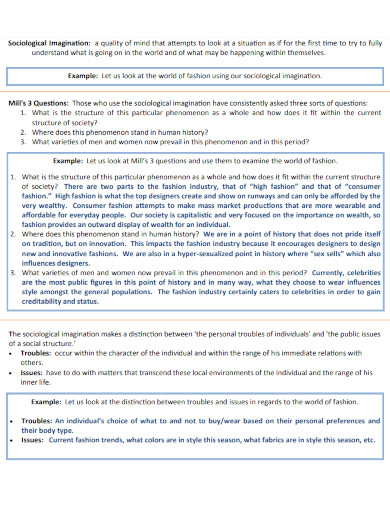
Sociological Imagination Examples to Download
Sociological imagination is a term coined by sociologist C. Wright Mills to describe the ability to see the connection between individual experiences and broader social, cultural, and historical forces. It refers to the capacity to understand the relationship between personal troubles and public issues.
1. Promise of the Sociological Imagination
2. Sociological Imagination Handout
3. Taking the Sociological Imagination to School
4. Developing a Critical Sociological Imagination
5. On Revisiting the Sociological Imagination
What is Sociological Imagination?
The sociological imagination enables individuals to see beyond their own personal experiences and understand how society shapes their lives and the lives of others. It allows individuals to analyze and interpret their experiences within the broader social context, identifying patterns and trends that are rooted in societal structures and institutions.
How to use Sociological Imagination
By using sociological imagination, individuals can develop a critical understanding of the world around them and the social, economic, and political forces that shape it. This perspective enables individuals to engage in informed social and political action, challenging existing social norms, and power structures and advocating for change in social issues like those involving capitalism.
Step 1: Identify a personal experience
Start by identifying a personality trait or experience or issue that you want to analyze using the sociological imagination. This could be a problem you are facing, a social interaction you had, or a social issue that you are interested in.
Step 2: Connect the experience to social structures
Next, connect your personal experience to broader social structures and institutions. Consider how social factors such as race, class, gender, and culture may have influenced your experience.
Step 3: Identify patterns and trends
Use your sociological imagination to identify patterns and trends in your personal experience. Look for common themes, stereotypes, and similarities between your experience and the experiences of others who share similar social characteristics.
Step 4: Analyze the issue from multiple perspectives
Analyze the issue from multiple perspectives, considering the viewpoints of different social groups and institutions and not just the common cliche. This will help you to develop a more comprehensive understanding of the issue and the social factors that contribute to it.
Step 5: Consider potential solutions
Finally, consider potential solutions or actions that could be taken to address the issue. Use your understanding of social structures and institutions to identify strategies for social change and advocacy.
FAQs
What are the benefits of using sociological imagination?
The benefits of using sociological imagination include a deeper understanding of social structures and institutions, a more critical perspective on social issues, and the ability to engage in informed social and political action.
How can sociological imagination be applied in everyday life?
Sociological imagination can be applied in everyday life by using it to analyze personal experiences, understand social issues, and identify potential solutions and actions that could be taken to address them.
How does sociological imagination differ from common sense?
Sociological imagination differs from common sense in that it involves a more critical and analytical approach to understanding social issues. While common sense relies on conventional wisdom and personal experience, sociological imagination involves a broader perspective that takes into account the social, cultural, and historical context of an issue.
By following these steps and using sociological imagination, you can gain a deeper understanding of your personal experiences and the broader social structures and institutions that shape them. This can help you to develop a critical perspective and engage in informed social and political action.