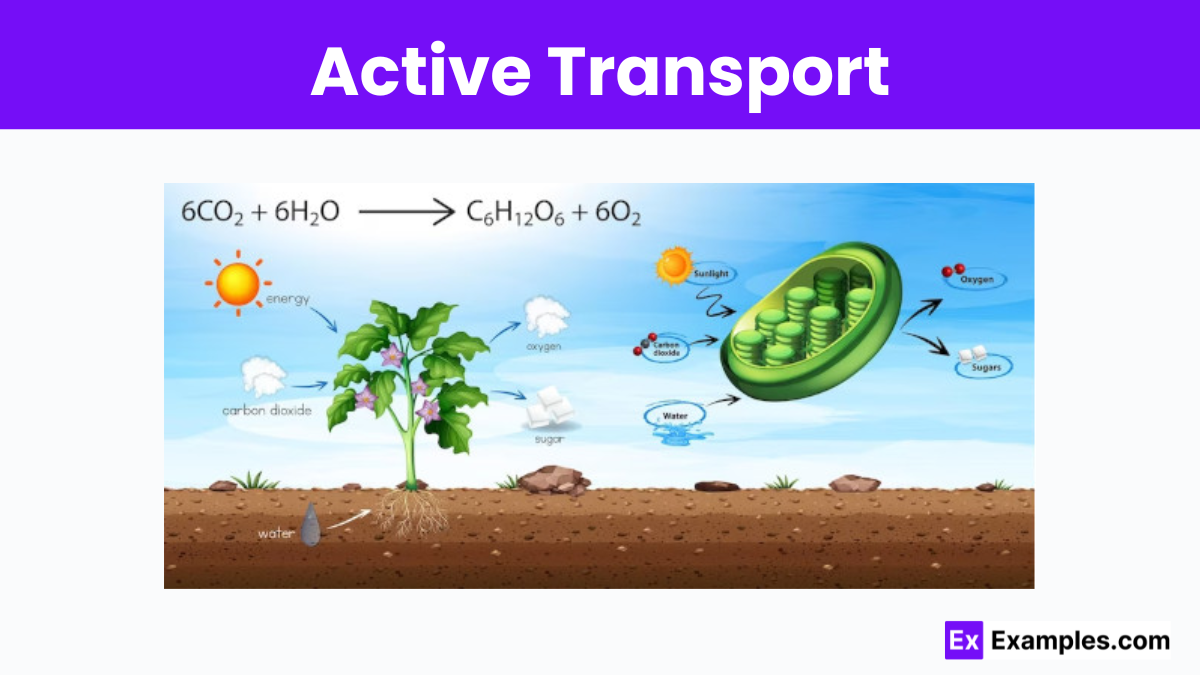
Which of the following best describes active transport in cells?
Movement of molecules from high to low concentration
Movement of molecules from low to high concentration using energy
Passive movement of molecules without energy
Movement of water through a semipermeable membrane