10+ MLA Format Works Cited Examples to Download
Academic writing is like a dance, where every move must be choreographed to perfection. In this dance, the Modern Language Association (MLA) format is the rhythm that sets the pace. Whether you are a student or a seasoned scholar, understanding MLA guidelines can help you master the art of scholarly writing and convey your ideas with clarity and precision.
1. MLA Format Preparing Notes and Works Cited
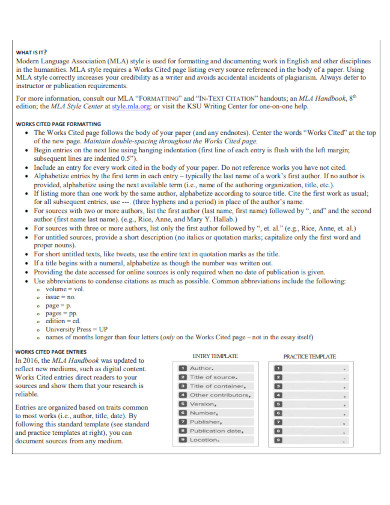
2. MLA Format Works Cited Page
3. MLA Format Works Cited Entries
4. Rules for MLA Works Cited Page
5. Sample MLA Format Works Cited Page
6. Student Resource MLA Works Cited Guide
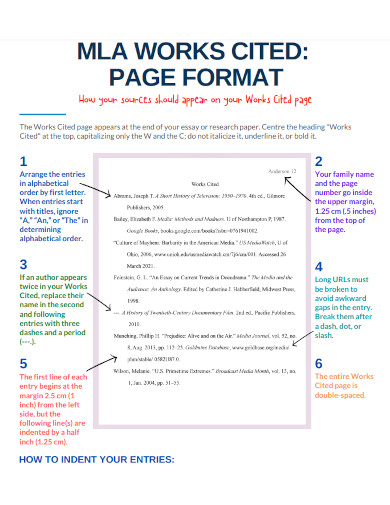
7. MLA Works Cited Page Format
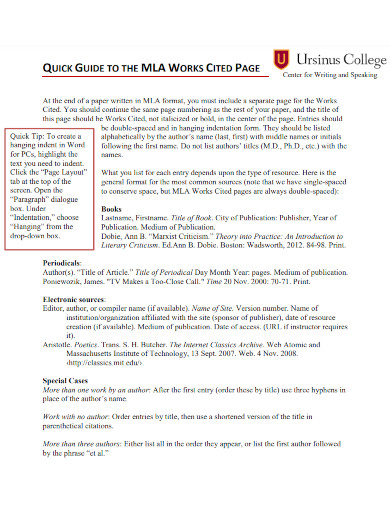
8. Quick Guide to MLA Works Cited Page
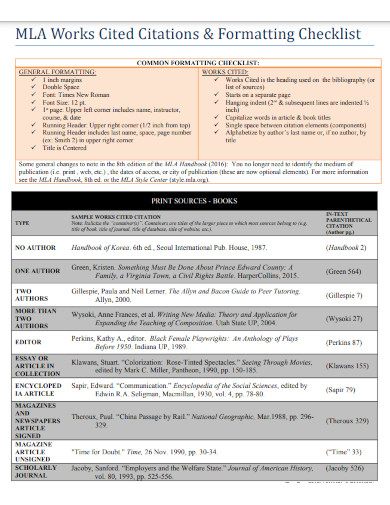
9. MLA Works Cited Formatting Checklist
10. MLA Works Cited Page Basic Format
11. MLA Format Works Cited Entry
What is MLA Format?
MLA (Modern Language Association) format is a citation and formatting style commonly used in academic writing, especially in the fields of literature, language, and humanities. It provides guidelines for how to format a paper, how to cite sources in the text of a paper, and how to create a Works Cited page. In MLA style, citations typically include the author’s name and the page number(s) of the source. The purpose of using MLA format is to give proper credit to the sources used in a paper and to allow readers to easily locate and verify the information cited.
How to write in MLA Format
When writing in MLA format, it’s important to format your document properly. Here are the steps to do so:
Step 1: Formatting Your Document
Start by setting your margins to 1 inch on all sides of the page. Next, choose a legible font, such as Times New Roman, in size 12. This will help ensure that your paper is easy to read and professional-looking. Double-space the entire document, including the Works Cited page. Create a header in the upper right-hand corner with your last name and the page number. Finally, include a title page centered on the first page of your document. Your title should be informative and concise, and it should give the reader an idea of what your research paper is about.
Step 2: In-Text Citations
Use author-page style for in-text citations. Place in-text citations at the end of the sentence, before the period. This makes it clear which information is being cited and helps the reader to locate the source on your Works Cited page. Use parentheses to enclose in-text citations. Include the author’s last name and the page number(s) in the in-text citation.
Step 3: Works Cited Page
List all sources alphabetically on the Works Cited page. Use hanging indentation for each entry. This means that the first line of each entry is flush with the left margin, while the subsequent lines are indented. Include the author’s name, the title of the source, the title of the container, other contributors, version, number, publisher, publication date, and location for each entry.
Step 4: Miscellaneous Guidelines
Use italics for titles of longer works, such as books or book journals. Use quotation marks for titles of shorter works, such as articles or chapters. See examples of how to write a chapter outline. Use title case for titles of works. This means that you should capitalize the first word, last word, and all major words in titles of works.
FAQs
What types of sources need to be cited in MLA format?
Any source that is used in a research paper needs to be cited in MLA format, including books, articles, websites, and other types of sources. The purpose of citation is to give credit to the original author or creator of the source and to allow readers to locate the source themselves.
Where can I find more information about MLA format?
There are many resources available for learning more about MLA format, including the official MLA Handbook, online guides and tutorials, and resources provided by your school or instructor. It’s important to consult reliable sources and to follow the specific guidelines provided by your instructor or department.
What are the key elements of MLA format?
The key elements of MLA format include formatting your document, in-text citations, and a Works Cited page. Proper formatting includes setting margins, choosing a font, and including a header with your last name and page number. In-text citations should include the author’s last name and the page number, and the Works Cited page should list all sources used in alphabetical order.
In conclusion, always consult your instructor or a reliable online resource for the most up-to-date guidelines and specific requirements. Following these steps will help you to write a paper that is clear, professional-looking, and easy to read.