Communication Skills vs Social Skills, Differences between – 19+ Examples
Embark on a comprehensive journey through the realms of Communication Skills vs Social Skills with our illuminating guide. Uncover the synergy between these vital abilities and explore diverse examples that showcase the dynamic interplay. Elevate your interactions in various scenarios, from professional marketing endeavours to impactful social media engagements. Join us in unravelling the intricacies of effective communication and strategic social finesse.
Communication Skills vs Social Skills? – Definition
Communication skills encompass the ability to convey information effectively, involving verbal and non-verbal cues. On the other hand, social skills pertain to adept interactions within social contexts, emphasizing empathy and relationship-building. In essence, communication skills focus on expression, while social skills emphasize the art of connection. Together, they form a dynamic duo crucial for navigating diverse personal and professional landscapes. This section delves into the distinct yet interwoven meanings of these vital skills.
Differences between Communication Skills and Social Skill
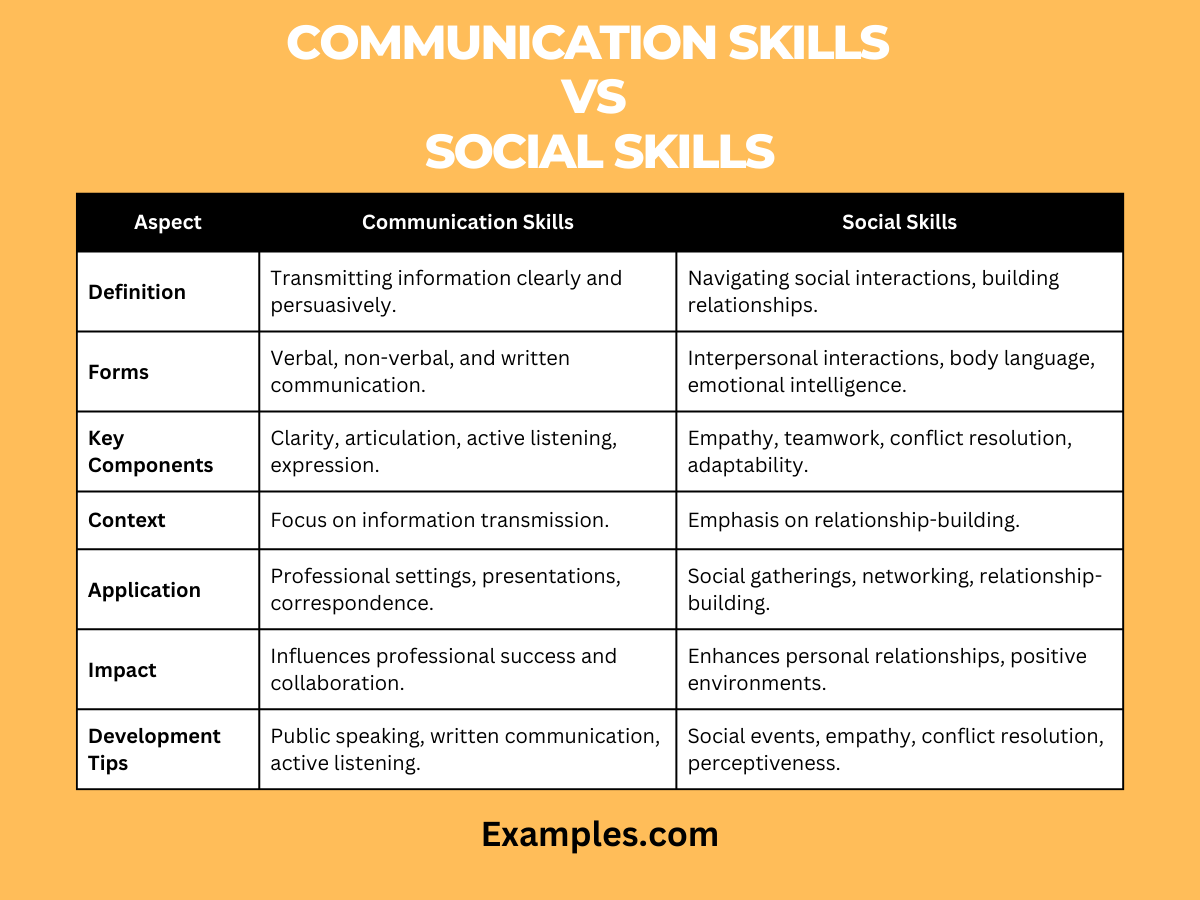
| Aspect | Communication Skills | Social Skills |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The ability to transmit information clearly and persuasively. | Proficiency in navigating social interactions, building relationships, and adapting to diverse social contexts. |
| Forms | Verbal, non-verbal, and written communication. | Interpersonal interactions, body language, and emotional intelligence. |
| Key Components | Clarity, articulation, active listening, and effective expression. | Empathy, teamwork, conflict resolution, adaptability, and social perceptiveness. |
| Context | Primarily focused on transmitting information. | Emphasizes building and maintaining relationships. |
| Application | Crucial in professional settings, presentations, and written correspondence. | Vital in social gatherings, networking, and relationship-building. |
| Impact | Influences professional success and effective collaboration. | Enhances personal relationships and fosters a positive social environment. |
| Development Strategies | Practice public speaking, enhance written communication, and engage in active listening exercises. | Participate in social events, develop empathy, practice conflict resolution in everyday interactions, and improve social perceptiveness. |
| Importance in Professional Sphere | Essential for leadership, teamwork, effective meetings, and client interactions. | Crucial for networking, team collaboration, conflict resolution, and creating a positive workplace culture. |
| Importance in Personal Sphere | Enhances family communication, fosters healthier relationships, and aids in conflict resolution. | Contributes to fulfilling personal relationships, social connections, and overall well-being. |
20 Communication Skills vs Social Skills Examples
Developing both communication and social skills is pivotal for personal and professional growth. Here are 50 examples that highlight the nuances of each.
10 Essential Communication Skills
Effective communication is a multifaceted skill set crucial for personal and professional success. Mastering these ten communication skills enhances interpersonal relationships, collaboration, and overall clarity in conveying ideas.
- Active Listening: The ability to fully concentrate, understand, respond, and remember what is being said fosters meaningful connections.
- Clear Articulation: Expressing thoughts coherently ensures that the intended message is easily understood, minimizing misunderstandings.
- Empathy: Understanding and sharing others’ emotions builds trust and strengthens relationships, contributing to a supportive environment.
- Non-Verbal Communication: Mastering body language, facial expressions, and gestures adds depth and nuance to verbal messages.
- Adaptability: Tailoring communication styles to different audiences and situations showcases flexibility and promotes effective interaction.
- Conflict Resolution: Navigating disagreements with diplomacy and finding common ground fosters a harmonious and productive environment.
- Assertiveness: Striking a balance between expressing opinions and respecting others’ views ensures effective communication without aggression.
- Clarity and Conciseness: Conveying messages in a straightforward and succinct manner prevents confusion and keeps communication focused.
- Feedback Delivery: Providing constructive feedback promotes growth and improvement, contributing to a positive and collaborative atmosphere.
- Cultural Competence: Being aware of and respecting cultural differences enhances communication in diverse and global settings.
10 Social Skills for Effective Interactions
1. Effective Communication: Mastering verbal and non-verbal communication ensures clarity in expressing thoughts and understanding others.
Example: During a team meeting, articulate your ideas clearly and use positive body language to enhance your message’s impact.
2. Active Listening: Being fully present and attentive when others speak fosters deeper connections and mutual understanding.
Example: In a conversation, demonstrate active listening by nodding, maintaining eye contact, and responding thoughtfully to show genuine interest.
3. Empathy: Understanding and sharing the feelings of others creates a supportive and compassionate social environment.
Example: When a friend faces a challenge, express empathy by acknowledging their emotions and offering assistance or a listening ear.
4. Conflict Resolution: Navigate conflicts with diplomacy, finding compromises that address concerns and maintain positive relationships.
Example: In a disagreement at work, practice conflict resolution by calmly discussing differences and finding common ground for a solution.
5. Building Relationships: Initiate and nurture connections by showing genuine interest, remembering details, and investing time in relationship-building.
Example: At a social event, initiate conversations, actively engage with others, and follow up with meaningful gestures to strengthen relationships.
6. Assertiveness: Expressing needs and opinions confidently without aggression ensures effective communication.
Example: In a group project, be assertive by expressing your ideas while respecting others’ input and encouraging collaborative decision-making.
7. Cultural Competence: Being aware and respectful of diverse cultures promotes inclusive and harmonious interactions.
Example: When working with international colleagues, demonstrate cultural competence by acknowledging cultural differences and adapting communication styles.
8. Adaptability: Flexibility in communication styles and behaviours allows for successful navigation of diverse social situations.
Example: In a dynamic work environment, showcase adaptability by adjusting your communication approach based on the context and audience.
9. Body Language Interpretation: Proficiently interpreting non-verbal cues enhances understanding and connection in social interactions.
Example: During a negotiation, pay attention to body language cues to gauge the other party’s reactions and adjust your approach accordingly.
10. Teamwork and Collaboration: Effectively collaborating with others involves clear communication, cooperation, and shared goal achievement.
Example: In a team project, foster teamwork by actively communicating, respecting diverse perspectives, and collectively working toward shared objectives.
Communication Skills vs Social Skills for Students
Navigating academic environments involves a blend of communication and social skills. Effective communication aids in presenting ideas, while social skills foster collaboration. Students benefit by honing these skills, excelling in group projects, and building positive peer relationships.

- Expressing Ideas Clearly: A student excels by articulating thoughts precisely during presentations, demonstrating strong communication.
- Peer Collaboration: Engaging in group activities fosters social skills, facilitating effective teamwork and shared learning experiences.
- Active Listening in Study Groups: Demonstrating social skills, a student excels by actively listening and contributing to study group discussions.
- Conflict Resolution: When conflicts arise, students with strong social skills address issues amicably, ensuring a positive learning environment.
- Effective Study Session Planning: Utilizing strong communication skills, students organize study sessions that enhance collaborative learning.
- Networking at Events: Students showcase social skills by networking at academic events, fostering connections for future opportunities.
- Clarity in Written Assignments: Displaying strong communication skills, students ensure clarity in written assignments, aiding understanding.
- Participation in Extracurriculars: Engaging in extracurricular activities hones social skills, contributing to a well-rounded educational experience.
- Effective Group Project Leadership: Students with robust communication skills lead group projects with precision, ensuring objectives are met.
- Adapting to Diverse Perspectives: Exhibiting strong social skills, students adapt to diverse perspectives, enhancing their overall learning experience.
Communication Skills vs Social Skills in Interview
Navigating interviews successfully requires a strategic blend of communication and social skills. Mastering the art of conveying strengths while connecting with interviewers is crucial for professional success.

- Eloquent Self-Presentation: During interviews, individuals with polished communication skills present themselves eloquently, leaving a lasting impression.
- Building Rapport: Demonstrating strong social skills, candidates build rapport with interviewers, creating a positive interview atmosphere.
- Active Listening: Candidates showcase social skills by actively listening to interview questions, responding thoughtfully and succinctly.
- Expressing Confidence: Communication skills come into play when candidates express confidence through clear and concise responses.
- Adaptability in Scenarios: Facing unexpected scenarios, candidates with strong social skills adapt seamlessly, showcasing their ability to navigate diverse situations.
- Non-Verbal Communication: Candidates convey professionalism through effective non-verbal communication, a vital aspect of both skills.
- Negotiation Skills: During salary discussions, individuals leverage strong communication skills to negotiate effectively, showcasing their value.
- Storytelling Techniques: Crafting compelling stories highlights effective communication skills, engaging interviewers and emphasizing suitability for the role.
- Expressing Enthusiasm: Candidates exhibit social skills by conveying genuine enthusiasm for the role, fostering a positive connection with interviewers.
- Professional Networking Mention: Candidates adept at social skills subtly incorporate professional networking experiences, showcasing a well-rounded professional approach.
Is Practicing Social Skills a Form of Communication?
Understanding the intricate relationship between social skills and communication is crucial for personal and professional development. Practicing social skills is indeed a nuanced form of communication that goes beyond verbal interactions.
- Non-Verbal Communication: Social skills encompass a wide range of non-verbal cues, including body language, facial expressions, and gestures. Practicing these enhances communication effectiveness.
- Active Listening: A fundamental social skill, active listening, contributes significantly to effective communication. It involves giving full attention, responding appropriately, and understanding the underlying emotions.
- Building Connections: Social skills involve the ability to build meaningful connections. This connection-building process is a subtle yet impactful form of communication that relies on empathy, rapport, and understanding.
- Adaptability: The practice of social skills often involves adapting to diverse social scenarios. This adaptability mirrors the flexibility required for effective communication in various situations.
- Conflict Resolution: Social skills play a pivotal role in resolving conflicts amicably. The ability to navigate disagreements and find common ground is a sophisticated communication skill.
- Expressing Emotions: Effectively expressing emotions is a social skill that significantly influences communication. Individuals proficient in this skill can convey their feelings authentically, fostering deeper connections.
- Cultural Sensitivity: Practicing social skills includes being culturally sensitive. This aspect of communication ensures that interactions are respectful and considerate of diverse backgrounds.
- Feedback and Social Signals: Social skills involve providing constructive feedback and interpreting social signals. Mastering these elements contributes to more nuanced and effective communication.
What Are Considered Social Skills?
Social skills are a collection of abilities that enable individuals to navigate social interactions successfully. These skills encompass a broad spectrum, ranging from basic manners to sophisticated interpersonal capabilities.
- Effective Communication: The cornerstone of social skills is the ability to communicate clearly, both verbally and non-verbally. This includes articulating thoughts, active listening, and adapting communication styles.
- Empathy: Understanding and sharing the feelings of others is a crucial social skill. It fosters deeper connections and enhances the overall quality of relationships.
- Active Listening: Attentive and focused listening is a fundamental social skill. It involves giving full attention, understanding the message, and responding appropriately.
- Conflict Resolution: Successfully resolving conflicts with tact and diplomacy is a sophisticated social skill. It requires effective communication, compromise, and problem-solving abilities.
- Building Relationships: Social skills include the capacity to initiate and nurture relationships. This involves making connections, maintaining friendships, and navigating social networks.
- Assertiveness: Striking a balance between expressing one’s needs and respecting others is an essential social skill. Assertiveness enables individuals to communicate effectively without aggression.
- Cultural Competence: Being aware and respectful of cultural differences is a vital social skill. It ensures harmonious interactions in diverse settings.
- Adaptability: Socially adept individuals can adapt to various social situations. Flexibility in communication styles and behaviours contributes to successful interactions.
- Body Language Interpretation: Proficiency in interpreting non-verbal cues, such as body language and facial expressions, enhances social understanding and communication effectiveness.
- Teamwork and Collaboration: Working collaboratively with others is a social skill crucial in both personal and professional settings. It involves effective communication, cooperation, and shared goal achievement.
Mastering both communication skills and social skills is essential for navigating the complexities of personal and professional relationships. From effective communication and active listening to empathy and adaptability, these skills collectively empower individuals to connect meaningfully with others, fostering understanding and collaboration. Integrating these skills enhances one’s social intelligence and contributes to success in diverse social scenarios.



