actions.”
Functions of Present Tense
The present tense in English serves several important functions, each related to the way we discuss time, habits, truths, and ongoing actions. Below are the key functions of the present tense:
- Expressing Daily Habits and Routines: The simple present tense describes regular actions or habits. For example:
- She walks to school every day.
- He reads the newspaper in the morning.
- Stating General Truths and Laws of Nature: This tense is used to describe general truths and facts that are not bound by time. For instance:
- Water boils at 100 degrees Celsius.
- The Earth revolves around the Sun.
- Describing Current Actions (Temporary or at the Moment of Speaking): The present continuous tense is perfect for actions that are happening at the present moment. Examples include:
- I am studying for my exams right now.
- They are playing football.
- Indicating Fixed Arrangements or Scheduled Events: Often used in a more official or formal context, the simple present can refer to scheduled future events. For example:
- The train leaves at 6 p.m. tonight.
- Our meeting starts at nine tomorrow.
- Highlighting Past Actions with Present Relevance: The present perfect tense connects past actions to the present, especially to indicate experiences, changes, or completed actions with current relevance. For example:
- I have finished my homework.
- She has visited Paris three times.
- Emphasizing the Duration of Current Continuous Actions: The present perfect continuous is used to show that an action started in the past and is still ongoing or has just finished, often focusing on the action’s duration. Examples are:
- He has been working here for five years.
- They have been watching TV since morning.
Present Tense Formulas
The present tense in English is crucial for describing actions, habits, and truths. It is divided into four main forms, each with its specific formula:
Simple Present Tense
Formula: Subject + Base Verb (add “s” or “es” for third person singular)
Examples:
She writes in her journal every day.
The train leaves at 9 PM.
Present Continuous Tense
Formula: Subject + Am/Is/Are + Verb(-ing)
Examples:
I am reading a book right now.
They are watching a movie.
Present Perfect Tense
Formula: Subject + Has/Have + Past Participle (Verb-ed or irregular form)
Examples:
She has completed her assignment.
We have seen that movie twice.
Present Perfect Continuous Tense
Formula: Subject + Has/Have been + Verb(-ing)
Examples:
He has been working here for three years.
They have been studying since morning.
Types of Present Tenses
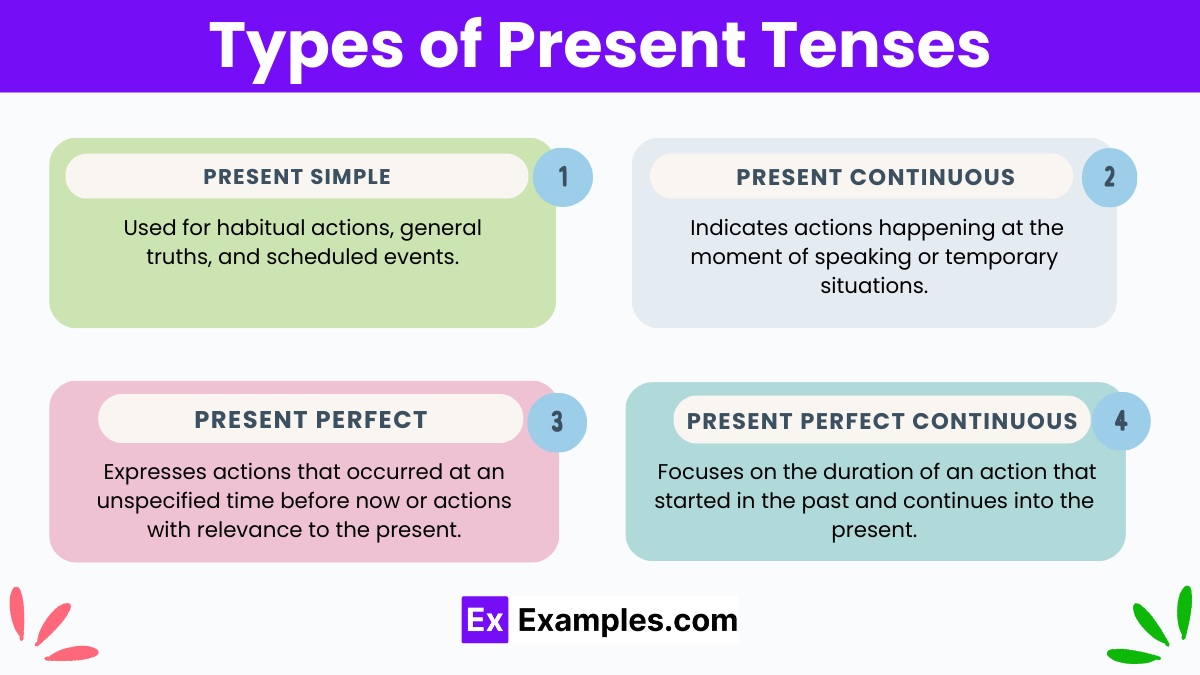
1. Present Simple:
- Used for habitual actions, general truths, and scheduled events.
- Structure: Subject + base form of the verb (s/es for third person singular).
- Example:
- She reads books every day.
- The sun rises in the east.
2. Present Continuous (Present Progressive):
- Indicates actions happening at the moment of speaking or temporary situations.
- Structure: Subject + “to be” verb (am/is/are) + present participle (-ing form of the verb).
- Example:
- They are playing football in the park.
- He is working on a project.
3. Present Perfect:
- Expresses actions that occurred at an unspecified time before now or actions with relevance to the present.
- Structure: Subject + have/has + past participle of the verb.
- Example:
- I have visited Paris several times.
- She has written a novel.
4. Present Perfect Continuous:
- Focuses on the duration of an action that started in the past and continues into the present.
- Structure: Subject + have/has been + present participle (-ing form of the verb).
- Example:
- He has been studying for three hours.
- They have been waiting for the bus since morning.
Present Tense vs. Past Tense
| Aspect | Present Tense | Past Tense |
|---|---|---|
| Usage | Describes actions or states currently happening, habitual actions, general truths, or scheduled events. | Describes actions or states that occurred at a specific point in the past. |
| Verb Forms | Subject + base form of the verb (with ‘s’ or ‘es’ for third person singular). | Subject + past tense forms of the verb (regular verbs add ‘ed’, irregular verbs have unique forms). |
| Examples | 1. She reads books every day. 2. They are playing football now. 3. The sun rises in the east. 4. I have visited Paris several times. 5. He has been studying for three hours. | 1. She read books yesterday. 2. They played football yesterday. 3. The sun rose in the east. 4. I visited Paris last year. 5. He studied for three hours yesterday. |
List of Present Tense Verbs
| Regular Verbs | Irregular Verbs |
|---|---|
| ask | be |
| call | become |
| dance | begin |
| eat | break |
| find | bring |
| give | build |
| have | buy |
| jump | catch |
| laugh | choose |
| play | come |
| read | do |
| sleep | draw |
| talk | drink |
| walk | drive |
| work | eat |
How Do We Use the Present Tense?
1. Describing Current Actions:
- The present tense is used to describe actions that are happening right now or at the moment of speaking. It conveys immediacy and provides a snapshot of the current situation.
- Example: “She is reading a book.” This sentence indicates that the action of reading is currently taking place.
2. Stating Habits and Routines:
- Present tense is also employed to talk about actions that occur regularly or as part of a routine. It signifies ongoing habits or activities.
- Example: “He plays tennis every weekend.” This sentence indicates that playing tennis is a habitual activity for him.
3. Expressing General Truths:
- The present tense is used to state facts or general truths that are universally accepted or always true.
- Example: “The Earth revolves around the Sun.” This statement expresses a scientific truth that applies at all times.
4. Indicating Scheduled Events:
- Present tense is used to discuss future events that are planned or scheduled. It conveys a sense of certainty about the timing of the event.
- Example: “The meeting starts at 9 AM tomorrow.” This sentence indicates a future event that is scheduled to occur.
5. Reporting in Literature or Presenting Narratives:
- Present tense is often used in literature or storytelling to create immediacy and engage the reader more directly in the narrative.
- Example: “The protagonist walks into the room and sees a mysterious figure.” This usage places the reader in the moment, experiencing the events as they unfold.
6. In Explanations or Instructions:
- Present tense is used to provide instructions or explain processes, especially when giving step-by-step guidance.
- Example: “First, you mix the ingredients, then you bake the cake.” This usage helps to make instructions clear and easy to follow.
7. In Sports Commentary or Live Broadcasts:
- Present tense is commonly used in sports commentary or live broadcasts to describe ongoing events as they happen in real-time.
- Example: “The player shoots and scores!” This usage adds excitement and immediacy to the commentary, enhancing the viewer’s experience.
Examples of Present Tense in Sentences
- She plays the piano beautifully.
- The sun shines brightly in the sky.
- They walk to school every morning.
- He drinks a cup of coffee before work.
- The teacher explains the lesson to the students.
- Birds sing melodiously in the trees.
- We watch our favorite TV show together.
- It rains heavily during the monsoon season.
- The dog barks loudly at strangers.
- Sarah reads a book in the library every afternoon.
Present Tense Interrogative Sentences Examples
The interrogative sentences are formed by starting with an auxiliary verb (do, does, is, are) followed by the subject and the base form of the main verb. This structure is used to ask questions about actions, states, habits, or events in the present tense.
- Do you like chocolate ice cream?
- Is she coming to the party tonight?
- Do they play tennis every weekend?
- Are you ready for the exam?
- Does he speak Spanish fluently?
- Are we going to the beach tomorrow?
- Do the birds sing in the morning?
- Is it raining outside right now?
- Do you know the answer to this question?
- Are they watching a movie tonight?
Present Tense Affirmative Sentences Examples
The affirmative sentences in the present tense affirm actions, habits, states, or general truths. They are formed by using the base form of the verb with the appropriate subject, indicating actions or situations that occur regularly, currently, or generally.
- She reads books every night before bed.
- They enjoy hiking in the mountains.
- He works as a teacher at the local school.
- The flowers bloom beautifully in the spring.
- We eat dinner together as a family every evening.
- It snows in the mountains during the winter.
- The children play in the park after school.
- I listen to music while I work.
- The sun shines brightly in the clear sky.
- They live in a small house by the river.
How to write Present Tense?
To write in the present tense, use the base form of the verb for most subjects, adding ‘s’ or ‘es’ for third person singular. It describes actions happening now, habitual actions, or general truths, providing immediacy and clarity to your writing.
How to identify Tenses?
Identifying tenses involves analyzing verb forms to determine when an action occurred relative to the present, past, or future. Pay attention to verb endings, auxiliary verbs, and time indicators to ascertain the tense.
What is Present Tense to Explain?
The present tense describes actions, states, or events that are currently happening, habitual, or timeless truths. It conveys immediacy and clarity, providing a snapshot of what is occurring at the moment of speaking.



