50+ Present Perfect Tense Examples
The Present Perfect Tense is a versatile aspect of English grammar that denotes actions or events that occurred at an unspecified time in the past but have relevance to the present moment. It expresses the idea of completion or experience without specifying when exactly the action took place. This tense is formed using the auxiliary verb ‘have’ or ‘has’ followed by the past participle of the main verb. Understanding how to use the Present Perfect Tense effectively can greatly enhance one’s ability to convey nuances of time and experience in English communication.
What is the Present Perfect Tense?
The Present Perfect Tense in English grammar denotes actions or events that happened at an unspecified time in the past but hold relevance to the present. It signifies completion or experience without specifying when. Formed with ‘have’ or ‘has’ + past participle, mastering this tense enhances one’s ability to convey time nuances effectively in English communication.
Present Perfect Tense Formula
The formula for forming the present perfect tense is:
Here’s how it works:
- For subjects like “I,” “you,” “we,” and “they,” you use “have.”
- For subjects like “he,” “she,” and “it,” you use “has.”
Then, you add the past participle form of the main verb.
For example:
- “I have eaten.”
- “She has finished her work.”
- “They have gone to the store.”
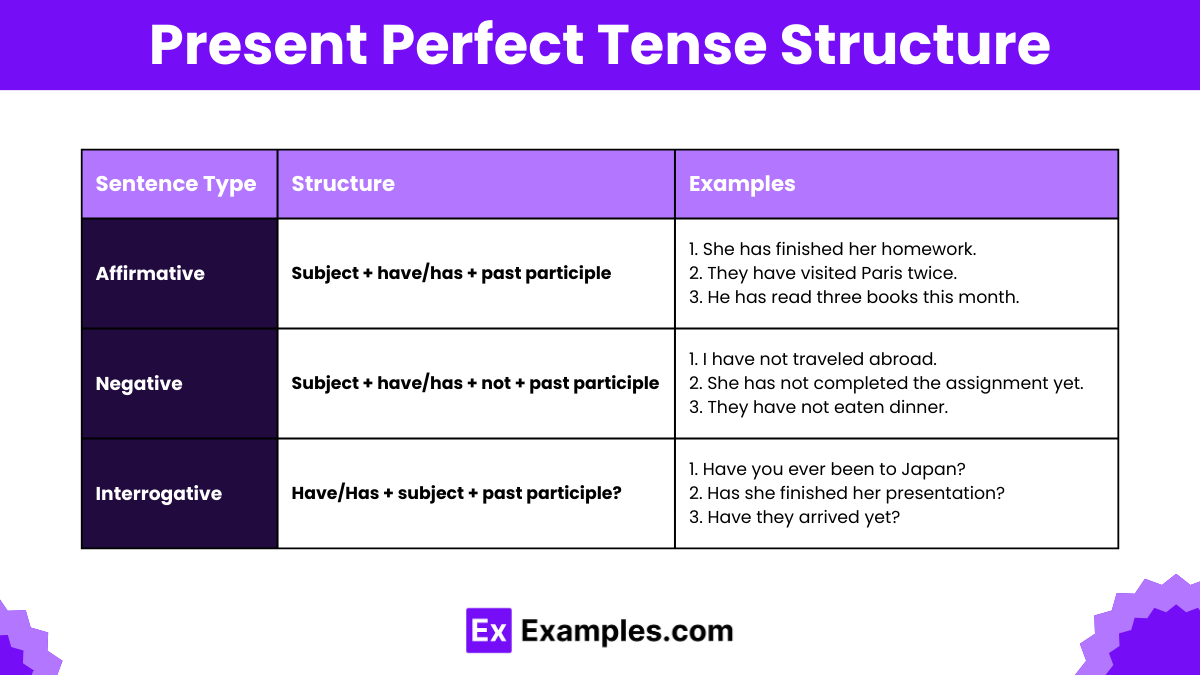
Present Perfect Tense Structure
| Sentence Type | Structure | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Affirmative | Subject + have/has + past participle | 1. She has finished her homework. 2. They have visited Paris twice. 3. He has read three books this month. 4. We have seen that movie before. 5. The team has won the championship. |
| Negative | Subject + have/has + not + past participle | 1. I have not traveled abroad. 2. She has not completed the assignment yet. 3. They have not eaten dinner. 4. He has not received the email. 5. We have not met the new manager. |
| Interrogative | Have/Has + subject + past participle? | 1. Have you ever been to Japan? 2. Has she finished her presentation? 3. Have they arrived yet? 4. Has he called you back? 5. Have we discussed this topic before? |
Present Perfect Tense Rules
The present perfect tense is used to express actions or events that have happened at an indefinite time in the past or have relevance to the present moment. Here are some key rules and guidelines for using the present perfect tense:
- Form: As mentioned earlier, the present perfect tense is formed by combining the auxiliary verb “have” (or “has” for third-person singular subjects) with the past participle of the main verb.
- Indefinite time frame: The present perfect tense is often used to describe actions or experiences that occurred at an unspecified time in the past. For example: “I have visited Paris.” This sentence indicates that the action of visiting Paris happened at some point in the past, but the exact time is not specified.
- Relevance to the present: The present perfect tense is also used to indicate that an action or event from the past has relevance or consequences in the present. For example: “I have lost my keys.” This suggests that the action of losing the keys happened in the past, but it has an impact on the present situation (e.g., the person cannot find their keys now).
- Continuing actions: The present perfect tense can be used to describe actions that started in the past and continue into the present. For example: “She has lived in New York for ten years.” This sentence indicates that the action of living in New York started in the past and continues up to the present moment.
- Multiple occurrences: The present perfect tense can also be used to express actions or events that have occurred multiple times up to the present. For example: “We have visited Italy several times.” This sentence suggests that the action of visiting Italy has happened multiple times in the past, and it may continue to happen in the future.
- Non-use with specific time expressions: The present perfect tense is typically not used with specific time expressions that refer to a particular point in the past (e.g., yesterday, last week, in 2005). Instead, it is used with time expressions that are more general or open-ended (e.g., ever, never, before, already, yet).
How to use the Present Perfect Tense?
The Present Perfect tense is an essential tool in English grammar, bridging past actions or events to the present moment. It combines aspects of the past and present, making it unique compared to other tenses. Below, you’ll find detailed guidance on how to form and use the Present Perfect tense.
Formation of the Present Perfect Tense
To construct the Present Perfect tense, you use the auxiliary verb “have” (or “has” for third person singular) followed by the past participle of the main verb.
- Affirmative form: Subject + have/has + past participle
- Negative form: Subject + have/has + not + past participle
- Interrogative form: Have/Has + subject + past participle?
Examples:
- He has finished his work.
- They have not seen that movie.
- Have you ever traveled to Australia?
Usage of the Present Perfect Tense
- Actions or States Continuing to the Present: Use this tense to describe situations or actions that started in the past and are still ongoing at the moment of speaking.Example:
- She has lived in New York for ten years.
- Completed Actions at an Undefined Time: This is used for actions completed at some point in the past; the exact time is not specified or important.Example:
- I have visited the Grand Canyon.
- Life Experiences: The tense is often used to discuss experiences up to the present time, without specifying when they occurred.Example:
- He has traveled to several countries.
- Changes Over Time: Describe changes that have happened over a period leading up to the present.Example:
- Our city has grown rapidly over the past decade.
- Accomplishments: It’s common to use this tense when describing achievements or completed actions, with no specific time given.Example:
- Scientists have discovered a new planet.
- Actions Repeated in an Indefinite Period: When an action has occurred multiple times in the past and can potentially continue in the future.Example:
- I have seen that movie three times.
Forming the Present Perfect Tense
Mastering the Present Perfect tense in English is essential for expressing actions that have a connection to the present moment, whether they were completed in the past or are still ongoing. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you understand and use this tense effectively, optimizing for clarity, SEO, and readability.
Step 1: Understand the Basics
The Present Perfect tense combines the auxiliary verb “have” (or “has” for third-person singular) with the past participle of the main verb.
- Structure: Subject + have/has + past participle
Step 2: Form the Past Participle
The past participle is crucial in forming the Present Perfect tense. For regular verbs, add “-ed” to the base form. Irregular verbs vary and must be learned individually.
- Regular Example: Walk → Walked
- Irregular Example: Write → Written
Step 3: Use the Correct Auxiliary Verb
Choose “have” or “has” based on the subject. Use “have” with I, you, we, and they. Use “has” with he, she, and it.
- Example: She has visited France.
Step 4: Apply the Tense Appropriately
Use the Present Perfect to discuss:
- Actions completed at an unspecified time in the past.
- Ongoing actions or states that started in the past and continue to the present.
- Life experiences up to the current moment.
Past Simple Tense vs. Present Perfect Tense
| Aspect | Past Simple Tense | Present Perfect Tense |
|---|---|---|
| Form | Subject + past verb form (V2) | Subject + have/has + past participle |
| Function | Describes actions completed at a specific time in the past. | Describes actions or states that began in the past and connect to the present, either continuing or impacting the current moment. |
| Time Reference | Always mentions or implies a specific time. | Time is usually unspecific or ongoing. |
| Keywords | Yesterday, last week, in 1998, two days ago, at that moment. | Already, just, yet, ever, never, for, since. |
| Examples | I watched a movie last night. She visited Rome two years ago. | I have watched that movie already. She has visited Rome. |
| Use in Questions | Did you see her yesterday? | Have you seen her recently? |
| Negation | I did not go to the party. | I have not gone to the party. |
| Typical Uses | To narrate events that happened at a definite point in time. | To relate past actions to the present without a specific time frame; to describe experiences or changes over time. |
| Time Frame | Closed: The action is finished and the time is past. | Open: The action may still be relevant or ongoing. |
Present Perfect Tense vs. Present Perfect Continuous Tense
| Aspect | Present Perfect Tense | Present Perfect Continuous Tense |
|---|---|---|
| Form | Subject + have/has + past participle | Subject + have/has + been + present participle (-ing form) |
| Function | Focuses on the completion or result of an action. | Emphasizes the duration or ongoing nature of an action. |
| Keywords | Already, just, yet, ever, never, for, since | For, since, all day, all morning, lately, recently |
| Examples | I have finished my work. She has visited Rome three times. | I have been finishing my work all morning. She has been visiting Rome since last week. |
| Use in Questions | Have you seen the new movie? | Have you been seeing anyone lately? |
| Negation | I have not seen that movie. | I have not been seeing any progress. |
| Typical Uses | To discuss experiences, changes, or completions without specific time. | To emphasize an action that started in the past and is still ongoing. |
| Time Reference | General past to present without specific focus on continuity. | Specific focus on the continuity and duration of the action. |
| Time Frame | Often indefinite: the exact duration or end point is not emphasized. | Clearly defined: emphasizes the ongoing nature and specific duration. |
Examples of Present Perfect Tense in Sentences
The Present Perfect tense is versatile, suitable for describing completed actions, experiences, or changes that continue to affect the present. Here are ten examples of sentences using the Present Perfect tense:
- I have visited the new art exhibit at the museum.
- We have seen this movie twice already.
- She has lived in this town since she was born.
- They have learned a lot about coding in the past semester.
- He has written three chapters of his book.
- You have cleaned the house, and it looks fantastic!
- Our teacher has explained the concept, but I still don’t understand it.
- The scientists have discovered a new species of bird in the Amazon.
- I have lost my keys, so I can’t open the garage.
- We have discussed changing the meeting schedule, but no decision has been made yet.
Present Perfect Tense Passive Voice Examples
The Present Perfect tense in the passive voice focuses on actions or events that have been completed by an unspecified agent, often emphasizing the action itself rather than who performed it. Here are some examples of sentences using the Present Perfect tense in the passive voice:
- The book has been read by many students in the class.
- A new supermarket has been opened in our neighborhood.
- The documents have been signed by all parties involved.
- A decision has been made by the committee.
- The letter has been sent to the client.
- The project has been completed successfully.
- The car has been repaired and is ready to be picked up.
- The meeting has been scheduled for next Monday.
- The rules have been changed recently.
- The movie has been highly praised by critics.
Present Perfect Tense Interrogative Examples
The Present Perfect tense in interrogative form is often used to ask about experiences, accomplishments, or changes that have relevance up to the present. Here are some examples of questions using the Present Perfect tense:
- Have you ever traveled to Asia?
- Has she finished her homework yet?
- Have they seen the latest Marvel movie?
- Has he decided on a university to attend?
- Have we met before?
- Have you read the book I recommended?
- Has it rained since this morning?
- Have you heard the news about the new company policy?
- Have they called you about the job offer?
- Has the package been delivered yet?
Present Perfect Tense Affirmative Examples
The Present Perfect tense in affirmative form is used to describe actions or situations that started in the past and have relevance or continue up to the present. Here are some examples of sentences using the Present Perfect tense in affirmative form:
- I have completed the report you requested.
- We have lived in this city for over twenty years.
- She has worked at that company since graduating from college.
- He has written several articles on climate change.
- They have been best friends since childhood.
- You have done a great job organizing the event.
- It has rained every day this week.
- The scientists have discovered a new type of renewable energy.
- Our team has won the championship three times in the last five years.
- I have always enjoyed learning new languages.
Present Perfect Tense Negative Examples
The Present Perfect tense in negative form is used to express that an action or condition has not occurred or been completed at any time up to the present. Here are some examples of sentences using the Present Perfect tense in negative form:
- I have not finished my assignment yet.
- We have not visited that new restaurant downtown.
- She has not seen the latest episode of her favorite series.
- He has not decided on his major at university.
- They have not met our new neighbors.
- You have not cleaned your room as I asked.
- It has not rained this month.
- The committee has not approved the proposal.
- I have not been to the gym this week.
- We have not received any complaints about the product.
What is the Rule for Present Perfect Tense?
Use the Present Perfect tense with “have” or “has” plus the past participle to describe actions that started in the past and continue or affect the present.
How to Explain Present Perfect Tense to a child?
The Present Perfect tense is like saying something started in the past and is still going on now, or it happened at some time before now. We use “have” or “has” with it!
When not to use the Present Perfect Tense?
Avoid the Present Perfect tense when specifying the exact time an action occurred, like “yesterday” or “last year.” Instead, use the Simple Past tense for actions that happened at a definite time and are completely finished.