Communication Skills vs Technical Skills – 19+ Examples
Unlock the power of professional prowess with our complete guide on Communication Skills vs Technical Skills. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the dynamic interplay of effective communication and technical acumen. Discover the art of balancing these crucial attributes with real-world communication examples. Whether you’re navigating the corporate landscape or sculpting the perfect resume, this guide equips you with insights and examples to finesse both realms and stand out in any professional arena.
Difference between Communication Skills and Technical Skills
In the ever-evolving professional landscape, the dynamic interplay between communication and technical skills is more critical than ever. This comprehensive guide aims to dissect the nuances of both skill sets, providing insights and examples that transcend theoretical understanding.
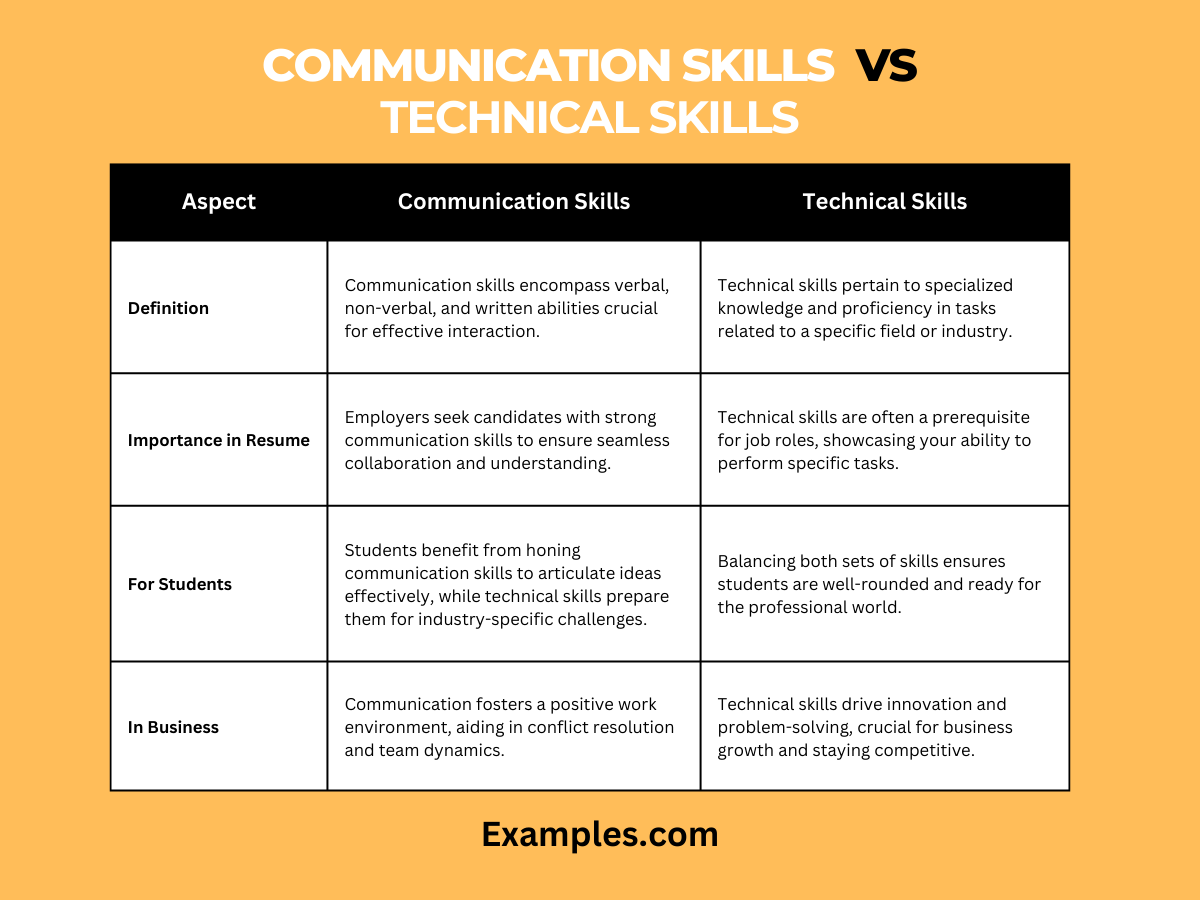
| Aspect | Communication Skills | Technical Skills |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Communication skills encompass verbal, non-verbal, and written abilities crucial for effective interaction. These skills are the bedrock of expressing ideas clearly and fostering collaboration. | Technical skills, on the other hand, pertain to specialized knowledge and proficiency in tasks related to a specific field or industry. They are the driving force behind problem-solving and innovation. |
| Importance in Resume | Employers seek candidates with strong communication skills, recognizing their role in ensuring seamless collaboration and understanding among team members. Technical skills, often job-specific, demonstrate the ability to perform tasks efficiently. | Crafting a compelling resume involves strategically showcasing both sets of skills. The document should reflect your proficiency in communication, as well as your technical prowess, aligning with the requirements of the job. |
| For Students | Students stand to gain immensely from honing their communication skills, as it equips them to articulate ideas effectively. Simultaneously, acquiring technical skills prepares them for the specific challenges presented by their chosen field of study. | The ideal student cultivates a balance, ensuring they are not only well-versed in their chosen technical domain but also possess the communication finesse to navigate diverse professional settings. |
| In Business | In the corporate landscape, effective communication fosters a positive work environment, aiding in conflict resolution and facilitating seamless team dynamics. Technical skills are the driving force behind business innovation and growth, ensuring companies stay competitive in the market. | Successful businesses are built on a foundation of both effective communication and technical proficiency. Companies seek individuals who can contribute not only through technical expertise but also by fostering a positive and collaborative workplace through communication. |
| In the Workplace | Within the workplace, effective communication enhances employee engagement, contributing to a healthy and productive atmosphere. Simultaneously, technical skills are crucial for task execution, ensuring that processes are efficient and goals are met. | Striking a balance within the workplace is key. A harmonious blend of communication skills contributes to a healthy organizational culture, while technical skills drive productivity and ensure the successful execution of tasks and projects. |
20 Examples of Communication Skills vs Technical Skills
Explore the delicate balance between Communication Skills vs Technical Skills through these vivid examples. This insightful guide not only defines each skill set but provides real-world instances, shedding light on their dynamic coexistence. Dive into the intricacies of effective communication and technical prowess, understanding how their synergy shapes success in various professional scenarios.
Communication Skills
- Active Listening: In a team meeting, showcase active listening by nodding and paraphrasing to convey understanding.
- Empathy: When a colleague faces challenges, express empathy by acknowledging their feelings and offering support.
- Clarity: In written communication, ensure clarity by organizing ideas logically and using concise language.
- Conflict Resolution: Resolve conflicts by initiating a calm dialogue, understanding perspectives, and finding common ground.
- Adaptability: Demonstrate adaptability by adjusting your communication style based on the audience and context.
- Body Language: During a presentation, use open body language to convey confidence and engagement.
- Assertiveness: Express your needs and opinions assertively, maintaining respect for others’ viewpoints.
- Cultural Sensitivity: In a multicultural setting, exhibit cultural sensitivity by respecting diverse customs and communication norms.
- Positive Reinforcement: Encourage team members with positive reinforcement, recognizing and appreciating their contributions.
- Collaboration: Promote collaboration by fostering open communication channels and valuing team input.
- Inclusive Communication: Ensure inclusivity by using language that embraces diversity and avoids stereotypes.
- Feedback Reception: When receiving feedback, express gratitude and seek clarification to better understand areas for improvement.
- Adaptation to Technology: Navigate virtual communication effectively, utilizing various platforms and tools for seamless interaction.
- Presentation Skills: Captivate an audience during a presentation by using engaging visuals and a confident delivery.
- Networking: Build professional relationships through effective networking, emphasizing genuine interest and active engagement.
- Conflict Management: Mitigate conflicts by addressing issues promptly and fostering an environment for open dialogue.
- Time Management: Communicate efficiently by respecting others’ time, keeping meetings concise, and prioritizing key points.
- Storytelling: Convey complex ideas through storytelling, making information relatable and memorable.
- Negotiation: In negotiations, find common ground by understanding the needs and motivations of all parties involved.
- Humour: Lighten the mood in appropriate situations with humour, fostering a positive and enjoyable atmosphere.
Technical Skills
- Programming Languages (e.g., Python): Mastering Python enables efficient and scalable software development, crucial for creating robust applications.
- Data Analysis (e.g., SQL): Proficiency in SQL allows for extracting actionable insights from complex datasets, driving informed decision-making.
- Cybersecurity (e.g., Ethical Hacking): Ethical hacking skills safeguard digital assets by identifying vulnerabilities, ensuring robust cybersecurity measures.
- Cloud Computing (e.g., AWS): AWS expertise facilitates scalable and flexible cloud solutions, optimizing resource management for businesses.
- Machine Learning (e.g., TensorFlow): Using TensorFlow empowers you to build and deploy machine learning models, advancing AI applications.
- Web Development (e.g., JavaScript): JavaScript proficiency is integral for creating dynamic and interactive web pages, enhancing user experience.
- Mobile App Development (e.g., Swift): Swift skills are vital for crafting seamless and innovative mobile applications across Apple devices.
- Database Management (e.g., MongoDB): Managing data efficiently with MongoDB ensures smooth and scalable database operations for applications.
- Network Administration (e.g., Cisco): Cisco networking skills are essential for designing and maintaining robust and secure network infrastructures.
- DevOps (e.g., Jenkins): Jenkins expertise streamlines the DevOps pipeline, automating software development processes for efficiency.
- UI/UX Design (e.g., Sketch): Sketch proficiency aids in creating visually appealing and user-friendly interfaces, enhancing overall design quality.
- Blockchain Development (e.g., Solidity): Solidity skills empower developers to create secure and decentralized blockchain applications.
- Data Science (e.g., R): R proficiency is crucial for statistical analysis, visualization, and deriving meaningful insights in data science projects.
- Artificial Intelligence (e.g., Natural Language Processing): NLP skills enable machines to comprehend and respond to human language, a core component of AI applications.
- Linux System Administration: Mastering Linux administration is vital for managing and securing server infrastructures in diverse computing environments.
- Database Design (e.g., Oracle): Oracle database skills are crucial for designing efficient and scalable database structures for applications.
- Automation Testing (e.g., Selenium): Selenium proficiency ensures robust and automated testing of web applications, enhancing software quality.
- Virtualization (e.g., VMware): VMware skills are essential for creating and managing virtualized environments, optimizing resource utilization.
- Internet of Things (IoT): IoT skills enable the development of interconnected devices, driving innovation in the realm of smart technologies.
- Full Stack Development: Full Stack Development skills encompass both frontend and backend technologies, allowing for end-to-end application development and deployment.
Comparison Between Communication Skills and Technical Skills
| Aspect | Communication Skills | Technical Skills |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Encompasses verbal, non-verbal, and written communication methods. | Involves specialized proficiency in tools, software, and technical processes. |
| Application | Relevant in various contexts, including business, education, and daily interactions. | Primarily applied in technical and specialized domains, such as IT, engineering, and sciences. |
| Key Components | Involves verbal articulation, active listening, adaptability, and effective written communication. | Encompasses proficiency in technical tools, problem-solving, coding, and data analysis. |
| Examples | Crafting impactful emails, delivering compelling presentations, and engaging discussions. | Coding, data analysis, project management in technical domains, and troubleshooting. |
| Importance in Business | Vital for clear communication, negotiations, and fostering professional relationships. | Crucial for executing technical tasks, problem-solving, and contributing to technical projects. |
| Skill Development Strategies | Develop active listening, refine written communication, and adapt style based on the audience. | Enhance proficiency in technical tools, problem-solving, coding, and project management |
Communication Skills vs Technical Skills in Resume
Navigate the nuanced world of crafting a compelling resume by understanding the distinct roles that communication and technical skills play. This guide explores how to strike the perfect balance, showcasing your proficiency in both realms to make your resume stand out in a competitive job market.
- Verbal Communication: In a resume, highlight your ability to communicate complex ideas succinctly, as demonstrated by successfully leading team meetings and presenting project updates.
- Programming Languages: List specific programming languages you’re adept in, showcasing your technical capabilities and fluency in the languages relevant to your field.
- Adaptability: Communicate your adaptability by citing instances where you quickly learned and applied new technical skills in response to project requirements.
- Interpersonal Skills: Highlight collaboration experiences, emphasizing your interpersonal skills in contributing positively to team dynamics and achieving common goals.
- Data Visualization: Incorporate visually appealing graphics and charts in your resume to demonstrate your proficiency in translating complex data into accessible insights.
- Problem-Solving: Describe how your technical skills have been instrumental in identifying and solving challenges within projects, showcasing your problem-solving acumen.
- Networking Skills: Detail your ability to build professional connections, both online and offline, emphasizing your networking skills in establishing valuable industry relationships.
- Coding Projects: Include a section showcasing coding projects you’ve undertaken, giving tangible evidence of your technical capabilities and hands-on experience.
- Negotiation Skills: Discuss instances where your negotiation skills facilitated successful collaborations or resolved conflicts within a project team.
- Technical Writing: Demonstrate your technical writing skills by succinctly articulating complex concepts or project details in a clear and accessible manner within your resume.
Communication Skills vs Technical Skills for Students
For students navigating their educational journey, understanding the significance of communication and technical skills is crucial. This guide explores practical examples tailored to students, providing insights on how to develop a well-rounded skill set for future professional success.
- Class Presentations: Students can showcase their verbal communication skills through successful class presentations, highlighting their ability to convey ideas confidently.
- Internship Experiences: Describe how your internship experiences allowed you to apply theoretical knowledge in real-world scenarios, emphasizing your practical technical skills.
- Group Projects: Highlight your teamwork and interpersonal skills through successful contributions to group projects, showcasing effective collaboration within a diverse team.
- Research Papers: Demonstrate strong written communication skills by showcasing well-researched and articulated papers, indicating your ability to convey complex ideas in writing.
- Coding Competitions: Participation in coding competitions or hackathons showcases your technical skills, emphasizing your ability to solve problems within a time constraint.
- Intrapersonal Communication: Discuss how you navigated challenges within group projects, showcasing your intrapersonal communication skills in resolving conflicts or misunderstandings.
- Internship Showcase: Create a portfolio showcasing technical projects completed during internships, demonstrating your hands-on technical expertise.
- Social Media Presence: Highlight a well-maintained and professional social media presence, showcasing your ability to communicate effectively in a digital environment.
- Peer Teaching: Describe instances where you helped peers understand complex concepts, indicating your strong interpersonal and teaching skills.
- Technical Workshops: Participation in technical workshops or seminars demonstrates your commitment to continuous learning and skill development within your field of study.
What Are Communication and Technical Skills?
In the dynamic landscape of professional development, understanding the nuances of communication and technical skills is paramount.
Communication Skills: Communication skills encompass the ability to convey thoughts, ideas, and information effectively. This includes verbal communication, written expression, and non-verbal cues such as body language. These skills are vital for fostering collaboration, building relationships, and navigating diverse professional environments.
Technical Skills: Technical skills, on the other hand, are specific competencies and knowledge related to a particular field or industry. They involve practical application of expertise in tasks ranging from coding and data analysis to project management and other specialized areas. Technical skills are crucial for problem-solving, innovation, and efficient task execution.
What are the 5 Basic Communication Skills?
Mastering the fundamentals of communication is pivotal for personal and professional success. The five basic communication skills include:
- Verbal Communication: The ability to express ideas and information through spoken words.
- Non-Verbal Communication: The use of gestures, body language, and facial expressions to convey messages.
- Listening Skills: Actively and empathetically receiving and comprehending information during interactions.
- Writing Skills: Articulating thoughts clearly and concisely through written communication.
- Interpersonal Skills: Building positive and effective relationships with others, fostering teamwork and collaboration.
Mastering the delicate dance between communication and technical skills is key to professional success. This guide has illuminated the nuances, providing insights and examples tailored for diverse contexts. Striking the right balance ensures not only an impressive resume but also the versatility to thrive in today’s dynamic job market. Elevate your career by seamlessly integrating these essential skills for a holistic and impactful professional journey.



