24+ Communication Skills Examples
In a world brimming with ideas, opinions, and dreams, effective communication becomes the thread that weaves through every successful interaction. From heartfelt conversations to impactful presentations, the ability to convey thoughts, understand others, and build connections is essential. Communication skills encompass a wide array of techniques, both verbal and nonverbal, that enable individuals to express themselves clearly and authentically. In this article, we delve into the significance of these skills, providing a step-by-step guide to their development, addressing common misconceptions, and exploring their relevance to tackling social issues. Let’s embark on a journey of mastering the art of communication to unlock our true potential.
What is a Communication Skill?
Communication skills refer to the aptitude and proficiency in conveying and receiving information, ideas, and emotions effectively. These skills encompass both verbal and nonverbal methods of communication, such as speaking, listening, writing, body language, and gestures. By honing these skills, individuals can express themselves clearly, understand others empathetically, and establish meaningful connections. Communication skills are pivotal in various aspects of life, including personal relationships, professional settings, and societal interactions. They enable individuals to articulate thoughts, resolve conflicts, build rapport, and collaborate harmoniously.
100 Communication Examples
Communication is the lifeblood of personal interaction and professional success. It encompasses a vast array of skills, from verbal articulation and active listening to nonverbal cues and digital correspondence. Effective communication is clear, concise, empathetic, and tailored to the audience, whether it’s a one-on-one conversation or a corporate presentation. Below are 100 unique and distinct examples of communication, each illustrating a specific skill or method, complete with explanations for context and effectiveness.
- Elevator Pitch: Concisely summarizing a complex idea into a 30-second speech.
- Feedback Session: Constructively discussing ways to improve work performance.
- Brainstorming Meeting: Collaboratively generating ideas in a group setting.
- Conflict Resolution: Mediating a dispute and finding a mutually acceptable solution.
- Sales Call: Persuasively presenting a product’s benefits to a potential customer.
- Therapeutic Listening: Providing a supportive ear with the aim to heal or counsel.
- Negotiation: Reaching an agreement that benefits all parties involved.
- Storytelling in Marketing: Crafting a narrative around a product to enhance its appeal.
- Crisis Communication: Delivering clear, calm instructions during an emergency.
- Networking: Engaging in conversation with potential professional contacts.
- Instructional Demo: Teaching how to use a product through a step-by-step guide.
- Customer Complaint Response: Addressing and resolving a customer’s issue.
- Motivational Speech: Inspiring a team to work towards common goals.
- Press Release: Announcing company news in a format for media distribution.
- Corporate Apology: Expressing regret for a mistake and outlining remedial steps.
- Exit Interview: Discussing the reasons for employment termination.
- Post-Interview Thank You Note: Expressing gratitude for the opportunity to interview.
- Webinar Presentation: Educating an online audience about a specific topic.
- Panel Discussion: Participating in a group conversation on a subject matter.
- Sign Language: Using hand signals to communicate with the hearing impaired.
- Mime: Telling a story through gestures and body movements without words.
- Graphic Design: Conveying messages through visual content.
- Social Media Post: Engaging an audience with content on digital platforms.
- Email Newsletter: Regularly updating subscribers with news and content.
- Podcast: Broadcasting a discussion or narrative to an online audience.
- Vlog: Sharing personal experiences or information through a video blog.
- Teleconference: Communicating with a group remotely via telephone or video.
- Public Service Announcement: Informing the public about health or safety matters.
- Fundraising Letter: Requesting donations for a cause or organization.
- Petition: A written appeal to authority in support of a cause.
- Speechwriting: Composing a speech for another person to deliver.
- Live Tweeting: Posting real-time updates on social media during an event.
- Counseling Session: Engaging in a dialogue aimed at offering advice and support.
- Comedy Routine: Delivering jokes and humorous stories to entertain an audience.
- Socratic Seminar: Facilitating a group discussion based on asking and answering questions to stimulate critical thinking.
- Debate: Engaging in a formal argument on a particular topic.
- Lecture: Delivering an educational speech to an audience.
- Book Reading: Reading aloud from a book to an audience.
- Radio Broadcast: Communicating with listeners over radio waves.
- TV Interview: Answering questions on television for viewers.
- Documentary Narration: Providing the commentary for a documentary film.
- Voiceover Work: Recording the voice to accompany visual media.
- Blogging: Writing regular articles or posts on a personal or company website.
- Online Forum Participation: Engaging in discussions on internet message boards.
- Customer Service Interaction: Assisting customers with inquiries or problems.
- User Manual Writing: Creating instructions for product use.
- Scriptwriting for Theater: Composing dialogue and directions for stage performances.
- Legal Argument: Presenting a case in court.
- Scientific Research Presentation: Sharing findings with the scientific community.
- Technical Support: Assisting users with technical problems and providing solutions.
- Language Translation: Converting spoken or written content from one language to another.
- Signage: Displaying information through signs.
- Body Language in Interviews: Nonverbally conveying confidence during a job interview.
- Artistic Performance: Communicating themes or stories through dance or theater.
- Musical Lyrics: Telling a story or expressing emotions through song.
- Political Campaigning: Conveying a candidate’s message to voters.
- Diplomatic Correspondence: Communicating between representatives of different countries.
- Healthcare Instructions: Explaining treatment plans to patients.
- Academic Thesis Defense: Presenting and defending research to a committee.
- Grant Proposal: Requesting funding by outlining the significance and plan for a project.
- Real Estate Listing: Describing the features of a property for sale.
- Travel Guide: Providing information and tips to tourists.
- Sports Coaching: Giving strategic advice and motivation to athletes.
- Film Critique: Analyzing and reviewing a film for an audience.
- Book Club Discussion: Sharing perspectives on a book with a group.
- Religious Sermon: Delivering a message of faith to a congregation.
- Environmental Advocacy: Promoting environmental protection and conservation.
- Fashion Show Commentary: Describing the designs and styles showcased on the runway.
- Gaming Live Stream: Broadcasting gameplay with commentary to an online audience.
- Culinary Class: Teaching cooking techniques and recipes.
- Fitness Instruction: Guiding individuals through exercise routines.
- Parent-Teacher Conference: Discussing a student’s progress and needs.
- Peer Review: Providing feedback on academic or professional work.
- Architectural Tour: Describing the design and history of buildings.
- Art Exhibition Guide: Explaining the significance and context of artworks.
- Safety Drill Instructions: Guiding individuals through safety procedures.
- Investor Pitch: Presenting a business idea to potential investors.
- Cultural Sensitivity Training: Educating about respectful communication across cultures.
- Grief Counseling: Offering support and understanding to those experiencing loss.
- Language Learning: Practicing speaking and understanding a new language.
- Community Meeting: Discussing local issues and developments with residents.
- Software Tutorial: Instructing users on how to use a software application.
- Historical Lecture: Sharing insights on historical events or figures.
- Travel Vlogging: Documenting travel experiences through video.
- Motivational Coaching: Encouraging clients to achieve personal or professional goals.
- Science Fair Presentation: Explaining a scientific project to judges and attendees.
- Children’s Storytelling: Reading stories to children to entertain and educate.
- Market Research Survey: Collecting consumer opinions through questionnaires.
- Conflict De-escalation: Reducing the tension in a heated conversation.
- Cultural Festival Presentation: Sharing the traditions and significance of cultural celebrations.
- Wedding Toast: Honoring the couple with a heartfelt speech.
- Eulogy: Paying tribute to someone’s life during a funeral service.
- Sports Commentary: Providing play-by-play narration of a sports event.
- Language Interpretation: Facilitating spoken communication between people who do not share a common language.
- Museum Docent Tour: Educating visitors about exhibits.
- News Reporting: Delivering news stories to the public.
- Public Relations Strategy: Crafting messages to shape public perception of a company or individual.
- Social Justice Rally Speech: Speaking to advocate for societal change and equality.
- Corporate Training Workshop: Teaching employees new skills or concepts.
- Environmental Impact Report: Communicating the potential effects of a project on the environment.
Each example represents a specific scenario where communication plays a pivotal role. From the precision required in a grant proposal to the emotional intelligence needed in grief counseling, these examples span the full spectrum of communication skills. Effective communication is not just about the transmission of information; it’s about ensuring that the message is understood and resonates with the audience. Whether through spoken word, written text, or nonverbal cues, mastering the art of communication is a powerful tool for connection and understanding in every aspect of life.
Communication Skills Examples for Students
Effective communication is pivotal for students to thrive in academic and social settings. It involves clear expression, active listening, and interpreting non-verbal cues. Here are five examples:
- Group Projects: Demonstrating leadership by coordinating tasks and ensuring everyone’s voice is heard.
- Class Discussions: Articulating thoughts clearly and respectfully challenging ideas to foster a dynamic learning environment.
- Presentations: Engaging the audience with a well-structured speech and visual aids to enhance understanding.
- Peer Tutoring: Listening attentively to a peer’s struggles and explaining concepts in an understandable manner.
- Feedback Reception: Accepting constructive criticism gracefully and using it to improve academic performance.
Communication Skills Examples for Interview
Strong communication skills can distinguish a candidate in interviews, showcasing their ability to interact effectively. Here are five examples:
- Elevator Pitch: Concisely summarizing one’s background and skills to capture the interviewer’s interest.
- Behavioral Responses: Sharing specific examples that demonstrate problem-solving and teamwork abilities.
- Non-Verbal Cues: Maintaining eye contact and an open posture to convey confidence and engagement.
- Clarifying Questions: Asking insightful questions that show a deep understanding of the role and company.
- Follow-Up: Sending a personalized thank-you note that reiterates interest in the position.
Communication Skills Examples for Performance Review
During performance reviews, communication is key to discussing achievements and areas for growth. Here are five examples:
- Goal Setting: Clearly defining objectives for future performance that align with team and organizational goals.
- Progress Highlighting: Articulating accomplishments and the impact they’ve had on the team’s success.
- Constructive Feedback: Offering well-thought-out suggestions for improvement in a positive tone.
- Self-Assessment: Reflecting on one’s own performance honestly and discussing steps taken towards personal development.
- Future Aspirations: Discussing career aspirations and seeking advice on professional growth opportunities.
Communication Skills Examples in the Workplace
In the workplace, effective communication fosters collaboration and efficiency. Here are five examples:
- Email Etiquette: Crafting clear and concise emails with appropriate tone and language for different recipients.
- Meeting Participation: Contributing valuable insights and summarizing points to ensure mutual understanding.
- Conflict Resolution: Mediating disputes by listening to all sides and facilitating a constructive dialogue.
- Project Updates: Regularly informing stakeholders about progress, challenges, and changes in project timelines.
- Interdepartmental Communication: Bridging gaps between departments to align goals and strategies.
Communication Skills Examples for Evaluation
Communication evaluations often focus on how well individuals convey and receive information. Here are five examples:
- Feedback Delivery: Providing clear, actionable, and balanced feedback to peers and subordinates.
- Active Listening: Demonstrating full attention to the speaker, acknowledging their points, and responding thoughtfully.
- Presentation Skills: Delivering information in a structured, engaging manner that resonates with the audience.
- Report Writing: Compiling detailed and coherent reports that effectively communicate the necessary information.
- Persuasion Techniques: Convincing others with well-reasoned arguments and compelling evidence.
Communication Skills Examples for Review
Reviews often highlight communication strengths and areas needing improvement. Here are five examples:
- Performance Summaries: Concisely summarizing key achievements and areas of development.
- Advocacy: Effectively representing and communicating the needs and interests of a team or project.
- Feedback Reception: Showing openness to receiving feedback and actively working on the areas highlighted.
- Instruction Giving: Providing clear, understandable instructions that facilitate accurate and efficient task completion.
- Negotiation Skills: Reaching mutually beneficial agreements by clearly articulating points and understanding the counterpart’s position.
Communication Skills Examples for Nursing
In nursing, communication is critical for patient care and coordination with healthcare teams. Here are five examples:
- Patient Interviews: Gathering comprehensive patient histories with empathy and attention to detail.
- Medical Terminology: Using clear and accurate language when documenting patient information and communicating with colleagues.
- Empathetic Listening: Providing emotional support by listening to patients’ concerns and responding with compassion.
- Team Briefings: Clearly summarizing patient statuses during shift changes to ensure continuity of care.
- Patient Education: Explaining treatment plans and procedures to patients and families in an understandable way.
Communication Skills Examples for Self Evaluation
Self-evaluation of communication skills involves introspection and a willingness to improve. Here are five examples:
- Personal Accountability: Acknowledging areas for improvement in one’s own communication style.
- Goal-Oriented Communication: Setting clear personal communication goals and tracking progress towards them.
- Soliciting Feedback: Actively seeking out and reflecting on feedback from peers and superiors.
- Adaptability: Demonstrating flexibility in communication methods to suit different situations and audiences.
- Reflective Practice: Regularly reflecting on interactions and considering how they could be improved for better outcomes.
Nonverbal Communication Examples
Nonverbal communication is a silent yet powerful form of interaction. It encompasses body language, facial expressions, and gestures that convey messages without words. Here are five examples:
- Facial Expressions: Smiling to convey friendliness or frowning to express disapproval.
- Gestures: Nodding to show agreement or shaking one’s head for disagreement.
- Posture: Standing tall to project confidence or slouching to suggest disinterest.
- Eye Contact: Maintaining eye contact to show engagement or looking away to indicate distraction.
- Proxemics: Adjusting physical space between individuals to communicate intimacy or formality.
Active Listening Examples
Active listening is a skill that involves fully concentrating, understanding, responding, and then remembering what is being said. Here are five examples:
- Paraphrasing: Restating the speaker’s message in your own words to show understanding.
- Questioning: Asking open-ended questions to encourage deeper conversation.
- Summarizing: Giving a brief overview of the speaker’s main points to confirm comprehension.
- Non-Verbal Feedback: Nodding or giving appropriate facial reactions to show attentiveness.
- Avoiding Interruption: Waiting for the speaker to finish before responding to demonstrate respect.
Writing Examples
Writing is a fundamental communication skill that involves expressing ideas clearly and effectively through text. Here are five examples:
- Business Reports: Presenting data and analyses in a structured format for decision-making.
- Creative Writing: Crafting stories or poems with compelling narratives and characters.
- Technical Writing: Producing manuals or instructions that explain complex information in simple terms.
- Academic Writing: Composing essays or research papers with a clear thesis and supporting arguments.
- Persuasive Writing: Creating content aimed at convincing readers to adopt a certain viewpoint.
Feedback Examples
Feedback is essential for growth and improvement, providing insights into performance and behavior. Here are five examples:
- Positive Reinforcement: Praising specific actions to encourage their repetition.
- Constructive Criticism: Offering practical suggestions for improvement in a supportive manner.
- Peer Review: Sharing insights on a colleague’s work to help refine their output.
- 360-Degree Feedback: Receiving comprehensive feedback from all levels within an organization.
- Self-Feedback: Self-assessing one’s work to identify strengths and areas for development.
Speech Examples
A speech is a formal address or discourse delivered to an audience. Here are five examples:
- Inspirational Speech: Motivating the audience to pursue their goals with passion.
- Informative Speech: Educating the audience about a particular topic or issue.
- Persuasive Speech: Convincing the audience to change their perceptions or actions.
- Acceptance Speech: Expressing gratitude for an award or recognition.
- Eulogy: Paying tribute to someone’s life and legacy during a funeral or memorial service.
Confidence Examples
Confidence is the belief in one’s abilities and making decisions without hesitation. Here are five examples:
- Public Speaking: Delivering a presentation without notes to a large audience.
- Decision Making: Choosing a course of action based on analysis and judgment.
- Networking: Approaching strangers at an event to make professional connections.
- Skill Demonstration: Performing a task with expertise in front of an audience.
- Assertiveness: Expressing one’s opinions firmly and respectfully in a group setting.
Visual Communication Examples
Visual communication involves the use of visual elements to convey messages and information. Here are five examples:
- Infographics: Presenting data or knowledge with compelling graphics and minimal text.
- Branding: Using consistent visual designs to represent a company’s identity.
- Signage: Providing directions or information through signs and symbols.
- Data Visualization: Displaying complex data through charts and graphs for easier comprehension.
- Web Design: Creating an intuitive and aesthetically pleasing website layout.
Language Communication Examples
Language communication refers to the use of spoken or written language to exchange information. Here are five examples:
- Multilingual Negotiation: Conducting business discussions proficiently in several languages.
- Poetry: Using figurative language and rhythm to evoke emotions and convey messages.
- Slang: Employing informal language to relate to a particular social group.
- Storytelling: Narrating events in a way that is compelling and easy to understand.
- Language Learning: Acquiring new languages to improve communication with diverse populations.
Public Speaking Examples
Public speaking is the art of delivering a message to an audience effectively and confidently. It’s a critical skill for leadership and persuasion. Here are five examples:
- Keynote Speeches: Influential talks given at major events to set the underlying tone and summarize the core message.
- TED Talks: Inspirational speeches that share ideas worth spreading in a compelling and educational manner.
- Sales Pitches: Presentations aiming to persuade potential clients or investors to buy a product or service.
- Academic Lectures: Informative talks given by educators to impart knowledge on a specific subject.
- Political Addresses: Speeches by politicians to convey their policies, win support, or provide information.
Listening Examples
Listening is a vital communication skill that involves not just hearing but actively understanding and processing information. Here are five examples:
- Therapeutic Listening: Psychologists attentively listening to clients to provide appropriate emotional support.
- Critical Listening: Analyzing and evaluating the content of a message for decision-making or problem-solving.
- Reflective Listening: Listening to understand and then reflecting back the message for clarification and empathy.
- Active Listening in Negotiations: Paying close attention to the counterpart’s terms to formulate a strategic response.
- Listening for Comprehension: Students focusing intently on a lecture to fully grasp the educational material.
Body Language Examples
Body language is a non-verbal form of communication where physical behavior, as opposed to words, is used to express or convey information. Here are five examples:
- Handshakes: A firm handshake to convey confidence and professionalism.
- Mirroring: Subtly copying the body language of a conversational partner to build rapport.
- Facial Expressions in Sales: A salesperson smiling to appear friendly and approachable to potential customers.
- Stance in Public Speaking: A speaker standing with an open stance to seem more welcoming and engaging.
- Gestures in Teaching: An educator using hand gestures to emphasize important points in a lesson.
Collaboration Examples
Collaboration involves working together to achieve a common goal or complete a task. Here are five examples:
- Cross-Functional Teams: Employees from different departments teaming up to work on a project.
- Brainstorming Sessions: Groups generating ideas collectively to solve a problem or create new projects.
- Joint Ventures: Two or more businesses coming together to undertake a project for mutual benefit.
- Community Partnerships: Local organizations working together to address community issues.
- Academic Group Work: Students collaborating on research projects to combine expertise and knowledge.
Persuasion Examples
Persuasion is the act of convincing someone to do or believe something through reasoning or the use of emotion. Here are five examples:
- Advertising Campaigns: Creating compelling messages to influence consumers’ buying decisions.
- Legal Arguments: Lawyers presenting evidence and arguments to persuade a jury or judge.
- Fundraising Appeals: Non-profits crafting messages that motivate people to donate.
- Editorial Articles: Writers using persuasive language to sway public opinion on issues.
- Social Media Influence: Influencers endorsing products or ideas to persuade their followers.
Assertiveness Examples
Assertiveness is the quality of being self-assured and confident without being aggressive. Here are five examples:
- Workplace Requests: Asking for a raise or promotion with confidence and clear justification.
- Boundary Setting: Communicating personal limits firmly and respectfully in personal relationships.
- Disagreeing Politely: Expressing a contrary opinion in a meeting without offending others.
- Self-Advocacy: Speaking up for one’s own needs and rights in a healthcare setting.
- Negotiating Terms: Assertively stating terms in a contract negotiation to reach a fair agreement.
Reading Examples
Reading is the process of interpreting written symbols and comprehending their meaning. Here are five examples:
- Critical Reading: Evaluating an academic text to understand its implications and arguments.
- Leisure Reading: Engaging with fiction or non-fiction for enjoyment and relaxation.
- Research Reading: Scouring through various sources to gather information for a research project.
- Proofreading: Examining a text carefully to find and correct typographical errors and inconsistencies.
- Speed Reading: Using techniques to quickly read and comprehend large volumes of material.
Conflict Management Examples
Conflict management involves handling and resolving disputes efficiently and diplomatically. Here are five examples:
- Mediation Sessions: Facilitating a dialogue between disputing parties to reach a mutually acceptable solution.
- De-escalation Techniques: Using calm communication to reduce tension in a heated argument.
- Problem-Solving Meetings: Bringing conflicting team members together to find a collaborative solution.
- Diplomatic Negotiation: Resolving international disputes through tactful discussion and compromise.
- Customer Service Resolution: Addressing and solving a customer’s complaint in a way that is satisfactory for both the company and the customer.
Presentation Skills Examples
Presentation skills are a blend of engaging storytelling, clear communication, and effective visual aids that together make information memorable. Here are five examples:
- Interactive Demos: Using product demonstrations within a presentation to create an engaging, hands-on experience.
- Storytelling in Sales: Incorporating customer success stories to make a sales pitch more relatable and compelling.
- Data-Driven Presentations: Utilizing charts and graphs to present complex data in an accessible way.
- Educational Workshops: Conducting workshops that combine lectures with interactive activities to enhance learning.
- Webinar Hosting: Leading online seminars with a mix of multimedia content to educate and engage a virtual audience.
Mediation Examples
Mediation is a conflict resolution process where a neutral third party helps disputants find a mutually satisfactory solution. Here are five examples:
- Workplace Dispute Resolution: Mediating between employees to resolve conflicts affecting team dynamics.
- Divorce Proceedings: Assisting separating couples in reaching agreements on sensitive issues like asset division.
- Community Disagreements: Facilitating discussions between community members over local issues or developments.
- Business Negotiations: Helping business partners reconcile differences to maintain a beneficial relationship.
- International Relations: Mediating between countries to address and resolve diplomatic conflicts.
Gesture Examples
Gestures are movements of the body that convey messages or emotions and are an integral part of non-verbal communication. Here are five examples:
- Thumbs Up: Signaling approval or a job well done in many cultures.
- Pointing: Using a finger to indicate direction or draw attention to something or someone.
- Waving: Raising a hand and moving it side to side as a greeting or farewell.
- Palms Open: Showing open hands to communicate honesty or submission.
- Head Tilt: Tilting the head to show interest or empathy during a conversation.
Empathy Examples
Empathy is the ability to understand and share the feelings of another, a crucial component of effective communication. Here are five examples:
- Active Listening in Counseling: Giving full attention to a client’s story to better understand their emotions.
- Customer Service Understanding: Recognizing a customer’s frustration and working to address their concerns.
- Peer Support: Offering a listening ear and understanding to a colleague going through a tough time.
- Healthcare Compassion: Medical professionals showing concern for a patient’s emotional and physical well-being.
- Mentoring Relationships: Mentors empathizing with mentees’ challenges to provide appropriate guidance and support.
Clarity Seeking Examples
Seeking clarity is about asking questions or for further explanation to ensure understanding. Here are five examples:
- Clarification Questions in Meetings: Asking specific questions to ensure the objectives of the meeting are clear.
- Follow-Up Emails: Requesting additional information to ensure tasks are completed accurately.
- Learning New Skills: Asking for detailed instructions when learning a new procedure or tool.
- Client Briefings: Ensuring all project requirements are understood before beginning work.
- Academic Understanding: Students seeking further explanation on complex topics for better comprehension.
Responsiveness Examples
Responsiveness is the timely and appropriate reaction to communication or needs, showing attentiveness and care. Here are five examples:
- Customer Inquiry Replies: Providing prompt and helpful answers to customer questions.
- Emergency Services Reaction: First responders quickly addressing urgent situations.
- Feedback Implementation: Actively applying constructive feedback received from peers or supervisors.
- Social Media Engagement: Brands quickly engaging with followers’ comments and messages online.
- Support Ticket Handling: Customer support resolving issues efficiently to ensure customer satisfaction.
Listening Skills Examples
Listening skills involve accurately receiving and interpreting messages in the communication process. Here are five examples:
- Note-Taking During Lectures: Writing down key points to ensure important information is retained.
- Active Engagement in Conversations: Showing interest by nodding and giving verbal affirmations.
- Emotional Intelligence in Discussions: Detecting subtle cues in tone and mood to fully understand the speaker’s message.
- Patient Listening in Therapy: Therapists maintaining focus on clients’ words to provide effective support.
- Feedback Reception in Performance Reviews: Employees attentively listening to performance feedback for professional growth.
Verbal Communication Skills Examples
Verbal communication skills are the abilities one uses when giving and receiving different kinds of information through speaking. Here are five examples:
- Clear Instructions: Providing unambiguous directions to team members on a new task.
- Eloquent Speeches: Delivering speeches with well-chosen words to inspire or inform an audience.
- Effective Sales Pitches: Using persuasive language to highlight the benefits of a product or service.
- Constructive Team Discussions: Engaging in open and positive dialogue to solve team issues.
- Diplomatic Negotiations: Articulating points in a negotiation with tact to reach a beneficial agreement.
24+ Communication Skills PDF
1. Communication Skills Mind Map Template
2. Communication Skills
3. English Communication Skills
4. Introduction to Communication Skills
5. Handbook of Communication Skills
6. Improve Your Communication Skills
7. Effective Communication Skills
8. Professional Communication Skills
9. Communication Skills Example
10. 20 Ways to Enhance Your Communication Skills
11. Developing Effective Communication Skills
12. Comprehension & Communication Skills
13. Certificate Communication Skills
14. Communication Skills and Personality Development
15. Communication Skill Notes
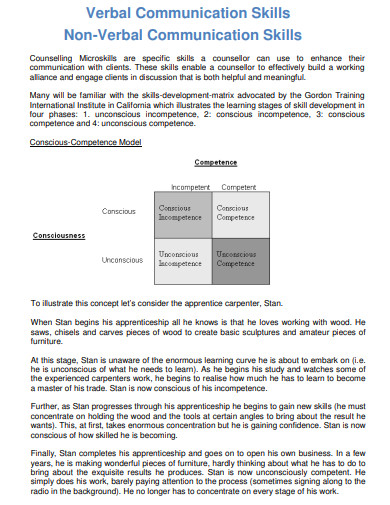
16. Verbal and Non Verbal Communication Skill
17. Student Communication Skill
18. Business Communication Skills for Managers
19. Written Communication Skills
20. English Language Communication Skills
21. Communication Skills for Business
22. Communication Skills Template
23. Essential Communication Skills
24. Simple Communication Skills
25. Communication Skills And Studies
What is an Example of a Communication Skill?
Communication skills are the tools and techniques that enable us to convey or exchange information effectively. An example of a communication skill is active listening. This involves not just hearing the words another person is saying but fully engaging with the content, meaning, and emotions behind their message. It requires full concentration, understanding, responding appropriately, and then remembering what is said. Active listeners use verbal affirmations, maintain eye contact, and provide feedback that shows comprehension and empathy. This skill is vital across various settings, from professional environments to personal relationships, ensuring that communication is two-way and effective.
How Can I Describe My Communication Skills?
Describing your communication skills involves reflecting on and articulating the various aspects of how you share and receive information. To effectively describe your communication skills, consider highlighting your proficiency in the following areas:
- Verbal Communication: Mention your ability to articulate ideas clearly and confidently in spoken words. You might note your skill in adjusting your tone and vocabulary to suit different audiences and contexts.
- Nonverbal Communication: Discuss your ability to use body language, facial expressions, and gestures to reinforce or complement your verbal messages. Mention your sensitivity to the nonverbal cues of others, enhancing mutual understanding.
- Written Communication: Highlight your capability to express ideas clearly in written form, whether it’s through emails, reports, or social media. Emphasize your attention to grammar, clarity, and tone.
- Listening: Explain your active listening skills, such as giving full attention to the speaker, showing understanding, and providing thoughtful feedback.
When describing your communication skills, provide specific examples or scenarios where you have effectively used these skills to achieve a goal or resolve a problem.
What are Some Good Communication Skills?
Good communication skills are essential for fostering effective exchanges of information, building relationships, and understanding others. Here are some key communication skills that are highly valued in personal and professional settings:
- Clarity and Concision: Being able to speak plainly and directly, avoiding unnecessary jargon or complexity.
- Active Listening: Engaging with the speaker, showing interest, and providing feedback that validates the message received.
- Empathy: Understanding and sharing the feelings of others, which can enhance the connection and communication.
- Confidence: Expressing oneself assertively and with assurance, without being aggressive.
- Open-Mindedness: Being willing to hear and consider other perspectives, and not shutting down conversations prematurely.
- Respect: Showing consideration for the opinions of others and acknowledging their input.
- Feedback: Providing constructive criticism that is helpful and actionable, as well as being receptive to receiving feedback from others.
- Nonverbal Communication: Using body language, facial expressions, gestures, and tone of voice to complement or reinforce your verbal messages.
Each of these skills contributes to the effectiveness of communication and can be developed with practice and awareness.
What is the Difference between Verbal and Nonverbal Communication?
When discussing communication, it’s important to differentiate between verbal and nonverbal methods, as both play a crucial role in how we interact with others. Below is a table that outlines the key differences between these two forms of communication:
| Aspect | Verbal Communication | Nonverbal Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The use of spoken or written words to convey a message. | The use of body movements, facial expressions, and gestures to communicate without words. |
| Components | Words, sentences, speaking, writing, language. | Body language, facial expressions, eye contact, posture, gestures, tone of voice, touch, space. |
| Expression | Can be both oral and written. | Mostly visual and sometimes auditory. |
| Clarity | Often more explicit and clear in conveying specific information. | Can be ambiguous and open to interpretation. |
| Feedback | Can be immediate in conversations or delayed in written communication. | Often immediate and continuous. |
| Cultural Variance | Language can vary greatly across cultures, but certain principles of structure and grammar are universal. | Highly subject to cultural interpretation, with the same gesture or expression meaning different things in different cultures. |
| Conscious Use | Typically a conscious choice of words and structure. | Can be both conscious and unconscious. |
| Emotional Expression | Can express emotions through tone, choice of words, and inflection. | Often a more direct indicator of a person’s emotional state. |
Understanding the nuances of both verbal and nonverbal communication can significantly enhance one’s ability to communicate effectively in diverse situations. Nonverbal communication, in particular, can provide a deeper insight into the true feelings and intentions behind the spoken word, making it a powerful tool for connecting with others.
How to Develop Communication Skills
Effective communication skills are not innate talents but rather abilities that can be cultivated through practice and conscious effort. Here is a step-by-step guide to enhancing your communication skills:
Step 1: Understand the Importance
Recognize the significance of communication skills in personal growth, career advancement, and fostering positive relationships. Acknowledge that these skills are not limited to specific contexts but are universally valuable.
Step 2: Active Listening
Sharpen your listening skills by actively engaging in conversations, focusing on the speaker, and demonstrating genuine interest. Practice empathetic listening, seeking to understand others’ perspectives without judgment.
Step 3: Clarity and Conciseness
Develop the ability to express your thoughts clearly and succinctly. Practice organizing your ideas, using precise language, and avoiding unnecessary jargon or ambiguity.
Step 4: Nonverbal Communication
Pay attention to your body language, facial expressions, and gestures. Maintain eye contact, use appropriate hand movements, and align your nonverbal cues with your verbal message to enhance overall communication.
Step 5: Empathy and Emotional Intelligence
Cultivate empathy by putting yourself in others’ shoes and striving to understand their emotions and experiences. Develop emotional intelligence to regulate your emotions and respond appropriately to different situations.
Step 6: Practice Effective Feedback
Learn to provide constructive feedback in a respectful and constructive manner. Focus on specific observations, offer suggestions for improvement, and emphasize the positive aspects of the person’s efforts.
Step 7: Adaptability and Flexibility
Be adaptable in your communication style to cater to diverse audiences and situations. Recognize cultural differences, adjust your tone and language accordingly, and embrace open-mindedness.
Tips for Improving Communication Skills
Improving communication skills is a lifelong process that can enhance personal and professional relationships. Here are some tips to help you communicate more effectively:
1. Listen Actively
- Practice active listening by focusing entirely on the speaker, showing interest, and responding to what they say.
- Avoid interrupting and wait for a natural pause to ask questions or make comments.
2. Engage in Empathy
- Try to understand the emotions and perspectives of others in your interactions.
- Respond in a way that acknowledges the other person’s feelings and point of view.
3. Practice Clarity and Concision
- Be clear and concise in your communication. Avoid using unnecessary jargon or complex language that could confuse the listener.
- Think before you speak to organize your thoughts more effectively.
4. Improve Your Nonverbal Communication
- Work on your body language, facial expressions, and eye contact to ensure they align with your verbal messages.
- Be aware of the nonverbal cues you are giving off and how they may be interpreted.
5. Enhance Your Emotional Intelligence
- Develop your emotional intelligence to better understand and manage your emotions in communication.
- Recognize the emotions of others to improve interactions and relationships.
6. Develop Your Listening Skills
- Listening is just as important as speaking in communication. Give your full attention to the speaker and avoid formulating a response while they are still talking.
- Show that you are listening through affirmative noises or phrases and appropriate facial expressions.
7. Work on Your Public Speaking
- Take opportunities to speak in public to increase your confidence and improve your verbal communication skills.
- Join groups or workshops that focus on public speaking to get constructive feedback.
8. Seek Constructive Feedback
- Ask for feedback on your communication skills from trusted friends, family, or colleagues.
- Use this feedback to identify areas for improvement and work on them systematically.
9. Continue to Educate Yourself
- Read books, take courses, and attend workshops on communication skills.
- Stay updated on communication theories and practices, as these can change with new research and societal shifts.
10. Practice Regularly
- Like any skill, communication improves with practice. Engage in conversations regularly, particularly in challenging situations that test your skills.
- Reflect on your interactions and consider what went well and what could be improved.
By following these steps and tips, you can enhance your communication skills, making your interactions more effective and fulfilling. Remember, communication is a two-way street, and improving your skills involves both conveying your own message effectively and being receptive to the messages of others.
FAQs
What is the difference between hard skills and soft skills?
Hard skills are specific technical or job-related abilities that are easily measurable and acquired through training or education. Soft skills, on the other hand, are more subjective and relate to personal attributes and interpersonal skills, such as communication, teamwork, and problem-solving. While hard skills are crucial for performing specific tasks, soft skills are essential for effective communication, collaboration, and adaptability in any role or environment.
Are communication skills only useful for certain careers?
No, communication skills are universally valuable and beneficial for individuals in any career or profession. Regardless of the industry or job role, effective communication is essential for building relationships, collaborating with colleagues, understanding clients or customers, and conveying ideas or information clearly. From healthcare professionals to engineers, entrepreneurs to artists, strong communication skills serve as a foundation for success in any field.
How can communication skills help address social issues?
Communication skills play a crucial role in addressing social issues by facilitating understanding, empathy, and dialogue. They enable individuals to express their perspectives, engage in meaningful conversations, and bridge gaps between different communities. Effective communication can help challenge stereotypes, promote inclusivity, and foster discussions that lead to positive change. By utilizing their communication skills, individuals can become advocates for social justice, contribute to meaningful conversations, and work towards creating a more equitable society.
In a world where words and actions hold immense power, communication skills are the key to unlocking doors of opportunity and connection. They empower individuals to express themselves authentically, navigate complexities, and bridge gaps between diverse communities. As you embark on the journey of developing these skills, remember that effective communication extends beyond mere words; it encompasses active listening, nonverbal cues, and empathy. By nurturing your communication skills, you not only enhance your personal and professional relationships but also contribute to a world where understanding, collaboration, and progress thrive. Embrace the power of effective communication, challenge stereotypes, address social issues, and pave your path toward fulfilling your career goals.