Concurrent Powers Examples
Dive into the intricate world of Concurrent Powers with our comprehensive guide. Unravel how federal and state governments share crucial responsibilities, from taxation to road construction. Our expert insights shed light on the balancing act that defines American governance, offering vivid examples to clarify this fundamental concept. Whether you’re a student, educator, or curious reader, our guide enriches your understanding of these shared powers, illuminating the cooperative backbone of U.S. federalism. Explore the synergy that shapes our nation’s fabric.
What is Concurrent Powers?
Concurrent powers are those powers in a federal system of government that are shared by both the central (or federal) government and the individual state governments. This means that both levels of government are authorized to exercise these powers independently of each other. Examples of concurrent powers include the power to tax, the power to build roads, and the power to create lower courts. The existence of concurrent powers allows for a more flexible and adaptable system of governance, where both state and federal governments can respond to the needs of their citizens, while also maintaining the balance of power between the two levels of government.
Concurrent Powers in the Constitution
Concurrent powers in the United States Constitution refer to the authority shared by both the federal government and the state governments. These powers enable both levels of government to function effectively in their respective spheres while also allowing them to work collaboratively on certain issues. Concurrent powers are fundamental to the federal system of governance in the United States, ensuring a balance between the powers of the national government and those of the states. Some key examples of concurrent powers include:
Taxation
Both the federal and state governments have the authority to levy taxes in order to fund their respective operations and services. This includes the power to tax incomes, sales, properties, and more. The ability to raise revenue is essential for both levels of government to fulfill their responsibilities.
Borrowing Money
The Constitution allows both federal and state governments to borrow money. This is crucial for financing public projects, addressing budget shortfalls, and managing emergencies. Borrowing enables governments to invest in infrastructure, education, healthcare, and other areas critical to public welfare and economic development.
Establishing Courts
While the federal government has its system of courts culminating in the Supreme Court, states also have the authority to establish their own judicial systems. State courts handle the vast majority of legal cases in the country, including criminal, civil, and family cases.
Law Enforcement
Both levels of government have the power to enforce laws, ensuring public safety and order. This includes the establishment of police forces and other law enforcement agencies. While the federal government enforces federal laws across the nation, state governments enforce state laws.
Building and Maintaining Infrastructure
The federal and state governments share the responsibility for building and maintaining infrastructure, such as roads, bridges, and water supply systems. This collaboration is crucial for supporting commerce, ensuring public safety, and promoting the general welfare.
Chartering Banks and Financial Institutions
Both the federal government and the states have the authority to charter banks and other financial institutions. This allows for a diverse banking system that can meet the varied needs of the American economy and its people.
Health and Safety Regulations
Both levels of government are involved in regulating health and safety to protect the public. This includes regulations related to food safety, environmental protection, and workplace safety. The concurrent authority ensures comprehensive coverage across different sectors and jurisdictions.
Welfare Programs
Both the federal and state governments can establish and manage welfare programs to support individuals and families in need. This includes programs related to healthcare, unemployment benefits, and aid for low-income families. The cooperative effort allows for a more responsive and effective welfare system.
Education
Education is primarily the responsibility of state governments, but the federal government also plays a significant role in setting educational standards, providing funding, and ensuring equal access to education. This shared power helps promote a strong and equitable education system nationwide.
Delegated, Reserved, and Concurrent Powers
The United States Constitution establishes a system of federalism, which divides powers between the national government and the state governments. This division is designed to ensure a balance of power, preventing any one entity from becoming too powerful. Within this framework, powers are categorized into three main types: delegated (or enumerated) powers, reserved powers, and concurrent powers. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for grasping the nuances of American federalism.
Delegated Powers
Delegated powers, also known as enumerated powers, are those specifically granted to the federal government by the Constitution. These powers are outlined primarily in Article I, Section 8 of the Constitution and include:
- The Power to Tax and Spend: The federal government can levy taxes and allocate funds to support its essential functions and provide for the common defense and general welfare of the United States.
- Regulation of Interstate and Foreign Commerce: Known as the Commerce Clause, this allows the federal government to regulate trade between states and with other countries.
- Foreign Policy Powers: Including the right to make treaties, declare war, and maintain diplomatic relations with other nations.
- Defense and Military Powers: The federal government is responsible for maintaining an army and navy and protecting the country against foreign threats.
- Coining Money: Only the federal government can issue and regulate the value of US currency.
- Establishing Federal Courts: Beyond the Supreme Court, whose existence is mandated by the Constitution, Congress can establish lower federal courts.
Reserved Powers
Reserved powers are those not delegated to the United States by the Constitution, nor prohibited by it to the States, are reserved to the States respectively, or to the people, as outlined in the Tenth Amendment. These include powers that are not explicitly stated in the Constitution but are inherently understood to belong to the state governments:
- Regulation of Intrastate Commerce: States have the authority to regulate commerce within their borders.
- Education: The responsibility for public education systems primarily lies with the states.
- Public Safety and Morals: States enforce laws on health, safety, and moral standards, including police power, building codes, and zoning laws.
- Local Government: States have the authority to create and govern local municipalities.
- Elections: States regulate the process of elections, including the times, places, and manner of holding elections for senators and representatives.
Concurrent Powers
Concurrent powers are those held and exercised simultaneously by both the federal and state governments. These powers overlap, allowing both levels of government to function effectively in these areas:
- The Power to Tax: Both state and federal governments can levy taxes to fund their respective functions.
- Borrow Money: Both can borrow money on the credit of the United States.
- Establish Courts: Both levels can establish and maintain their own court systems.
- Make and Enforce Laws: Both federal and state governments have the authority to create and enforce laws, provided that these laws do not conflict with the Constitution.
- Charter Banks and Corporations: Both can grant charters for banks and corporations within their respective jurisdictions.
- Spend Money for the General Welfare: Both can spend public funds to better their jurisdictions, focusing on the welfare of their citizens.
- Eminent Domain: Both levels of government have the power to take private property for public use, with just compensation.
Importance of Concurrent Powers
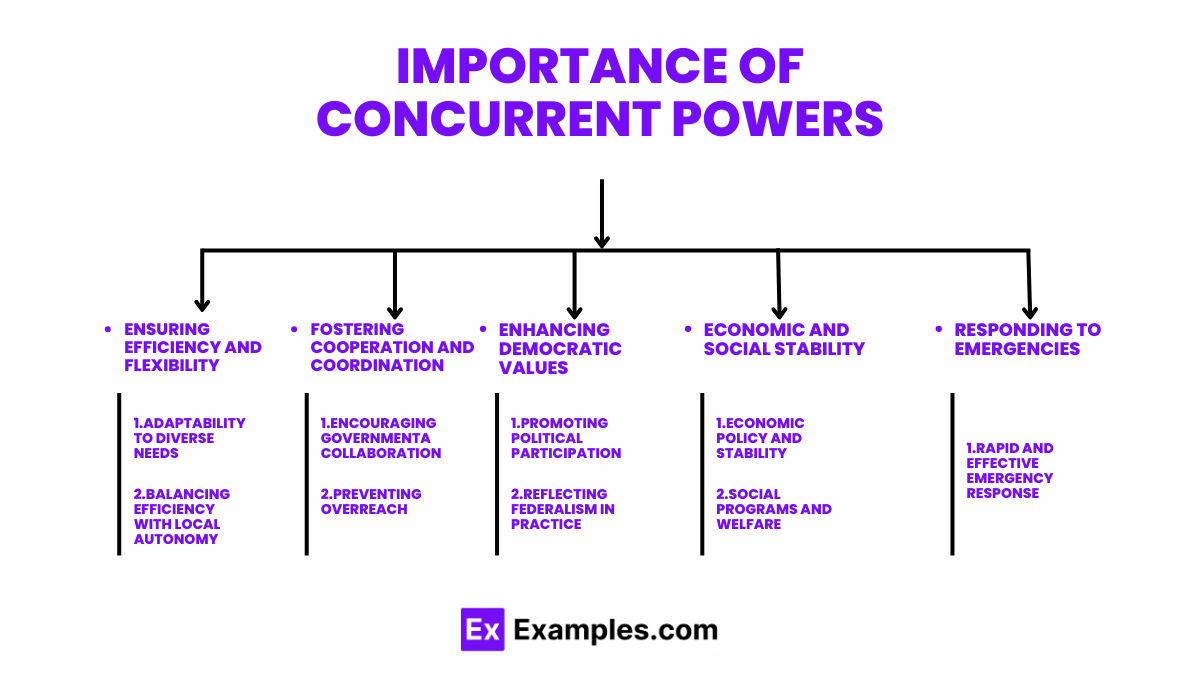
Concurrent powers, shared by both the federal and state governments, play a crucial role in the United States’ federal system of governance. These powers ensure that both levels of government can operate effectively in their spheres while also allowing for collaboration and flexibility in addressing the needs of the nation and its citizens. Here’s why concurrent powers are so important:
Ensuring Efficiency and Flexibility
- Adaptability to Diverse Needs: Concurrent powers allow both federal and state governments to adapt to and address the diverse needs of different regions and communities. For example, the ability to tax and spend enables both levels of government to fund essential services and respond to emergencies or specific local needs.
- Balancing Efficiency with Local Autonomy: By sharing powers such as enforcing laws and creating courts, the system ensures that laws are effectively implemented across the entire country while allowing states to adjust these laws to better suit local conditions and preferences.
Fostering Cooperation and Coordination
- Encouraging Governmental Collaboration: Concurrent powers necessitate coordination and cooperation between the federal and state governments, promoting a more unified approach to governance. This is particularly evident in disaster response and public health efforts, where resources and responsibilities are shared.
- Preventing Overreach: By distributing powers between two levels of government, the system helps prevent overreach by either level, ensuring that no single government entity becomes too powerful. This balance protects the rights and freedoms of citizens.
Enhancing Democratic Values
- Promoting Political Participation: Concurrent powers encourage political participation at all levels, as citizens can engage with both their state and federal governments. This involvement can lead to more responsive and representative governance.
- Reflecting Federalism in Practice: The sharing of powers between federal and state governments is a practical embodiment of federalism, allowing the system to balance unity with diversity. It acknowledges the importance of state sovereignty while ensuring the federal government has the necessary authority to perform its duties.
Economic and Social Stability
- Economic Policy and Stability: The ability of both levels of government to tax and borrow money allows for more nuanced economic policies that can address national priorities and local needs. This dual capacity can lead to greater economic stability and responsiveness to economic challenges.
- Social Programs and Welfare: Concurrent powers enable both the federal and state governments to invest in social programs and welfare, ensuring a broader safety net for citizens. This can lead to more comprehensive and accessible public services, from education to healthcare.
Responding to Emergencies
- Rapid and Effective Emergency Response: In times of crisis, such as natural disasters or national security threats, concurrent powers allow both federal and state governments to respond quickly and effectively. This dual response capability can save lives and mitigate damage.
Examples of Concurrent Powers
Concurrent powers are shared by both the federal and state governments in the United States, allowing both levels to legislate, enforce, and administer in certain areas simultaneously. Here are some concrete examples of concurrent powers in action:
1. Taxation
Both the federal and state governments have the authority to levy taxes to generate revenue. This includes income taxes, sales taxes, and property taxes. While the federal government collects income tax from all eligible individuals and corporations across the nation, states can also impose their own income taxes, with rates and regulations varying from state to state. Similarly, sales taxes can be collected at both levels, with states and even local governments setting their own rates.
2. Borrowing Money
Both levels of government can borrow money to finance their operations, fund public projects, or manage deficits. This is done through the issuance of bonds or taking loans. The ability to borrow money is crucial for managing economic fluctuations and financing large-scale projects, such as infrastructure development or emergency relief efforts.
3. Establishing Courts
While the federal government has the authority to establish federal courts below the Supreme Court, states have the power to create their own judicial systems to interpret and apply state laws. This means that both federal and state court systems can operate simultaneously, each handling cases that fall under their respective jurisdictions.
4. Building Infrastructure
Both federal and state governments can invest in and oversee the construction and maintenance of infrastructure, such as highways, bridges, and public buildings. Often, these projects involve cooperation and funding from both levels, highlighting the collaborative aspect of concurrent powers. For instance, the federal government may provide funds for interstate highways, while state governments manage the construction and maintenance of state roads.
5. Law Enforcement
The enforcement of laws is a responsibility shared by federal and state governments. While federal law enforcement agencies, such as the FBI or DEA, enforce federal laws across the nation, state and local police enforce state and local laws. In many cases, these entities work together to ensure public safety and law enforcement.
6. Health and Safety Regulations
Both levels of government are involved in creating and enforcing health and safety regulations. For example, while the federal government sets minimum health and safety standards through agencies like the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), states can implement their own regulations that are stricter than federal standards.
7. Environmental Protection
The federal government, through the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), enforces national environmental protection standards. However, states also have the authority to enact and enforce environmental regulations that meet or exceed federal standards. This allows states to address specific environmental concerns within their borders while still adhering to national guidelines.
8. Education Funding and Standards
Both the federal and state governments play roles in funding education and setting educational standards. The federal government provides funding through various programs to support national education goals, while states are primarily responsible for the operation and funding of public schools, curriculum standards, and teacher certification requirements.
Characteristics of Concurrent Powers
Concurrent powers, integral to the structure of federalism in the United States, allow both the federal and state governments to exercise authority over the same areas of policy and governance. These powers are fundamental to ensuring that governance is efficient, responsive, and adaptable to the needs of a diverse nation. The characteristics of concurrent powers reflect the complex balance between central authority and regional autonomy. Here are some key characteristics:
Shared Jurisdiction
- Overlap in Governance: Concurrent powers cover areas where both federal and state governments have the authority to legislate, enforce laws, and implement policies. This overlap requires coordination and cooperation to ensure that efforts are complementary rather than contradictory.
Flexibility and Adaptability
- Tailored Responses to Local Needs: While the federal government sets broad policies, states can adapt these policies to better fit their specific circumstances. This flexibility allows for more nuanced and effective governance.
- Innovation and Experimentation: States can serve as “laboratories of democracy,” testing new ideas and policies. Successful initiatives can be adopted at the national level, fostering innovation in governance.
Cooperation and Conflict
- Collaboration between Levels of Government: Concurrent powers often necessitate cooperation between federal and state governments, particularly in areas like emergency response, public health, and infrastructure development.
- Potential for Jurisdictional Disputes: The shared nature of concurrent powers can sometimes lead to conflicts over jurisdiction and authority, requiring judicial resolution to determine the appropriate level of governance for certain issues.
Checks and Balances
- Preventing Concentration of Power: By distributing powers across both levels of government, the federal system prevents the concentration of too much authority in either the federal or state governments, helping to protect individual and state rights.
- Multiple Avenues for Policy Implementation: Concurrent powers provide multiple pathways for addressing national issues, ensuring that there are varied approaches to problem-solving and governance.
Responsiveness to Citizens
- Enhanced Representation: The shared powers allow for governance that is closer to the people, as state governments can be more responsive to the needs and preferences of their local populations.
- Diverse Policy Approaches: Concurrent powers enable different states to adopt policies that reflect the values and priorities of their citizens, leading to a more diverse and representative political landscape.
Economic and Social Stability
- Coordinated Economic Policies: Both levels of government can enact economic policies, such as taxation and borrowing, allowing for a coordinated approach to economic stability and development.
- Comprehensive Welfare Programs: The ability of both federal and state governments to spend on welfare and social programs ensures a more comprehensive safety net for citizens, addressing a wide range of social and economic needs.
Concurrent powers exemplify the essence of federalism, blending national unity with state autonomy. This system enables both federal and state governments to legislate and act on shared matters, fostering cooperation while respecting local nuances. Despite potential conflicts, it ensures a balanced governance approach, crucial for addressing the diverse needs of a federated nation effectively.
FAQS
What is the Concurrent List power?
The “Concurrent List” refers to a concept in federal systems like India, where it denotes a list of subjects on which both the central and state governments can legislate. This arrangement allows for shared legislative powers, ensuring flexibility and a balanced approach to addressing issues that require both uniformity across the nation and sensitivity to local conditions. Topics under this list might include education, environmental protection, and marriage laws. While it fosters cooperation between different government levels, it also specifies that in case of conflicting laws on the same subject, the central government’s law prevails, ensuring national consistency.
What does concurrent mean in powers?
In the context of government powers, “concurrent” refers to the authority that both federal and state governments simultaneously possess within a federal system, like that of the United States. These shared powers allow both levels of government to legislate, enforce, and administer in certain areas. Examples include the power to tax, borrow money, and establish court systems. Concurrent powers facilitate cooperation and ensure a balance between the need for national uniformity and the advantages of localized governance. However, they can also lead to jurisdictional conflicts, necessitating clear mechanisms for resolving disputes between federal and state laws.
What is the difference between Union List and Concurrent List?
In countries with a federal system like India, the Union List and the Concurrent List are two distinct categories that define legislative competencies. The Union List includes subjects only the central government can legislate on, focusing on national importance issues like defense, foreign affairs, and railways. On the other hand, the Concurrent List contains subjects on which both the central and state governments can make laws, such as education and marriage. While laws made by the central government prevail on the Concurrent List in case of conflict, the Union List gives exclusive legislative power to the central government, emphasizing central authority on critical national matters.