Shall vs Should- Meanings, Differences, Usage, Examples,Tricks
Unlock the intricacies of “Shall vs Should” in this comprehensive guide. Navigate through their definitions, meanings, and compound usages for effective communication. Delve into real-world examples to grasp their subtle differences and master their applications. Enhance your language skills and decision-making abilities with this indispensable resource on “Shall vs Should” in the realm of communication.
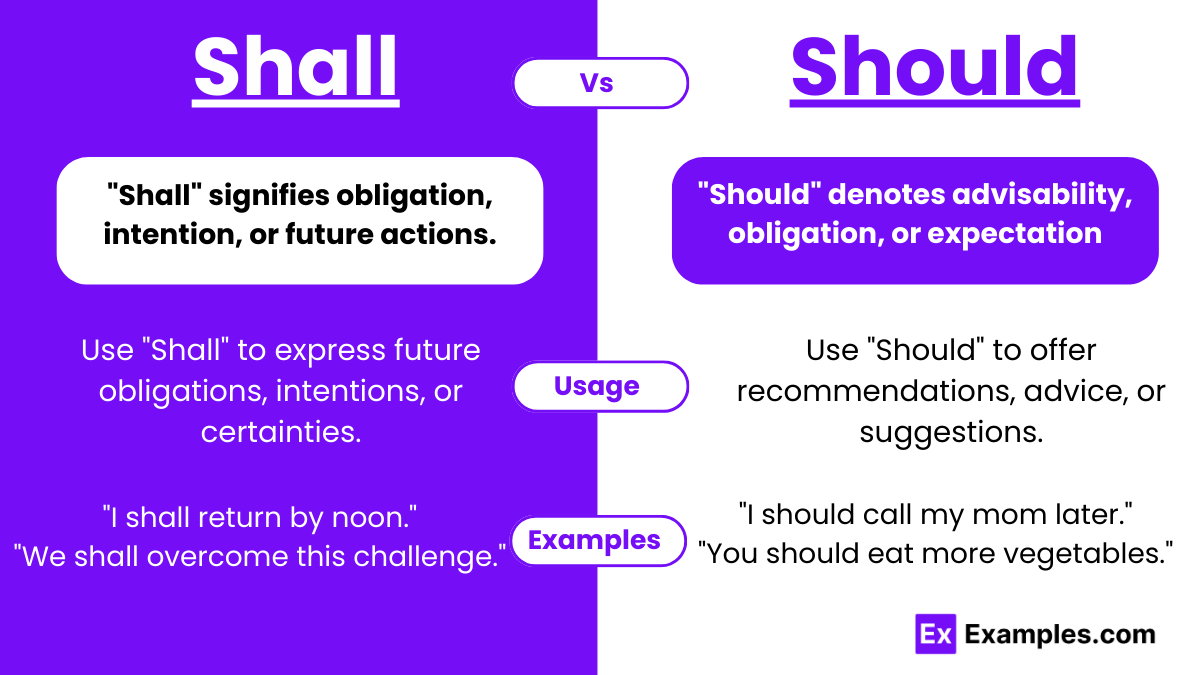
Shall vs Should – Meanings
Shall: “Shall” typically denotes an expression of obligation, duty, or future certainty. It’s often used in formal contexts, legal documents, or promises. For example, “I shall attend the meeting tomorrow” implies a firm intention or commitment.
Should: “Should” suggests recommendations, advisability, or expectations. It’s commonly employed in giving advice, making suggestions, or expressing opinions. For instance, “You should study regularly for better grades” implies a suggestion or advice for optimal outcomes.
Summary
How To Pronounce Far and Fare
How to Pronounce Shall
- Break “Shall” into two syllables: “sh” and “all.”
- Emphasize the first syllable, pronounced like “sh.”
- The second syllable is pronounced like “all,” rhyming with “call.”
- Combine the syllables smoothly: “sh-all.”
How to Pronounce Should
- Split “Should” into two syllables: “sh” and “ould.”
- Stress the first syllable, similar to “sh.”
- The second syllable is pronounced as “ould,” rhyming with “could” and “would.”
- Merge the syllables fluidly: “sh-ould.”
Differences Between Far and Fare
| Aspect | Shall | Should |
|---|---|---|
| Obligation | Implies obligation or future certainty. | Suggests recommendations or advisability. |
| Formality | Often used in formal or legal contexts. | Can be less formal, used in various settings. |
| Certainty | Indicates a stronger sense of certainty. | Less certain, offers suggestions or advice. |
| Intent | Reflects a firm intention or commitment. | Offers guidance or opinions for consideration. |
| Usage | Found in promises, laws, or formal documents. | Commonly used in advice, suggestions, or opinions. |
How to Remember the Tricks Between “Far” and “Fare”
Certainty vs. Suggestion:
- Distinguish between the stronger certainty implied by “Shall” and the softer suggestion conveyed by “Should.”
Formal vs. Casual:
- Note the formality contrast: “Shall” is often used in legal or formal contexts, while “Should” is more casual and versatile.
Intent vs. Advice:
- Recognize that “Shall” indicates a firm intention or obligation, whereas “Should” offers advice or recommendations.
Obligation vs. Recommendation:
- Remember that “Shall” implies obligation or duty, while “Should” suggests advisable actions or choices.
Authority vs. Flexibility:
- Consider the authoritative tone of “Shall” compared to the flexible and suggestive nature of “Should.”
Future vs. Present:
- Associate “Shall” with future actions or obligations, while “Should” often refers to present or future recommendations.
Legal vs. Everyday Usage:
- Differentiate between the legal or formal contexts where “Shall” is prevalent and the everyday conversations where “Should” is commonly used.
Personal vs. External:
- Understand that “Shall” may imply personal commitments, while “Should” typically addresses external actions or decisions.
Certainty Cue:
- Recall that “Shall” sounds similar to “will,” indicating a stronger sense of certainty, while “Should” offers softer guidance.
Advice Reminder:
- Keep in mind that “Should” often prompts the offering of advice, resembling the word “could,” suggesting possibilities rather than certainties.
When to Use Shall and Should
Usage of “Shall”
- Use “Shall” to express future obligations, intentions, or certainties, especially in formal or legal contexts, such as contracts, promises, or laws.
- Employ “Shall” for suggestions or proposals, often in first-person statements or questions, indicating a firm commitment or duty.
Usage of “Should”
- Use “Should” to offer recommendations, advice, or suggestions, indicating advisability or desirability, especially in second- or third-person statements.
- Employ “Should” in various contexts, including everyday conversations, giving opinions, making polite requests, or providing guidance.
Shall and Should Examples
Examples of “Shall”
- I shall attend the meeting tomorrow as scheduled.
- Shall we proceed with the project plan as discussed?
- The contract specifies that payment shall be made upon delivery.
- Shall I book the tickets for the conference next month?
- We shall not tolerate any form of discrimination in the workplace.
Examples of “Should”
- You should eat more vegetables for a balanced diet.
- Should I bring an umbrella in case it rains later?
- If you’re feeling unwell, you should see a doctor.
- Should we consider alternative solutions to this problem?
- Employees should submit their reports by the end of the week.
Synonyms For Shall and Should
| Shall Synonyms | Should Synonyms |
|---|---|
| Will | Ought |
| Must | Need to |
| Intend | Ought to |
| Promise | Advise |
| Command | Recommend |
| Direct | Suggest |
| Order | Advocate |
| Pledge | Propose |
| Decide | Encourage |
| Commit | Urge |
Exercise
Instructions: Fill in the blanks with the appropriate word, “Shall” or “Should,” to complete each sentence correctly.
- I ________ attend the meeting tomorrow as scheduled.
- ________ we proceed with the project plan as discussed?
- The contract specifies that payment ________ be made upon delivery.
- ________ I book the tickets for the conference next month?
- We ________ not tolerate any form of discrimination in the workplace.
- You ________ take the necessary precautions to ensure safety.
- Should we consider alternative solutions to this problem?
- ________ I inform the team about the changes in the schedule?
- She ________ consult a professional before making a decision.
- We ________ make an effort to reduce our carbon footprint.
Answers:
- Shall
- Shall
- Shall
- Shall
- Shall
- Should
- Should
- Shall
- Should
- Should
FAQ’S
Does anyone still use shall?
Yes, “shall” is still used, particularly in formal or legal contexts, in certain dialects, and for expressing offers, suggestions, or requirements, though its usage has become less common in everyday speech.
Is shall more polite?
In some contexts, “shall” can convey a sense of politeness or formality, especially in offers, suggestions, or invitations, but its perceived politeness may vary depending on cultural norms and linguistic conventions.
What is stronger should or shall?
“Shall” often implies obligation or necessity, while “should” typically suggests recommendation or expectation. However, the strength can vary based on context, formality, and regional usage norms.
What is the negative of shall?
The negative form of “shall” is “shall not” or “shan’t” in informal contexts. It indicates a lack of obligation, intention, or permission. In contracted form, it’s often used in spoken language.