Quickly convert Watt-hours to US Therms and vice versa with examples.com. Achieve accurate energy conversions effortlessly!
Wh to US Therm
Formula: Energy in US Therm (US Therm) = Energy in Watt-hour (Wh) x 3.41296E-5
Watt-hour :
US Therm :
| Watt-hours | US Therms |
|---|---|
| 1 | 0.0000341296 |
US Therm to Wh
Formula: Energy in Watt-hour (Wh) = Energy in US Therm (US Therm) ÷ 3.41296E-5
US Therm :
Watt-hour :
| US Therms | Watt-hours |
|---|---|
| 1 | 29300.079696216773 |
Energy Converters to Watt hour
Energy Converters to US Therm
Conversion Factors:
- Watt-Hours to US Therm : 1 US Therm = 29,300 Watt-hours
- US Therm to Watt-hour : 1 Watt-hour = 3.413e-5 US Therms
How to Convert Watt-hours to US Therms:
To convert Watt-hours to US Therms, multiply the number of Watt-hours by 3.413e-5.
US Therms=Watt-hours×3.413e−5
Example:
Convert 50,000 Watt-hours to US Therms.
US Therms=50,000×3.413e−5
US Therms=1.7065 US Therms
How to Convert US Therms to Watt-hours:
To convert US Therms to Watt-hours, divide the number of US Therms by 3.413e-5.
Watt-hours=US Therms/3.413e−5
Example:
Convert 2 US Therms to Watt-hours.
Watt-hours=2/3.413e−5
Watt-hours=2/0.00003413
Watt-hours≈58,585.05 Watt-hours
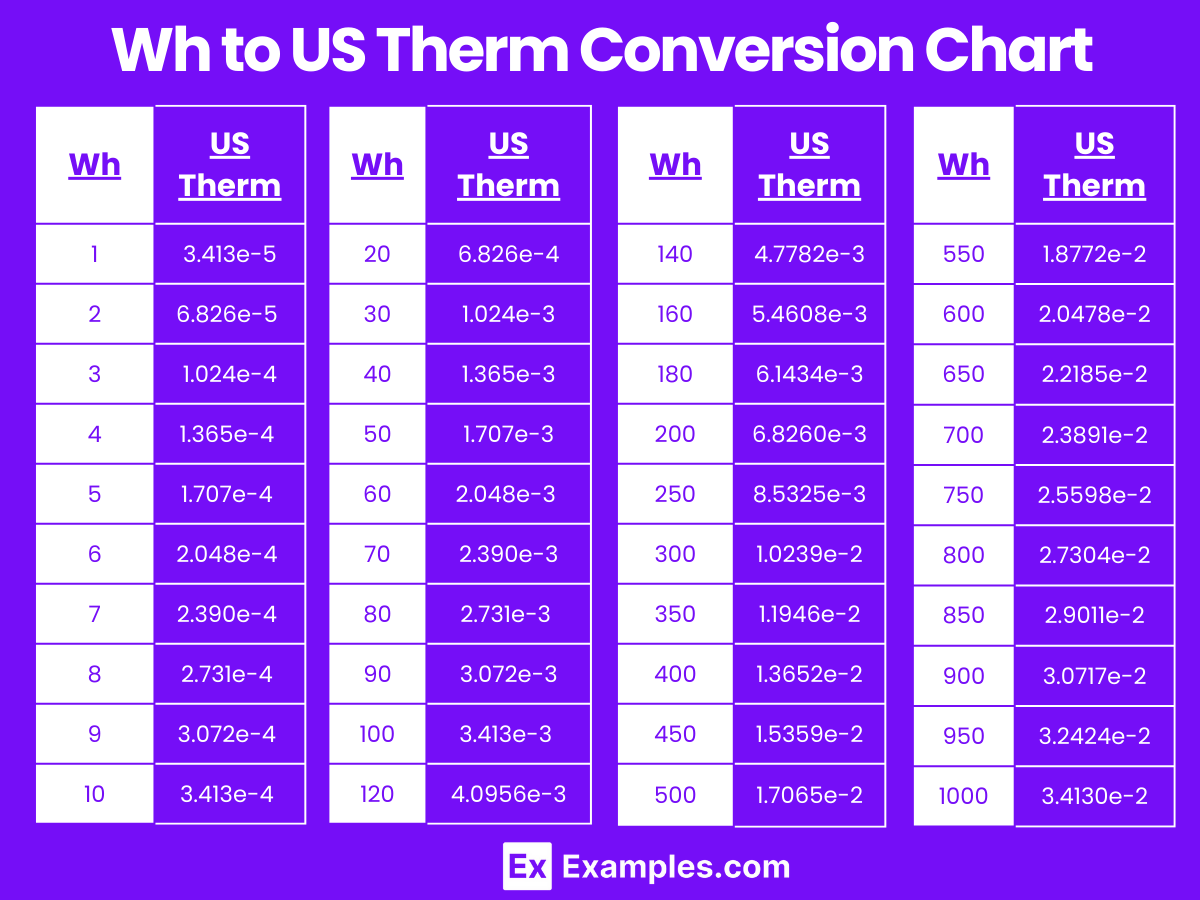
Watt-hour to US Therm Conversion Table
| Watt-hours (Wh) | US Therms (US Therms) |
|---|---|
| 1 Wh | 3.413e-5 US Therms |
| 2 Wh | 6.826e-5 US Therms |
| 3 Wh | 1.024e-4 US Therms |
| 4 Wh | 1.365e-4 US Therms |
| 5 Wh | 1.707e-4 US Therms |
| 6 Wh | 2.048e-4 US Therms |
| 7 Wh | 2.390e-4 US Therms |
| 8 Wh | 2.731e-4 US Therms |
| 9 Wh | 3.072e-4 US Therms |
| 10 Wh | 3.413e-4 US Therms |
| 20 Wh | 6.826e-4 US Therms |
| 30 Wh | 1.024e-3 US Therms |
| 40 Wh | 1.365e-3 US Therms |
| 50 Wh | 1.707e-3 US Therms |
| 60 Wh | 2.048e-3 US Therms |
| 70 Wh | 2.390e-3 US Therms |
| 80 Wh | 2.731e-3 US Therms |
| 90 Wh | 3.072e-3 US Therms |
| 100 Wh | 3.413e-3 US Therms |
Wh to US Therm Conversion Chart
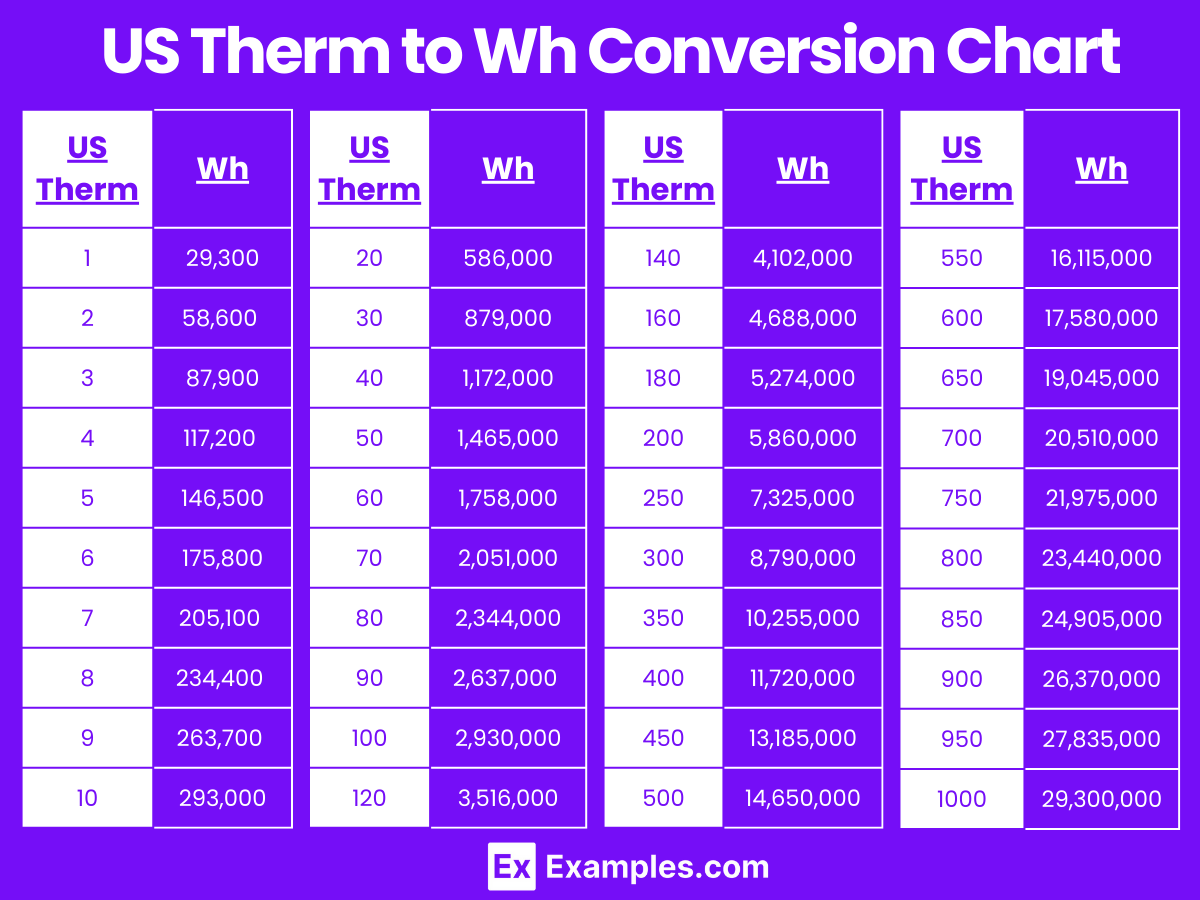
US Therm to Watt-hour to Conversion Table
| US Therms (US Therms) | Watt-hours (Wh) |
|---|---|
| 1 US Therm | 29,300 Wh |
| 2 US Therms | 58,600 Wh |
| 3 US Therms | 87,900 Wh |
| 4 US Therms | 117,200 Wh |
| 5 US Therms | 146,500 Wh |
| 6 US Therms | 175,800 Wh |
| 7 US Therms | 205,100 Wh |
| 8 US Therms | 234,400 Wh |
| 9 US Therms | 263,700 Wh |
| 10 US Therms | 293,000 Wh |
| 20 US Therms | 586,000 Wh |
| 30 US Therms | 879,000 Wh |
| 40 US Therms | 1,172,000 Wh |
| 50 US Therms | 1,465,000 Wh |
| 60 US Therms | 1,758,000 Wh |
| 70 US Therms | 2,051,000 Wh |
| 80 US Therms | 2,344,000 Wh |
| 90 US Therms | 2,637,000 Wh |
| 100 US Therms | 2,930,000 Wh |
US Therm to Wh Conversion Chart
Difference Between Watt-hour to US Therm
| Aspect | Watt-hour (Wh) | US Therm (US Therms) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A unit of energy equivalent to one watt of power consumed for one hour. | A unit of heat energy primarily used in the United States. |
| Usage | Commonly used in electrical applications to measure energy consumption. | Used primarily for measuring the energy content of natural gas. |
| Conversion Factor | 1 Wh = 3.413e-5 US Therms | 1 US Therm = 29,300 Wh |
| Typical Context | Electricity bills, battery capacities, and appliance energy use. | Natural gas billing and heating energy content. |
| Measurement Scale | Suitable for smaller quantities of energy, like in household appliances. | Suitable for large quantities of energy, such as heating systems. |
| Common Units | Kilowatt-hour (kWh), Megawatt-hour (MWh) | Therms, Dekatherms |
| Calculation | Multiply wattage by hours to get watt-hours. | Based on the energy content of gas in BTUs. |
| Standardization | Internationally recognized unit of energy. | Mainly used in the United States. |
1. Solved Examples on Converting Watt-hour to US Therm
Example 1:
Convert 1,000 Watt-hours to US Therms.
US Therms=1,000×3.413e−5
US Therms=0.03413 US Therms
Example 2:
Convert 5,000 Watt-hours to US Therms.
US Therms=5,000×3.413e−5
US Therms=0.17065 US Therms
Example 3:
Convert 10,000 Watt-hours to US Therms.
US Therms=10,000×3.413e−5
US Therms=0.3413 US Therms
Example 4:
Convert 25,000 Watt-hours to US Therms.
US Therms=25,000×3.413e−5
US Therms=0.85325 US Therms
Example 5:
Convert 50,000 Watt-hours to US Therms.
US Therms=50,000×3.413e−5
US Therms=1.7065 US Therms
2. Solved Examples on Converting US Therm to Watt-hour
Example 1:
Convert 1 US Therm to Watt-hours.
Watt-hours=1/3.413e−5
Watt-hours=29,300 Wh
Example 2:
Convert 2 US Therms to Watt-hours.
Watt-hours=2/3.413e−5
Watt-hours=58,600 Wh
Example 3:
Convert 5 US Therms to Watt-hours.
Watt-hours=5/3.413e−5
Watt-hours=146,500 Wh
Example 4:
Convert 10 US Therms to Watt-hours.
Watt-hours=10/3.413e−5
Watt-hours=293,000 Wh
Example 5:
Convert 20 US Therms to Watt-hours.
Watt-hours=20/3.413e−5
Watt-hours=586,000 Wh
Why do we need to convert Watt-hours to US Therms?
Converting Watt-hours to US Therms is useful for understanding energy consumption in different contexts, especially when comparing electrical energy usage (measured in Watt-hours) to natural gas energy usage (measured in Therms).
How accurate is the conversion factor of 3.413e-5?
The conversion factor of 3.413e-5 is a standard value used for converting between Watt-hours and US Therms. It provides a high level of accuracy for most practical purposes.
Is there a quick way to estimate the conversion without a calculator?
For rough estimates, you can remember that 1 US Therm is roughly equal to 29,300 Watt-hours. Therefore, dividing your Watt-hours by 29,300 gives an approximate number of US Therms.
Are there any tools or calculators available for this conversion?
Yes, many online calculators and tools can quickly convert Watt-hours to US Therms, making it easier for users to perform these calculations without manual effort.
Can I reverse the conversion from US Therms to Watt-hours?
Absolutely. To convert US Therms to Watt-hours, divide the number of US Therms by 3.413e-5, or multiply by 29,300.
Are Watt-hours and US Therms used globally?
Watt-hours are used globally, especially for electrical energy. US Therms are primarily used in the United States for measuring natural gas energy, but understanding the conversion is useful for international energy comparisons.

