13+ Formal Report Examples to Download
A formal report is a structured document designed to relay complex information clearly and efficiently. Typically used in professional and academic settings, these reports help organizations make informed decisions by presenting facts, analyses, and conclusions in a format that’s easy to navigate. Whether you’re a student, a business professional, or a researcher, understanding how to create and utilize formal reports can be crucial. In this guide, we’ll explore the key components of a formal report, show you how to assemble your information, and share tips to enhance your reporting skills.
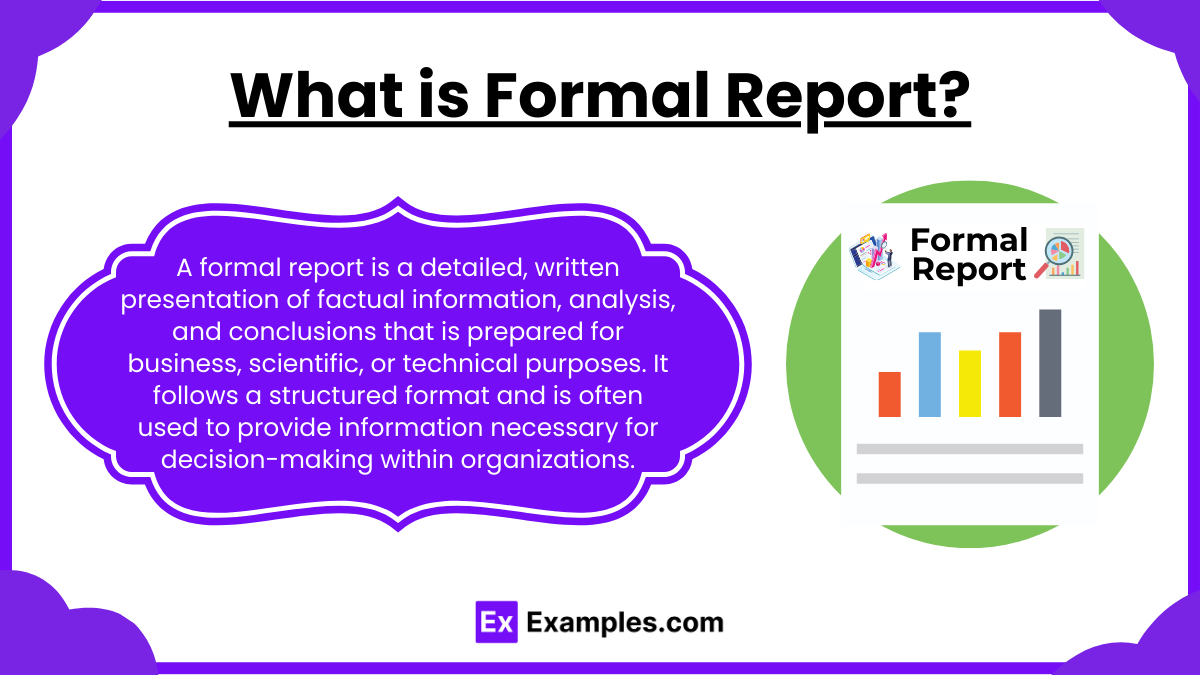
What is Formal Report?

Formal Report Format
Title Page
The title page includes the report’s title, the name of the author, and the date of submission.
Abstract
A brief summary of the report’s content, including the main findings and conclusions.
Table of Contents
A list of the report’s sections, sub-sections, and page numbers to help readers navigate the document.
Introduction
An overview of the report’s purpose, objectives, and the significance of the topic being addressed.
Methodology
A description of the methods used to gather and analyze data.
Findings
A detailed presentation of the data collected, often accompanied by charts, graphs, and tables.
Discussion
An interpretation of the findings, including their implications and limitations.
Conclusions and Recommendations
A summary of the findings and the suggested actions based on the report’s analysis.
References
A list of all sources cited in the report.
Appendices
Additional material that is relevant to the study but not essential to its main text.
Formal Report Example
Title: Annual Marketing Analysis Report
Author: John Doe
Date: January 24, 2025
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the annual marketing efforts of XYZ Corporation, highlighting key trends, performance metrics, and strategic recommendations for the upcoming year. The analysis is based on data collected from various digital marketing channels throughout 2024.
The purpose of this report is to evaluate the effectiveness of XYZ Corporation’s marketing strategies in 2024 and to offer insights for potential improvements. This evaluation covers various aspects of the digital marketing strategy, including social media, email campaigns, and online advertising.
The data for this report was collected using analytics tools such as Google Analytics and social media insights. A combination of quantitative and qualitative methods was employed to assess campaign performance and consumer behavior.
The company’s social media campaigns generated a 30% increase in engagement compared to the previous year.
Email marketing campaigns had a 20% higher open rate in 2024.
Online advertisements contributed to a 15% increase in overall website traffic.
The findings suggest that the increased engagement on social media directly correlates with the newly implemented content strategy that focuses more on customer interaction rather than promotional content. However, despite high engagement rates, conversion rates did not increase as expected, indicating potential areas for improvement in sales funnel strategies.
Based on the analysis, it is recommended that XYZ Corporation:
Enhances its content strategy to not only engage but also convert viewers into customers.
Revisits the targeting criteria for its email campaigns to improve conversion rates.
Increases budget allocation for high-performing channels to maximize ROI.
Google Analytics Data Reports, 2024.
XYZ Corporation Internal Marketing Analysis Documents.
Appendix A: Detailed Graphs of Monthly Engagement Rates.
Appendix B: Email Campaign Performance Statistics.
Formal Report Examples
Formal Report for Students

Formal Report for Science Fair Project

Formal Report for Business

More Examples on Formal Report
- Formal Report in Technical Writing
- Formal Report in Criminology
- Formal Report for Grade 12
- Short Formal Report
- Labs Formal Report
- Semi Formal Report
- Chemistry Formal Report
Formal Report Example

Download this well-made formal report template as it will make your daily business operations smooth and hassle-free. As it is ready-made, it is easy to edit and customize any content that you want to be replaced. Once you have downloaded this template, you may open it on any software device in any file format.
Collection Report Example

Formal Business Report

Formal Accident Sample Report
Types of Formal Report
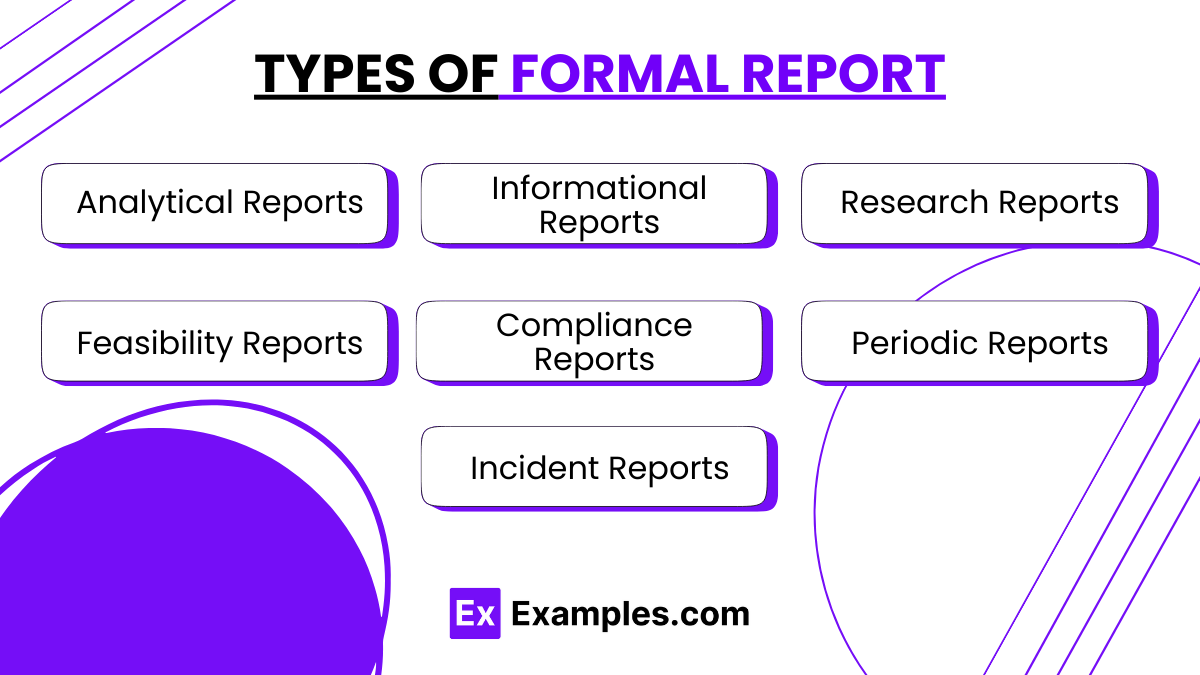
Analytical Reports
Analytical reports examine complex issues, analyze data, and provide recommendations based on the analysis. They are crucial in business, science, and policy making, helping decision-makers understand detailed aspects of particular problems and potential solutions.
Informational Reports
Informational reports focus on delivering factual data without providing any analysis or recommendations. They typically include summaries of events, updates on project progress, or data compilation. These reports are essential for keeping stakeholders informed about various aspects of operations without bias or interpretation.
Research Reports
Research reports document the methodology, process, and results of research activities. They are fundamental in academic, scientific, and commercial fields where sharing in-depth discoveries and innovations is necessary. These reports often contribute to the body of knowledge in a particular discipline or aid in the development of products and services.
Feasibility Reports
Feasibility reports evaluate the viability of a project or business venture, analyzing potential outcomes and recommending whether to proceed. These reports are critical in the planning phases of projects to ensure that resources are not wasted on unviable ideas.
Compliance Reports
Compliance reports verify and document adherence to laws, regulations, or standards. Companies in regulated industries, such as finance, healthcare, and environmental services, regularly produce these reports to demonstrate compliance with legal and regulatory frameworks.
Periodic Reports
Periodic reports are issued at regular intervals to update on the ongoing status of an entity or project. Common examples include annual, quarterly, or monthly reports that provide consistent updates on financial performance, project progress, or market trends.
Incident Reports
Incident reports provide a detailed account of unexpected events, such as accidents, security breaches, or system failures. These reports are crucial for documenting the occurrence, impact, and measures taken in response to the incident, often used in improving safety protocols and preventing future occurrences.
How to Write a Formal Report
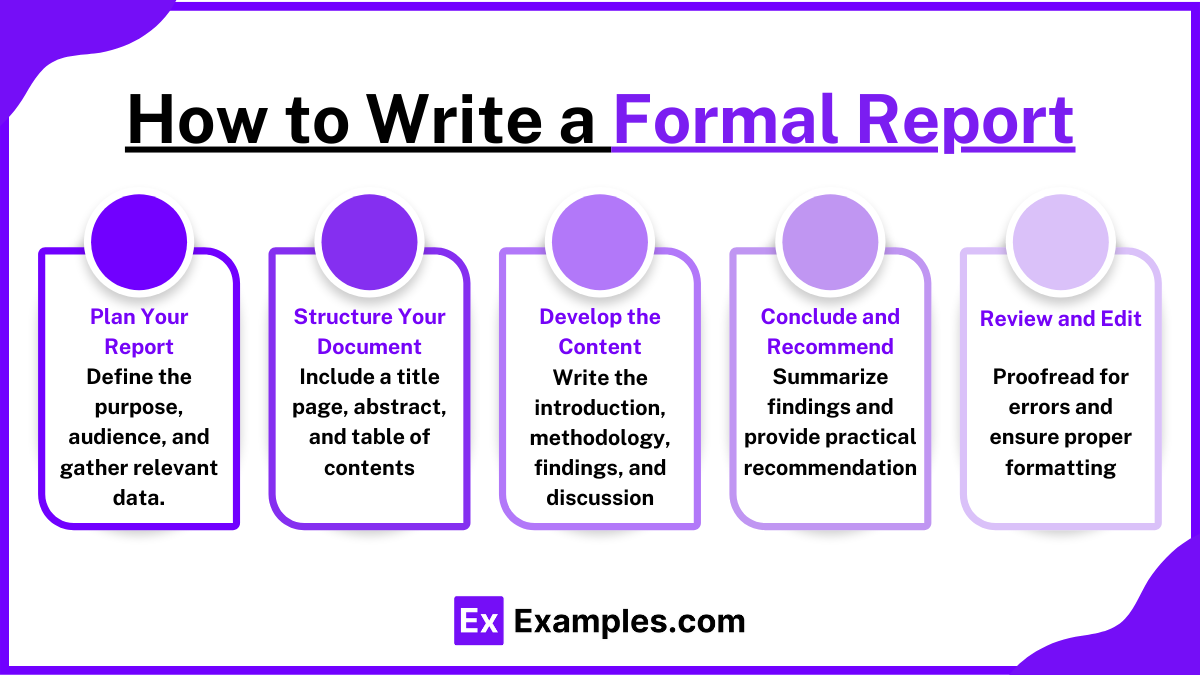
- Plan Your Report:
- Start by understanding the purpose of your report. Determine what information is necessary and who your audience is. Gather all the relevant data you need, such as research, surveys, or interviews.
- Structure Your Document:
- Begin with a title page that includes the report’s title, your name, and the date.
- Write an abstract or executive summary that briefly summarizes the content and conclusions of the report.
- Create a table of contents to help readers navigate through the report.
- Develop the Content:
- Introduction: Outline the background, the purpose of the report, and any hypotheses or questions it aims to address.
- Methodology: Describe how you gathered and analyzed the data.
- Findings: Present the data in a structured way, using charts, graphs, and tables where appropriate.
- Discussion: Interpret the findings, discuss how they relate to your hypothesis or the questions outlined in the introduction.
- Conclude and Recommend:
- Summarize the main findings and their implications. Be clear about how the results relate to your initial questions or hypotheses.
- Provide recommendations based on your findings. Make sure these suggestions are practical and justified by your research.
- Review and Edit:
- Carefully proofread your report to correct any spelling, grammar, or punctuation errors. Make sure the data presented is accurate and well-supported by your research.
- Ensure that the report is formatted according to any specific guidelines provided. This might include font size, margins, and citation style.
How To Create a Formal Report
- Define Objectives: Clearly define what you want to achieve with the report. Understand your audience’s needs and expectations to tailor the content accordingly.
- Gather Information: Collect all relevant data and information needed to support the report’s objectives. Use reliable sources such as academic journals, official databases, and credible interviews.
- Analyze Data: Carefully analyze the collected information to identify patterns, trends, and insights. Use statistical tools if necessary to handle large data sets and ensure accuracy in your findings.
- Organize Information: Sort your information logically. Start with a brief introduction that outlines the purpose of the report and your approach. Group similar data together in the body for coherent sections that support your conclusions.
- Draft the Report: Begin writing the report by expanding on the outline you’ve created. Ensure each section flows logically into the next. Explain your methodology, present your findings, and then interpret these results in the discussion section.
- Review and Revise: After drafting, take a break and come back with fresh eyes to edit your report. Look for areas where you can improve clarity, coherence, and conciseness. Check for any grammatical errors or inaccuracies and adjust the layout for readability.
- Incorporate Feedback: If possible, have someone else review your report. They can provide valuable feedback on how well your report meets its objectives and how effectively the information is communicated.
- Finalize the Document: Make all necessary revisions based on the feedback received and your own critical review. Ensure that the formatting meets any specific guidelines provided. Add a cover page, table of contents, and appendices if needed.
- Prepare for Presentation: If you need to present your report, prepare visual aids and a speech outline based on your report’s content. Practice presenting the main points clearly and confidently.
Benefits of a Formal Report
- Structured Information: Formal reports provide a structured format that helps organize complex data and information logically and coherently. This structure makes it easier for the reader to understand and navigate through the content.
- Detailed Analysis: They allow for detailed analysis and comprehensive discussion of issues. This depth is beneficial for making informed decisions based on thorough evaluations of all relevant factors.
- Credibility: The formal presentation and thorough documentation of sources and methodologies enhance the credibility of the information presented. This is crucial in professional environments where decision-making relies on accurate and reliable data.
- Record Keeping: Formal reports serve as an official record that can be referred to in the future. This archival function is important for tracking progress, reviewing historical data, and planning future actions based on past experiences.
- Communication Tool: They are an effective communication tool that can convey findings and recommendations to a wide audience, including stakeholders, management, and colleagues, facilitating informed decision-making and strategic planning.
FAQs
How is a formal report different from an informal report?
A formal report follows a structured format with detailed sections, while an informal report is less rigid, concise, and often used for internal communication.
Why are formal reports important?
Formal reports provide a clear structure to present detailed information, ensuring informed decision-making, credibility, and effective communication for stakeholders.
What are the key components of a formal report?
A formal report includes a title page, abstract, table of contents, introduction, methodology, findings, discussion, conclusion, recommendations, and references.
Who uses formal reports?
Formal reports are used by professionals, students, researchers, and organizations across various fields like business, science, education, and government.
What is the purpose of a formal report?
The purpose of a formal report is to provide detailed information, analysis, and recommendations to help organizations make informed decisions.


